Innervation Anatomy
A nerve is an enclosed cable like bundle of nerve fibres called axons in the peripheral nervous system. The supply or distribution of nerve fibres to any part of the body.
The plexus is formed by the anterior rami divisions of the sacral spinal nerves s1 s2 s3 and s4.
:watermark(/images/watermark_only.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/cardiac-plexus/iz7LM8VWP3kipeZE0ZUelw_Plexus_cardiacus_02.png)
Innervation anatomy. Teachme anatomy part of the teachme series the medical information on this site is provided as an information resource only and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. The innervation of the heart refers to the network of nerves that are responsible for the functioning of the heart. The lumbar plexus forms in the lower back from the merger of spinal nerves l1 through l4 while the sacral plexus forms in the pelvic region from spinal nerves l4 l5 and s1 through s4.
The femoral saphenous obturator and lateral femoral cutaneous nerves all extend from the lumbar plexus into the muscles and skin of the thigh and leg. The network of nerves supplying the heart is called the cardiac plexus. Each spinal nerve corresponds to a skin region of the body described as a dermatome.
The heart is innervated by sympathetic and parasympathetic fibres from the autonomic branch of the peripheral nervous system. The 31 spinal nerves are split into 5 groups named for the 5 regions of the vertebral column. The axillary nerve is a branch of the brachial plexus which contains nerve fibres from c5 and c6 it provides sensory innervation to the skin on the regimental badge area of the upper arm and motor innervation to the deltoid and teres minor muscles.
The spinal nerves receive messages including touch temperature position vibration and pain from the small nerves in the skin muscles joints and internal organs of the body. The provision of nerve stimuli to a muscle gland or other nerve. It is located on the surface of the posterior pelvic wall anterior to the piriformis muscle.
The names of the cranial nerves relate to their function and they are also numerically identified in roman numerals i xii. The first two nerves olfactory and optic arise from the cerebrum whereas the remaining ten emerge from the brain stem. A nerve provides a common pathway for the electrochemical nerve impulses called action potentials that are transmitted along each of the axons to peripheral organs or in the case of sensory nerves from the periphery back to the central nervous system.
Extending from the left and right sides of the spinal cord are 31 pairs of spinal nerves. The sacral plexus is a network of nerve fibres that supplies the skin and muscles of the pelvis and lower limb. In this article we shall summarise the anatomy of the cranial nerves.
The spinal nerves are mixed nerves that carry both sensory and motor signals between the spinal cord and specific regions of the body.
 Innervation Of The Heart Preview Human Anatomy Kenhub
Innervation Of The Heart Preview Human Anatomy Kenhub
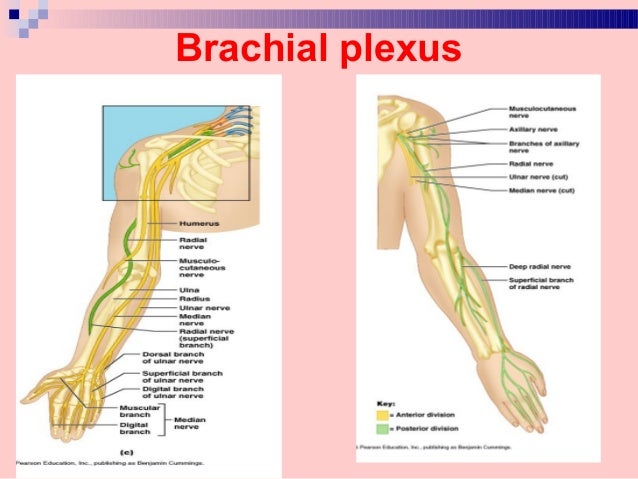 Blood Supply Innervation Of Upper Limb
Blood Supply Innervation Of Upper Limb
 Sural Nerve Innervation Anatomy
Sural Nerve Innervation Anatomy
 Trigeminal Nerve Innervation Diagram Cranial Nerves Nerve
Trigeminal Nerve Innervation Diagram Cranial Nerves Nerve
 Nerve Innervation Of The Upper Extremities 24 X 36
Nerve Innervation Of The Upper Extremities 24 X 36
:watermark(/images/watermark_only.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/cardiac-plexus/iz7LM8VWP3kipeZE0ZUelw_Plexus_cardiacus_02.png) Innervation Of The Heart Sympathetic And Parasympathetic
Innervation Of The Heart Sympathetic And Parasympathetic
 Heart Nerve Anatomy Cardiac Innervation
Heart Nerve Anatomy Cardiac Innervation
 File Radial Nerve Anatomy Innervation Distribution
File Radial Nerve Anatomy Innervation Distribution
 15069 02xv2 Innervation Of Spinal Nerves Anatomy Exhibits
15069 02xv2 Innervation Of Spinal Nerves Anatomy Exhibits
 Bladder Urethra Anatomy Renal Medbullets Step 1
Bladder Urethra Anatomy Renal Medbullets Step 1
 Autonomic Innervation An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Autonomic Innervation An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
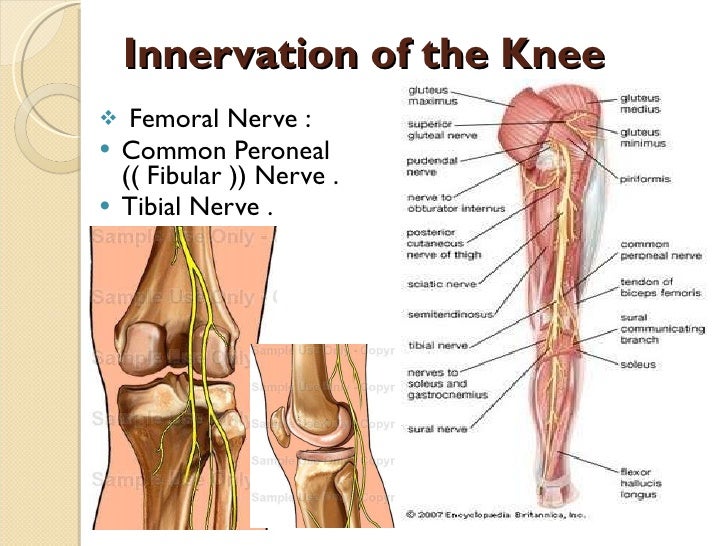 Innervation Of The Knee Ul Li Femoral
Innervation Of The Knee Ul Li Femoral
 File Musculocutaneous Nerve Innervation Anatomy Human
File Musculocutaneous Nerve Innervation Anatomy Human
Dental Malpractice Central Anatomy Of The Lingual Nerve
 Brachial Plexus Distal Nerve Innervation Anatomy
Brachial Plexus Distal Nerve Innervation Anatomy
 Anatomy And Innervation Of The Mental Nerve Notes The
Anatomy And Innervation Of The Mental Nerve Notes The
.jpg) Lower Limb Vessels And Innervation Part1 Proprofs Quiz
Lower Limb Vessels And Innervation Part1 Proprofs Quiz
 19 Origins Of The Cardiac Autonomic Nervous System And
19 Origins Of The Cardiac Autonomic Nervous System And
Gsanatomy G32 Visceral Innervation Of The Abdomen Anatomy
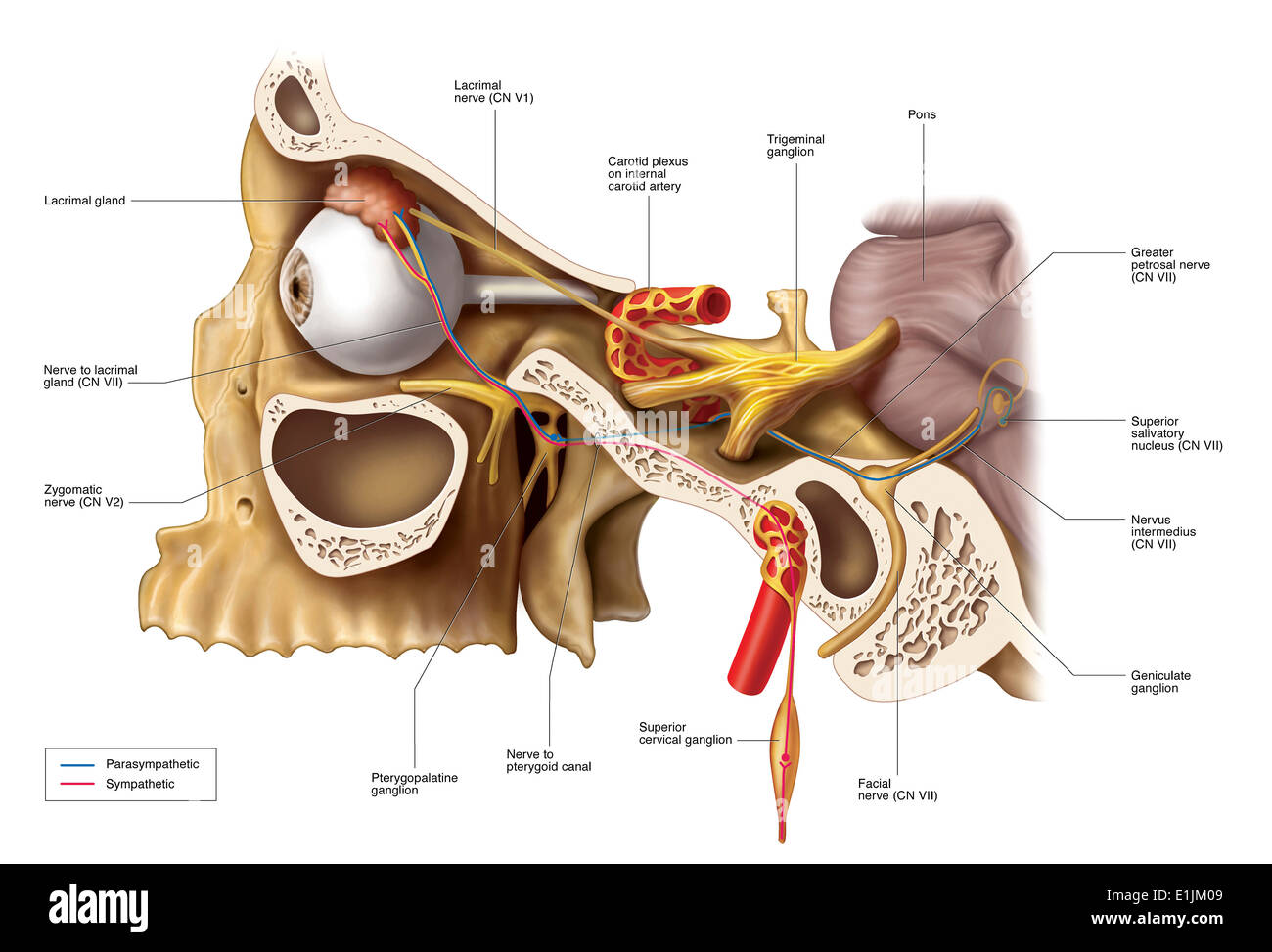 Anatomical Pathways Of Innervation To The Lacrimal Gland
Anatomical Pathways Of Innervation To The Lacrimal Gland
 Airway Innervation Anatomy Mark Harris Md Mph Https
Airway Innervation Anatomy Mark Harris Md Mph Https
 Drawing Medical Didactic Board Anatomy Human Stock Vector
Drawing Medical Didactic Board Anatomy Human Stock Vector
 Vagus Nerve Anatomy Britannica
Vagus Nerve Anatomy Britannica
 Muscle Innervation Complete Anatomy
Muscle Innervation Complete Anatomy


Belum ada Komentar untuk "Innervation Anatomy"
Posting Komentar