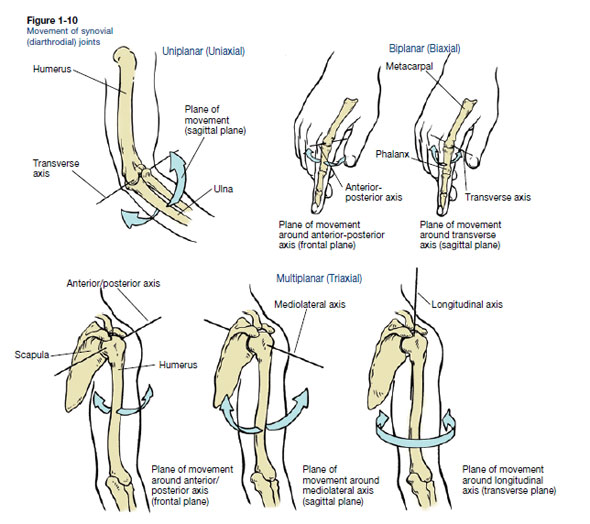
Axis Of Rotation Anatomy
Perpendicular to the long axis of the body. Axis of rotation anterior posterior axis.
Cot S Learning Center Chiropractic Principles
Rotation of the forearm that makes the palm face in.
Axis of rotation anatomy. Axis anatomy by the atlanto axial joint it forms the pivot upon which the first cervical vertebra the atlas which carries the head rotates. Takes place in a plane about an axis. Mediolateral means that we take our imaginary pin and insert it from a lateral.
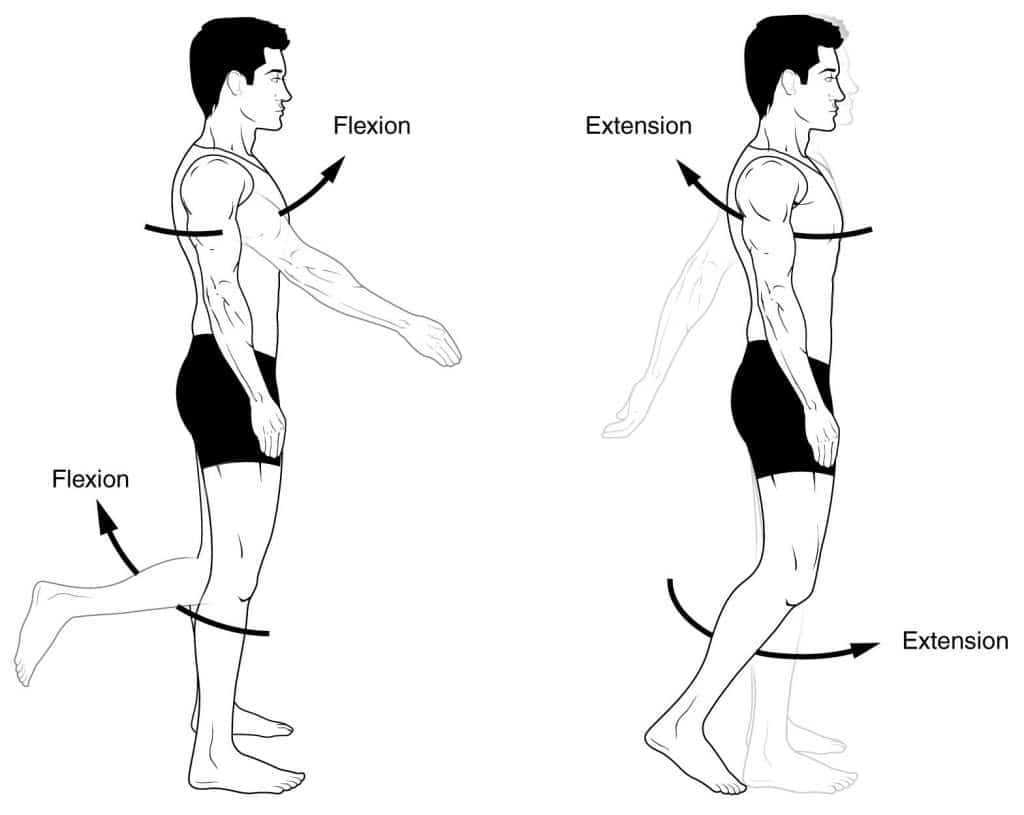
There are three axes of rotation. This is medial rotation of the hip. If we insert our pin through the joint from top to bottom.
The frontal axis passes horizontally from left to right and is formed by the. Axes of rotation the human body is also divided into anatomical axes axis of rotation is an imaginary line point of rotation that passes through a joint or the body to describe the movement. An axis is an imaginary line about which the body or limb rotates.
Sagital axis frontal axis vertical axis the sagital axis passes horizontally from posterior to anterior and is formed by the intersection of the sagital and transverse planes. Medial and lateral rotation describe movement of the limbs around their long axis. Movement around a longitudinal axis of a bone from the midline outward lateral rotation pronation inward rotation of forearm.
The most distinctive characteristic of this bone is the strong odontoid process known as the dens which rises perpendicularly from the upper surface of the body. Imagine a pin that inserts through a joint from front to back. Medial rotation is a rotational movement towards the midline.
There are three axes of rotation. Frontal axis passes horizontally from left to right and is formed by the intersection of the frontal and transverse planes. It is sometimes referred to as internal rotation.
Frontal horizontal axis invisible line that travels from left to the right side of the body vertical axis invisible line that travels from the top of the head to the bottom of the feet sagittal horizontal axis. Parallel to the back. Circumduction supination pronation dorsi plantar flexion inversion eversion elevation depression.
The three axes of movement include. Sagittal axis passes horizontally from posterior to anterior and is formed by the intersection of the sagittal and transverse planes. Dividing the body to right and left parts.
Firstly with a straight leg rotate it to point the toes inward. Anatomy physiology exercise physiology anatomical position anatomical planes. Sagittal section on midline dividing into right and left halves.
Anatomical axis flexion extension abduction adduction internal external rotation superficial deep. To understand this we have two scenarios to imagine.
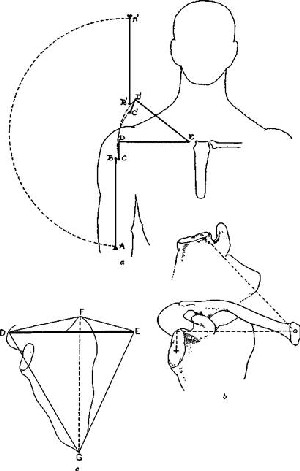 Normal Motions Of The Shoulder Joint Shoulderdoc By Prof
Normal Motions Of The Shoulder Joint Shoulderdoc By Prof
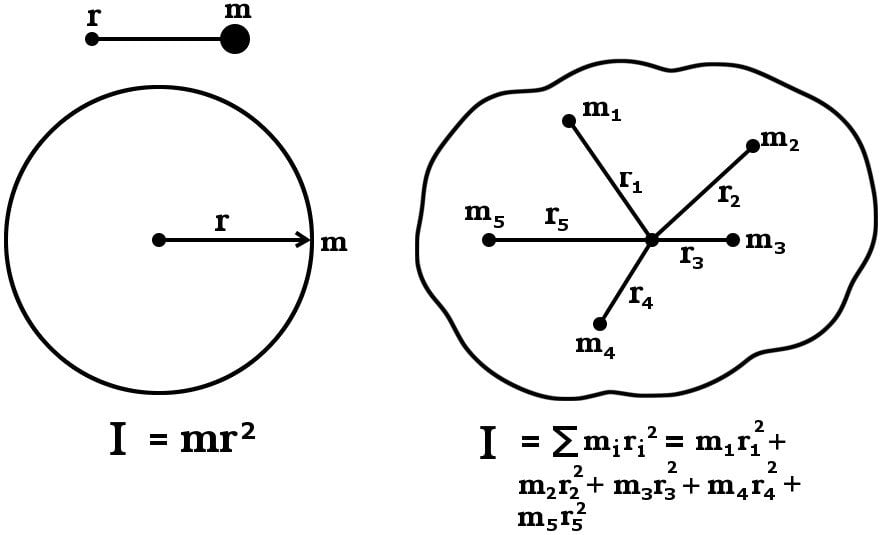 What Is Moment Of Inertia And How To Calculate It For A Rod
What Is Moment Of Inertia And How To Calculate It For A Rod
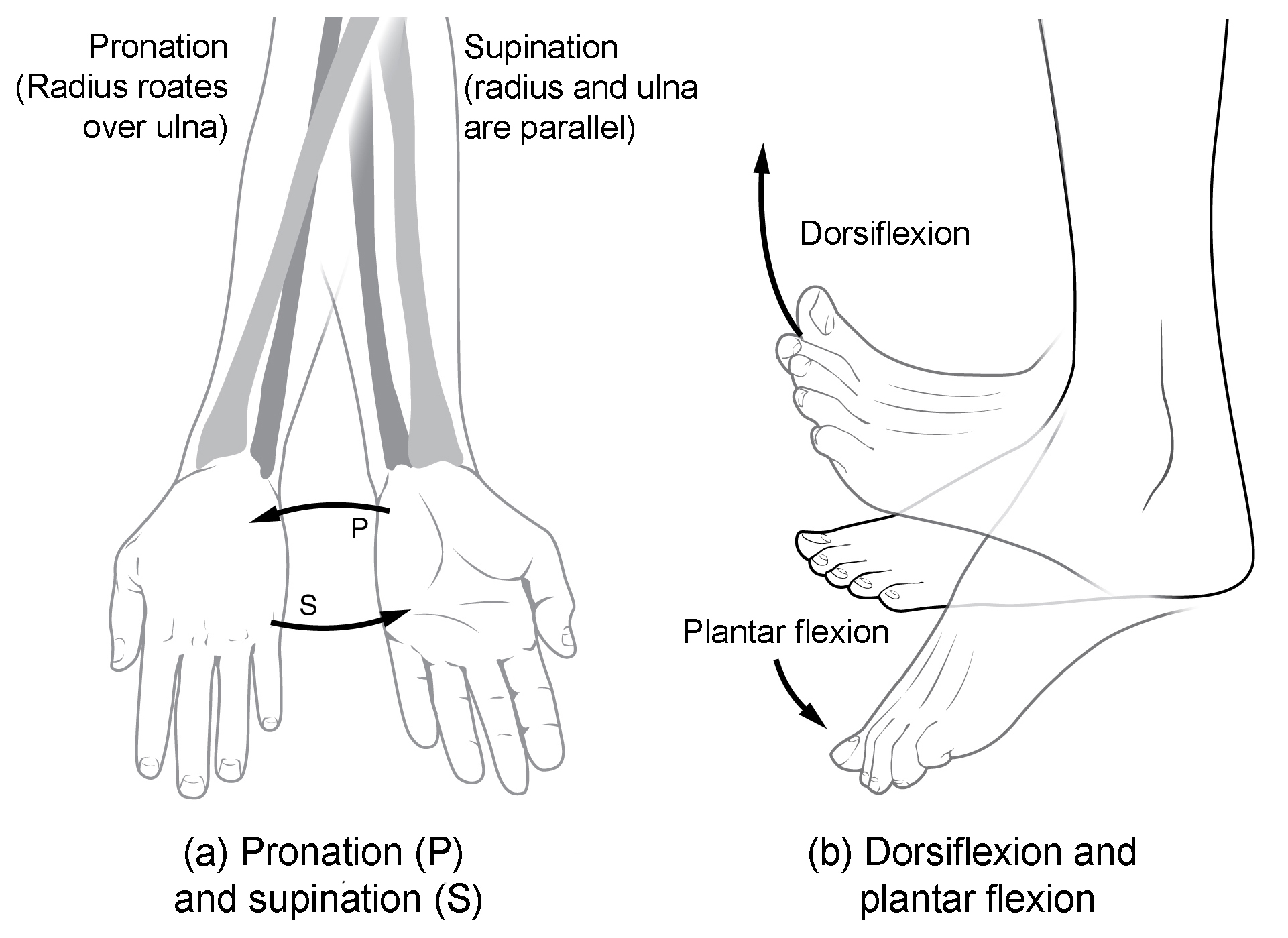 Types Of Body Movements Anatomy And Physiology I
Types Of Body Movements Anatomy And Physiology I
 Biomechanics Of The Ankle Sciencedirect
Biomechanics Of The Ankle Sciencedirect
 Kinect Joint Rotation The Definitive Guide Vangos Pterneas
Kinect Joint Rotation The Definitive Guide Vangos Pterneas
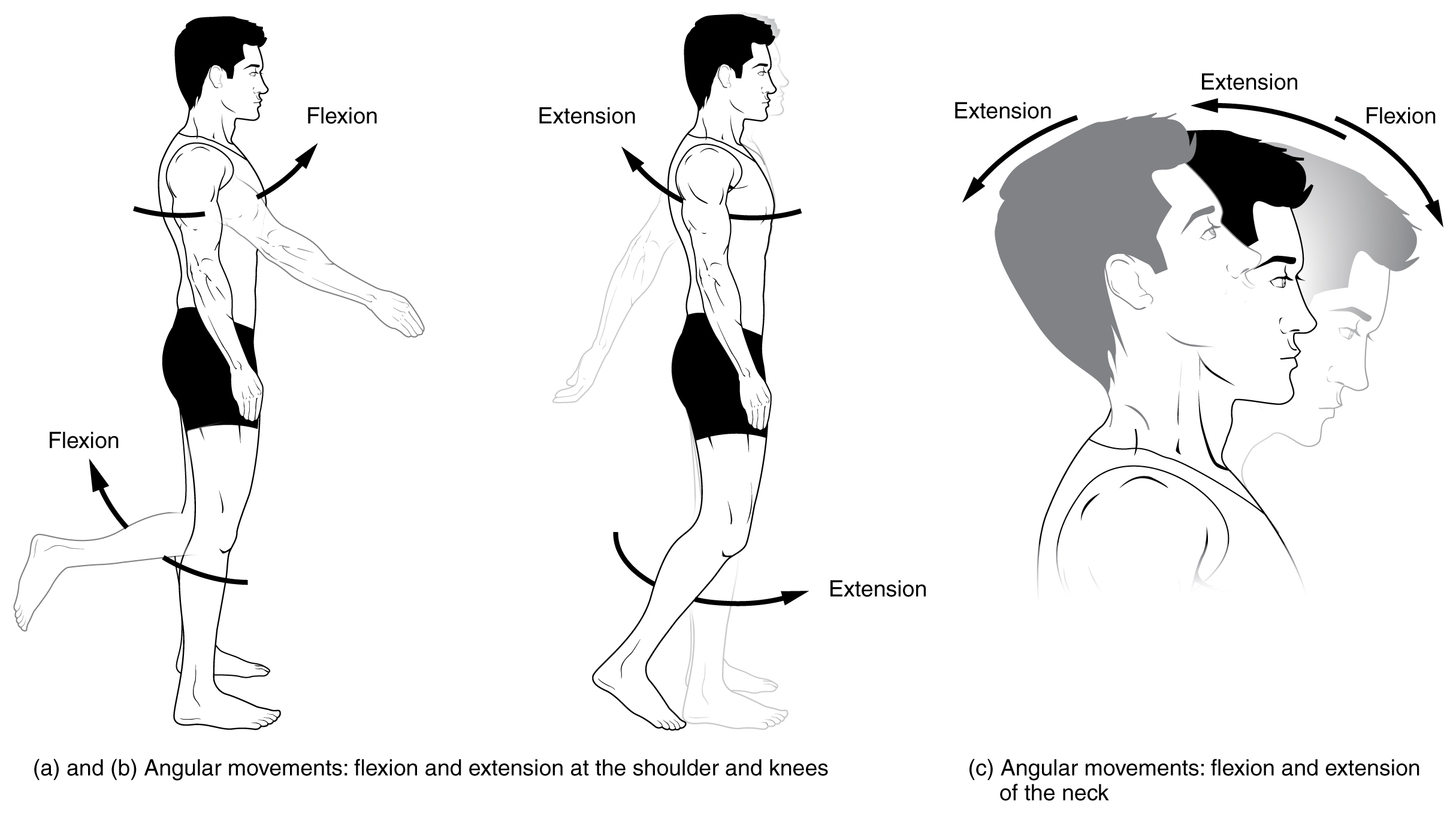 Anatomical Terms Of Motion Wikipedia
Anatomical Terms Of Motion Wikipedia
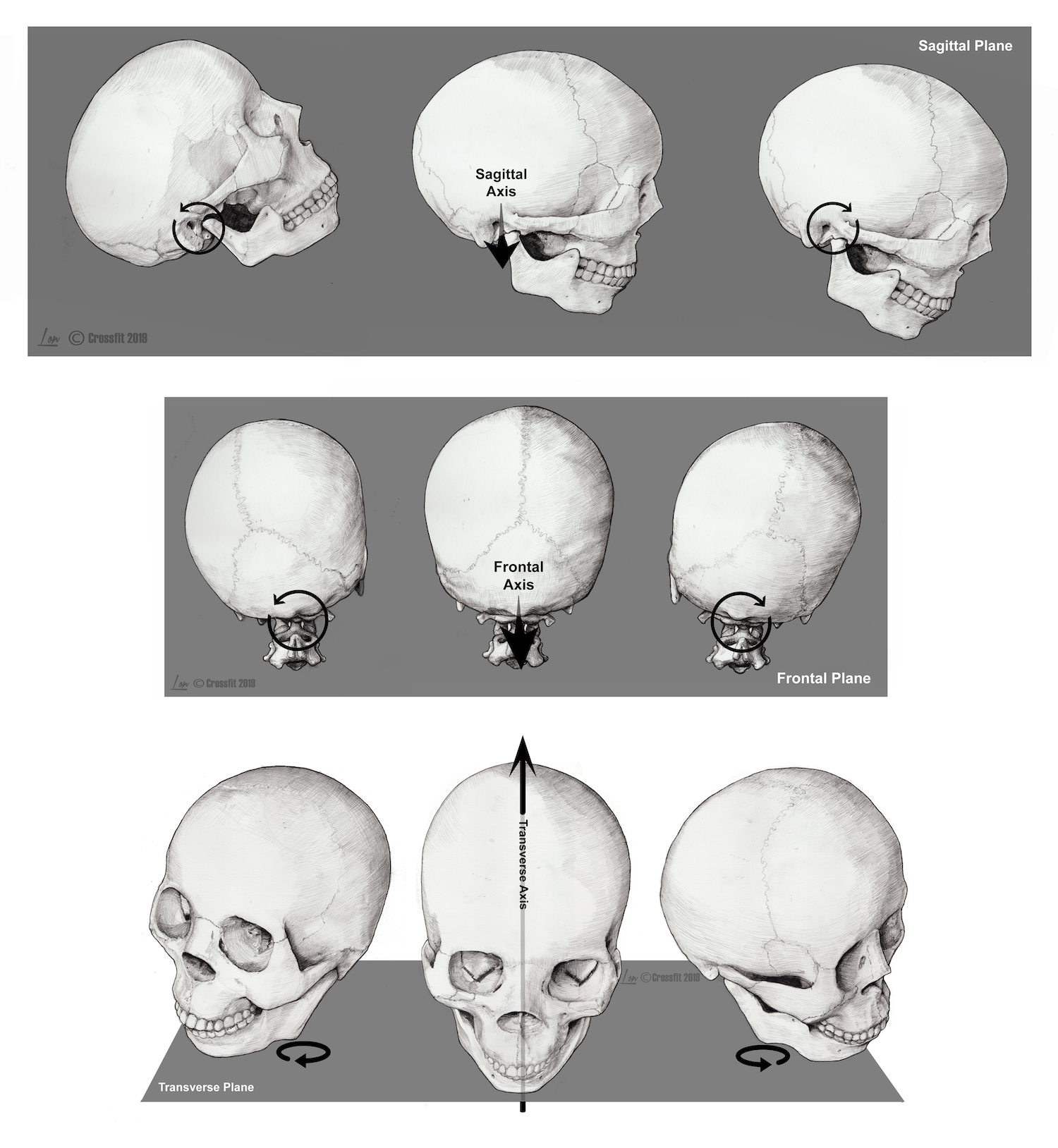 Crossfit Anatomical Planes Axes
Crossfit Anatomical Planes Axes
 Levers Work To Create Movement In The Human Body Human
Levers Work To Create Movement In The Human Body Human
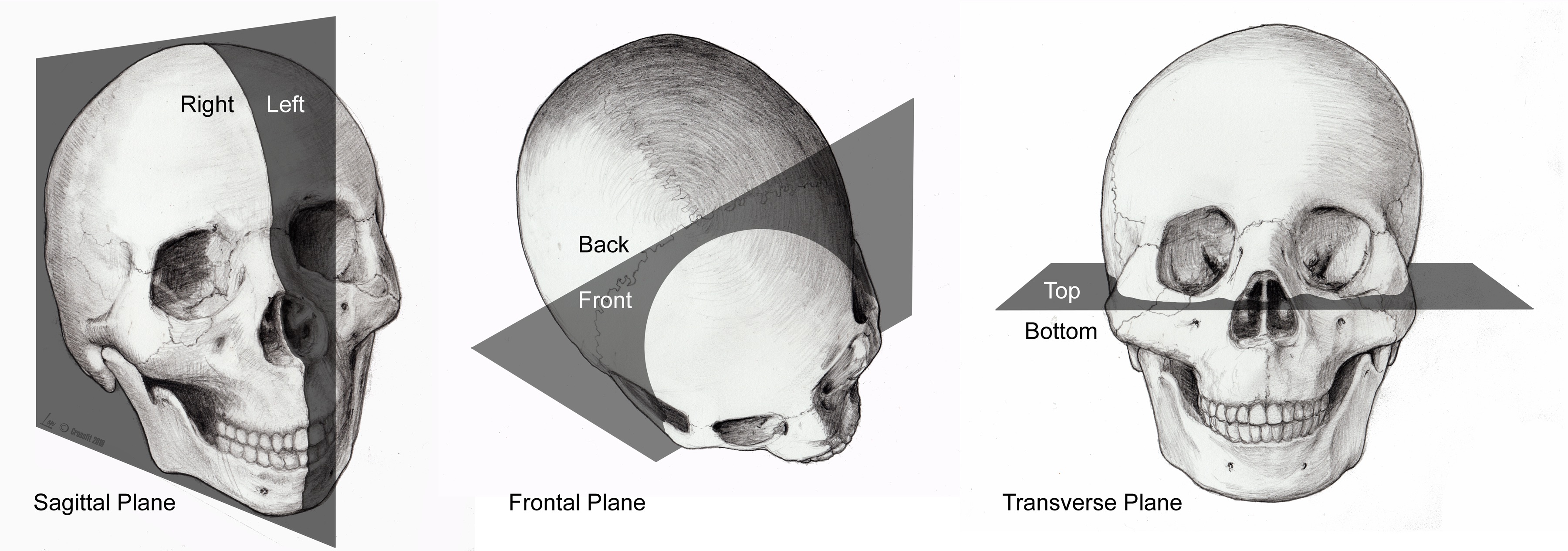 Crossfit Anatomical Planes Axes
Crossfit Anatomical Planes Axes
Plos One Comparative Anatomy Of The Bony Labyrinth Inner
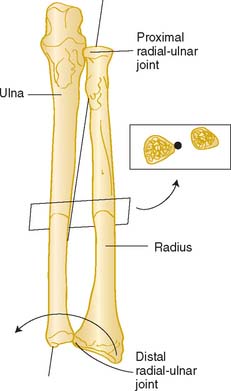 Biomechanics Of The Elbow Clinical Gate
Biomechanics Of The Elbow Clinical Gate
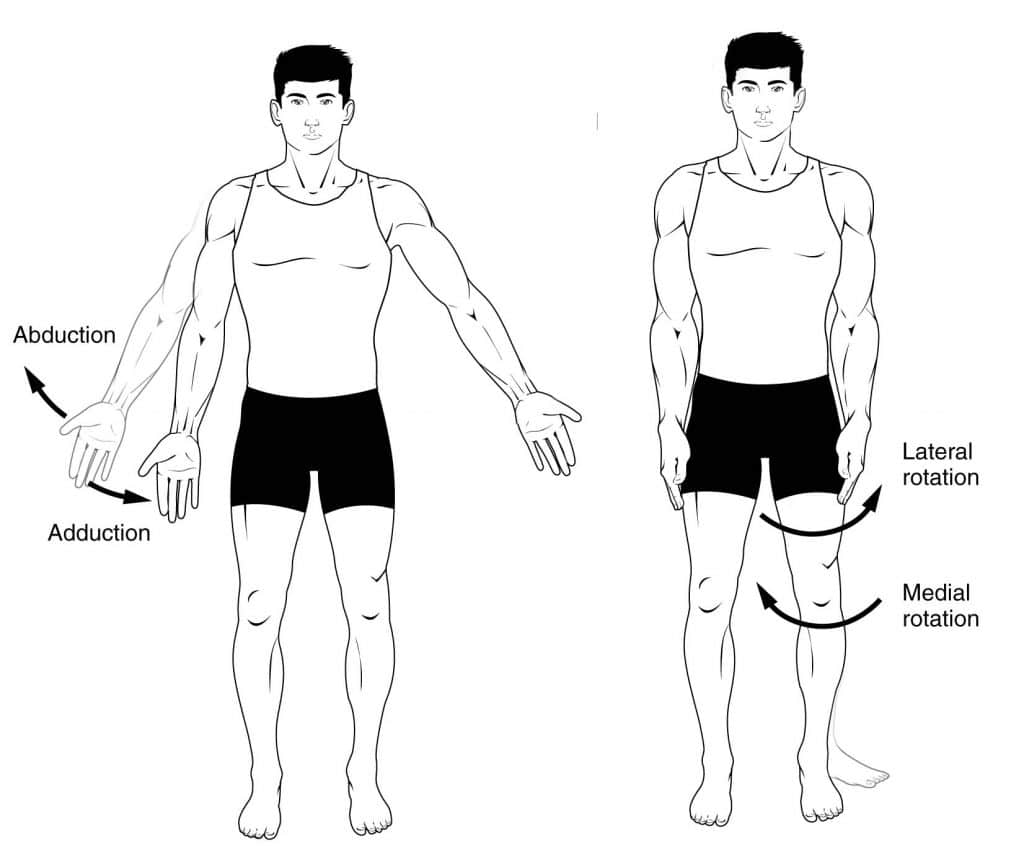 Anatomical Terms Of Movement Flexion Rotation
Anatomical Terms Of Movement Flexion Rotation
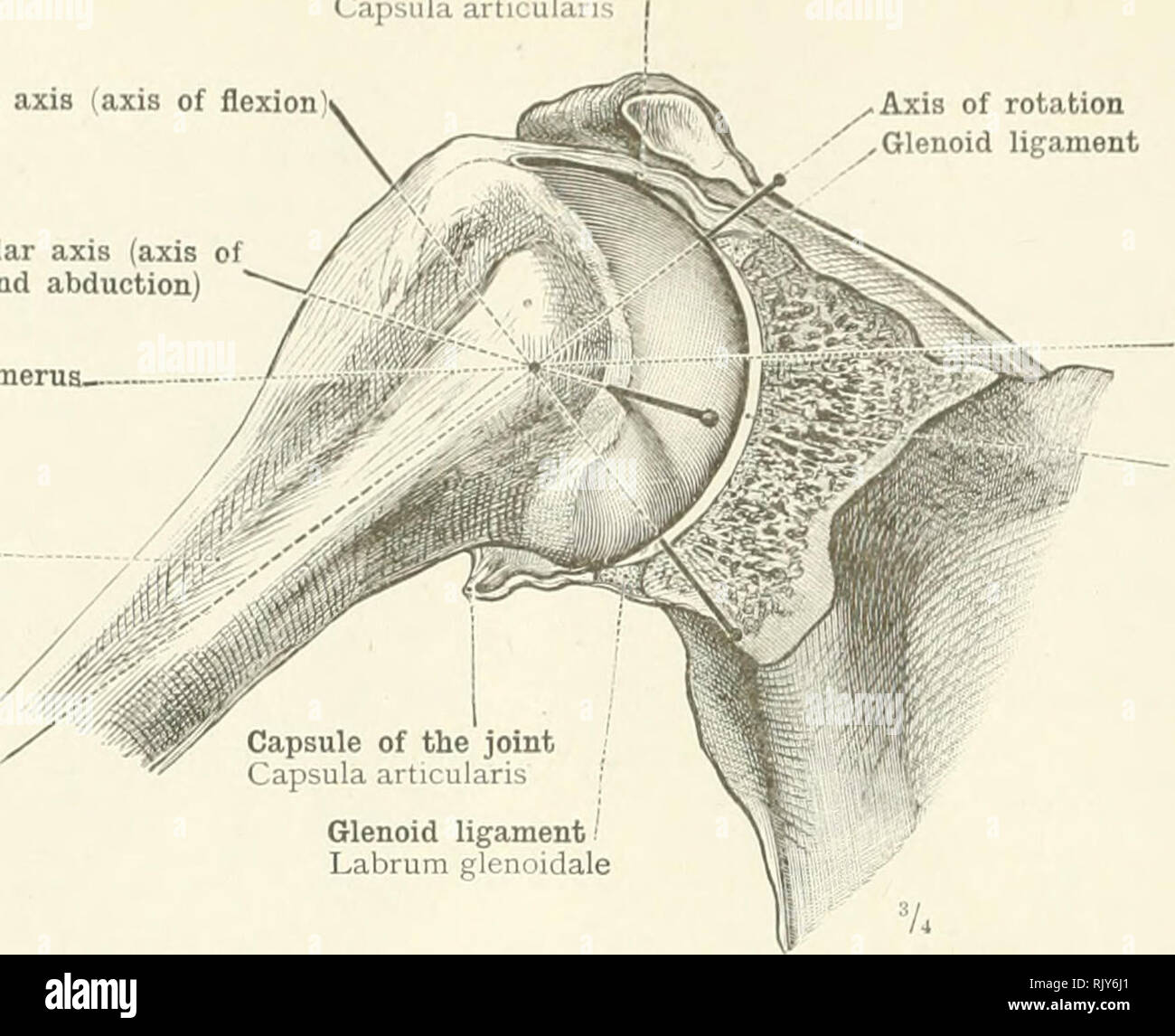 An Atlas Of Human Anatomy For Students And Physicians
An Atlas Of Human Anatomy For Students And Physicians
Chapter 9 The Hip Joint And Pelvic Girdle
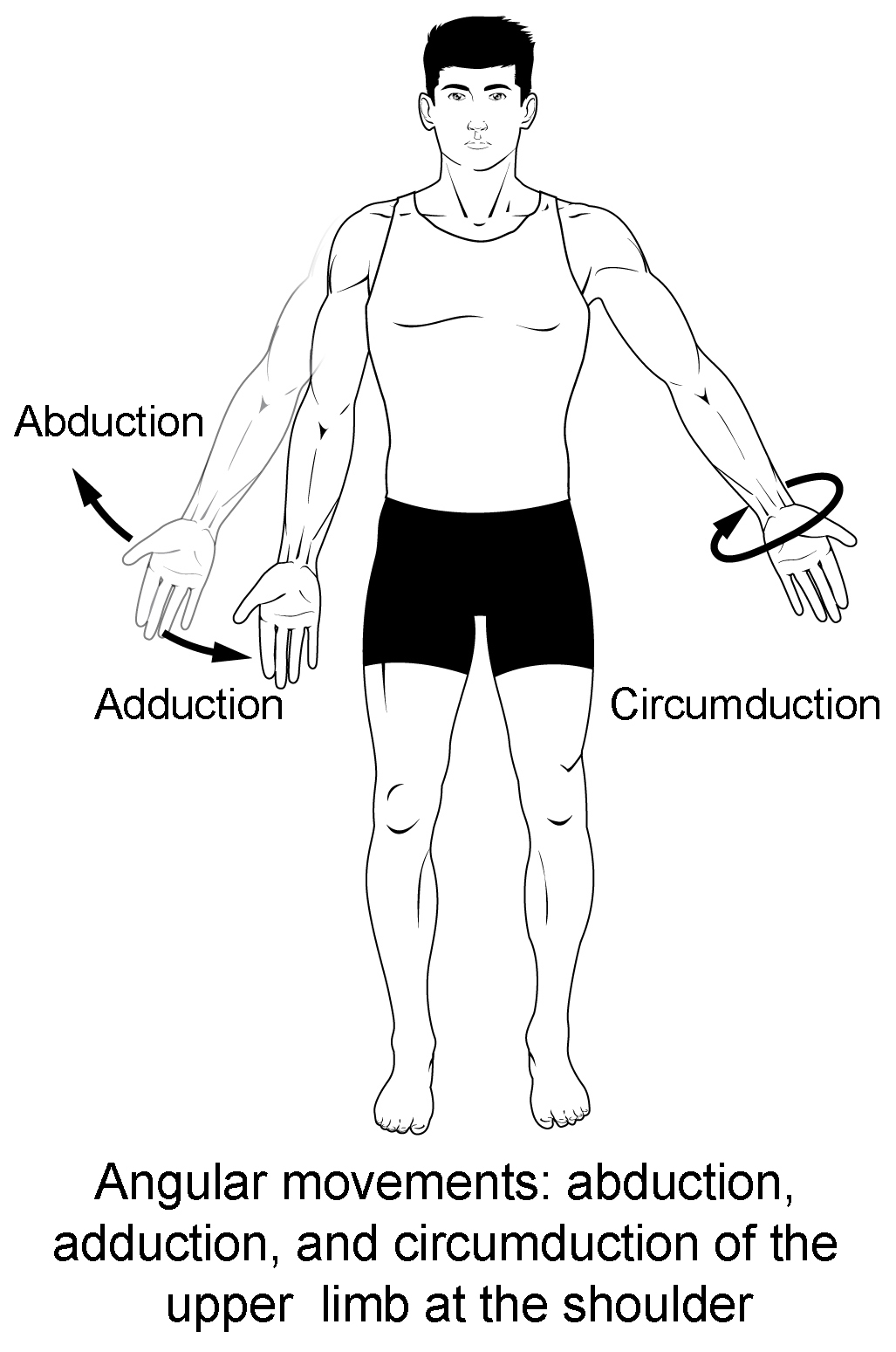 Types Of Body Movements Anatomy And Physiology I
Types Of Body Movements Anatomy And Physiology I
 Drexel Engineer S Discovery Turns Artificial Ankle Research
Drexel Engineer S Discovery Turns Artificial Ankle Research
 Axis Of Rotation Diagram Quizlet
Axis Of Rotation Diagram Quizlet
 Kinesiology Of The Shoulder Complex
Kinesiology Of The Shoulder Complex
 Axis Of Rotation Anatomy Human Body Axis 1 Transverse Axis
Axis Of Rotation Anatomy Human Body Axis 1 Transverse Axis
 Anatomical Terms Of Movement Flexion Rotation
Anatomical Terms Of Movement Flexion Rotation
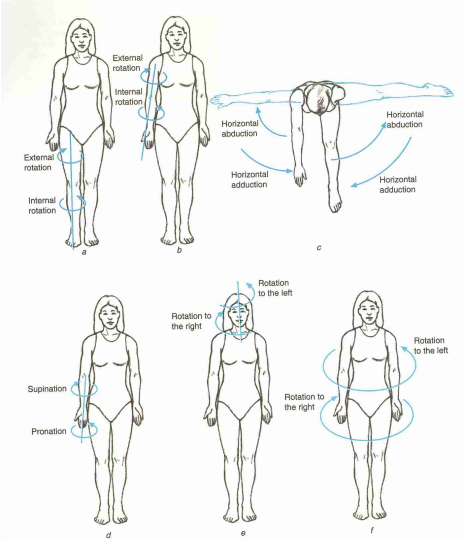 Cardinal Planes And Axes Of Movement Physiopedia
Cardinal Planes And Axes Of Movement Physiopedia
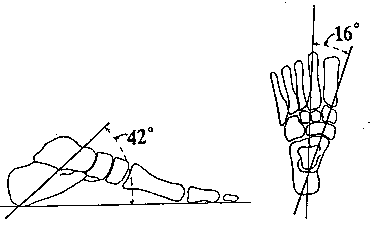 Subtalar Joint Motion Open Chain
Subtalar Joint Motion Open Chain


Belum ada Komentar untuk "Axis Of Rotation Anatomy"
Posting Komentar