Human Anatomy Bladder
In the human the bladder is a hollow muscular and distensible organ that sits on the pelvic floor. The bladder has four layers.
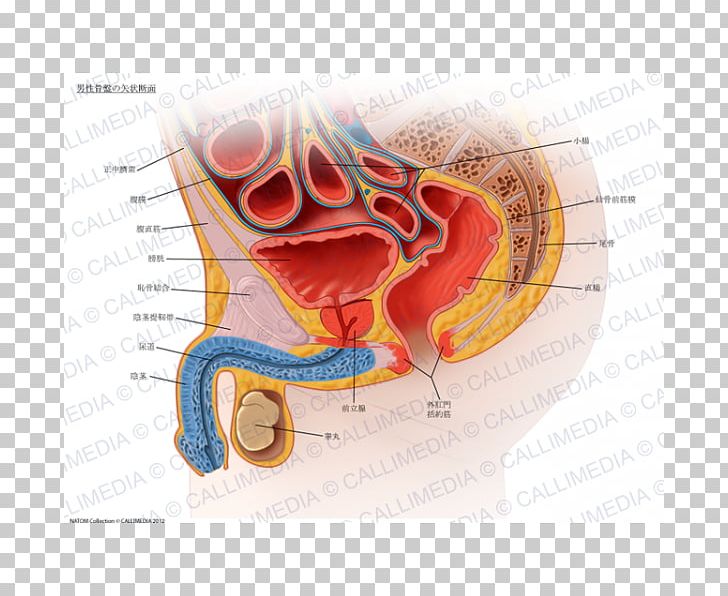 Sagittal Plane Pelvis Human Anatomy Urinary Bladder Png
Sagittal Plane Pelvis Human Anatomy Urinary Bladder Png
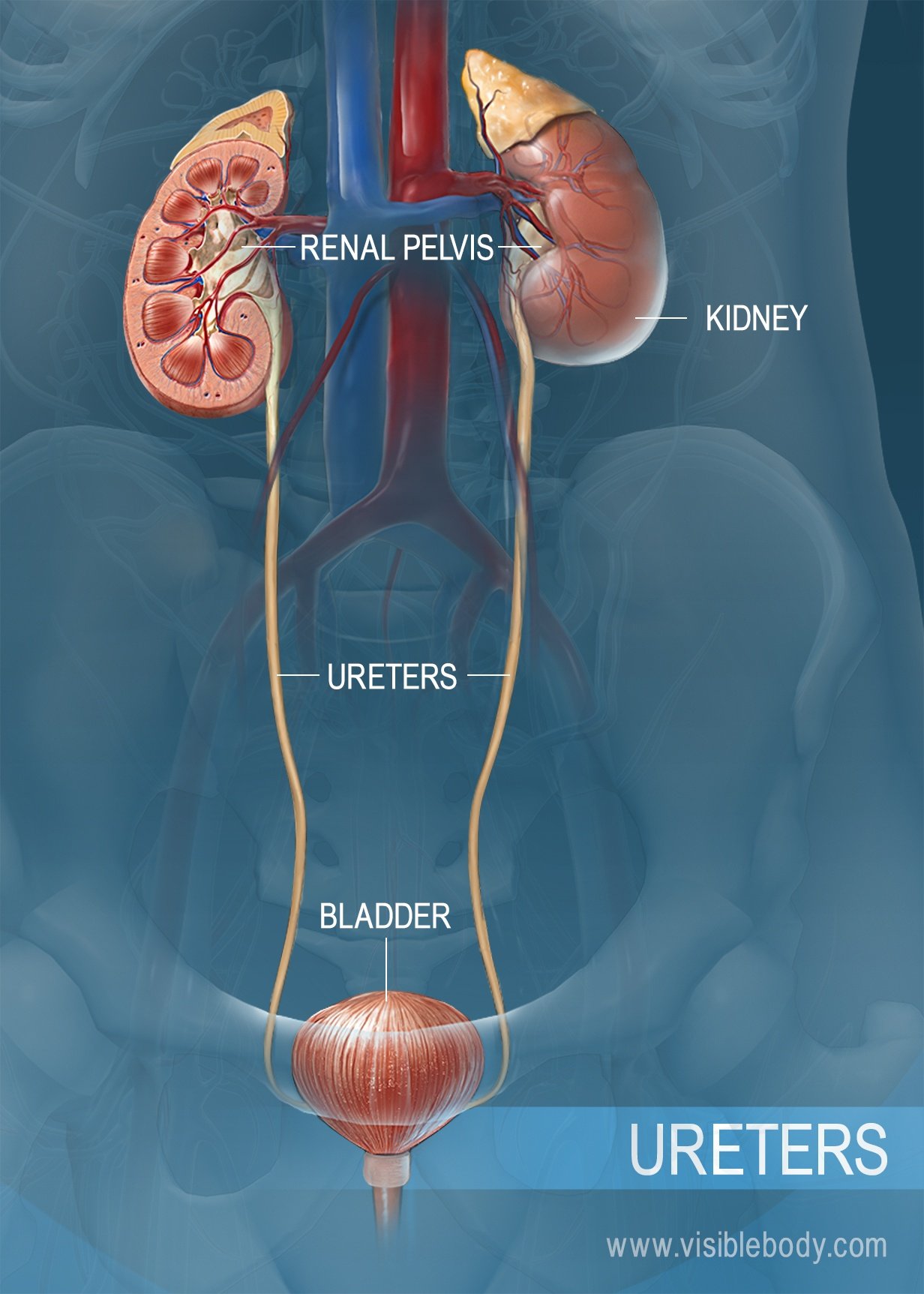
The bladder is connected to the kidneys by two long tubes called ureters.

Human anatomy bladder. Unlike the mucosa of other hollow organs the urinary bladder is lined with transitional epithelial tissue that is able to stretch significantly to accommodate large volumes of urine. The urethra is the tube through which urine passes from the bladder to the exterior of the body. The urinary bladder is made of several distinct tissue layers.
The brain is the most important organ in the human body. A urinary bladder is present in fish as an expansible part of the urinary duct in amphibians and bladder possessing reptiles sphenodon turtles most lizards as a pocket in the cloaca. Urine enters the bladder via the ureters and exits via the urethra.
When urine is produced by the kidneys it travels down the ureters to the bladder where it is stored. The typical human bladder reaches its capacity between 16 to 24 ounces of urine but the urge to urinate comes when the bladder is about one quarter full. During urination the bladder muscles squeeze and two sphincters.
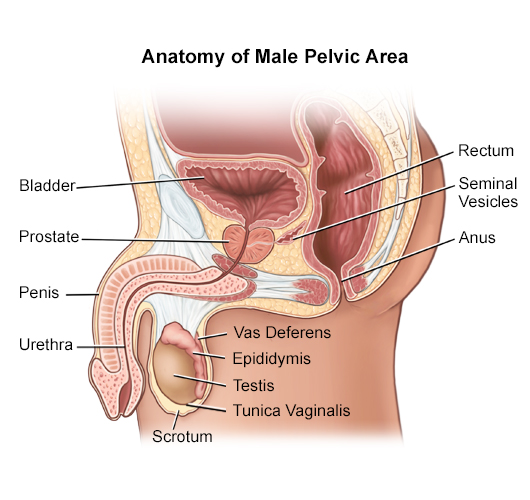
The female urethra is around 2 inches long and ends inferior to the clitoris and superior to the vaginal opening. The innermost layer of the bladder is the mucosa layer that lines the hollow lumen. The bladder is a hollow muscular organ that is located in the pelvis behind the pubic bone.
If your child is starting to learn human biology give him a great study sheet with this anatomy worksheet about the pancreas. In males the urethra is around 8 to 10 inches long and ends at the tip of the penis. From the inside out the epithelium is the first layer on the inside of the bladder.
The urinary bladder is a hollow muscular organ in humans and vertebrates that collects and stores urine from the kidneys before disposal by urination. The kidneys produce urine and it travels down to the bladder via two tubes called ureters. The bladder is lined by layers of muscle tissue that stretch to hold urine.
Urine is stored in the bladder until it is ready to be expelled from the body. In mammals it is a greatly expandible muscular sac. The typical human bladder will hold between 300 and 500 ml before the urge to empty occurs but can hold considerably more.
Get a basic grasp on the parts and functions of the brain with this anatomy info sheet. The normal capacity of the bladder is 400 600 ml. It stretches to accommodate the volume of urine produced by the kidneys.
 Ureter An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Ureter An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
 Psoas And Urinary Bladder Connection Tight Psoas Psoas
Psoas And Urinary Bladder Connection Tight Psoas Psoas
 Human Urinary System Kidneys With Stock Footage Video 100 Royalty Free 1019348002 Shutterstock
Human Urinary System Kidneys With Stock Footage Video 100 Royalty Free 1019348002 Shutterstock
 Urinary Bladder Function Location And Pictures In Males And
Urinary Bladder Function Location And Pictures In Males And
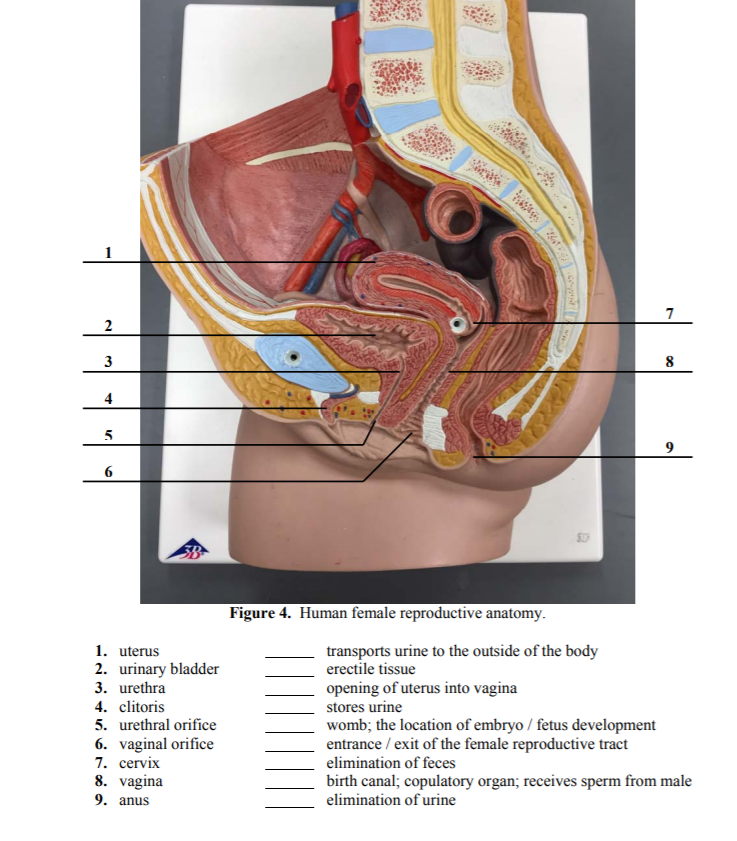 Solved 7 2 3 8 4 5 6 Figure 4 Human Female Reproductive
Solved 7 2 3 8 4 5 6 Figure 4 Human Female Reproductive
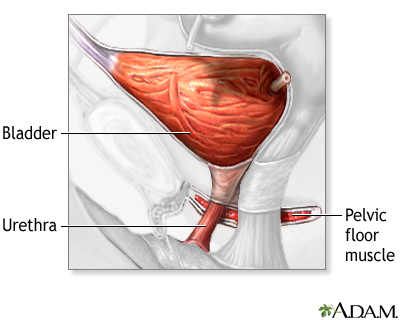 Bladder And Urethral Repair Series Normal Anatomy
Bladder And Urethral Repair Series Normal Anatomy
Painful Urination Dysuria Cleveland Clinic
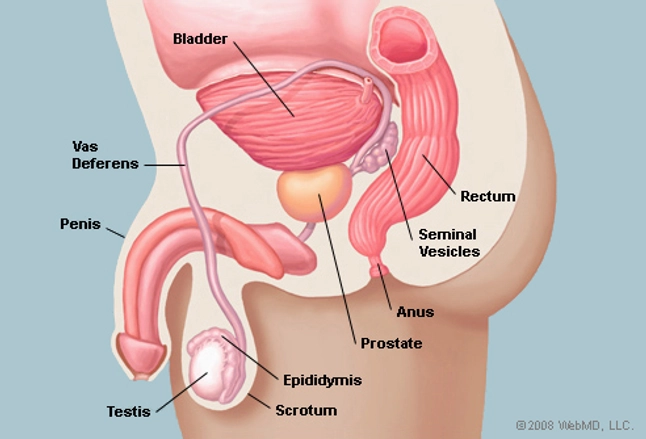 Prostate Gland Human Anatomy Prostate Picture Definition
Prostate Gland Human Anatomy Prostate Picture Definition
 Urinary Bladder Anatomy 3d Medical Vector Illustration
Urinary Bladder Anatomy 3d Medical Vector Illustration
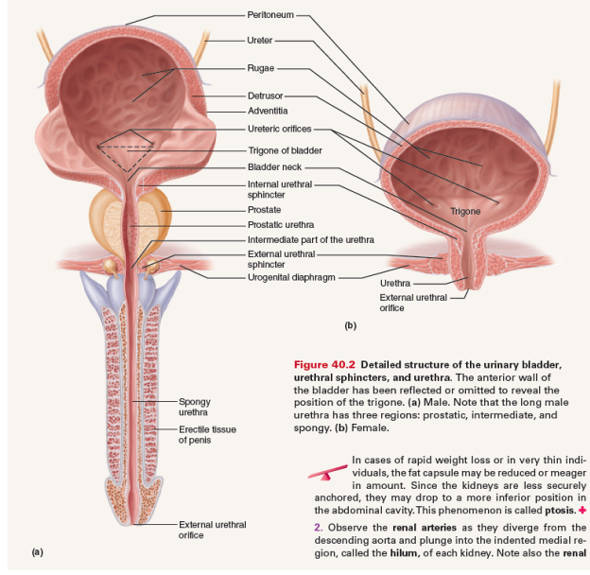 Chapter 40 Solutions Human Anatomy Physiology Laboratory
Chapter 40 Solutions Human Anatomy Physiology Laboratory
 Neurogenic Bladder Symptoms Diagnosis Treatment
Neurogenic Bladder Symptoms Diagnosis Treatment
 Visual Guide To Bladder Cancer
Visual Guide To Bladder Cancer
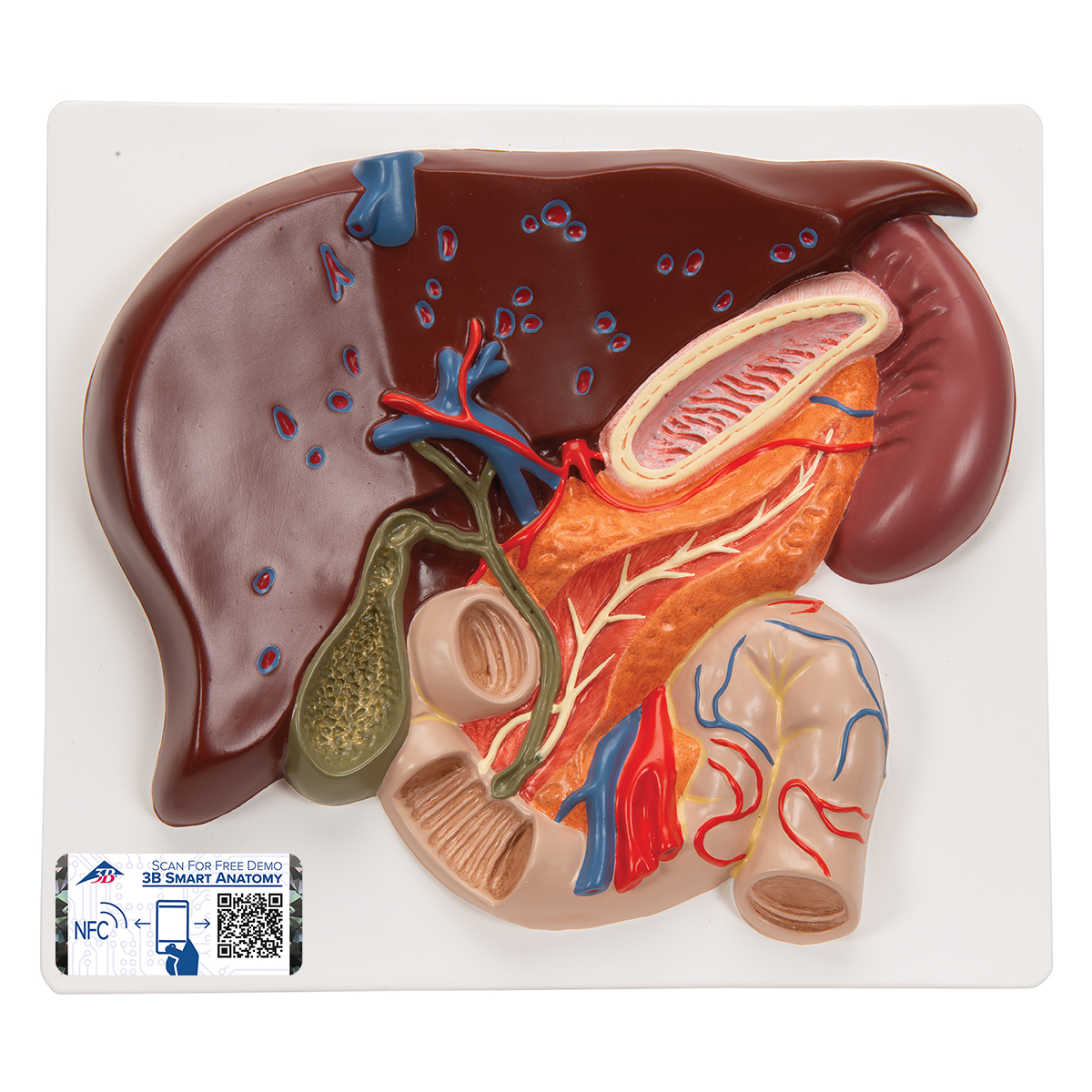 Anatomical Teaching Models Plastic Human Digestive Models
Anatomical Teaching Models Plastic Human Digestive Models
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-651425467-5bba561cc9e77c0051c260ac.jpg) Female Urology And External Sexual Anatomy
Female Urology And External Sexual Anatomy
 Urinary Bladder Human Anatomy Britannica
Urinary Bladder Human Anatomy Britannica
 Amazon Com Human Anatomy Bladder Prostate Penis Print Sra3
Amazon Com Human Anatomy Bladder Prostate Penis Print Sra3

 Bladder Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock
Bladder Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock
 Cancer Bladder Diagram Showing The Stages Of Bladder Cancer
Cancer Bladder Diagram Showing The Stages Of Bladder Cancer
 Anatomy And Normal Microbiota Of The Urogenital Tract
Anatomy And Normal Microbiota Of The Urogenital Tract
 Definition Of Stage Iii Bladder Cancer Nci Dictionary Of
Definition Of Stage Iii Bladder Cancer Nci Dictionary Of
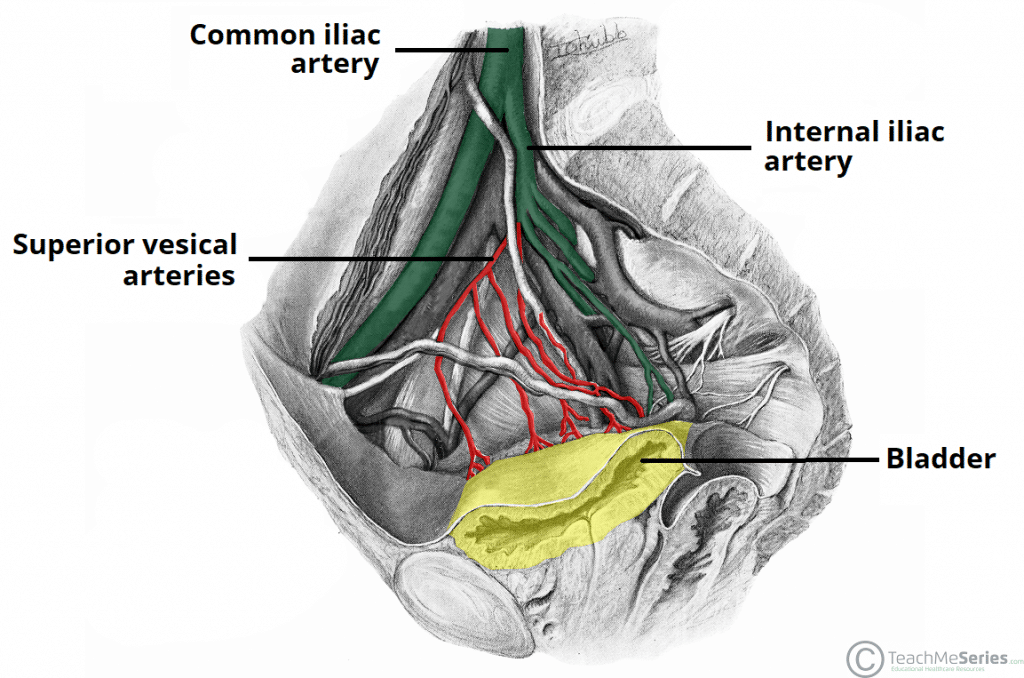 The Urinary Bladder Structure Function Nerves
The Urinary Bladder Structure Function Nerves
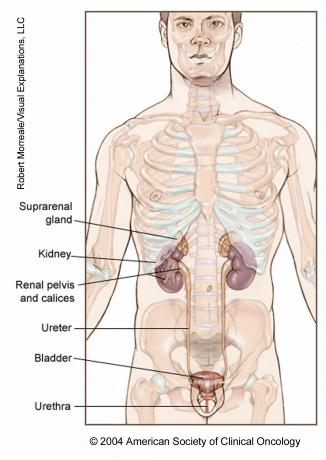


Belum ada Komentar untuk "Human Anatomy Bladder"
Posting Komentar