What Is The Orbit Anatomy
Start studying anatomy and physiology. By definition the orbit bony orbit or orbital cavity is a skeletal cavity comprised of seven bones situated within the skull.

Orbit anatomy in anatomy the orbit is the cavity or socket of the skull in which the eye and its appendages are situated.
What is the orbit anatomy. Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools. Orbit can refer to the bony socket or it can also be used to imply the contents. ōrbit ta the bony cavity containing the eyeball and its adnexa.
What is a sty. Anatomy of the orbit the skull is composed of two segments the cranium and the face. The cranium is the major portion and it consists of three unpaired bones the sphenoid occipital and ethmoid bones and three paired bones the frontal parietal and temporal bones.
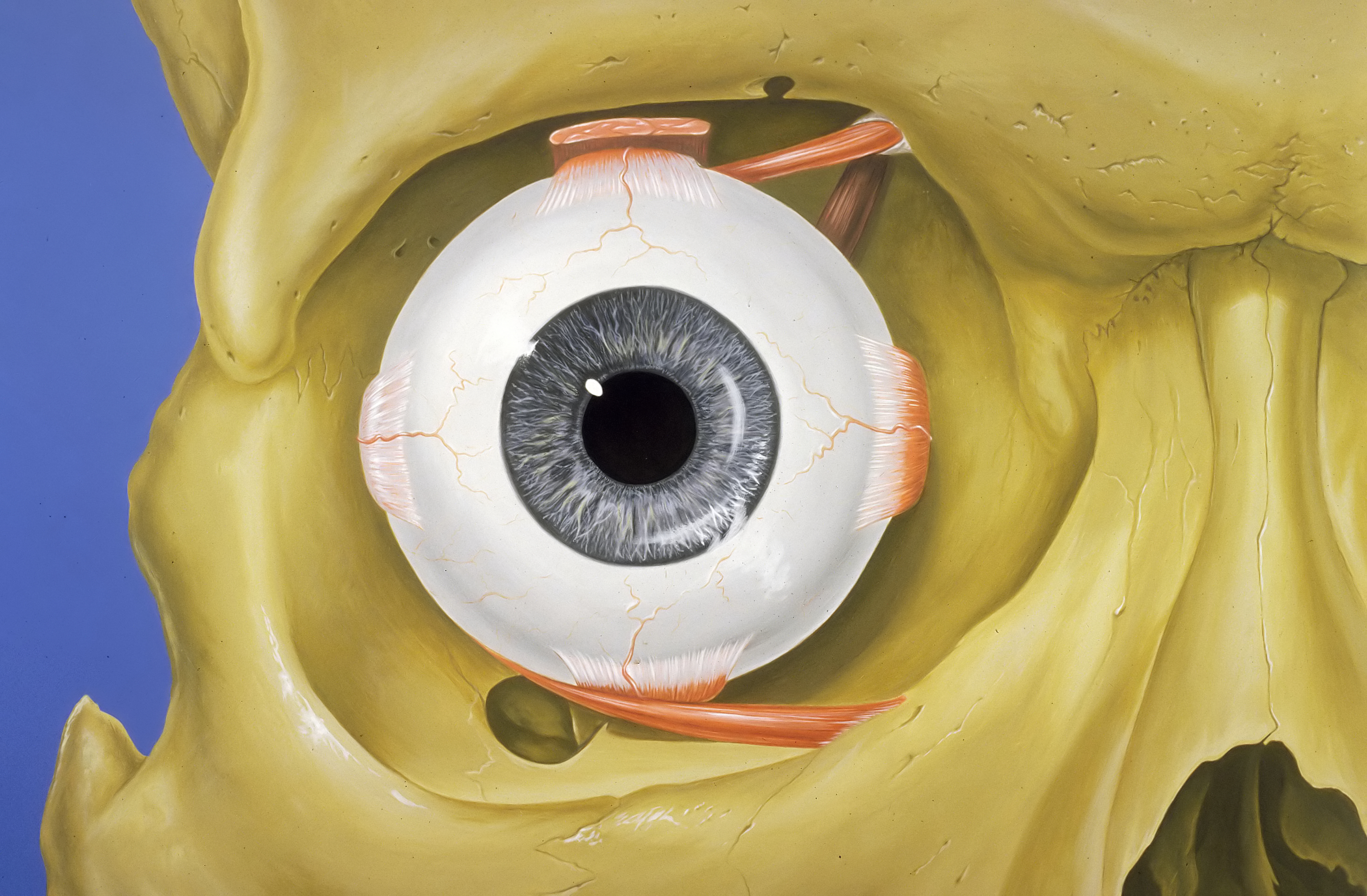
The boundaries of the orbit are formed by seven bones. Although the orbit is commonly described as pyramidal in shape it is not an angular structure and the walls are not regular. It protects the eye ball as a defense and gives it a cushion for support.
The orbit can be thought of as a pyramidal structure with the apex pointing posteriorly and the base situated anteriorly. Size shape and purpose. Seven bones conjoin to form the orbital structure as shown in the image below.
Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools. Orbita ta orbital cavity. The orbit which protects supports and maximizes the function of the eye is shaped like a quadrilateral pyramid with its base in plane with the orbital rim.
Orbit is eye socket and is made of seven bones. It is formed of parts of the frontal maxillary sphenoid lacrimal zygomatic ethmoid and palatine bones. What is the function of adipose tissue wrapped in the orbit of the eyeball.
The orbits are conical structures dividing the upper facial skeleton from the middle face and surround the organs of vision. The cavity surrounds and provides mechanical protection for the eye and soft tissue structures related to it. 101 us fl oz.
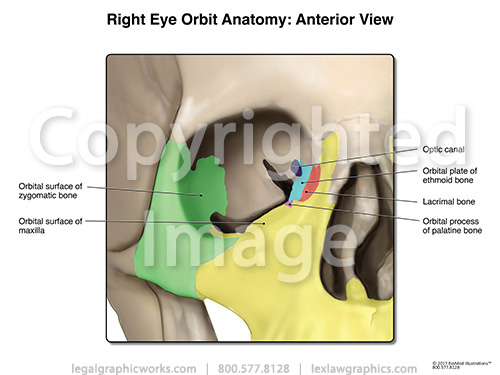
It is also important to consider the anatomical relations of the orbital cavity this is clinically relevant in the spread of infection and in cases of trauma. Start studying anatomy the orbit. Frontal bone maxilla lacrimal ethmoid sphenoid.
In the adult human the volume of the orbit is 30 millilitres 106 imp fl oz.
 Anatomy Flashcards Orbit And Contents
Anatomy Flashcards Orbit And Contents
Anatomy Of Orbit And Clinical Aspect Of Orbital Disease
 Anatomy Of The Left Orbital Apex Highlighting The
Anatomy Of The Left Orbital Apex Highlighting The
 Local And Regional Anesthesia For Ophthalmic Surgery Nysora
Local And Regional Anesthesia For Ophthalmic Surgery Nysora
Anatomy 9 Vasculature Of Orbit Anatomy 9 Orbit And Its
 Orbits And Eyes Anatomical Illustrations
Orbits And Eyes Anatomical Illustrations
 Superior Orbital Fissure Wikipedia
Superior Orbital Fissure Wikipedia
 Orbital Tumor Eye Socket Cancer Anatomy
Orbital Tumor Eye Socket Cancer Anatomy
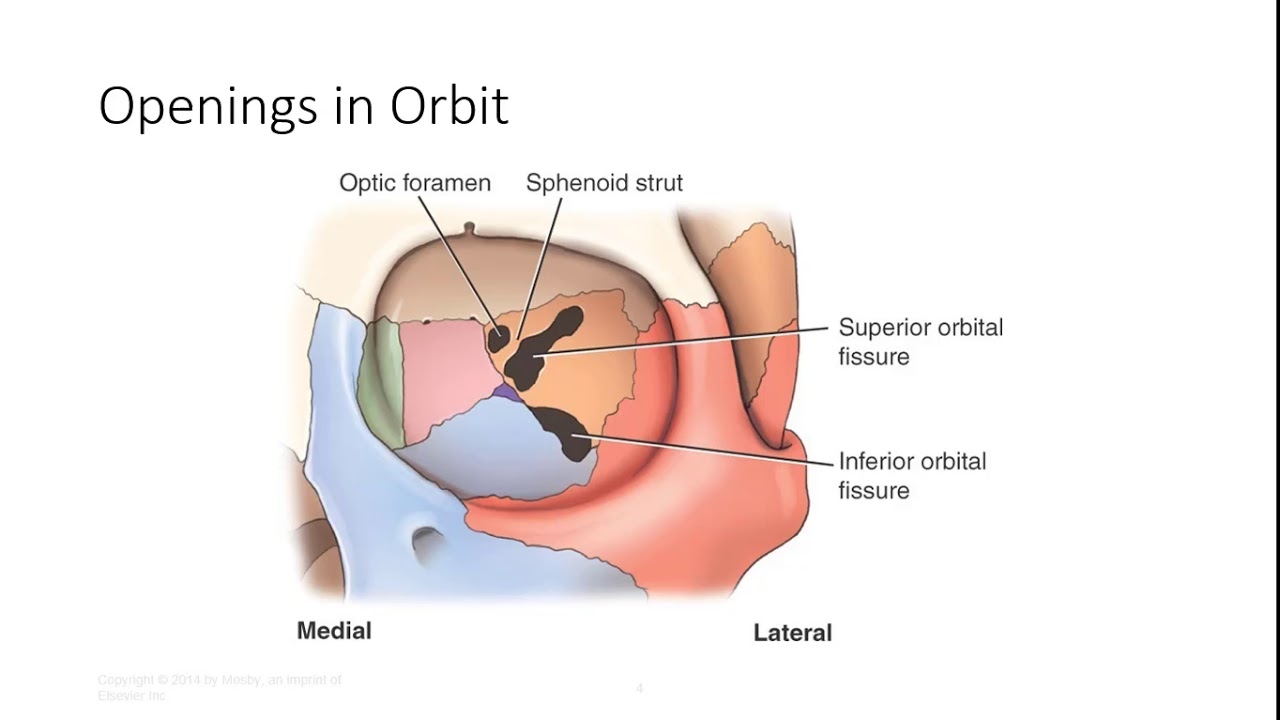 Anatomy And Pathology Of The Orbits
Anatomy And Pathology Of The Orbits
:watermark(/images/watermark_5000_10percent.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/atlas_overview_image/1029/H5pVML9dsoS5SfAG1P7fpA_anatomy-superior-orbital-fissure_english.jpg) Eye Anatomy Muscles Arteries Nerves And Lacrimal Gland
Eye Anatomy Muscles Arteries Nerves And Lacrimal Gland
 Orbital Floor Blowout Fracture Brown Emergency Medicine
Orbital Floor Blowout Fracture Brown Emergency Medicine
 The Orbit Anatomy Flashcards Quizlet
The Orbit Anatomy Flashcards Quizlet
Orbital Compartment Syndrome Curriculum
 Orbit Anatomy At University Of Waterloo Studyblue
Orbit Anatomy At University Of Waterloo Studyblue
 Periorbita An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Periorbita An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
:watermark(/images/watermark_5000_10percent.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/atlas_overview_image/777/IOA26SbYNKr5nhVqAvklQ_bones-of-the-orbit_english.jpg) Lacrimal Bone Anatomy Borders And Function Kenhub
Lacrimal Bone Anatomy Borders And Function Kenhub
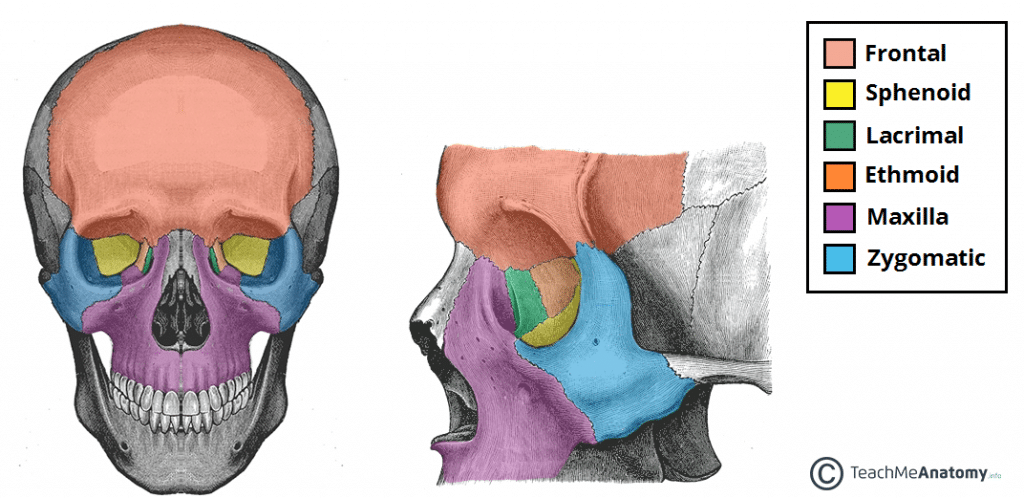 The Bony Orbit Borders Contents Fractures Teachmeanatomy
The Bony Orbit Borders Contents Fractures Teachmeanatomy
Orbital Anatomy Ophthalmology Review
 Normal Orbital Anatomy Axial Computed Tomographic Ct
Normal Orbital Anatomy Axial Computed Tomographic Ct
Orbit In Cross Section Anatomy The Eyes Have It
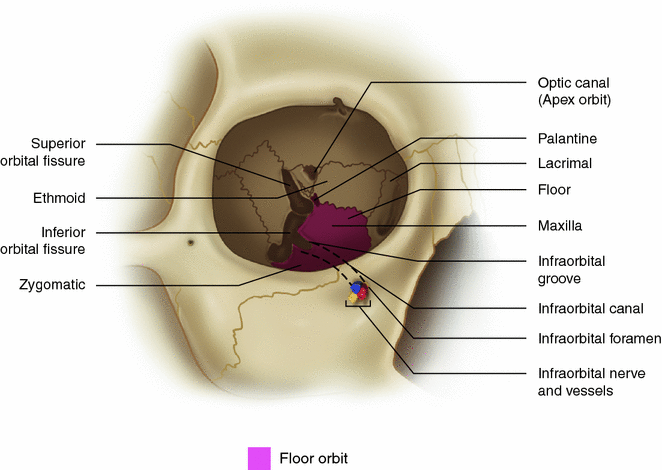 Anatomy Of The Orbit Springerlink
Anatomy Of The Orbit Springerlink
Orbital Compartment Syndrome Curriculum
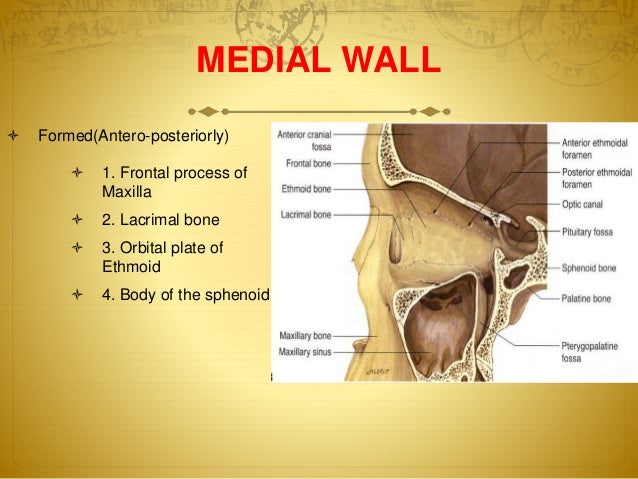




Belum ada Komentar untuk "What Is The Orbit Anatomy"
Posting Komentar