Cartilage Anatomy
It contains no nerve cells or blood vessels and is. Articular cartilage acts as a shock absorber cushioning bones against impacting each other during a.
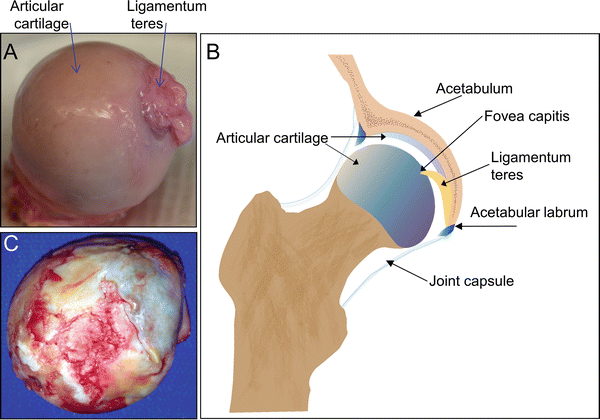 Anatomy Cartilage Springerlink
Anatomy Cartilage Springerlink
Cartilage is not innervated and therefore relies on diffusion to obtain nutrients.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/vector-illustration-of-a-meniscus-tear-and-surgery-871162428-03ac23d73f854954a8082f2ae3ce9219.jpg)
Cartilage anatomy. It is composed of a cartilage connective tissue forming the skeleton of mammalian embryos before bone formation begins and persisting in parts of the human skeleton into adulthood. Cartilage is the only component of the skeletons of certain primitive vertebrates including lampreys and sharks. The cartilage completely encircles the airway marking the inferior border of the larynx at the level of c6.
When a cartilage calcifies the. It is avascular and its microarchitecture is less organized than bone. Cartilage is a flexible connective tissue that differs from bone in several ways.
A firm elastic flexible type of connective tissue of a translucent whitish or yellowish color. Auricular cartilage is flexible connective tissue sometimes referred to as gristle. Articular cartilage has two primary purposes.
A part or structure composed of cartilage. Two c shaped pieces of cartilage called the medial and lateral menisci act as shock absorbers between the femur and tibia. Numerous bursae or fluid filled sacs help the knee move smoothly.
Cartilage has no nerves and therefore it is insensitive. Cartilage is a robust and viscoelastic connective tissue that can be found in joints between bones the rib cage intervertebral discs the ear and the nose. This type of cartilage is known as elastic cartilage.
The cricoid is the only complete circle of cartilage in the larynx or trachea. Extremely slippery articular cartilage allows bones to glide over each other as a joint flexes and straightens. Characteristic features of cartilage.
While more rigid and less flexible than muscle cartilage is not as stiff as bone. This is of clinical relevance during emergency intubation as pressure can be applied to the cricoid to occlude the oesophagus and thus prevent. Cartilage has no blood vessels or lymphatics and the nutrition of the cells diffuses through.
Cartilage is a resilient and smooth elastic tissue a rubber like padding that covers and protects the ends of long bones at the joints and is a structural component of the rib cage the ear the nose the bronchial tubes the intervertebral discs and many other body components. This causes it to heal very slowly. Cartilage is surrounded by a fibrous membrane known as the perichondrium.
It articulates with the paired arytenoid cartilages posteriorly as well as providing an attachment for the inferior horns of the thyroid cartilage.
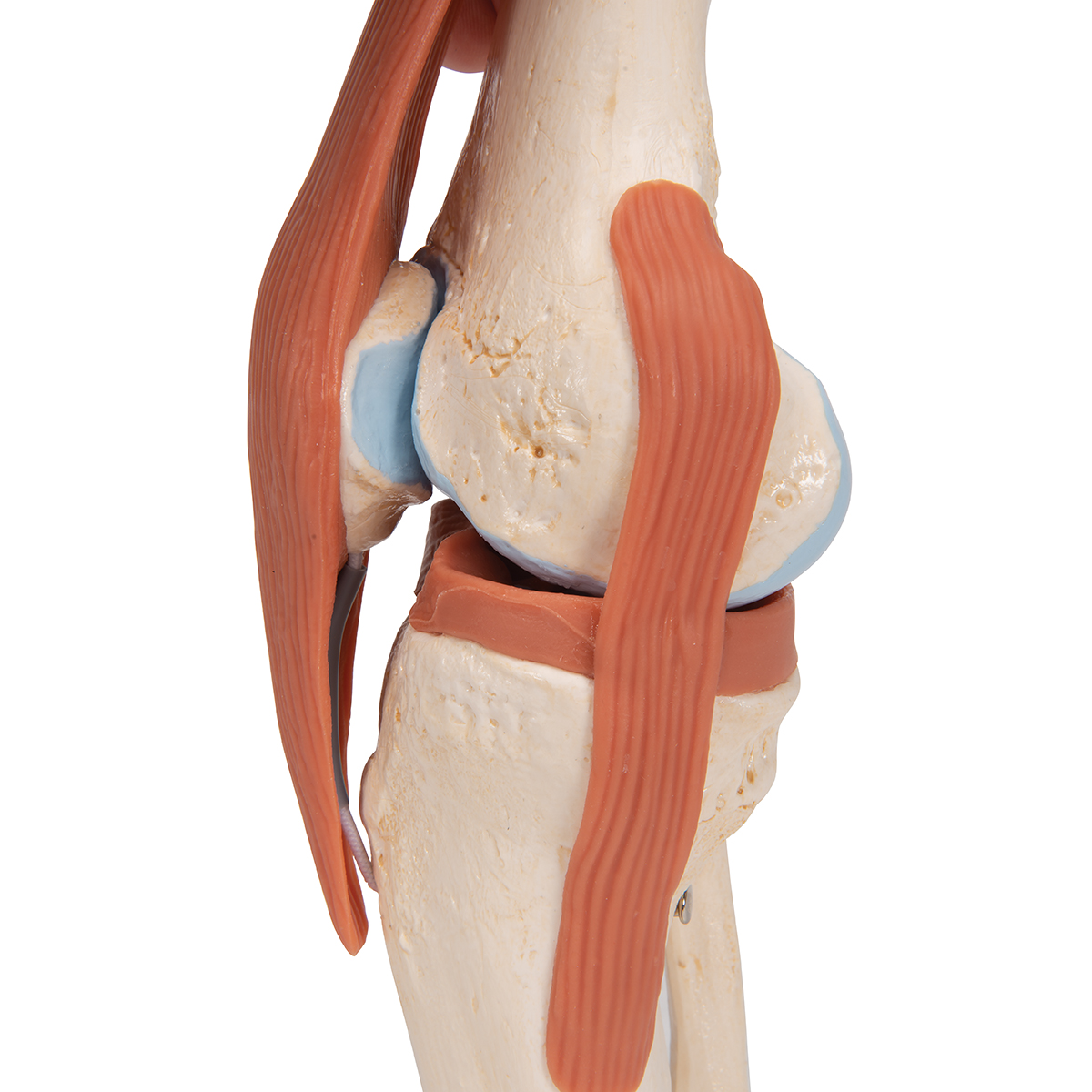 Deluxe Functional Knee Joint Model Anatomical Models
Deluxe Functional Knee Joint Model Anatomical Models
Adolescent Sports Injuries Of The Knee Cleveland Clinic
 Anatomy 7 Bones Cartilage And Joints Medicine 1st Year
Anatomy 7 Bones Cartilage And Joints Medicine 1st Year
 Larynx An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Larynx An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
 Imagenes Fotos De Stock Y Vectores Sobre Cartilage Anatomy
Imagenes Fotos De Stock Y Vectores Sobre Cartilage Anatomy
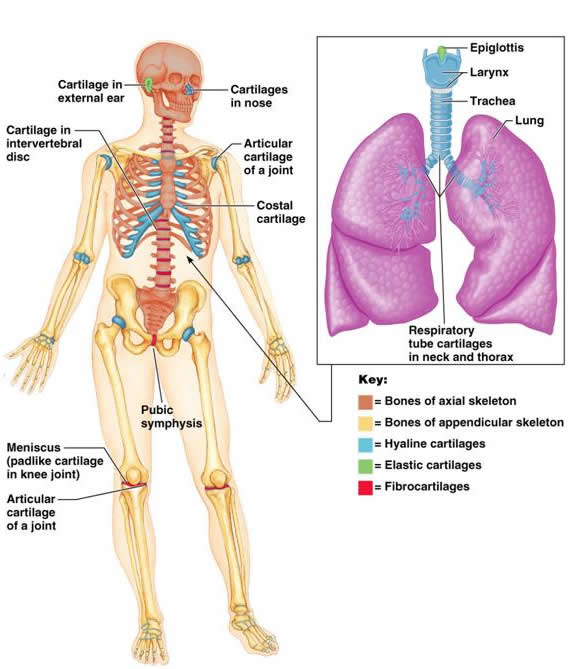 Skeletal Cartilages Anatomy Physiology
Skeletal Cartilages Anatomy Physiology
 Articular Cartilage Basic Science Orthobullets
Articular Cartilage Basic Science Orthobullets
:watermark(/images/watermark_only.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/articular-cartilage-of-the-trochlear-notch/pf6G5qBDyFNQFIvGCl4Mw_articular_cartilage_of_the_trochlear_notch_magnified.png) Cartilage Anatomy Histology Types And Functions Kenhub
Cartilage Anatomy Histology Types And Functions Kenhub
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/vector-illustration-of-a-meniscus-tear-and-surgery-871162428-03ac23d73f854954a8082f2ae3ce9219.jpg) Meniscus Vs Cartilage Tear Of The Knee
Meniscus Vs Cartilage Tear Of The Knee
 Articular Cartilage Basic Science Orthobullets
Articular Cartilage Basic Science Orthobullets
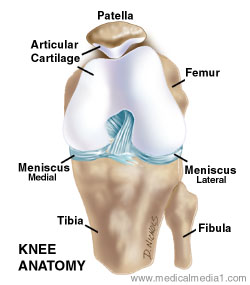 Anatomy Of The Knee Joint Paley Orthopedic Spine Institute
Anatomy Of The Knee Joint Paley Orthopedic Spine Institute
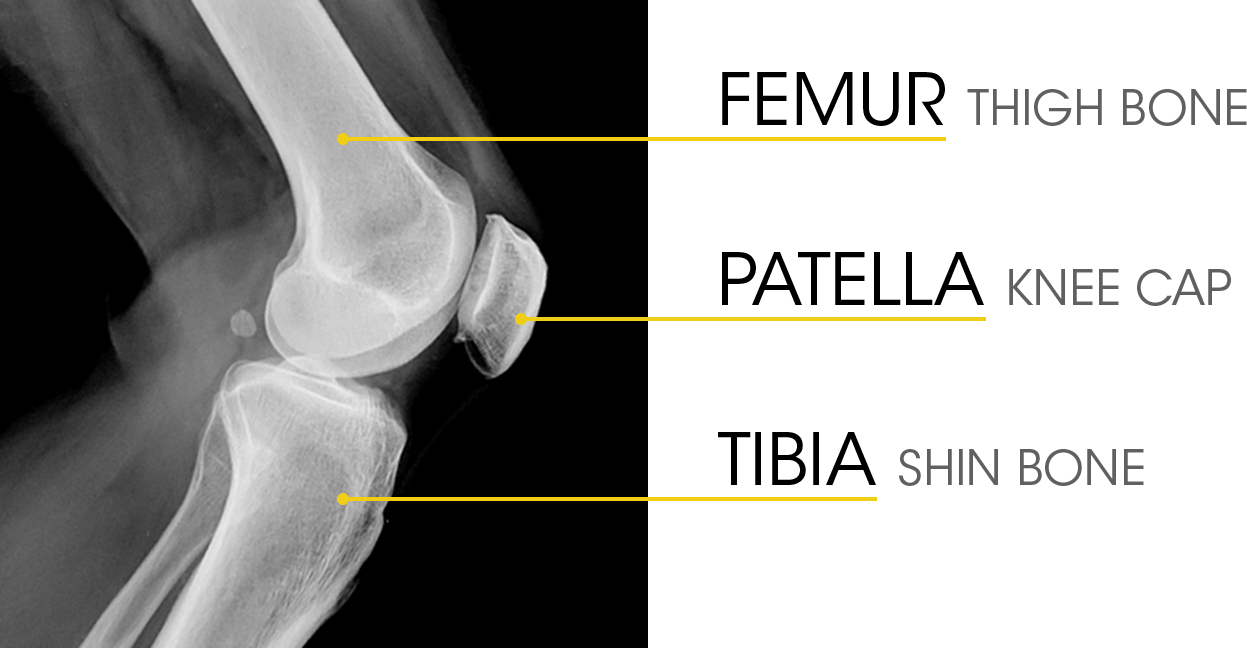 Understanding The Role Of Cartilage In The Knee
Understanding The Role Of Cartilage In The Knee
 Imagenes Fotos De Stock Y Vectores Sobre Cartilage Anatomy
Imagenes Fotos De Stock Y Vectores Sobre Cartilage Anatomy
 Free Art Print Of Articular Cartilage Anatomy
Free Art Print Of Articular Cartilage Anatomy
 Anatomy Of Bone And Cartilage 1
Anatomy Of Bone And Cartilage 1
Articular Cartilage Restoration Orthoinfo Aaos
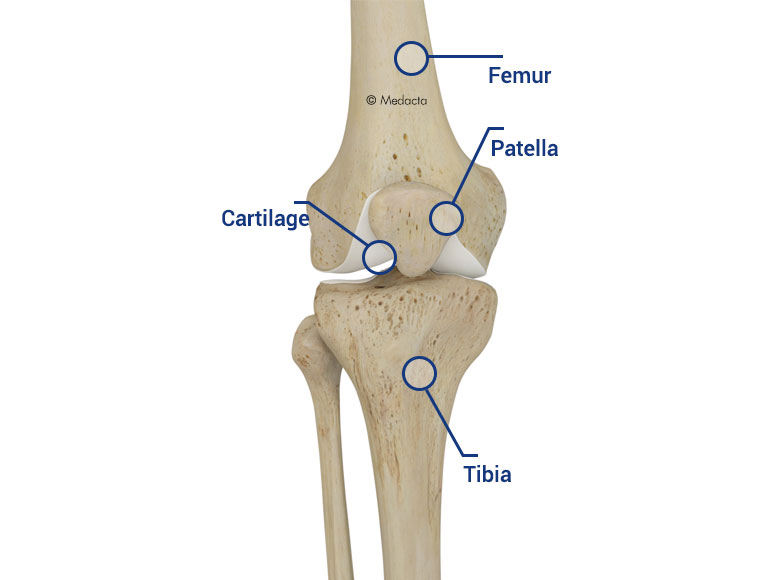 Medacta Corporate Knee Anatomy
Medacta Corporate Knee Anatomy
 Knee Anatomy Including Ligaments Cartilage And Meniscus
Knee Anatomy Including Ligaments Cartilage And Meniscus
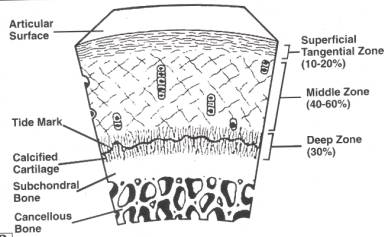 Articular Cartilage Anatomy Team Bone
Articular Cartilage Anatomy Team Bone
Anatomy Knee Restoration Center Of Indiana
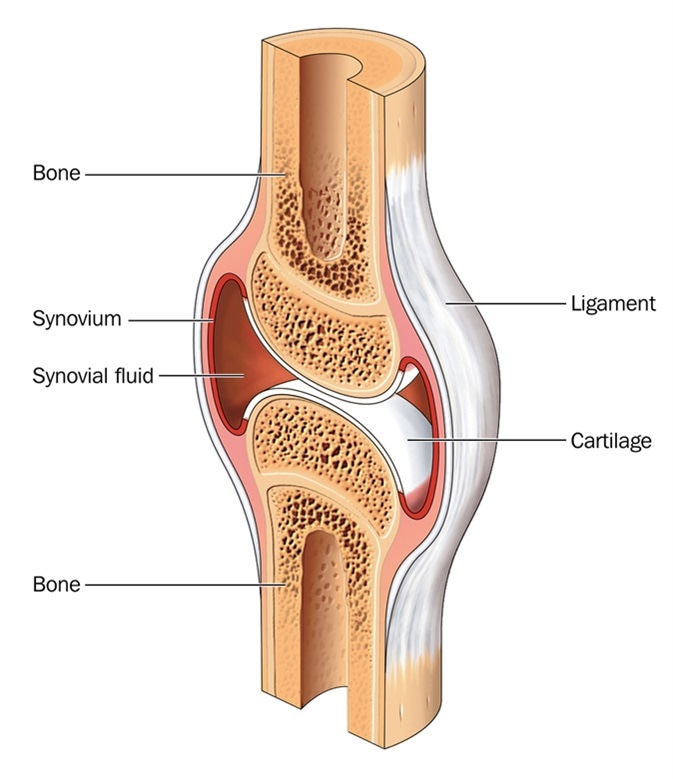
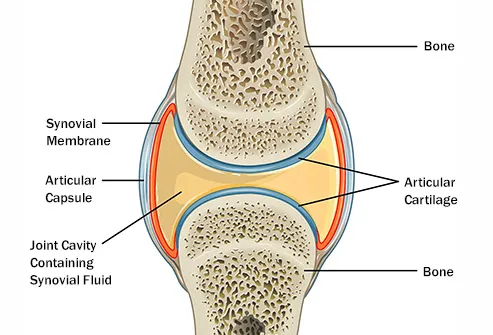 Why Are My Joints So Stiff What Can I Do
Why Are My Joints So Stiff What Can I Do
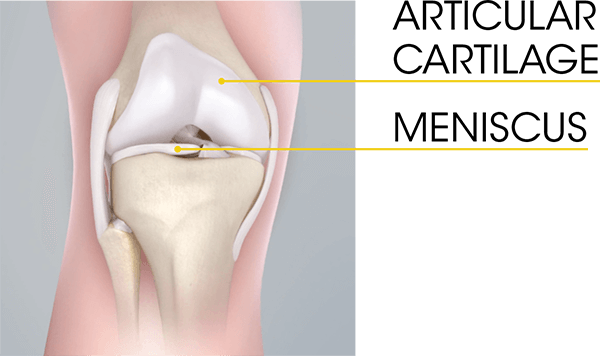 Understanding The Role Of Cartilage In The Knee
Understanding The Role Of Cartilage In The Knee
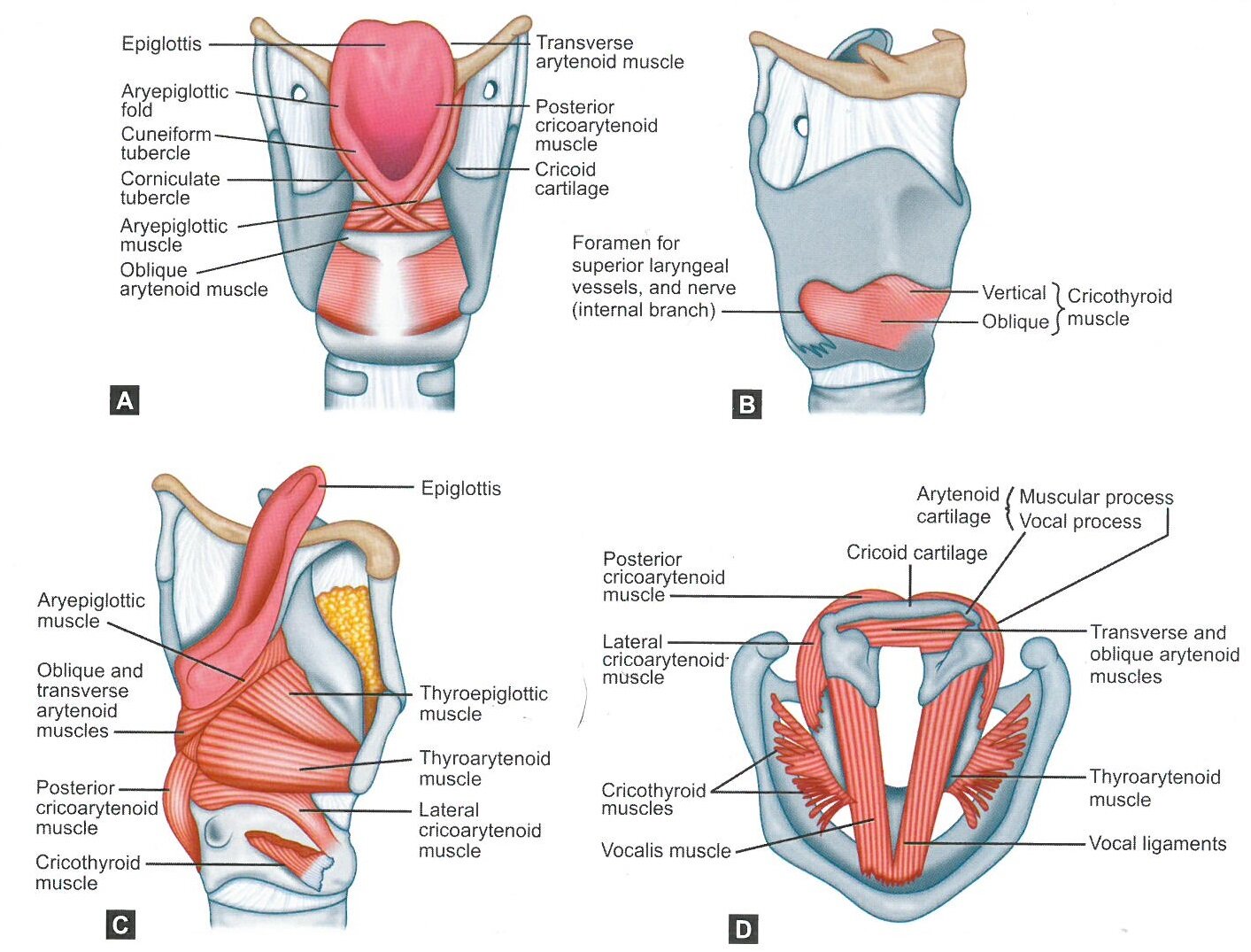 Anatomy Philadelphia Ear Nose And Throat Associates Penta
Anatomy Philadelphia Ear Nose And Throat Associates Penta

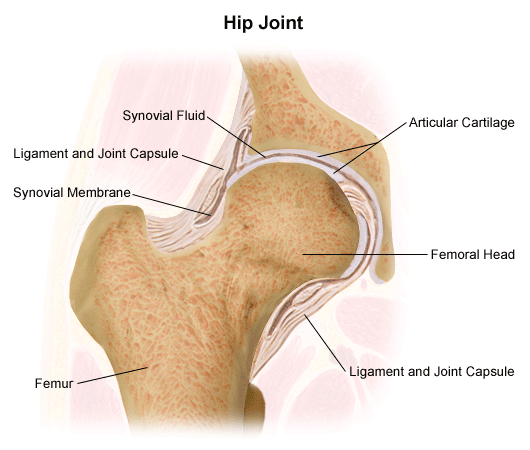
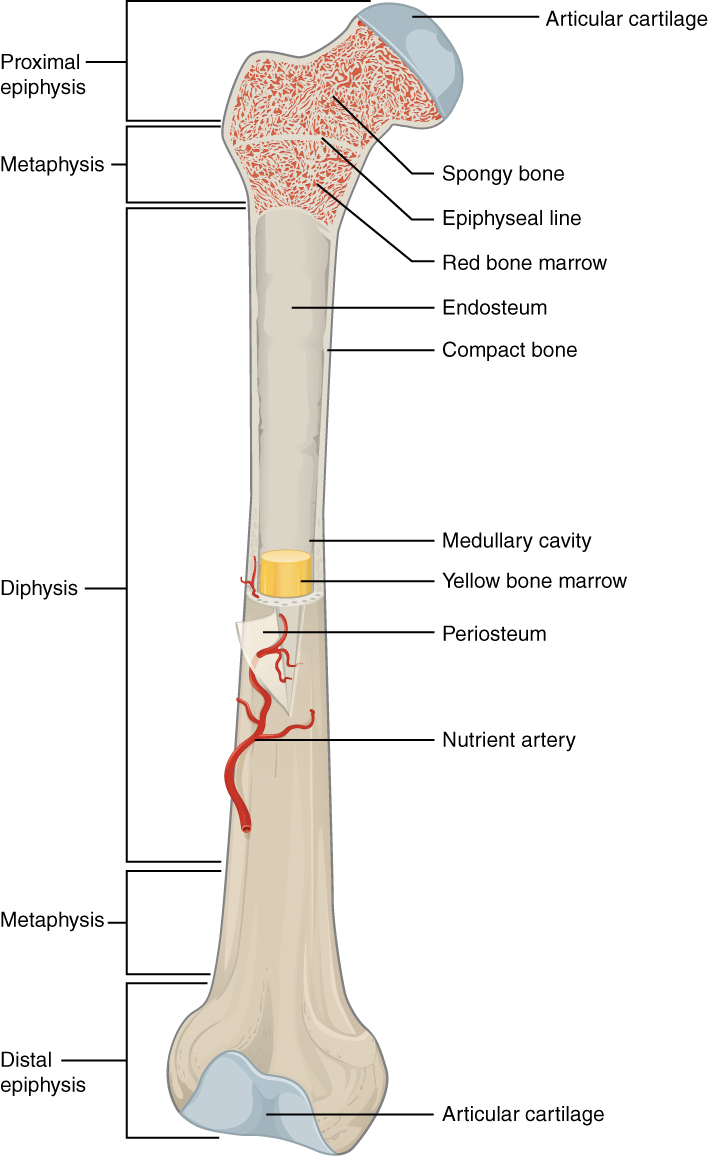
Belum ada Komentar untuk "Cartilage Anatomy"
Posting Komentar