Inclusions Anatomy
Lab and study packet. Glycogen glucose molecules are connected by α1 4 linkages and branched off by α1 6 linkages to form the complex structure of glycogen which also aids in rapid breakdown.
 Unique Characteristics Of Prokaryotic Cells Microbiology
Unique Characteristics Of Prokaryotic Cells Microbiology
Anatomy of a muscle fiber.

Inclusions anatomy. A gaseous liquid or solid foreign body enclosed in a mass as of a mineral b. Most carbohydrate inclusions are stored as polysaccharide glycogen within liver cells. Inclusion bodies sometimes called elementary bodies are nuclear or cytoplasmic aggregates of stable substances usually proteins.
Something that is included. Stored secretory inclusions may consist of proteins enzymes acids or crystalline substances. The muscular system introduction to the muscular system.
Axial muscles of the head neck and back. Hemosiderin is a complex found within the cell membrane that is a storage location for iron. Axial muscles of the abdominal wall and thorax.
Cell inclusion a usually lifeless often temporary constituent in the cytoplasm of a cell. The state of being included. Fetal inclusion a partially developed embryo enclosed within the body of its twin.
Cytoplasmic inclusions that store sugar in the form of glycogen glucose is broken down and stored as glycogen then released when it is needed. Interactions of skeletal muscles. 326b and foreign bodies such as dust particles viruses and intracellular bacteria.
Inclusions are considered to be nonliving components of the cell and are not bounded by membranes. Examples of cell inclusions are glycogen lipids and pigments such as melanin lipofuscin and hemosiderin. Inclusions are of two kinds.
The act of including. Cell inclusion a usually lifeless often temporary constituent in the cytoplasm of a cell. Anything that is enclosed.
The act of enclosing or the condition of being enclosed. A passive usually temporary product of cell activity such as a starch grain within the cytoplasm or nucleus. The most common inclusions are lipid droplets crystals glycogen and pigments.
Anything that is enclosed. Inclusions are never enclosed in a unit membrane and unlike the organelles and cytoskeleton they are not essential to cell survival. Asked in gems and.
Some minerals are contained within the cell as inclusions. The act of enclosing or the condition of being enclosed. Stored cellular products such as glycogen granules pigments and fat droplets see fig.
They typically represent sites of viral multiplication in a bacterium or a eukaryotic cell and usually consist of viral capsid proteins.
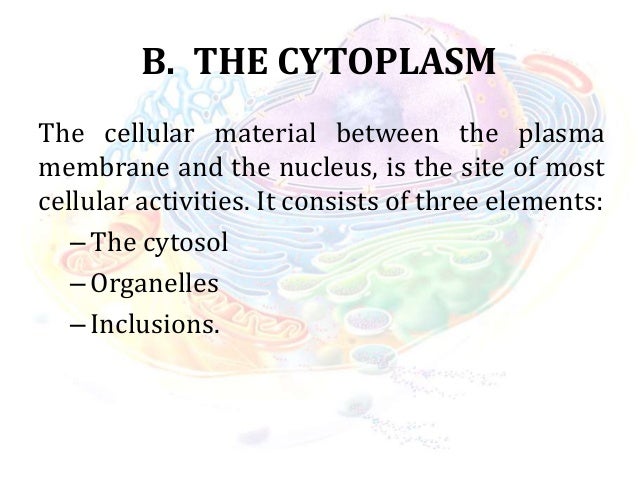
 The Cytoplasm Is The Cellular Material Outside The Nucleus
The Cytoplasm Is The Cellular Material Outside The Nucleus
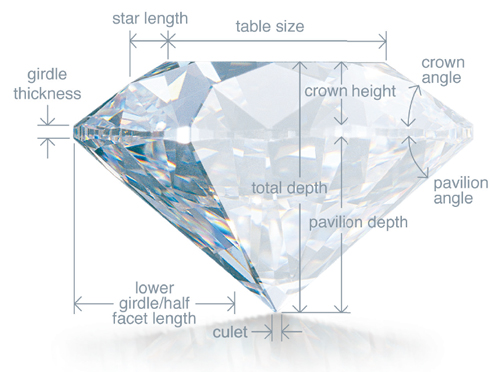 Learn The 4 Cs Of Diamonds Diamond Gold Warehouse
Learn The 4 Cs Of Diamonds Diamond Gold Warehouse
Ultrastructural Studies In Fetal I Cell Disease
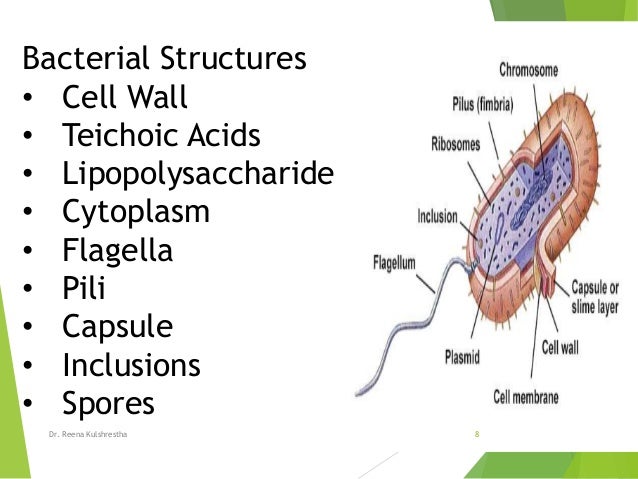
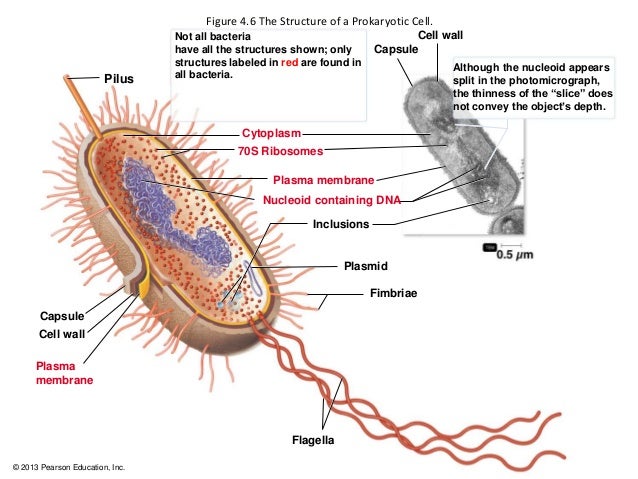 1 Microbial World And Prokaryotic Cell Anatomy
1 Microbial World And Prokaryotic Cell Anatomy
 The Anatomy Of A Diamond Grading Report Sparkle Cut
The Anatomy Of A Diamond Grading Report Sparkle Cut
Ch03 Cell Organelles Cytoskeleton
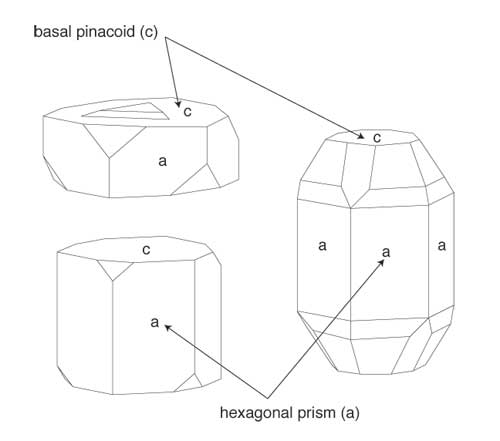 Gem Inclusions The Symmetry Of Crystals Inside Out
Gem Inclusions The Symmetry Of Crystals Inside Out
The Art Of Anatomy Louis Allen Vaught Art Agenda Phaidon
 Natural Inclusions In Diamonds Cape Town Diamond Museum
Natural Inclusions In Diamonds Cape Town Diamond Museum
Structure And Function Of Bacterial Cells
 Evaluation Of The Petrogenetic Significance Of Melt
Evaluation Of The Petrogenetic Significance Of Melt
Inside Out Inclusions The Symmetry Of Crystals Lotus
Study Of Cell And Cell Inclusions Plant Anatomy
 Ch03 Cell Organelles Cytoskeleton
Ch03 Cell Organelles Cytoskeleton
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/cell-membrane-373364_final-5b5f300546e0fb008271ce52.png) Cytoplasm Definition And Function
Cytoplasm Definition And Function
 The Making Of A Lewy Body The Role Of A Synuclein Post
The Making Of A Lewy Body The Role Of A Synuclein Post
 Human Anatomy Physiology Unit 3 Part 2 Review Worksheet Body Tissues
Human Anatomy Physiology Unit 3 Part 2 Review Worksheet Body Tissues
What Is The Difference Between Cell Organelles And Cell
 Diamond School Anna Sheffield Jewelry
Diamond School Anna Sheffield Jewelry
Lecture 4 Microbial Anatomy 2 Biol2830u Uoit Studocu
 Human Anatomy And Physiology I Ppt Video Online Download
Human Anatomy And Physiology I Ppt Video Online Download
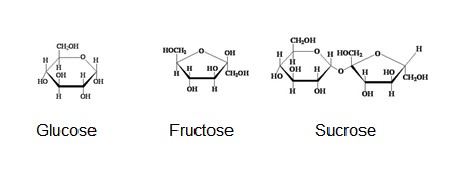 Cytoplasmic Inclusions Biology Educare
Cytoplasmic Inclusions Biology Educare
 Organelle Definition Function Types And Examples
Organelle Definition Function Types And Examples
 Anatomy And Cell Biology 3309 Lecture Notes Fall 2017
Anatomy And Cell Biology 3309 Lecture Notes Fall 2017


Belum ada Komentar untuk "Inclusions Anatomy"
Posting Komentar