Upper Airway Anatomy
In this first aid blog post we will look closer at the anatomy of the upper airway. The larynx consists of a framework of cartilages and fibroelastic membranes covered by a sheet of muscles and lined with mucous membrane.
Resource Webpage Upper Airway Essential Learning Activities
The upper airway consists of the pharynx and the nasal cavities.
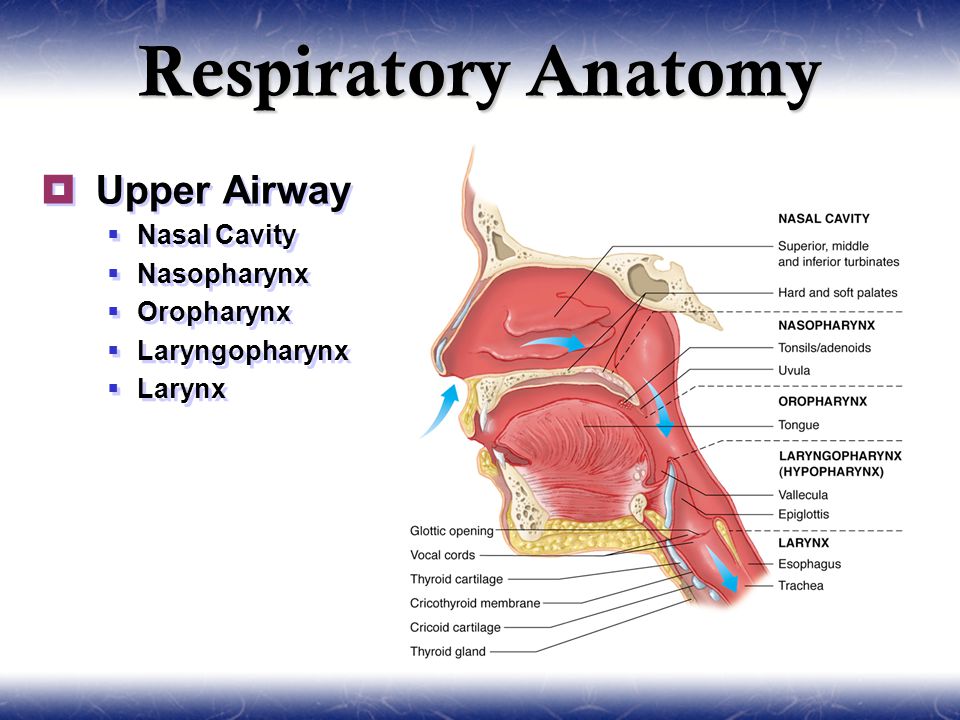
Upper airway anatomy. The anterior attachments of the middle constrictor are the hyoid bone and the stylohyoid ligament. Unlike the trachea and bronchi the upper airway is a collapsible compliant tube. The upper respiratory and upper digestive tracts diverge after the laryngopharynx.
However some authors include the larynx and trachea as well. The airway consists of chambers and pipes which conduct air with its 21 oxygen content to the alveoli and carry away the waste carbon dioxide that diffuses from the blood into the alveoli. The airway changes in size shape and position throughout its development from the neonate to the adults.
The nose is composed of bone and cartilage which are in turn attached to the facial skeleton. It evolved as a protective valve mechanism at the upper end of the lower airway necessitated by an unusual crossover between the airway and alimentary canal. Upper airway anatomy functions warm filter and humidify air nasal cavity and nasopharynx formed by union of facial bones nasal floor towards ear not eye lined with mucous membranes cilia tissues are delicate vascular adenoids lymph tissue filters bacteria commonly infected.
The nostrils the two round or oval holes below the external nose are the primary entrance into the human respiratory system 5. Functional anatomy of the upper airway. Anatomy and physiology of the respiratory system duration.
The pharynx is can be divided into the nasopharynx oropharynx and laryngopharynx. The upper airway extends from the mouth to the trachea. The rear of the laryngopharynx merges with the esophagus to continue the digestive tract.
The superior constrictor is suspended from the base of the skull the medial pterygoid plate the pterygomandibular raphe the mylohyoid line of the mandible and the lateral tongue. Lying just after the nostrils are the two nasal cavities lined with mucous membrane and tiny hair like projections called cilia 6. The laryngopharynx is the posteriormost portion of the pharynx reaching from the hyoid to the cricoid cartilage.
Knowledge of the functional anatomy of the airway in these forms the basis of understanding the pathological conditions that may occur. Carbon dioxide co 2 is transferred from returning blood back into gaseous form in the lungs and exhaled through the lower respiratory tract and then the upper to complete the process of breathing. Upper airway anatomy and function.
Upper respiratory tract structural and functional anatomy nose and nasal cavity.
 An Overview Of Airway Anatomy Emt Training Base
An Overview Of Airway Anatomy Emt Training Base
 Airway Anatomy Nurse Anesthesia Nran 788 With Hadenfeldt
Airway Anatomy Nurse Anesthesia Nran 788 With Hadenfeldt
 Upper Airway Anatomy Snoring Sleep Apnea Stock Vector
Upper Airway Anatomy Snoring Sleep Apnea Stock Vector
 Upper Airway Evaluation In Snoring And Obstructive Sleep
Upper Airway Evaluation In Snoring And Obstructive Sleep
Airway Anatomy And Physiology Clinical Essentials
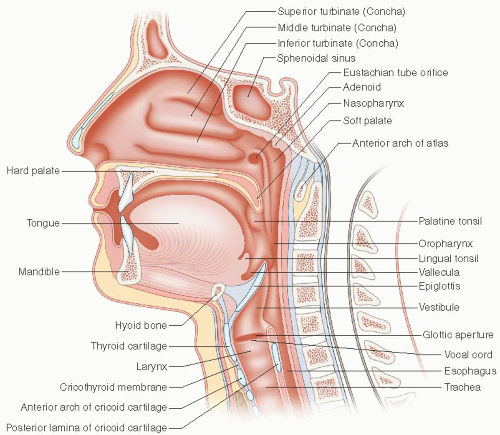 Applied Functional Anatomy Of The Airway Anesthesia Key
Applied Functional Anatomy Of The Airway Anesthesia Key
 Smoking Clipart Respiratory Distress Upper Airway Anatomy
Smoking Clipart Respiratory Distress Upper Airway Anatomy
 Anatomy Of Upper Airway Medical Illustration Human
Anatomy Of Upper Airway Medical Illustration Human
 Pulmonology Ppt Video Online Download
Pulmonology Ppt Video Online Download
 Airway Airway Anatomy Basic Airway Anatomy
Airway Airway Anatomy Basic Airway Anatomy
 Upper Airway Collapsibility Dilator Muscle Activation And
Upper Airway Collapsibility Dilator Muscle Activation And
Upper Airway Anatomy Flashcards Memorang
Airway Management Module 2 1 Ceu Continuing Education From
 Upper Airway Anatomy Snoring Sleep Apnea Stock Vector
Upper Airway Anatomy Snoring Sleep Apnea Stock Vector
 Upper Airway Human Vector Photo Free Trial Bigstock
Upper Airway Human Vector Photo Free Trial Bigstock
 Human Respiratory System Description Parts Function
Human Respiratory System Description Parts Function
 Chapter 6 Essential Anatomy Of The Airway Emergency
Chapter 6 Essential Anatomy Of The Airway Emergency
 Emt Chapter 9 Airway Management At Estrella Mountain
Emt Chapter 9 Airway Management At Estrella Mountain
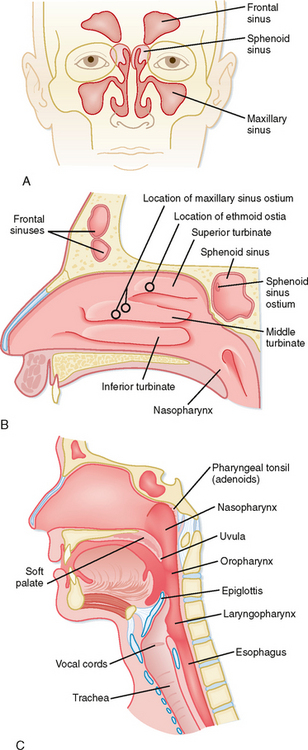 Structure And Function Of The Respiratory System
Structure And Function Of The Respiratory System
B2w6 Laryngeal Anatomy Upper Airway Anatomy Flashcards
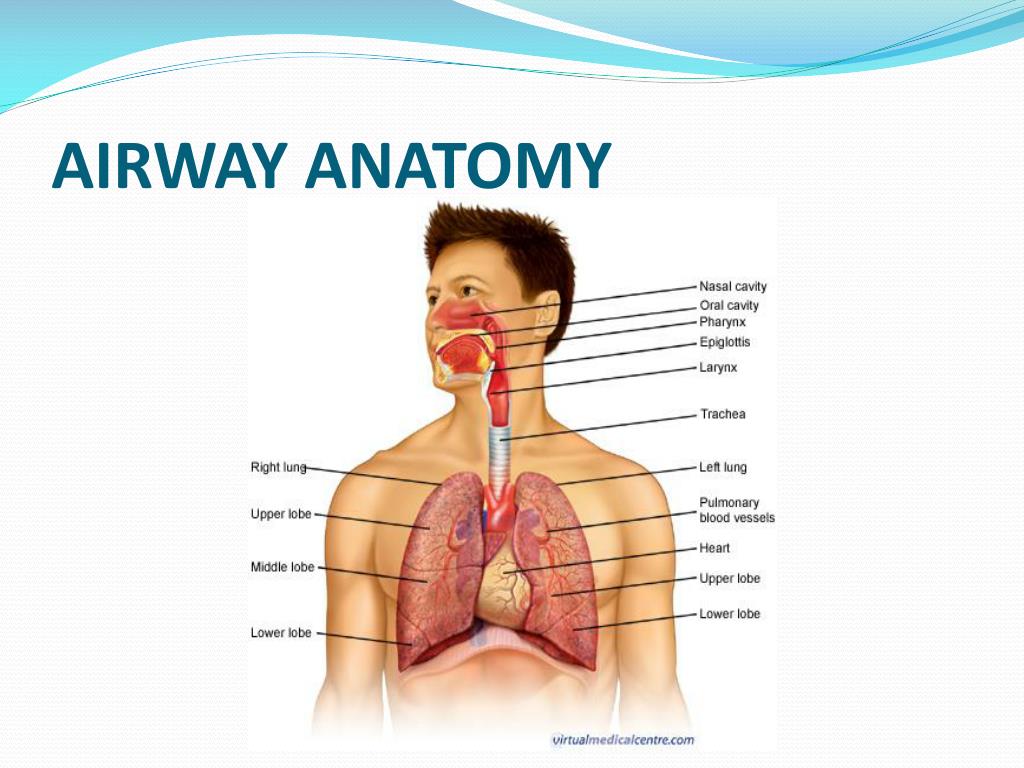 Ppt Airway Management Powerpoint Presentation Free
Ppt Airway Management Powerpoint Presentation Free

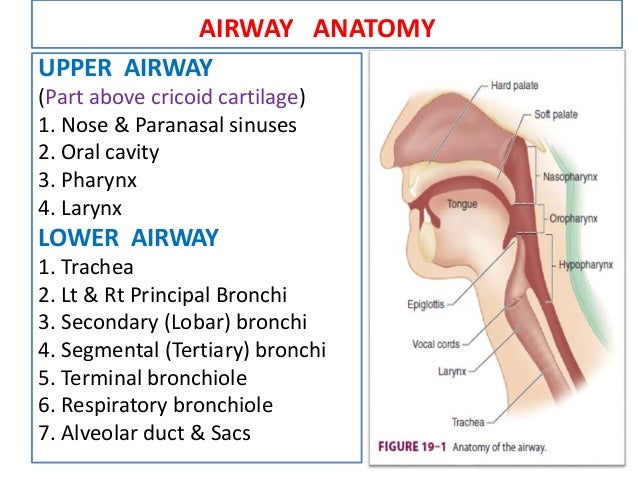




Belum ada Komentar untuk "Upper Airway Anatomy"
Posting Komentar