Human Tongue Anatomy
The base of the tongue is the most posterior part of the organ. Tongue anatomy occupying most of the oral cavity and oropharynx your tongue is a mass of muscles.
 Anatomy Of Base Of Tongue Cancer Headandneckcancerguide Org
Anatomy Of Base Of Tongue Cancer Headandneckcancerguide Org
It is highly mobile and can be shifted into a number of different positions and also assume various shapes.

Human tongue anatomy. The tongue is a muscular organ in the mouth. Here are ten human tongue facts including some of its functions. Tongue anatomy parts pictures diagram of human tongue.
To learn more about the body see our series of human anatomy sheets. Click to find similar content by grade or subject. The tongue consists of partially interdigitated muscles we consider the muscle volumes in two ways.
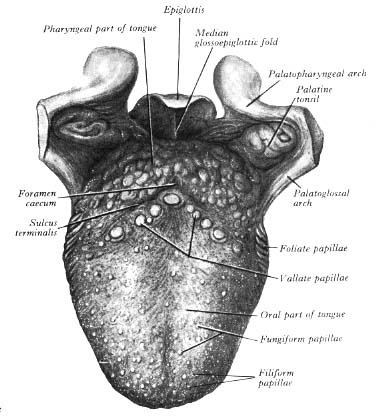
Taste buds are collections of nerve like cells that connect to nerves running into the brain. The human tongue is divided into anterior and posterior parts by the terminal sulcus which is a v shaped groove. Anatomy of the tongue.
The functional muscle volume encompasses the region of the tongue served by the muscle. The specific arrangement of muscle fibers allows it to move freely in any direction inside the mouth cavity to performs several different tasks including eating swallowing speaking licking sucking oral cleansing and catching pray etc. Diagram of human tongue anatomyincluding various types of papillae and the taste bud.
The tongue is covered with moist pink tissue called mucosa. The posterior tongue sits near the back of the throat and measures the other one third in length. Tiny bumps called papillae give the tongue its rough texture.
The tongue consists of two parts. Source human tongue anatomy you may think your tongue is a single muscle. It lies partly in the mouth cavity and partly in the oropharynx.
The anterior tongue is mostly visible and about two thirds of the tongues total length. The average tongue is four inches long. The human tongue is a muscular organ that is covered by a thin mucous membrane.
It has a rough dorsal superior surface that abuts the palate and is populated with taste buds and lingual papillae and a smooth ventral inferior surface that is attached to the floor of the oral cavity by the lingual frenulum. The tongue is unique in that it is the only muscle that isnt connected to bone at both ends. The apex of the terminal sulcus is marked by a blind foramen the foramen cecum which is a remnant of the median thyroid diverticulum in early embryonic development.
The tongues primary physiologic function is gustatory sensation tasting and aiding in mastication chewing. It is connected on one end to the hyoid bone which is also unique as it is the only bone not connected to any other bone in the body. Thank you for your input.
Thousands of taste buds cover the surfaces of the papillae.

 Tongue Anatomy Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock
Tongue Anatomy Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock
 Human Tongue Anatomy Of Papillae And Taste Buds
Human Tongue Anatomy Of Papillae And Taste Buds
 Human Tongue Anatomy Vector Image 1815127 Stockunlimited
Human Tongue Anatomy Vector Image 1815127 Stockunlimited
 Muscles Of Tongue And Floor Of Mouth Acrylic Print
Muscles Of Tongue And Floor Of Mouth Acrylic Print
 Tongue Anatomy Anatomy Physiology Anatomy Physiology
Tongue Anatomy Anatomy Physiology Anatomy Physiology
:watermark(/images/watermark_only.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/sulcus-terminalis-linguae/9Zd4nDH6Ju5Ye6iHcEYBA_Sulcus_terminalis_01.png) Tongue Anatomy Muscles Taste Buds Gustatory Pathway Kenhub
Tongue Anatomy Muscles Taste Buds Gustatory Pathway Kenhub

 Tongue Taste Bud Botones Gustativos Human Anatomy Png
Tongue Taste Bud Botones Gustativos Human Anatomy Png
:watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/musculus-longitudinalis-superior-linguae/Fuhj5VYk1QUFwmgaKHSKIg_Superior_longitudinal_muscle_of_tongue_01.png) Tongue Anatomy Muscles Taste Buds Gustatory Pathway Kenhub
Tongue Anatomy Muscles Taste Buds Gustatory Pathway Kenhub


Sensory Organ Tongue Taste Ssds Science2014 5775
 Amazon Com Anatomy Mouth Teeth Tongue Print Sra3 12x18
Amazon Com Anatomy Mouth Teeth Tongue Print Sra3 12x18
 Us 310 0 Throat Structure Features Enlarge Model Larynx Laryngeal Human Teeth Throat Tongue Model Laryngeal Anatomy Tongue Gasen Ebh008 In Medical
Us 310 0 Throat Structure Features Enlarge Model Larynx Laryngeal Human Teeth Throat Tongue Model Laryngeal Anatomy Tongue Gasen Ebh008 In Medical
 What Your Tongue Can Tell You About Your Health Health
What Your Tongue Can Tell You About Your Health Health
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/9232/structure-of-tongue_english.jpg) Tongue Anatomy Muscles Neurovasculature And Histology
Tongue Anatomy Muscles Neurovasculature And Histology
 Human Tongue Parts Functions With Details And Diagram
Human Tongue Parts Functions With Details And Diagram
 Cartoon Of Human Tongue Anatomy
Cartoon Of Human Tongue Anatomy



Belum ada Komentar untuk "Human Tongue Anatomy"
Posting Komentar