Corneal Anatomy
Cornea dome shaped transparent membrane about 12 mm 05 inch in diameter that covers the front part of the eye. Except at its margins the cornea contains no blood vessels but it does contain many nerves and is very sensitive to pain or touch.
 The Cornea And Its Highlights Part 2 Anatomy Of The
The Cornea And Its Highlights Part 2 Anatomy Of The
It is nourished and provided with oxygen anteriorly.
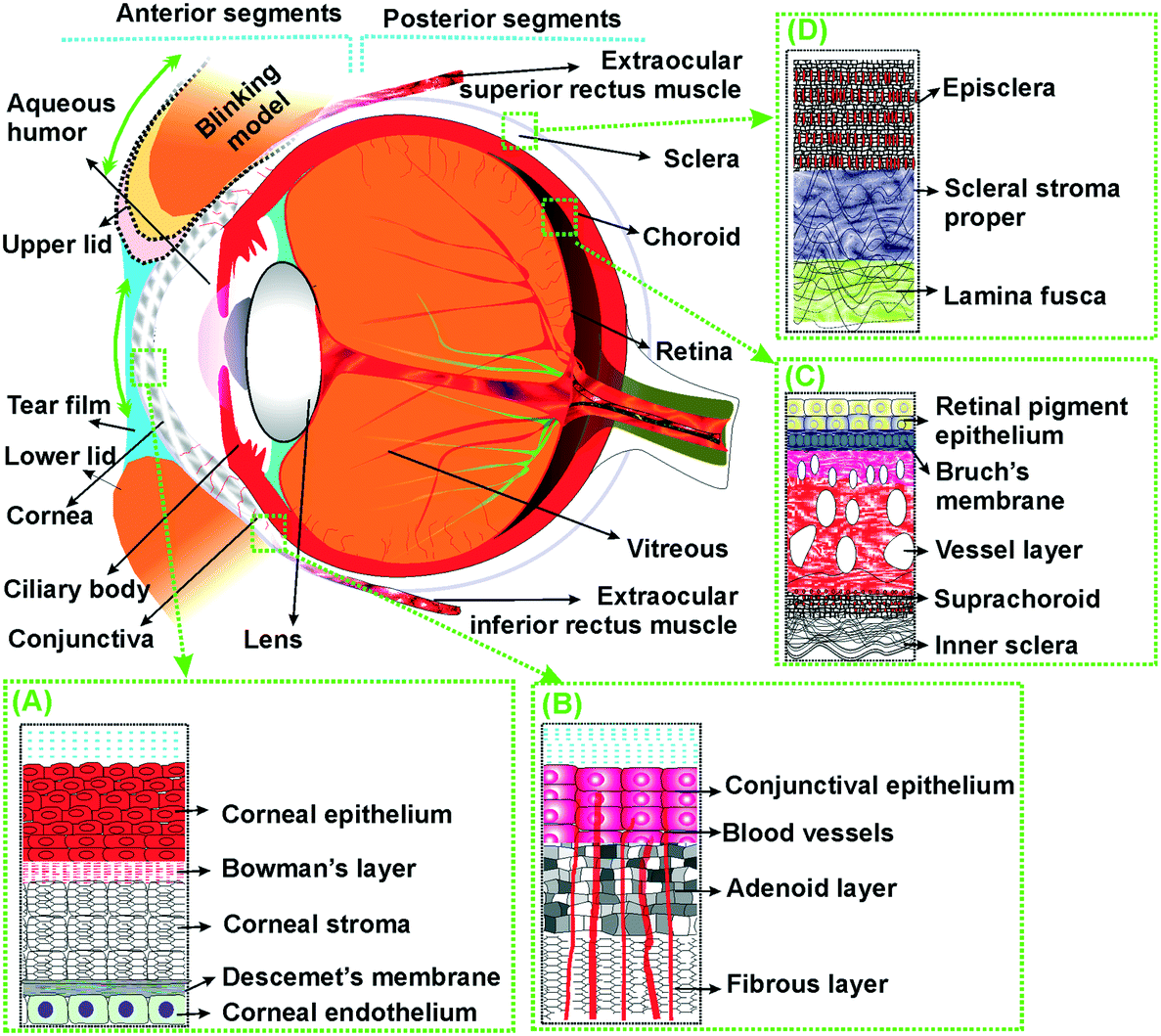
Corneal anatomy. In a number of ways the human eye works much like a digital camera. The cornea is the transparent part of the eye that covers the front portion of the eye. In humans the refractive power of the cornea is approximately 43 dioptres.
The iris of the eye functions like the diaphragm of a camera controlling the amount. Corneal anatomy the cornea is the transparent front part of the eye that covers the iris pupil and anterior chamber. Light is focused primarily by the cornea the clear front surface of the eye.
The cornea is the transparent front part of the eye that covers the iris pupil and anterior chamber. The cornea with the anterior chamber and lens refracts light with the cornea accounting for approximately two thirds of the eyes total optical power. The anatomy and structure of the adult human cornea.
The cornea composes the outermost layer of the eye. Transparent refract light contain the intraocular pressure provide a protective interface sbj. To meet the diverse functional demands the cornea must be.
It covers the pupil the opening at the center of the eye iris the colored part of the eye and anterior chamber the fluid filled inside of the eye. This magnified image of a section of the eye demonstrates the structure of the cornea and the limbus. Yet without its clarity the eye would not be able to perform its necessary functions.
The cornea the cornea is a transparent avascular tissue with a smooth convex outer surface and concave inner surface which resembles a small watch glass. The cornea lacks the neurobiological sophistication of the retina and the dynamic movement of the lens. The cornea is a transparent structure that together with the lens provides the refractive power of the eye.
The corneas main function is to refract or bend light. Together with the lens the cornea refracts light accounting for approximately two thirds of the eyes total optical power. The importance of the cornea to the ocular structure and visual system is often overlooked because of the corneas unassuming transparent nature.
The eyes crystalline lens is located directly behind the.
 Keratitis A Clinical Approach Intechopen
Keratitis A Clinical Approach Intechopen
 Eye Anatomy A Closer Look At The Parts Of The Eye
Eye Anatomy A Closer Look At The Parts Of The Eye
 Cornea Disease Dulles Eye Associates
Cornea Disease Dulles Eye Associates
 The Cornea Ocular Surface Center Berlin
The Cornea Ocular Surface Center Berlin
 Do Corneal Epithelial Cells Multiply After They Are Damaged
Do Corneal Epithelial Cells Multiply After They Are Damaged
 New Layer Of The Human Cornea Discovered
New Layer Of The Human Cornea Discovered
 The Cornea Ocular Surface Center Berlin
The Cornea Ocular Surface Center Berlin
 The Cornea Anatomy And Function Springerlink
The Cornea Anatomy And Function Springerlink
 Vision And The Eye S Anatomy Healthengine Blog
Vision And The Eye S Anatomy Healthengine Blog
 Corneal Transplant Series Normal Anatomy Medlineplus
Corneal Transplant Series Normal Anatomy Medlineplus
 Corneal Anatomy Flashcards On Tinycards
Corneal Anatomy Flashcards On Tinycards
 The Eyes Human Anatomy Diagram Optic Nerve Iris Cornea
The Eyes Human Anatomy Diagram Optic Nerve Iris Cornea
 2a Anatomy Review Cornea Human Physiology 116 With
2a Anatomy Review Cornea Human Physiology 116 With
 Evaluation And Management Of Corneal Abrasions American
Evaluation And Management Of Corneal Abrasions American
 Frontiers A Review Of Structural And Biomechanical Changes
Frontiers A Review Of Structural And Biomechanical Changes
 Fuchs Corneal Dystrophy Littleton Corneal Transplant
Fuchs Corneal Dystrophy Littleton Corneal Transplant
 Keratoplasty Ukraine Anatomy Of The Eye The Structure Of
Keratoplasty Ukraine Anatomy Of The Eye The Structure Of
 Microengineered Biomimetic Ocular Models For
Microengineered Biomimetic Ocular Models For
 Full Lecture Corneal Anatomy And Physiology
Full Lecture Corneal Anatomy And Physiology
 Anatomy And Physiology Of The Cornea Sciencedirect
Anatomy And Physiology Of The Cornea Sciencedirect
 The Anatomy Of The Eye Anterior Segment Precision Family
The Anatomy Of The Eye Anterior Segment Precision Family
 Corneal Flash Burns What You Need To Know
Corneal Flash Burns What You Need To Know
 Optimed Eye And Laser Clinic Anatomy The Cornea The
Optimed Eye And Laser Clinic Anatomy The Cornea The
 Anatomy Of The Cornea A Section Of The Anterior Part Of
Anatomy Of The Cornea A Section Of The Anterior Part Of
 Cornea Definition And Detailed Illustration
Cornea Definition And Detailed Illustration
 External And Internal Eye Anatomy Medlineplus Medical
External And Internal Eye Anatomy Medlineplus Medical
 Eye Anatomy Explaining Pupil And Cornea
Eye Anatomy Explaining Pupil And Cornea
 Biomaterials For Corneal Bioengineering Iopscience
Biomaterials For Corneal Bioengineering Iopscience






Belum ada Komentar untuk "Corneal Anatomy"
Posting Komentar