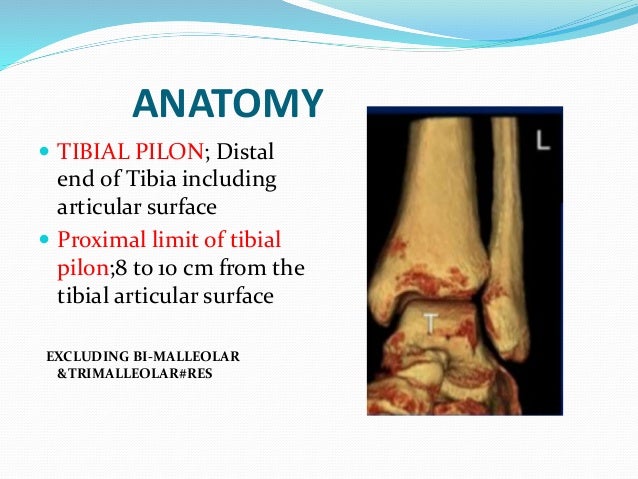
Tibial Plafond Anatomy
Distal tibia forms an inferior quadrilateral surface and pyramid shaped medial malleolus. Plafond fractures are infrequent injuries accounting for 7 10.
 Pilon Fractures Of Tibia Presentation And Treatment Bone
Pilon Fractures Of Tibia Presentation And Treatment Bone
It is also known as pilon fracture and explosion fracture.

Tibial plafond anatomy. 35 40 years. First branch of popliteal artery. Mechanism typically occurs as a result of an axial loading injury which drives the talus into the tibial.
Up to 50 incidence of associated injuries. Soft tissues very poor thin skin absence of muscle and adipose tissue lack of deep veins. Passes between 2 heads of tibialis posterior and interosseous membrane iom.
Especially vunerable over anteromedial tibia. Anterior tibial artery. Pilon fractures are caused by rotational or axial forces mostly as a result of falls from a height or motor vehicle accidents.
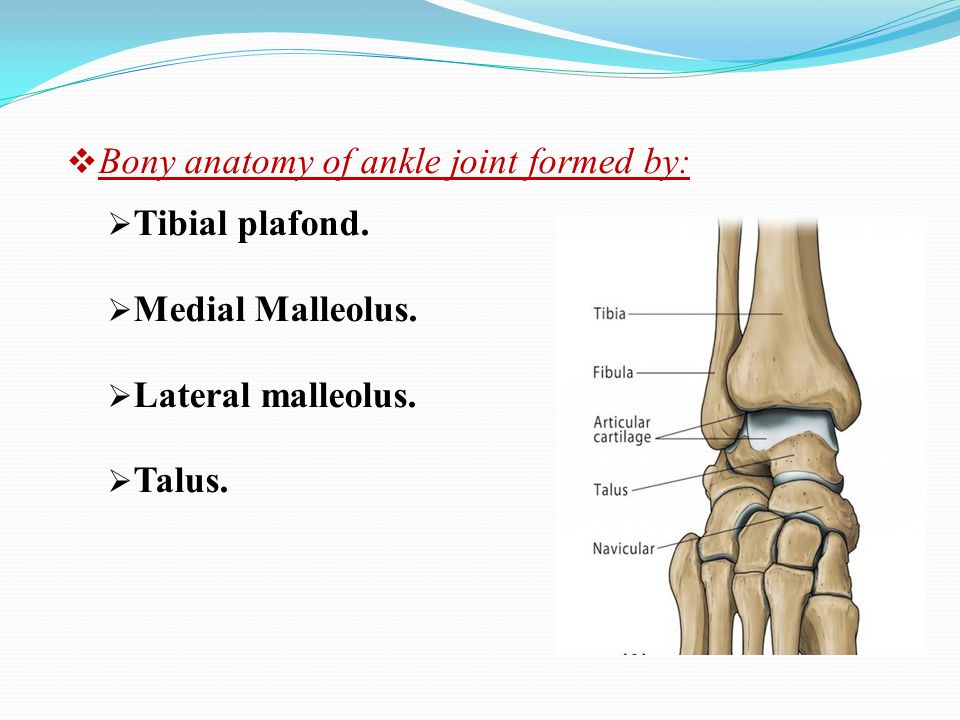
Although the ligaments are needed to give the ankle its full stability the bony congruity of the mortise and the talus is a necessary component as well forming the most congruent joint in the lower extremity. Males 3 x. The distal portion of the tibia is known as the plafond which.
A pilon fracture is a type of fracture involving the distal tibia. Tibial plafond fracture is an uncommon fracture occurring in the distal region of the tibia. Fracture of tibial weight bearing surface due to axial compression.
1 a pilon fracture also called a plafond fracture is a fracture of the distal part of the tibia involving its articular surface at the ankle joint. It involves the articular surface of the ankle joint. Rapid axial load very high energy.
Tibial plafond fracture orif with anterolateral approach and plate fixation ankle and hindfoot ankle simple bimalleolar fracture orif with 13 tubular plate and cannulated screw of medial malleol. These are considered to represent 1 10 of all lower limb fractures 6. The tibial plafond lateral malleolus and medial malleolus form a mortise a socket in which the talus sits figure 2.
Articulates with the talus and fibula laterally via the fibula notch. 11 originally proposed an anatomical nine zone grid scheme to the articular surface of the talus to more easily describe the location of an ocl and have also applied this to the articular surface of the distal tibial plafond figure 1. The cause of tibial plafond fracture is axial or rotational forces occurring from motor vehicle accidents or falling from a height.
Radiographic examination of the ankle bones. Clinical features of pain swelling deformity and crepitus about the. Tibial plafond fractures introduction.
Prospective Study Of Management Of Distal Tibia Fracture
 High Energy Tibial Pilon Fractures An Instructional Review
High Energy Tibial Pilon Fractures An Instructional Review

Ankle Fractures Tibia And Fibula Orthopaedia
 7 Knee Injury Diagnosis Ppt Video Online Download
7 Knee Injury Diagnosis Ppt Video Online Download
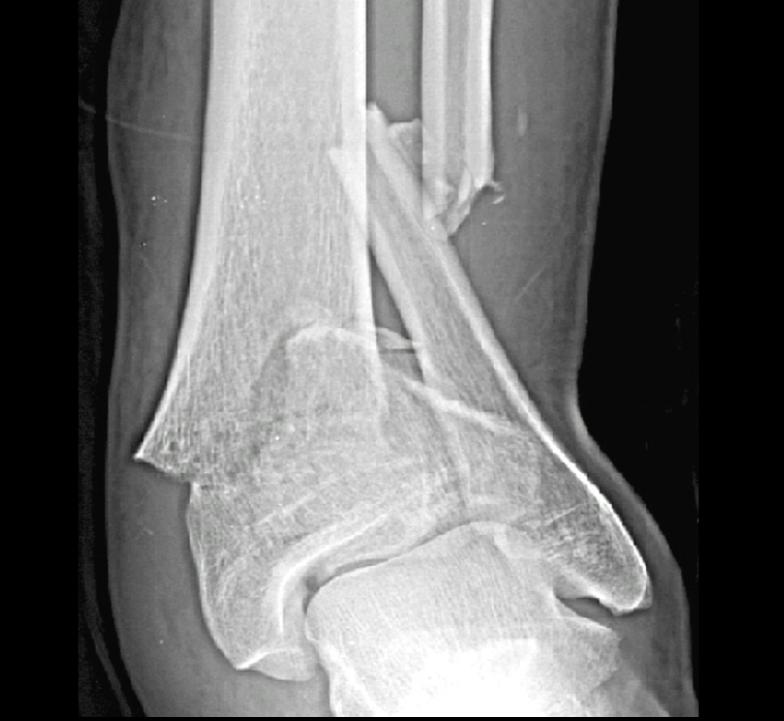 Tibial Plafond Fractures Trauma Orthobullets
Tibial Plafond Fractures Trauma Orthobullets
 Tibial Plafond Fracture Classifications Symptoms Treatment
Tibial Plafond Fracture Classifications Symptoms Treatment
Current Concepts In Trauma Ankle And Pilon Fractures
 Management Of Ankle Impingement By Dr Ppt Video Online
Management Of Ankle Impingement By Dr Ppt Video Online
 Treatment Of Malreduced Pilon Fracture A Case Report And
Treatment Of Malreduced Pilon Fracture A Case Report And
 Medial Collateral Ligaments Orthopaedic Trauma Lecture
Medial Collateral Ligaments Orthopaedic Trauma Lecture
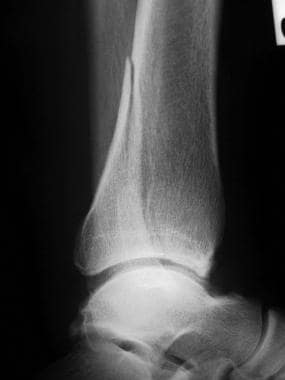 Pilon Fractures Workup Laboratory Studies Imaging Studies
Pilon Fractures Workup Laboratory Studies Imaging Studies
 Tibial Plafond Fractures Trauma Orthobullets
Tibial Plafond Fractures Trauma Orthobullets
 Distal Tibia Reduction Fixation Orif Compression
Distal Tibia Reduction Fixation Orif Compression
Tibial Plafond The Bone School
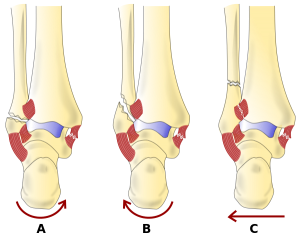 Ankle And Foot Fractures Physiopedia
Ankle And Foot Fractures Physiopedia
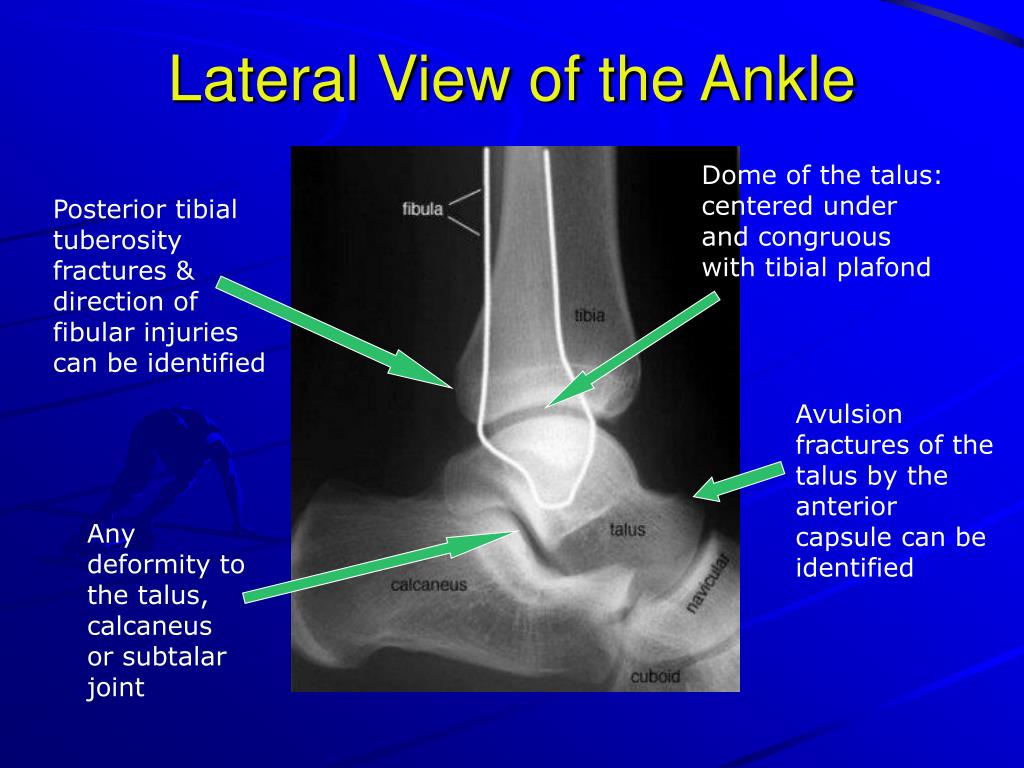 Ppt X Ray Rounds Plain Radiographic Evaluation Of The
Ppt X Ray Rounds Plain Radiographic Evaluation Of The
 These Four Tibial Plafond Fracture Radiographs Illustrate
These Four Tibial Plafond Fracture Radiographs Illustrate
 Anatomy 101 Ankle Syndesmosis Distal Tibiofibular Joint
Anatomy 101 Ankle Syndesmosis Distal Tibiofibular Joint
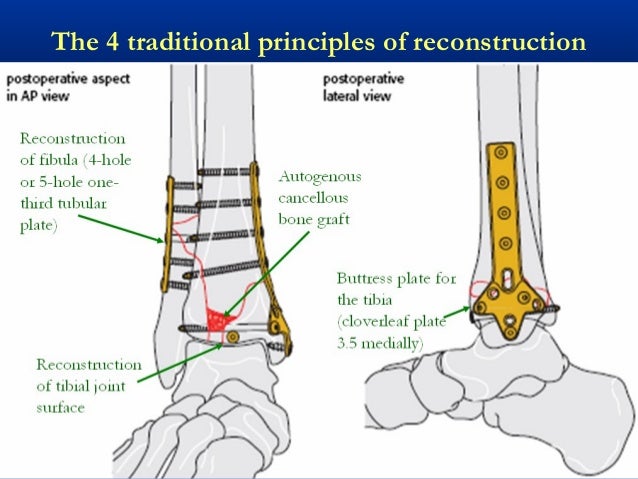 39 Tibial Plafond Pilon Fractures
39 Tibial Plafond Pilon Fractures
 Pilon Fractures Of The Ankle Orthoinfo Aaos
Pilon Fractures Of The Ankle Orthoinfo Aaos
Ankle Fractures Tibia And Fibula Orthopaedia
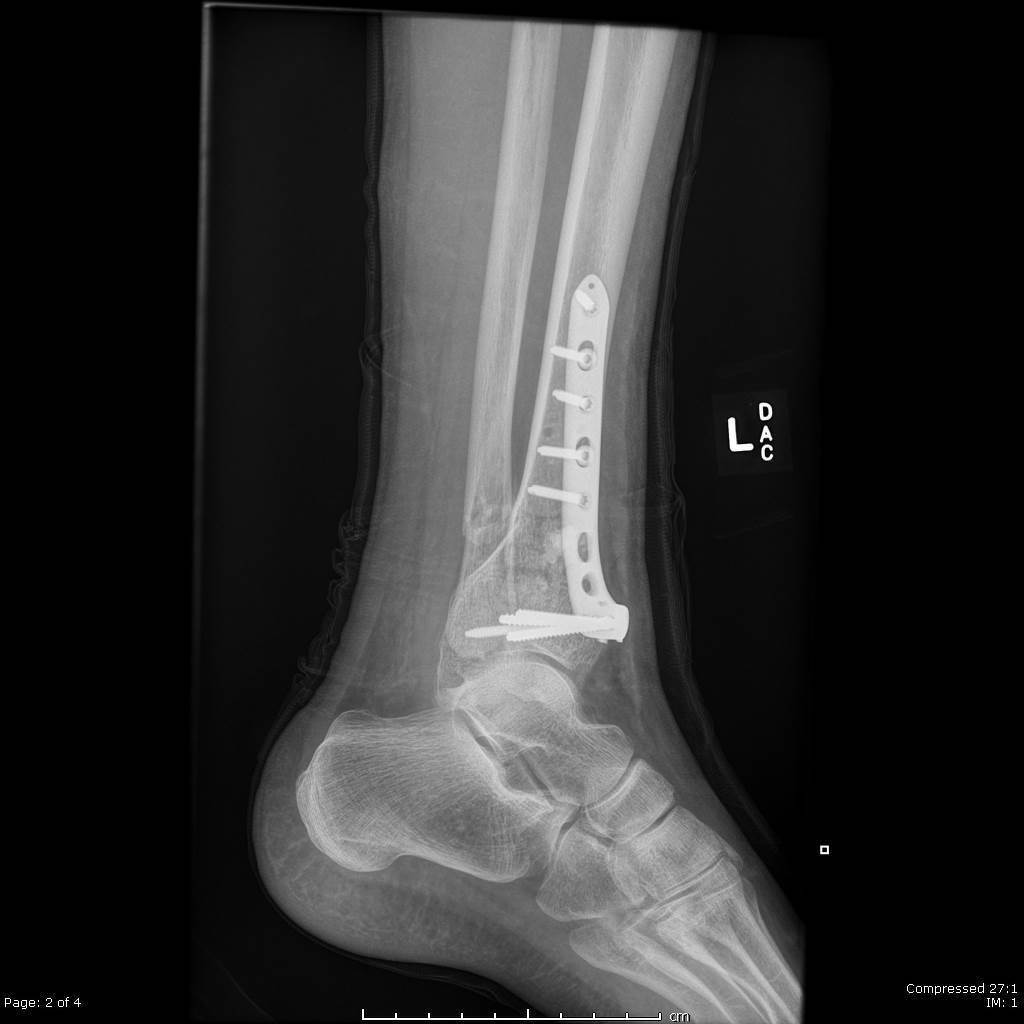 Pilon Fracture Radiology Case Radiopaedia Org
Pilon Fracture Radiology Case Radiopaedia Org


Belum ada Komentar untuk "Tibial Plafond Anatomy"
Posting Komentar