Anatomy Of Heart Valves
Blood passes through a valve before leaving each chamber of the heart. Other articles have discussed at length the gross anatomy of the heart and its four chambers.
 Heart Valves Function Purpose And How Many Heart Valves In
Heart Valves Function Purpose And How Many Heart Valves In
There are four valves of the heart which are divided into two categories.
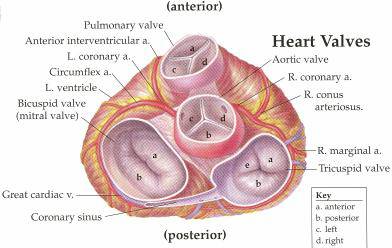
Anatomy of heart valves. The valve between the left atrium and the left ventricle is called the mitral valve. When closed it allows the. The valves prevent the backward flow of blood.
The four valves in the mammalian heart are. The chordae tindineae and papillary muscles tether the av valves to the ventricular walls. This heart valve is located between the left atrium and left ventricle.
Introduction to the anatomy of the heart valves. The left atrium receives oxygenated blood from the lungs and pumps it to the left ventricle. It is responsible for propelling blood to every organ system including itself.
Semilunar valves control blood flow out of your heart. The valve between the right atrium and the right ventricle is called the tricuspid valve. When closed it allows oxygen depleted blood returning to.
The pulmonary valve and aortic valve. What are heart valves. Atrioventricular valves control blood flow between your hearts upper and lower chambers.
The right ventricle receives blood from the right atrium and pumps it to the lungs where it is loaded with oxygen. The tricuspid valve and mitral bicuspid valve. Valves are actually flaps leaflets that act as one way inlets for blood coming into a ventricle and one way outlets for blood leaving a ventricle.
This heart valve is located between the right atrium and the right ventricle. They are located between the atria and corresponding ventricle. The heart has 4 chambers 2 upper chambers atria and 2 lower chambers ventricles.
They are located between the. The two atrioventricular av valves the mitral valve bicuspid valve and the tricuspid valve which are between the upper chambers atria and the lower chambers ventricles. The heart is one of the most important organs in the body.
The two semilunar sl valves the aortic valve and the pulmonary valve. Thin tendon like cords chordae tendineae connect the av valves to cone shaped muscles that extend upward from the myocardium the papillary muscles. The left ventricle the strongest chamber pumps oxygen rich blood to the rest of the body.
Atrioventricular av valves tricuspid valve. Special mention has also been made of the fact that the heart has a dual circuit of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood flowing parallel to each other. Understanding heart valves anatomy is important in grasping the overall function of the heart.
 Aortic Calcification An Early Sign Of Heart Valve Problems
Aortic Calcification An Early Sign Of Heart Valve Problems
 Problem Heart Valve Regurgitation American Heart Association
Problem Heart Valve Regurgitation American Heart Association
 Heart Anatomy Chambers Valves And Vessels Anatomy
Heart Anatomy Chambers Valves And Vessels Anatomy
 Mitral Valve Anatomy Overview Gross Anatomy Microscopic
Mitral Valve Anatomy Overview Gross Anatomy Microscopic
 Surface Anatomy Of Heart Valves And Great Vessels
Surface Anatomy Of Heart Valves And Great Vessels
 The Anatomy Of A Heart Central Georgia Heart Center
The Anatomy Of A Heart Central Georgia Heart Center
 Heart Valves Anatomy Tricuspid Aortic Mitral Pulmonary Kenhub
Heart Valves Anatomy Tricuspid Aortic Mitral Pulmonary Kenhub
 Aortic Stenosis Causes Symptoms And Progression What Is
Aortic Stenosis Causes Symptoms And Progression What Is
 Heart Valves Anatomy And Function
Heart Valves Anatomy And Function
 Novel Technique Reduces Obstruction Risk In Heart Valve
Novel Technique Reduces Obstruction Risk In Heart Valve
 Heart Anatomy Structure Valves Coronary Vessels Kenhub
Heart Anatomy Structure Valves Coronary Vessels Kenhub
 Types Of Valve Disease Cleveland Clinic
Types Of Valve Disease Cleveland Clinic
 Mitral Valve Leaflets Anatomy Pictures Problems
Mitral Valve Leaflets Anatomy Pictures Problems
 Heart Valves Showing Pulmonary Valve Mitral Valve And Tricuspid Framed Art Print
Heart Valves Showing Pulmonary Valve Mitral Valve And Tricuspid Framed Art Print
 Valve Replacement Willard Walker Heart Institute
Valve Replacement Willard Walker Heart Institute
 Structural Heart And Valve Care
Structural Heart And Valve Care
 Acquired Heart Valve Disease Symptoms
Acquired Heart Valve Disease Symptoms
 Mitral Valve Annulus Anatomy Structure Pictures
Mitral Valve Annulus Anatomy Structure Pictures




Belum ada Komentar untuk "Anatomy Of Heart Valves"
Posting Komentar