Effector Anatomy
The sensors integrating center and effectors are the basic components of every homeostatic response. An effector is any organ or tissue that receives information from the integrating center and acts to bring about the changes needed to maintain homeostasis.
 Nervous Tissue Ch Ppt Video Online Download
Nervous Tissue Ch Ppt Video Online Download
The sensory receptor recognizes the stimulus and sends it to the sensory neuron.
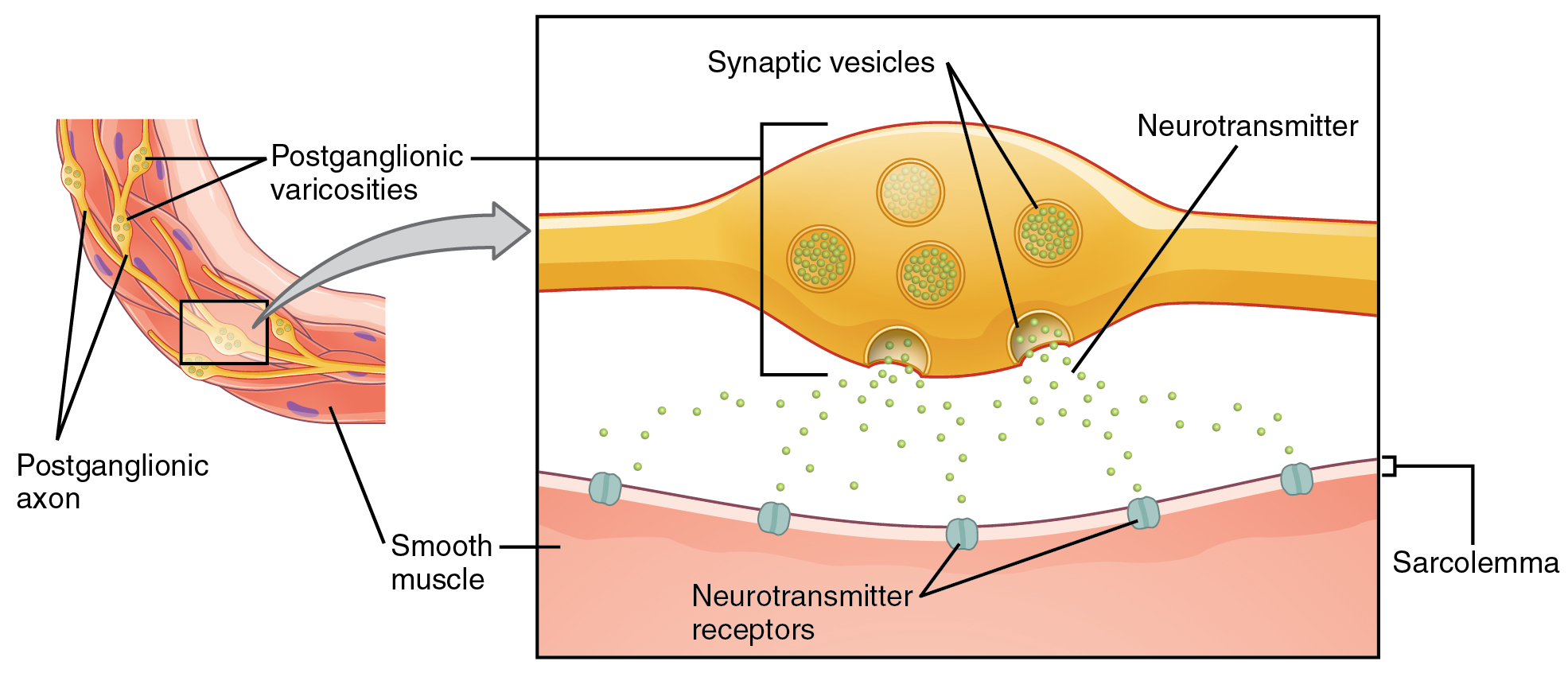
Effector anatomy. Simplest level of structural organization in the body. Biochemistry a small molecule or protein that alters biochemical processes in a cell. The motor neuron organizes the action.
The science of body functions. An organ a gland or muscle that becomes active in response to nerve impulses. How the body parts work and carry out their life sustaining activities.
The study of body structure. The other four components are motor neuron the sensory receptor the sensory neuron and the interneurons. The term effector is used in other fields of biology.
Illustrated anatomical parts with images from e anatomy and descriptions of anatomical structures. Filters blood produces bile. Body temprature blood pressure ph blood glucose levels.
An effector is the component in a feedback system that causes a change to reverse the situation and return the value to the normal range. Studies the structure of body parts and their relationships to one another. One example is the kidney which retains water if blood pressure is too low.
A muscle gland or organ capable of responding to a stimulus especially a nerve impulse. The effector organ is one of the five basic components of a reflex arc. Effector effector anatomical parts.
Studies the function of the body. Effector biology in some cases proteins can be considered to function as effector molecules especially in cellular signal transduction cascades. Study of the tissues.
Effector general anatomy definition. Keeping the organ system of the body in balance maintaining a stable environment functions of the liver. Any change or deviation from the normal range of function is opposed or resistedopposed.
A nerve ending that carries impulses to a muscle gland or organ and activates muscle. For instance the effector end of a neuron is the terminus where an axon makes contact with the muscle or organ that it stimulates or suppresses.
 Sympathetic Division Human Anatomy Organs
Sympathetic Division Human Anatomy Organs
 Reflex Action And Reflex Arc What Happens When You
Reflex Action And Reflex Arc What Happens When You
 Physiology Of Synapse Human Anatomy And Physiology Quiz
Physiology Of Synapse Human Anatomy And Physiology Quiz
 Chapter Twelve Anatomy Notes Bms 507 Unh Studocu
Chapter Twelve Anatomy Notes Bms 507 Unh Studocu
 21 2 Barrier Defenses And The Innate Immune Response
21 2 Barrier Defenses And The Innate Immune Response
 Spinal Reflex Arc Scheme Vector Illustration Stock Vector
Spinal Reflex Arc Scheme Vector Illustration Stock Vector
 Solved Pre Lab Activity 4 Examining The Functional Anato
Solved Pre Lab Activity 4 Examining The Functional Anato
 15 1 Divisions Of The Autonomic Nervous System Anatomy And
15 1 Divisions Of The Autonomic Nervous System Anatomy And
 A P Chapter 14 The Autonomic Nervous System Flashcards
A P Chapter 14 The Autonomic Nervous System Flashcards
 Neuron Synapsis Mind The Graph
Neuron Synapsis Mind The Graph
 Reflex Action And Reflex Arc Concepts Solved Questions And
Reflex Action And Reflex Arc Concepts Solved Questions And
 Visceral Effector Organs Human Anatomy Organs
Visceral Effector Organs Human Anatomy Organs
 Feedback Loops Anatomy And Physiology I
Feedback Loops Anatomy And Physiology I
 A P Chapters 1 11 Final Study Guide Vocab
A P Chapters 1 11 Final Study Guide Vocab
 Human Anatomy Endocrine 091400 Uts Studocu
Human Anatomy Endocrine 091400 Uts Studocu
 John D Mccorvy Phd Assistant Professor Medical College
John D Mccorvy Phd Assistant Professor Medical College
 Neuro Review Guide Docx Honors Anatomy Chapters 11 13
Neuro Review Guide Docx Honors Anatomy Chapters 11 13
 Divisions Of The Autonomic Nervous System Anatomy And
Divisions Of The Autonomic Nervous System Anatomy And
 Anatomy And Physiology I Lec 7 12 Mat4183 Uottawa
Anatomy And Physiology I Lec 7 12 Mat4183 Uottawa
 Autonomic Nervous System Anatomy Physiology Wikivet
Autonomic Nervous System Anatomy Physiology Wikivet
 Homeostasis Boundless Anatomy And Physiology
Homeostasis Boundless Anatomy And Physiology
 Human Anatomy And Physiology Theory
Human Anatomy And Physiology Theory
 Anatomy And Physiology Neuron Neuron Axon
Anatomy And Physiology Neuron Neuron Axon


Belum ada Komentar untuk "Effector Anatomy"
Posting Komentar