Anatomy Of Fungi
Fungi reproduce both sexually and asexually and they also have symbiotic associations with plants and bacteria. They acquire their food by absorbing d.
 Mushrooms How To Identify And Gather Wild Mushrooms And
Mushrooms How To Identify And Gather Wild Mushrooms And
A taxonomic division.

Anatomy of fungi. For example fungi include the microscopic yeasts the molds seen on contaminated bread and the common mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom fungi which is separate from the other eukaryotic life kingdoms of plants and animals. A symbiotic association between a fungus and the roots of a vascular plant.
The hyphae of most fungi are divided into cells by internal walls called septa singular septum. Any of many symbiotic organisms being associations of fungi and algae. Each hypha consists of one or more cells surrounded by a tubular cell wall.
A tangled mass of hyphae visible to the unaided eye is a mycelium plural mycelia. A fungus is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds as well as the more familiar mushrooms. The suggested formula for fungus chitin is c 22 h 54 n 21 n.
The filaments are called hyphae singular hypha. Structure and physiology of fungi. Physiology of fungi a.
A characteristic that places fungi in a different kingdom from plants bacteria and some protists is chitin in their cell walls. Because there are so many hyphae packed together they are easily seen forming black bootlaces. These can spread through a woodland infecting neighboring trees.
A mass of hyphae make up the body of a fungus which is called a mycelium plural mycelia. Not photosynthetic decomposers saprophytic cell walls impregnated with chitin. Molds consist of long branching filaments of cells called hyphae singular hypha.
A reproductive particle usually a single cell released by a fungus alga. Some fungi such as honey fungus which is a parasite of woodland trees have hyphae collected together into long cables called rhizomorphs. Fungus are a kingdom of usually multicellular eukaryotic organisms that are heterotrophs cannot make their own food and have important roles in nutrient cycling in an ecosystem.
In the majority of fungi the wall lacks cellulose but contains a form of chitin known as the fungus cellulose which is strictly not identical with insect chitin. The chemical products of digestion are therefore. Fungi produce spores in both asexual and sexual life cycles mushrooms let out spores from their pores that are carried by the wind to meet other spores and become a new fungi yeast are unicellular and divide into new fungal cells mitosis.
Similar to animals fungi are heterotrophs. Electron microscope studies reveal that chitin occurs as elongated variously oriented microfibrillar units. Most fungi contain complex enzymes and other chemical substances which when diffused into the host break down the complex substances available wood vegetation leather bread and so forth into simpler substances that can be used for food.

 Fungi Vector Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock
Fungi Vector Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock
 190 Fungal Anatomy Foxhugh Superpowers List
190 Fungal Anatomy Foxhugh Superpowers List
 190 Fungal Anatomy Foxhugh Superpowers List
190 Fungal Anatomy Foxhugh Superpowers List
 190 Fungal Anatomy Foxhugh Superpowers List
190 Fungal Anatomy Foxhugh Superpowers List
 Fungi Biology 211 With Scholtens At College Of Charleston
Fungi Biology 211 With Scholtens At College Of Charleston
What Are Truffles Casa Truffle Fresh Alba S White
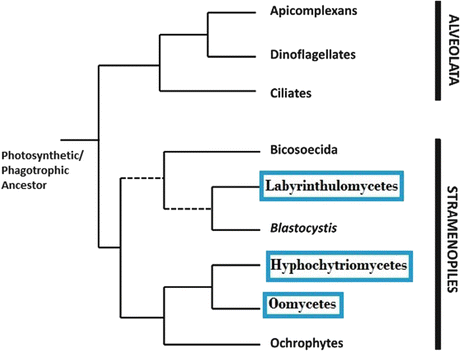 Evolution Of Fungi Basic Electrical Wiring Theory
Evolution Of Fungi Basic Electrical Wiring Theory
Threadlike Fungal Filaments Are Called Minimalist Interior
 Fungi Biology For Science Lecture Notes Docsity
Fungi Biology For Science Lecture Notes Docsity
 Anatomy Of A Mushroom Note All Parts Shown Here Are Not
Anatomy Of A Mushroom Note All Parts Shown Here Are Not
 190 Fungal Anatomy Foxhugh Superpowers List
190 Fungal Anatomy Foxhugh Superpowers List
 What Is The Anatomy Of Fungi Cells Quora
What Is The Anatomy Of Fungi Cells Quora
 Basidiomycetes Coprinus Mushroom Anatomy Microscope Slide
Basidiomycetes Coprinus Mushroom Anatomy Microscope Slide
 Ilustraciones Imagenes Y Vectores De Stock Sobre Hyphae
Ilustraciones Imagenes Y Vectores De Stock Sobre Hyphae
 I Fungi A Characteristics Heterotrophs Feed Off Other
I Fungi A Characteristics Heterotrophs Feed Off Other
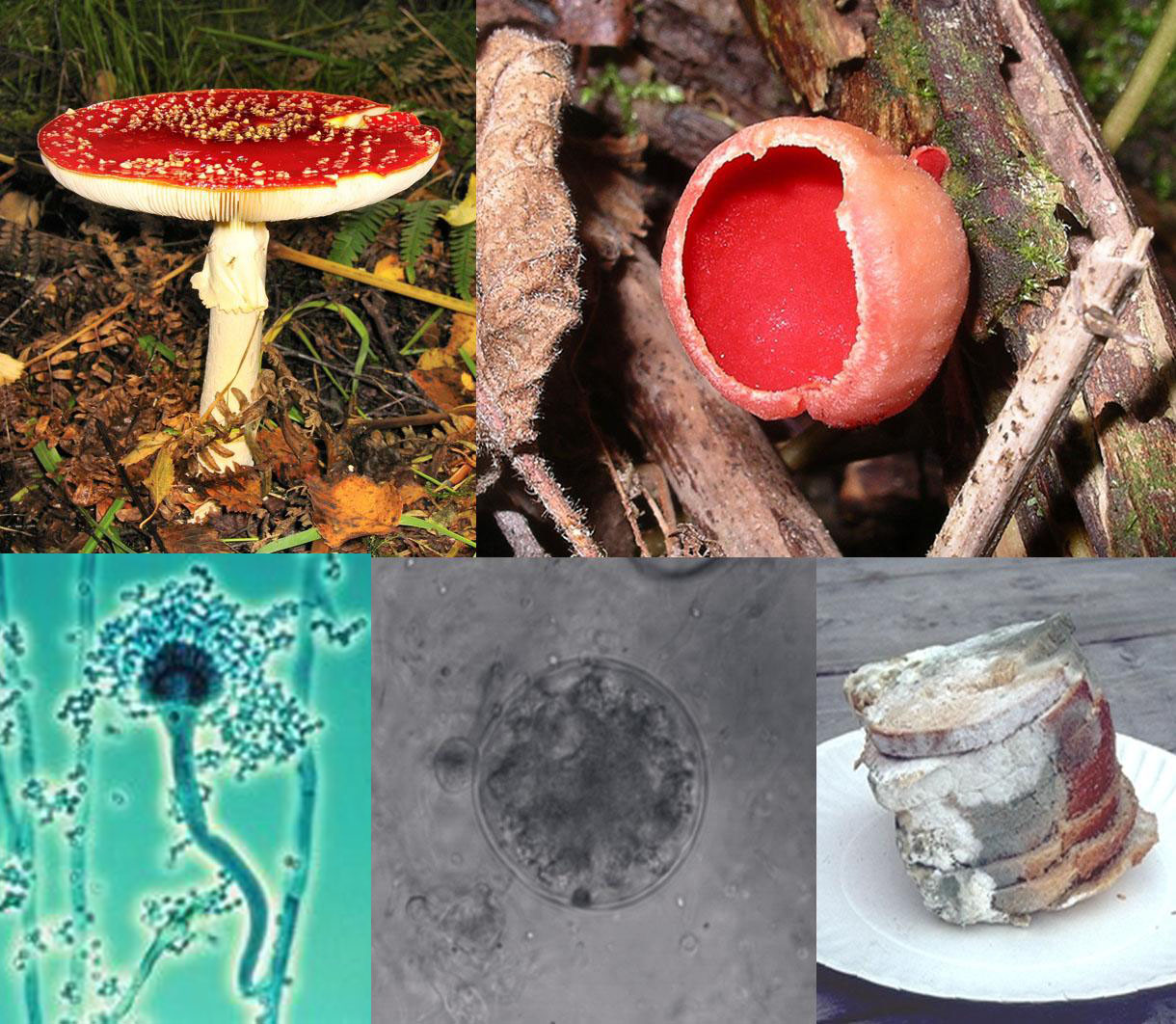






Belum ada Komentar untuk "Anatomy Of Fungi"
Posting Komentar