Scallop Anatomy
Note that the intestines are embedded within the gonad and that portions of the left side principally the gills and the shell are not shown. Occasionally both shells are bright yellow or orange but these individuals are rare.
The bay scallop is a member of phylum mollusca in the class bivalvia.
Scallop anatomy. Scallop anatomy although the entire animal is edible and is eaten in other countries the abductor muscle which is responsible for opening and closing the shells is the only part usually eaten in the united states. Scallops are a cosmopolitan family of bivalves which are found in all of the worlds oceans although never in fresh water. Original anatomy of the right side of a scallop including detailed information on the circulation and nervous systems as well as all the major organs.
Some people may be allergic to scallops however so anyone with previous allergies. They are the only migratory bivalve. The bay scallops upper shell is a dark mottled color and its lower shell is typically white.
Scallop anatomy anatomy like the true oysters family ostreidae scallops have a central adductor muscle and thus the inside of their shells has a characteristic central scar marking the point of attachment for this muscle. Scallops have a central. Via chordae tendineae small tendons which ensure that the leaflets do not prolapse the valve leaflets are attached to two major papillary muscles anterolateral en posteromedial in the left ventricle.
Large well developed abductor muscle which allows them to swim. Where the two shells meet they flare out to make a wing. Scallops are edible bivalves similar to oysters and clams.
Scallops have up to 100 simple eyes appear around the edges of their shells. They are one of very few groups of bivalves to be primarily free living with many species capable of rapidly swimming short distances and even of migrating some distance across the ocean floor. Scallops are bivalve mollusks they have fan like shells that are really hard.
They are found both in bay waters and in the sea. Anterior leaflet is not anatomically divided into scallops like the posterior leaflet is but for pathological guidance the anterior scallops mimic the posterior leaflets scallops are labeled 1 to 3 based from lateral to medial segments. Their shells have characteristics ribs grooves and concentric growth rings.
Inside the valves there are a row of tentacles and blue eyes on the the edge of the mantle. The mitral valve consists of two valve leaflets the anterior leaflet amvl and the posterior leaflet pmvl which together have a surface of 4 6 cm 2. Scallops are sea dwelling bivalve mollusk of the family pectinidae found in many of the worlds oceans.
Bivalves have two valves or shells joined by a hinge. In terms of texture they are somewhat similar to white fish and have a fairly sweet flavor that is ideal for many different dishes.
Fresh Water Mussel Collection Introduction Anatomy
 Adductor Muscles Bivalve Wikipedia
Adductor Muscles Bivalve Wikipedia
 The Habits Anatomy And Embryology Of The Giant Scallop
The Habits Anatomy And Embryology Of The Giant Scallop
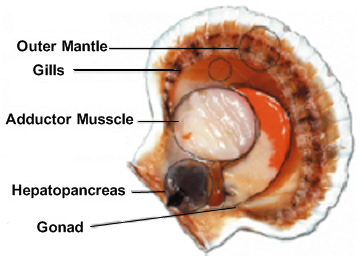 Shellfish Information Scallops Barnegat Bay
Shellfish Information Scallops Barnegat Bay
The Hatchery Culture Of Bivalves A Practical Manual
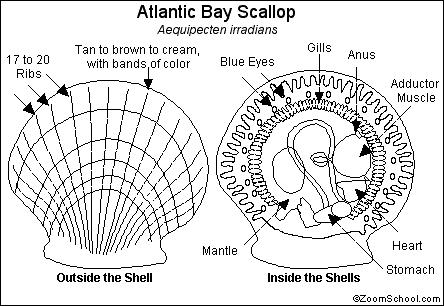 Scallop Printout Enchanted Learning Software
Scallop Printout Enchanted Learning Software
 Preoperative Scallop By Scallop Assessment Of Mitral
Preoperative Scallop By Scallop Assessment Of Mitral
 Ecoventures The Wonders Of The Atlantic Sea Scallop
Ecoventures The Wonders Of The Atlantic Sea Scallop
The Hatchery Culture Of Bivalves A Practical Manual
 Scallop Guide Explaining Differences Between Each Type Of
Scallop Guide Explaining Differences Between Each Type Of
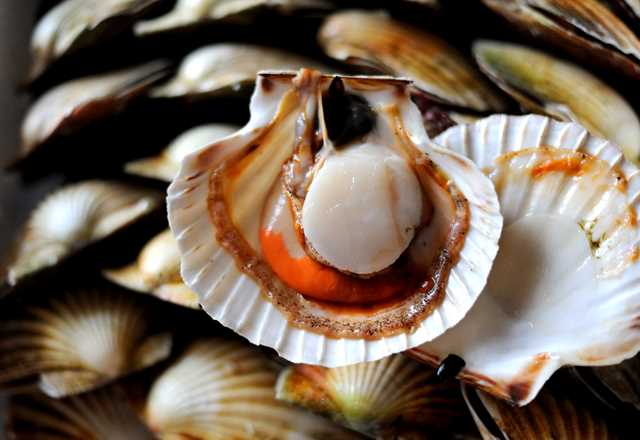 How To Cook Scallops Great British Chefs
How To Cook Scallops Great British Chefs
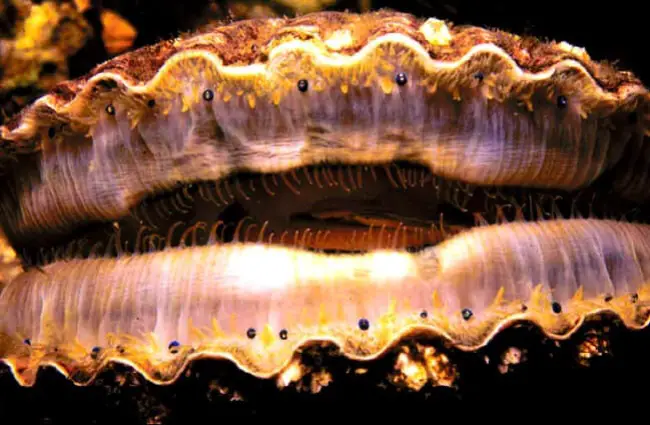 Scallop Description Habitat Image Diet And Interesting
Scallop Description Habitat Image Diet And Interesting

The Hatchery Culture Of Bivalves A Practical Manual
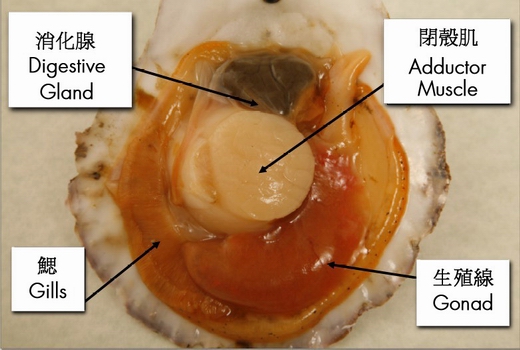 Frozen Scallops And Paralytic Shellfish Poisoning
Frozen Scallops And Paralytic Shellfish Poisoning
File Scallop Neurological Diagram Svg Wikipedia
 Figure 2 From Anatomical Distribution Of Heavy Metals In The
Figure 2 From Anatomical Distribution Of Heavy Metals In The
 A Simple Method To Reduce The Risk Of Cadmium Exposure From
A Simple Method To Reduce The Risk Of Cadmium Exposure From







Belum ada Komentar untuk "Scallop Anatomy"
Posting Komentar