Anatomy Of Cerebral Cortex
A number of disorders result from damage or death to. Sulci and gyri form a more or less constant pattern on the basis of which in human nervous system.
 Functional Systems Of The Cerebral Cortex Boundless
Functional Systems Of The Cerebral Cortex Boundless
Pyramidal cells fusiform cells and stellate granular cells.
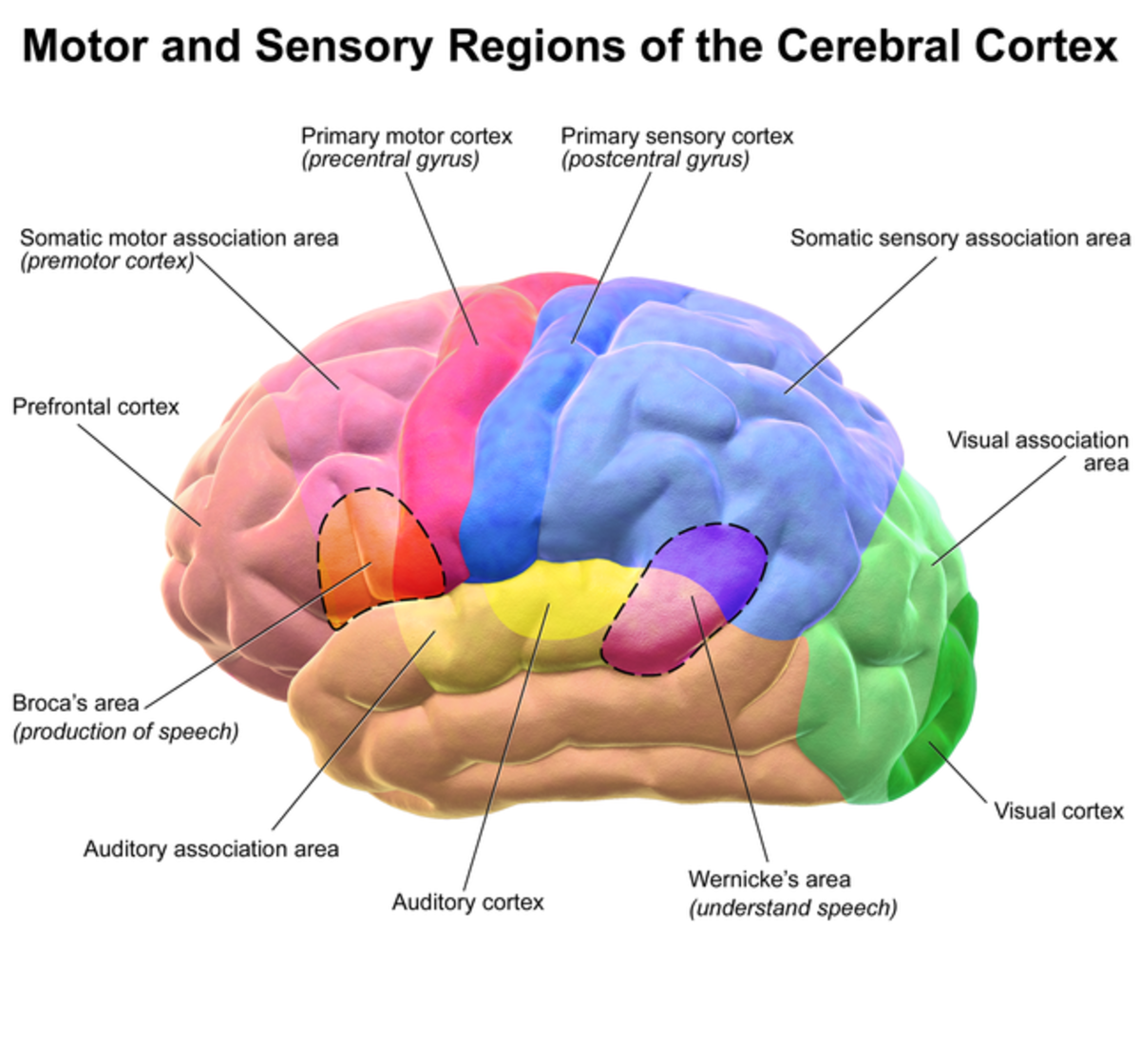
Anatomy of cerebral cortex. Organs with well defined cortical layers include kidneys adrenal glands ovaries the thymus and portions of the brain including the cerebral cortex the best known of all cortices. Physiologic anatomy of the cerebral cortex. The midbrain is often considered the smallest region of the brain.
Additional striking external features of the cerebral cortex are the poles. It is separated into two cortices by the longitudinal fissure that divides the cerebrum into the left and right cerebral hemispheres. It plays a key role in attention perception aw.
The cerebral cortex consists of the hundreds of billions of neurons and all of them are different variations of only three morphological shapes. These pointed ends are the poles of the cerebral cortex. The cerebral cortex contains sensory areas and motor areas.
The pons connects the cerebral cortex to the medulla and to the cerebellum and serves a number. The cortex covers the outer portion 15mm to 5mm of the cerebrum and cerebellum. The cortex thin layer of tissue is gray because nerves in this area lack the insulation that makes most other parts of the brain appear to be white.
The cerebral cortex is the layer of the brain often referred to as gray matter. The cerebral cortex is the largest site of neural integration in the central nervous system. When the cerebrum is viewed from the lateral aspect each cerebral hemisphere has the appearance in which three somewhat pointed ends can be recognised.
Other types of cells seen in the cortex are a modification one of those three. The crest of a single convolution is known as a gyrus and the fissure between two gyri is known as a sulcus. The functional part of the cerebral cortex is a thin layer of neurons covering the surface of all the convolutions of the cerebrum.
Changes in the cerebral cortex. The cerebral cortex also known as the cerebral mantle is the outer layer of neural tissue of the cerebrum of the brain in humans and other mammals. The medulla is located directly above the spinal cord in the lower part of the brain stem.
What does the brains cerebral cortex do. This layer is only 2 to 5 millimeters thick with a total area of about one quarter of a square meter. The total cerebral cortex contains about 100 billion neurons.
Directionally the cerebrum and the cortex that covers it is the uppermost part of the brain. Cortex anatomy in anatomy and zoology the cortex latin for bark rind shell or husk is the outermost or superficial layer of an organ. The cerebral cortex is highly convoluted.
The two hemispheres are joined beneath the cortex by the corpus callosum.
 Parasagittal View Of Cerebral Cortex Primary Motor Sensory
Parasagittal View Of Cerebral Cortex Primary Motor Sensory
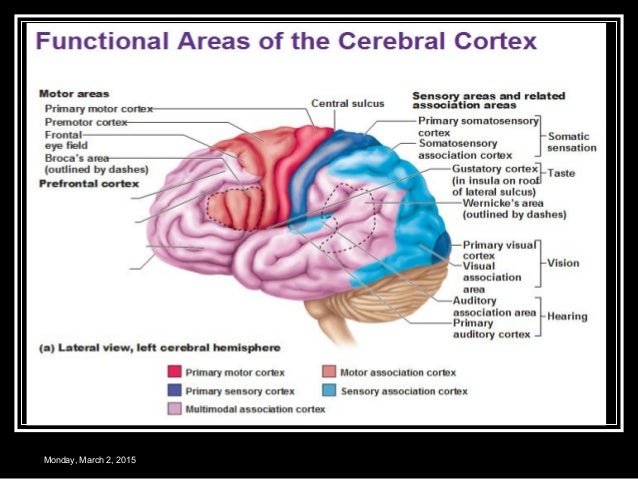
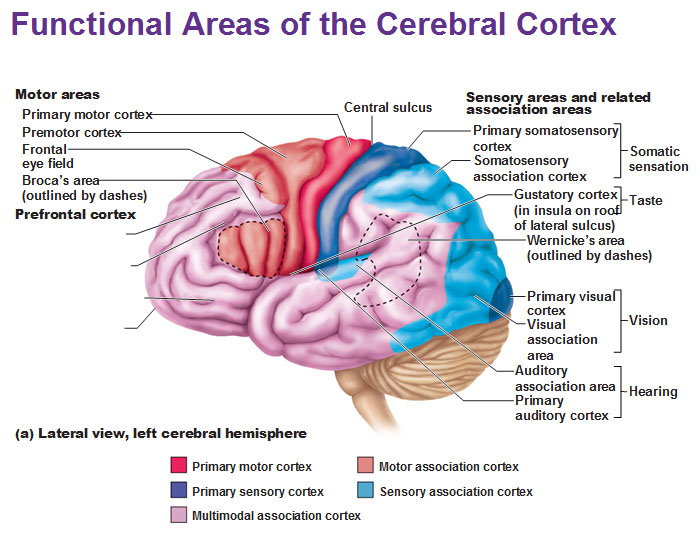 Functional Areas Of The Cerebral Cortex
Functional Areas Of The Cerebral Cortex
Nervous System Josi S Anatomy And Physiology
 The Brain Broca S And Wernicke S Areas And The Circle Of
The Brain Broca S And Wernicke S Areas And The Circle Of

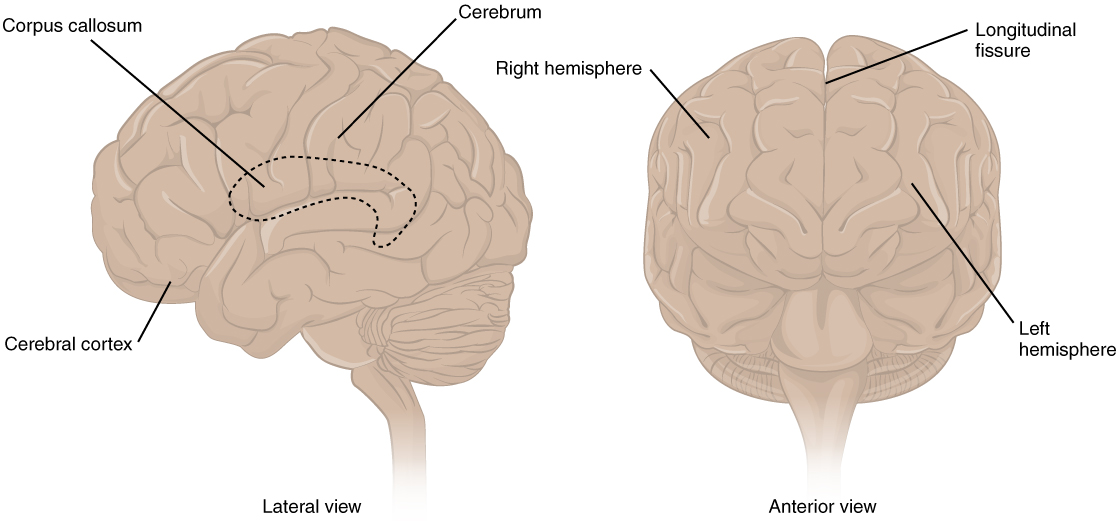 13 2 The Central Nervous System Anatomy And Physiology
13 2 The Central Nervous System Anatomy And Physiology
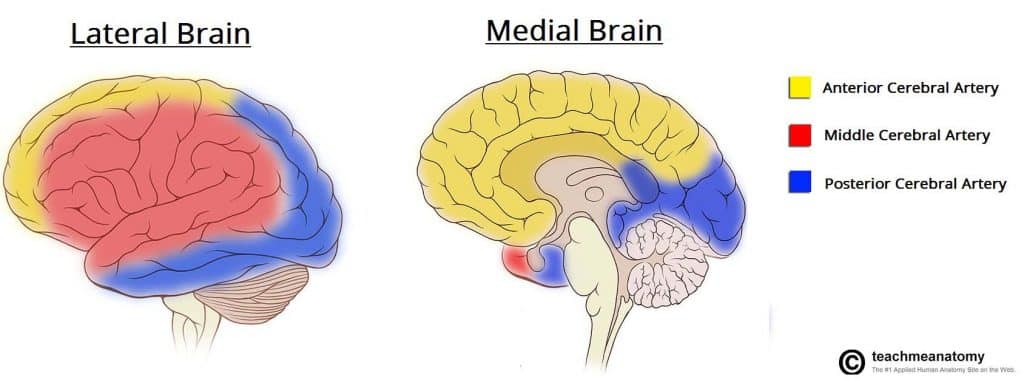 The Cerebrum Lobes Vasculature Teachmeanatomy
The Cerebrum Lobes Vasculature Teachmeanatomy
:watermark(/images/watermark_only.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/sulcus-precentralis/U3yyVwQaMmcx6yiqDdJssw_Sulcus_precentralis_01.png) Cerebrum And Cerebral Cortex Anatomy And Function Kenhub
Cerebrum And Cerebral Cortex Anatomy And Function Kenhub
 Functional Areas Of The Cerebral Cortex High Impact
Functional Areas Of The Cerebral Cortex High Impact

 Human Brain Anatomy Neuroscience Cerebral Cortex Brain Png
Human Brain Anatomy Neuroscience Cerebral Cortex Brain Png
 2017 Group Project 1 Embryology
2017 Group Project 1 Embryology
 Anatomy Of Cerebral Cortex Thalamus Interconnexions J
Anatomy Of Cerebral Cortex Thalamus Interconnexions J
 Cerebral Cortex Localization Of Function And Association
Cerebral Cortex Localization Of Function And Association
 Anatomy Human Brain Areas Cerebral Cortex Stock Vector
Anatomy Human Brain Areas Cerebral Cortex Stock Vector
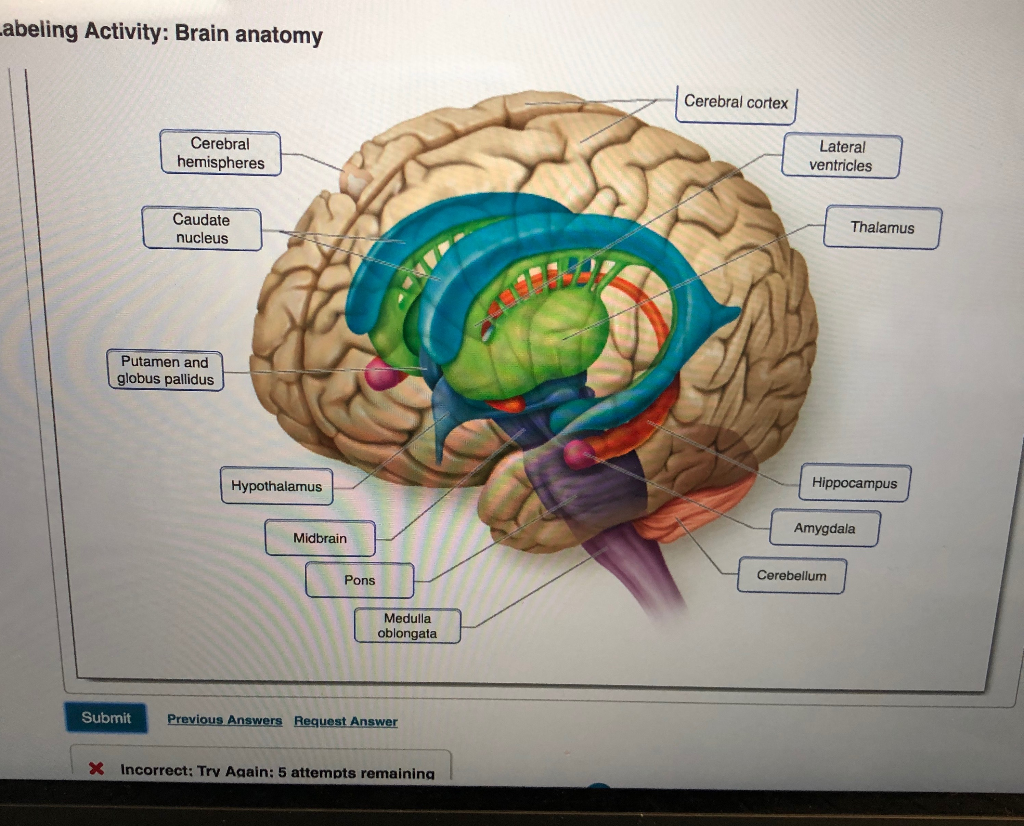 Solved Abeling Activity Brain Anatomy Cerebral Cortex Ce
Solved Abeling Activity Brain Anatomy Cerebral Cortex Ce
 Human Brain Cerebral Cortex Anatomy Lobes Of The Brain
Human Brain Cerebral Cortex Anatomy Lobes Of The Brain
 5 The Different Lobes Of The Cerebral Cortex The Occipital
5 The Different Lobes Of The Cerebral Cortex The Occipital
4 2 Our Brains Control Our Thoughts Feelings And Behaviour
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/11463/basal-view-of-the-brain_english.jpg) Cerebrum And Cerebral Cortex Anatomy And Function Kenhub
Cerebrum And Cerebral Cortex Anatomy And Function Kenhub

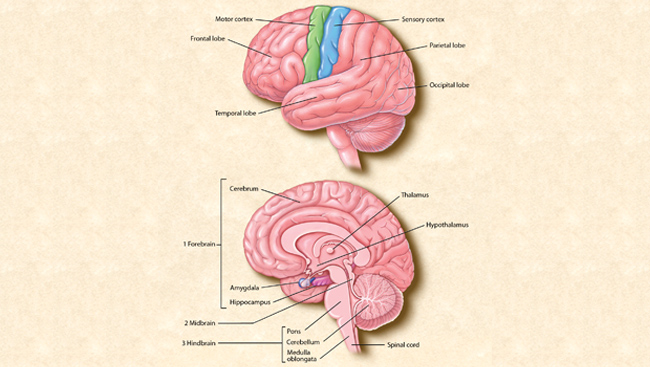
Belum ada Komentar untuk "Anatomy Of Cerebral Cortex"
Posting Komentar