Tulip Anatomy
The function of the stem of a tulip is to receive water from the roots and sunlight from the sun and send it to the leaves. On the stem the leaves are attached to it.
The purpose of this activity is to observe and record growth of a tulip and to identify its flower parts.

Tulip anatomy. The recommended hole depth is 4 to 8 inches 10 to 20 cm deep and is measured from the top of the bulb to the surface. Tulips should be planted 4 to 6 inches 10 to 15 cm apart from each other. Some tulip blossoms are single colored while others are striped swirled flamed from the bottom or margined.
Students will observe spring tulip growth in the school garden. Teachers talkingscience recommends that you hand out to your students printed copies of a diagram of the parts of a flowers anatomy that are explored in this activity. Transcript of anatomy of a tulip flower.
Tulip with red and white stripes botanical illustration floral pink tulip botanical illustration by kendyll hillegas vintage inspired watercolor and colored pencil painting for packaging and home decor. It has normal growth when the temperature is more than 8 and it can be resistant to 14. Tulip is a steppe and winter rain mediterranean vegetation.
The color of a leaf is always green because of the pigment even though if the leaf if purple. They will record tulip growth by creating a bar graph and label flower parts by drawing a tulip flower in their journal. Before you present this lesson become familiar with the anatomy of a flower by researching and viewing diagrams or images online or at the library.
The blossoms may be single or double and the flowers come in nearly every color except true blue. As you have seen in this article some flowers have caused curious stories and a great impact on our society. This stigma accepts pollen deposited onto the tip where it travels down the style to the ovary of the tulip to pollinate the unfertilized seeds inside known as the ovules.
The female portion of the tulip the pistil has a rounded bottom and a tapered top known as the stigma. Also you have had the opportunity to observe in detail the tulips structure. All tulip flowers have six petals and the petals can be smooth fringed or ruffled.
Tulip genus tulipa any of a group of cultivated bulbous herbs in the family liliaceae. Female reproductive organ ovary and 3 stigmas photo taken by adriel acosta. Tulip bulbs are typically planted around late summer and fall in well drained soils.
The genus tulipa consists of about 100 species that are native to eurasia from austria and italy eastward to japan with two thirds of them native to the eastern mediterranean and the southeastern parts of the soviet union. Parts of tulip flower. Tulipa is also a long day flower likes the sunny sheltered or warm and humid areas in winter.
 Nature Picture Library Section Through The Flower Of A
Nature Picture Library Section Through The Flower Of A

 Stamen Anther Style Anatomy Of Cultivated Tulip Flower
Stamen Anther Style Anatomy Of Cultivated Tulip Flower
 Forcing Bulbs Recreate Nature In Your Home Tulip Bulbs
Forcing Bulbs Recreate Nature In Your Home Tulip Bulbs
 Botanical Flower Tulip Anatomy 3 Botanical Prints
Botanical Flower Tulip Anatomy 3 Botanical Prints
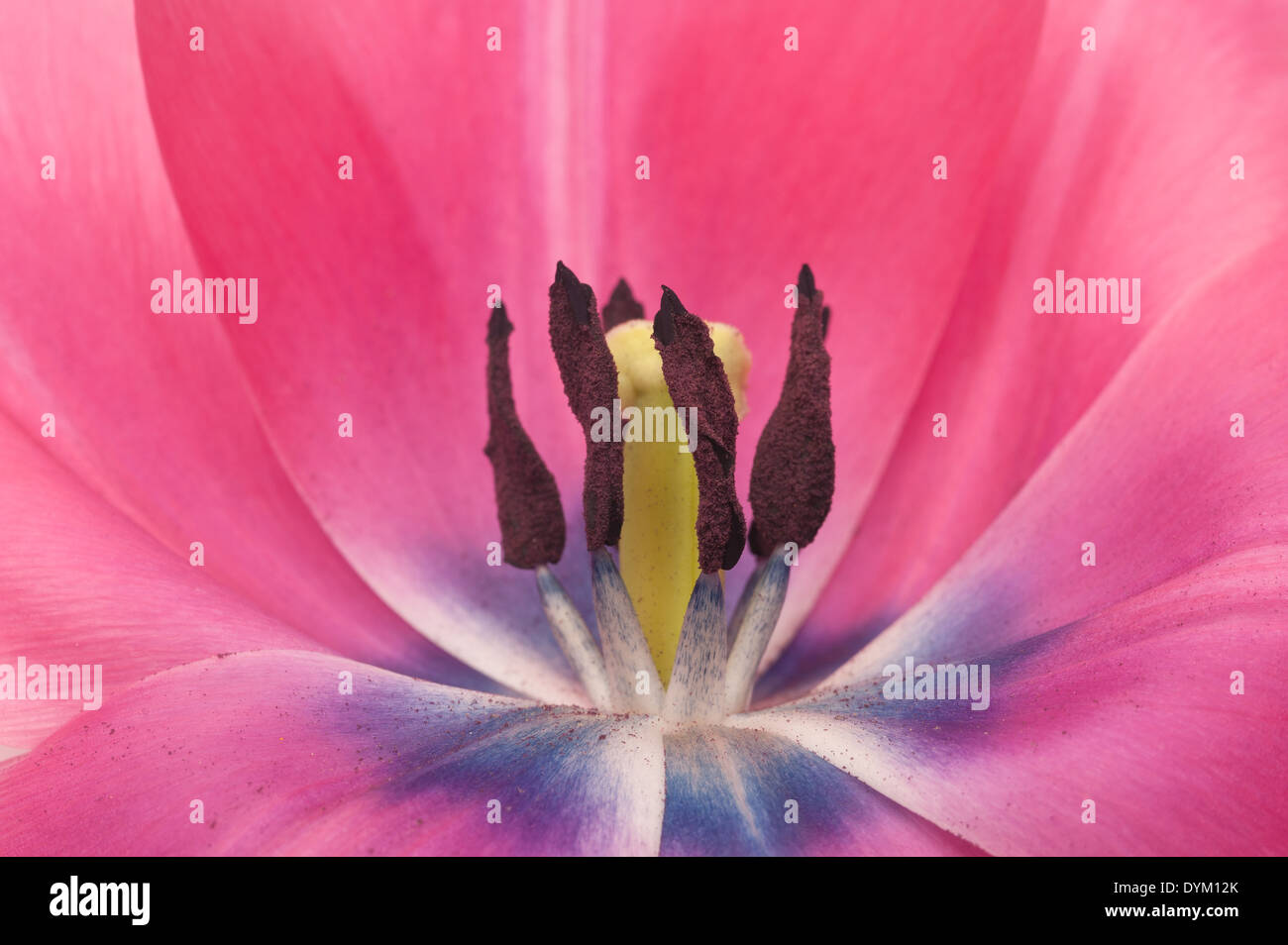 Stamen Anther Style Anatomy Of Cultivated Tulip Flower
Stamen Anther Style Anatomy Of Cultivated Tulip Flower
 Botanical Flower Tulip Anatomy 1 Vintage Botanical
Botanical Flower Tulip Anatomy 1 Vintage Botanical
 The Antiquarium Antique Print Map Gallery Michael
The Antiquarium Antique Print Map Gallery Michael
 Tulip Anatomy Chart Vintage Style Poster
Tulip Anatomy Chart Vintage Style Poster
 Stamen Anther Style Anatomy Of Cultivated Tulip Flower
Stamen Anther Style Anatomy Of Cultivated Tulip Flower
 T U L I P Deconstruction Botanicaldeconstruction Tulip
T U L I P Deconstruction Botanicaldeconstruction Tulip
 Anatomy Of An Object Afshar Tulip Rug Hali
Anatomy Of An Object Afshar Tulip Rug Hali
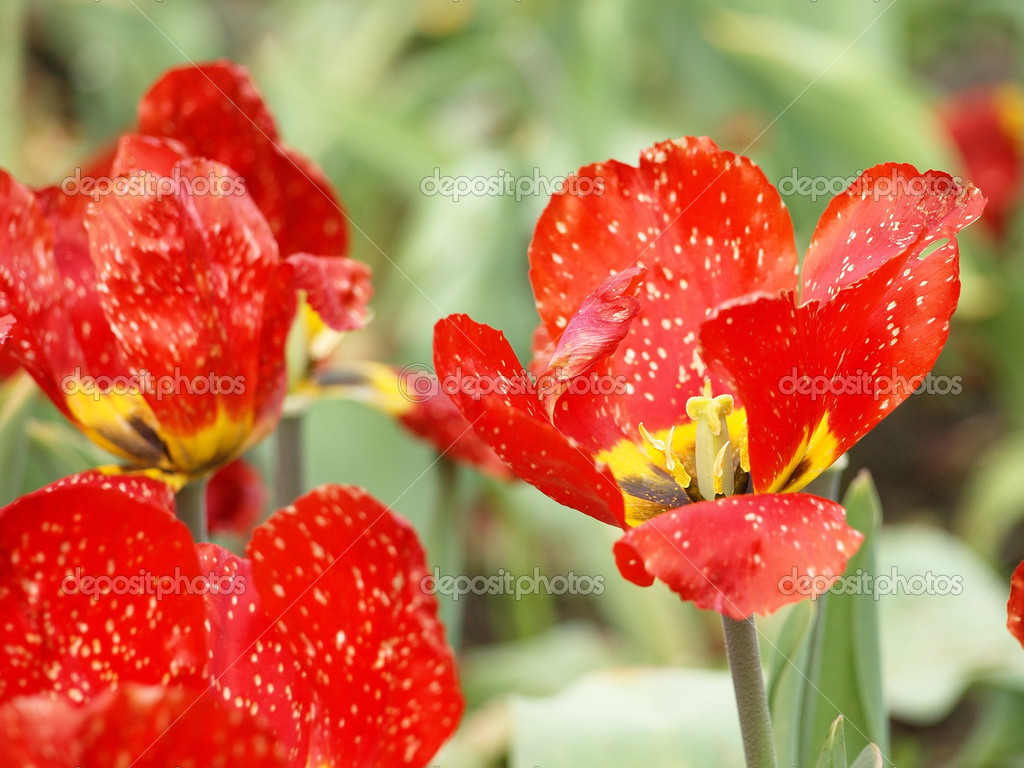 Anatomy Of A Tulip Stock Photo C Biker11960 45607711
Anatomy Of A Tulip Stock Photo C Biker11960 45607711

 Tulip Anatomy Botanical Illustration Floral Pink
Tulip Anatomy Botanical Illustration Floral Pink
 Anatomy Tulip Stock Illustrations 7 Anatomy Tulip Stock
Anatomy Tulip Stock Illustrations 7 Anatomy Tulip Stock
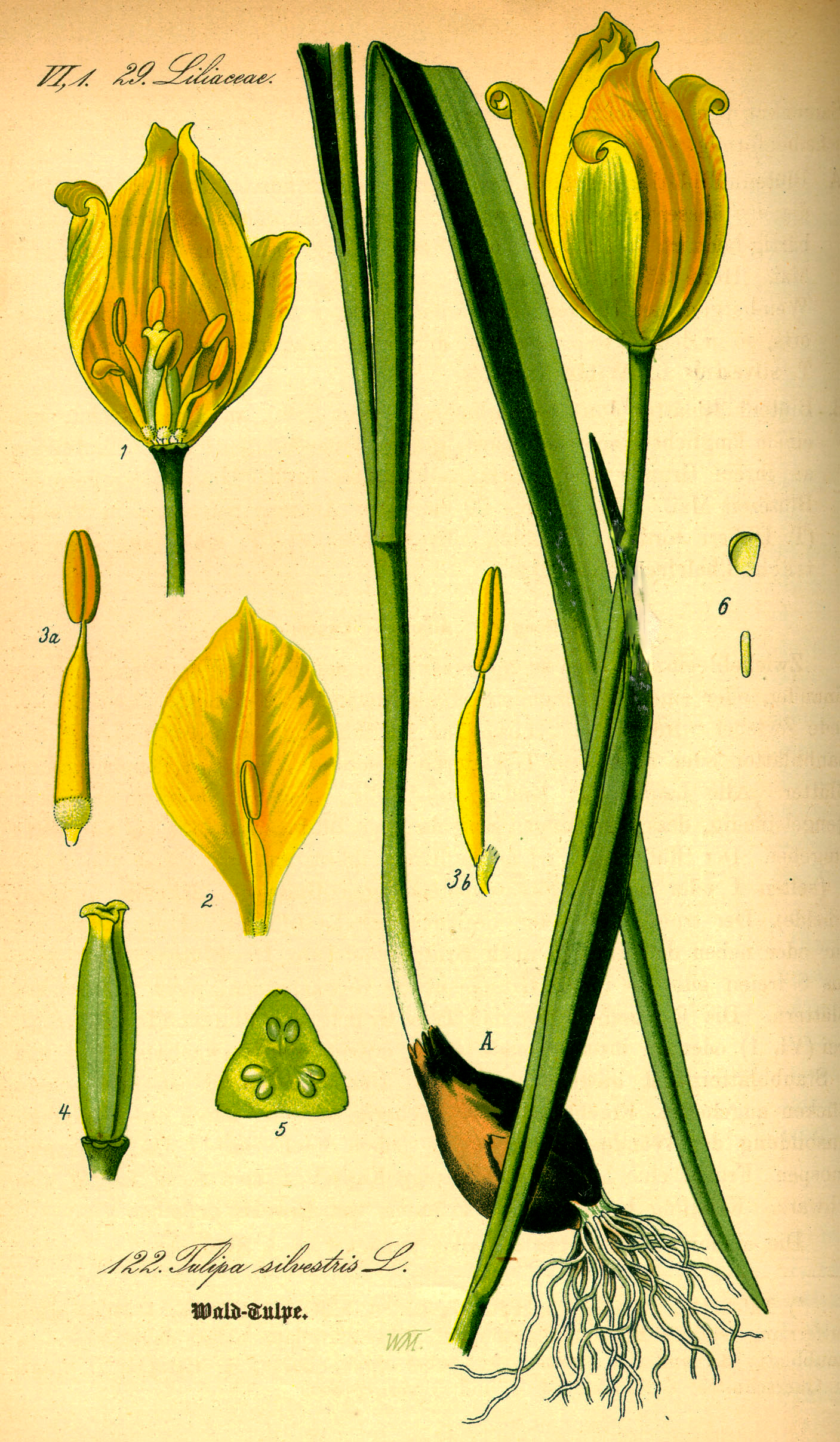 Beautiful Vintage Tulip Paintings To Download For Free
Beautiful Vintage Tulip Paintings To Download For Free
 Anatomy Of A Tulip By Gene Walls Redbubble
Anatomy Of A Tulip By Gene Walls Redbubble
 Tulip Anatomy Botanical Illustration Tulips Botanical Art
Tulip Anatomy Botanical Illustration Tulips Botanical Art
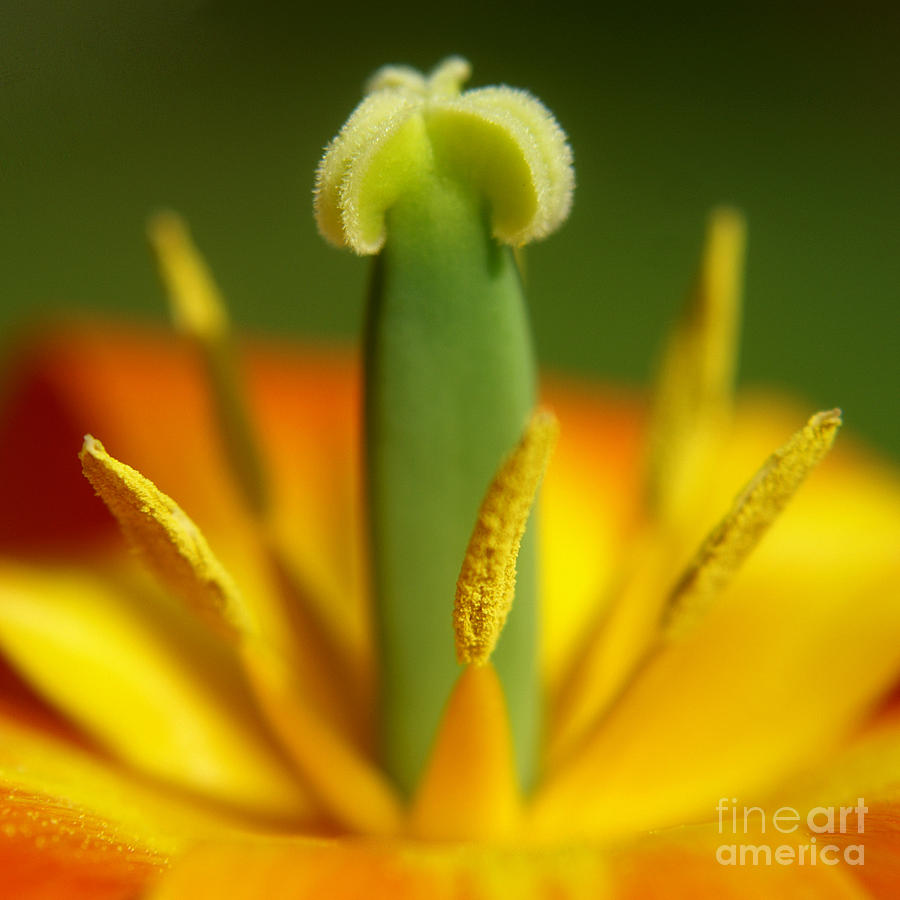
Anatomy Of A Tulip Joetography
 How To Store Plant Your Bulbs The Garden Generalist
How To Store Plant Your Bulbs The Garden Generalist







Belum ada Komentar untuk "Tulip Anatomy"
Posting Komentar