Anatomy Of Skeletal Muscle
64 102 skeletal muscle skeletal muscle fibers. The muscle tendon is the strong fibrous rope that keeps the muscles from slipping off their attachment points on bones.
Structure of skeletal muscle explained.

Anatomy of skeletal muscle. There are three classes of levers but the vast majority of the levers in the body are third class levers. Unlike smooth muscle and cardiac muscle skeletal muscle is under voluntary control. Each organ or muscle consists of skeletal muscle tissue connective tissue nerve tissue and blood or vascular tissue.
For more information and help learning muscle structure and composition visit. Muscle that connects bone and skin cells are long and cylinidrical with multiple peripheral nuclei striated strongest type of tissue fastest to contract requires the most energy and has the lowest endurance only voluntary muscle. Muscles fibres actin and myosin.
The epimysium is a particularly important component in the anatomy of the skeletal muscles because it along with other connective tissues forms the muscle tendon. Skeletal muscles contribute to the maintenance of homeostasis in the body by generating heat. Skeletal muscles as levers.
Its long thin multinucleated fibres are crossed with a regular pattern of fine red and white lines giving the muscle a distinctive appearance. Skeletal muscle anatomy the smallest contractile unit of skeletal muscle is the muscle fiber or myofiber which is a long cylindrical cell that contains many nuclei mitochondria and sarcomeres figure 1 58. The bone that the muscle moves acts as the lever.
Skeletal muscles are attached to bones by tendons and they produce all the movements of body parts in relation to each other. Similar to cardiac muscle however skeletal muscle is striated. Another specialization of the skeletal muscle is.
The joint acts as the fulcrum. Because skeletal muscle cells are long and cylindrical. Structure of skeletal muscle a whole skeletal muscle is considered an organ of the muscular system.
And the object being moved acts as the load. The muscle acts as the effort force. Skeletal muscles also protect internal organs particularly abdominal and pelvic organs by acting as an external barrier or shield to external trauma and by supporting the weight of the organs.
The striated appearance of skeletal muscle fibers is due to the arrangement.

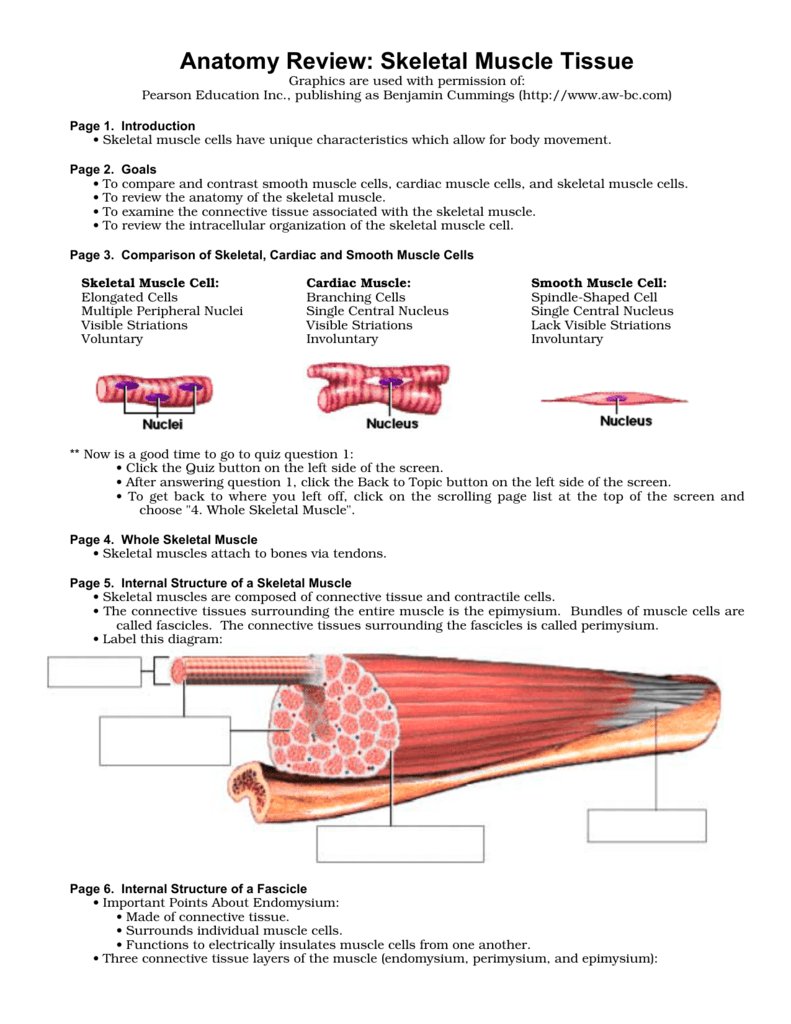 Anatomy Review Skeletal Muscle Tissue
Anatomy Review Skeletal Muscle Tissue
 Nomenclature Skeletal Muscle Anatomy
Nomenclature Skeletal Muscle Anatomy
 Skeletal Muscle Gross Anatomy Diagram Quizlet
Skeletal Muscle Gross Anatomy Diagram Quizlet
 Skeletal Muscle Structure Muscular System Anatomy Muscle
Skeletal Muscle Structure Muscular System Anatomy Muscle
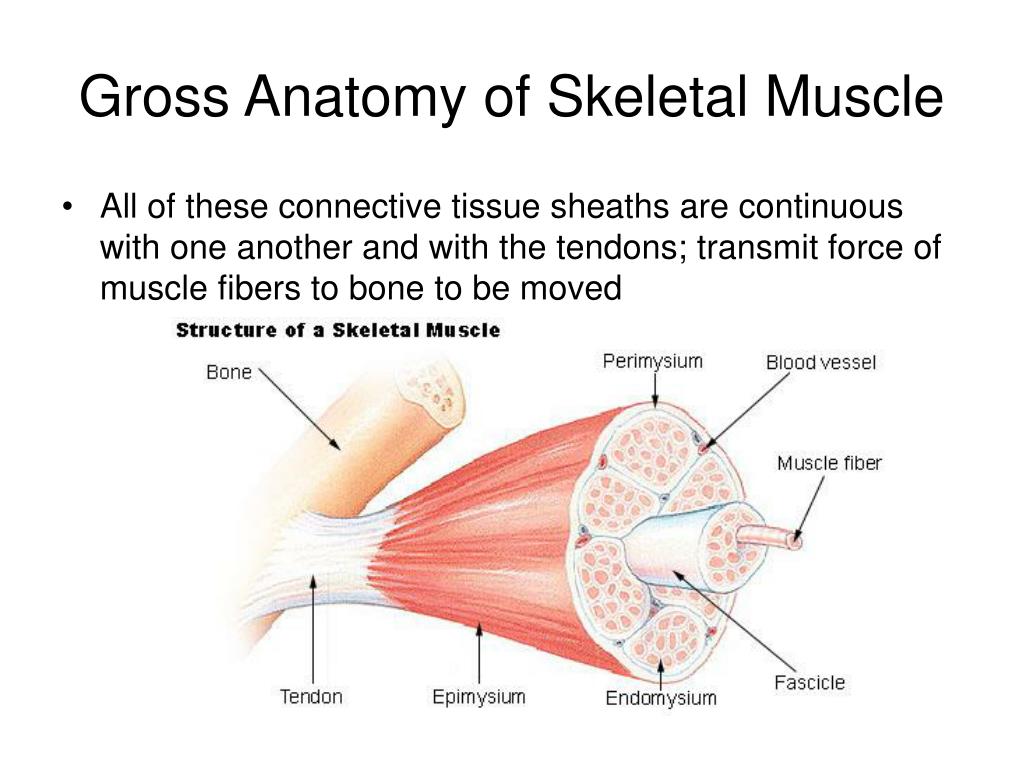 Ppt Gross Anatomy Of Skeletal Muscle Powerpoint
Ppt Gross Anatomy Of Skeletal Muscle Powerpoint
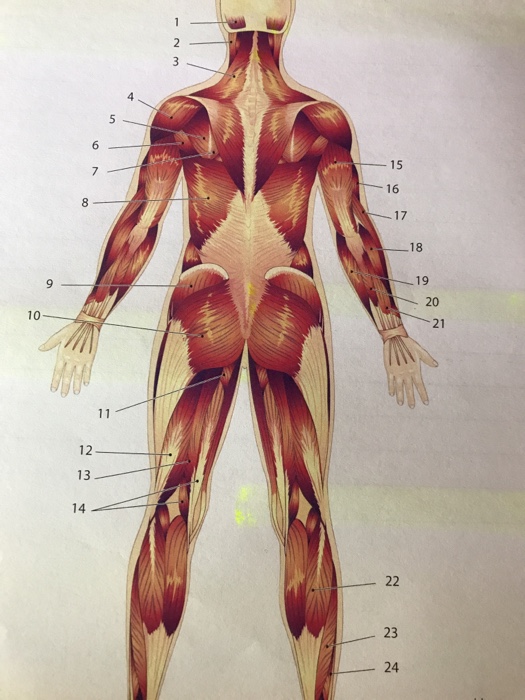
 Muscle Anatomy Skeletal Muscles Groin Muscles Calf Muscles
Muscle Anatomy Skeletal Muscles Groin Muscles Calf Muscles
General Principles Skeletal Muscle Anatomy
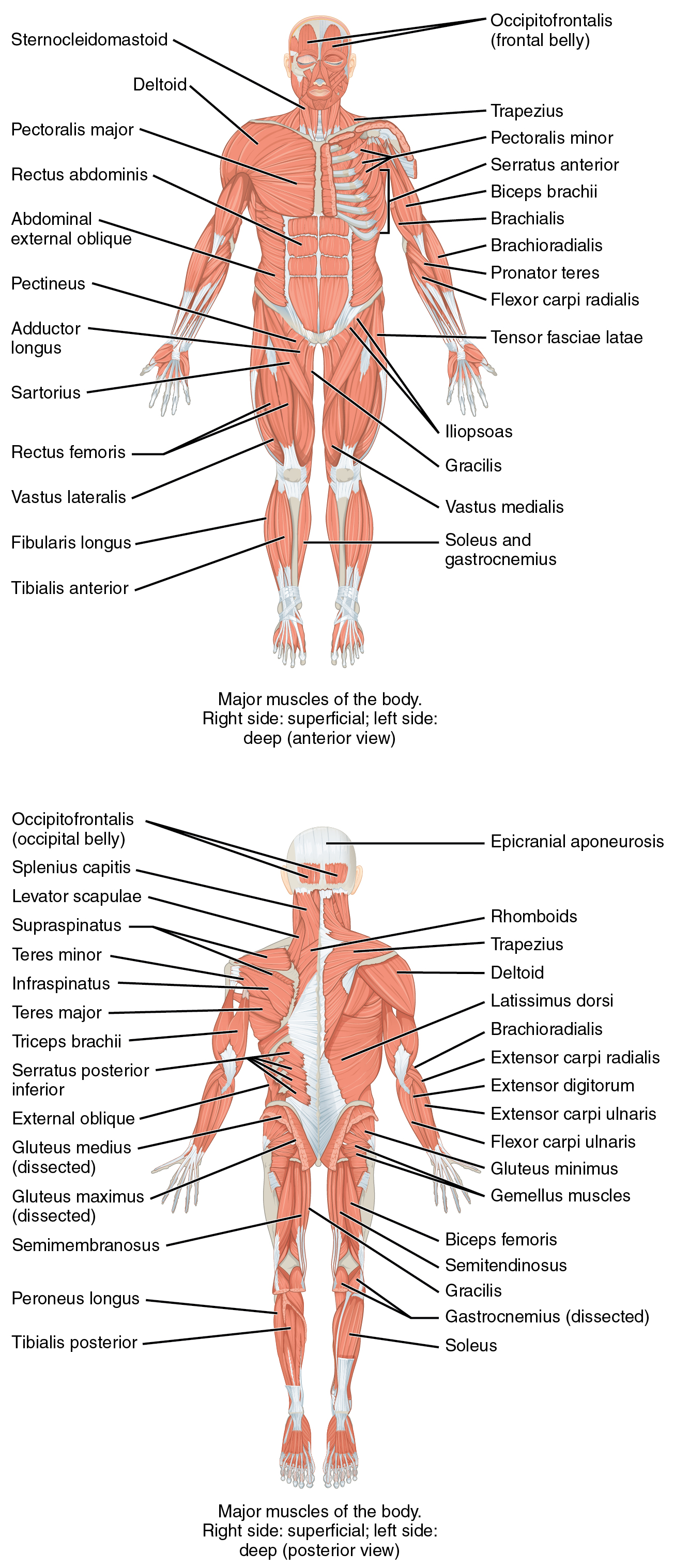 11 2 Naming Skeletal Muscles Anatomy And Physiology
11 2 Naming Skeletal Muscles Anatomy And Physiology
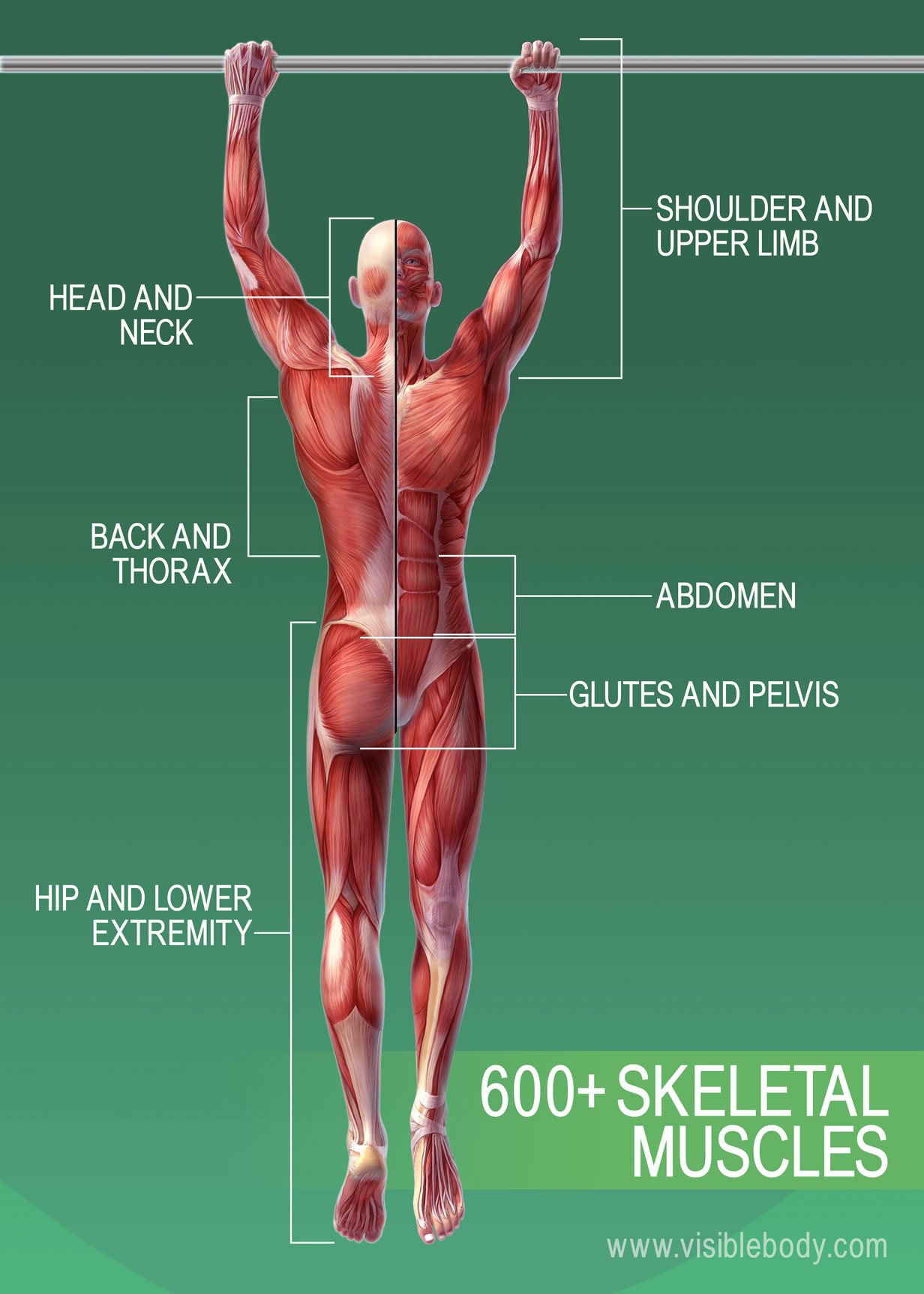 Muscular System Learn Muscular Anatomy
Muscular System Learn Muscular Anatomy
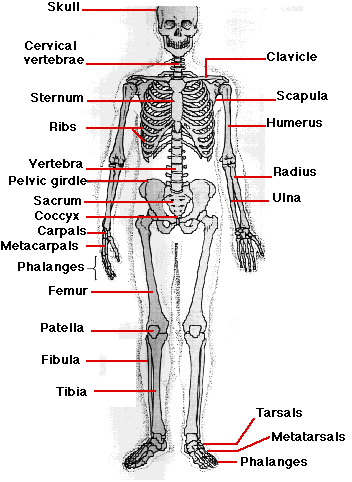
 Palace Learning Muscular Skeletal System Anatomical Poster Set Laminated 2 Chart Set Human Skeleton Muscle Anatomy Double Sided 18 X 27
Palace Learning Muscular Skeletal System Anatomical Poster Set Laminated 2 Chart Set Human Skeleton Muscle Anatomy Double Sided 18 X 27
 Gross Anatomy Of Skeletal Muscle The Muscular System Micro
Gross Anatomy Of Skeletal Muscle The Muscular System Micro
 Basic Anatomy Of Skeletal Muscle 27 Download Scientific
Basic Anatomy Of Skeletal Muscle 27 Download Scientific
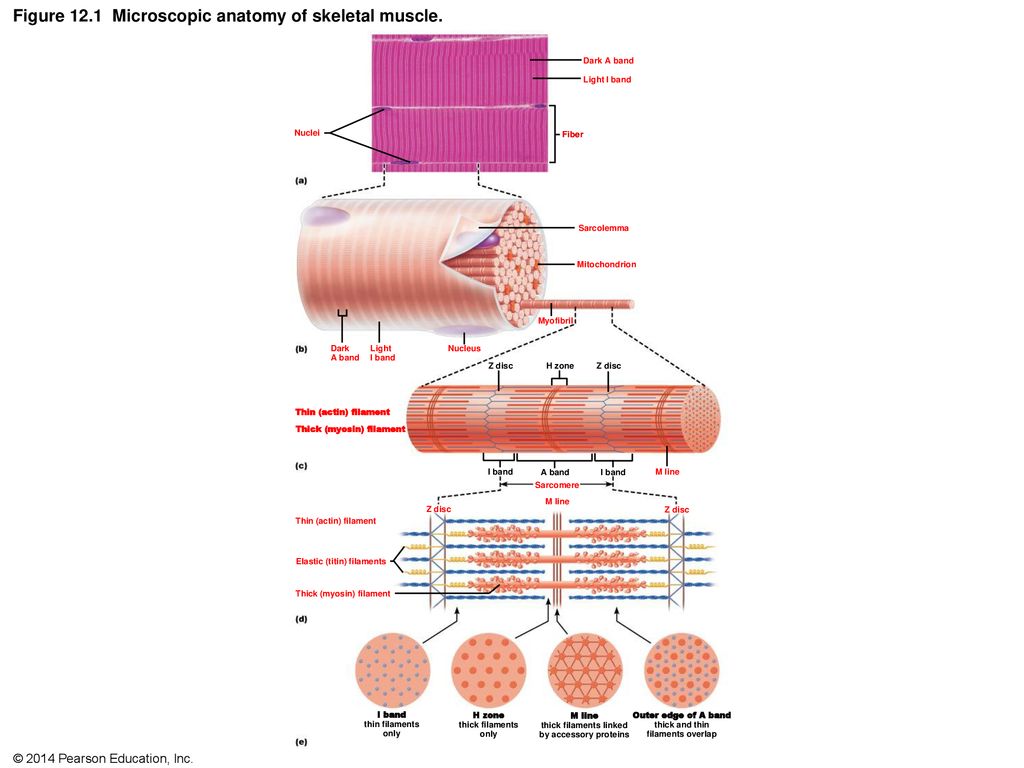 Figure 12 1 Microscopic Anatomy Of Skeletal Muscle Ppt
Figure 12 1 Microscopic Anatomy Of Skeletal Muscle Ppt
 Muscle Fundamentals Components Characteristics And
Muscle Fundamentals Components Characteristics And
 The Muscular System Gross Anatomy Over 600 Human Skeletal
The Muscular System Gross Anatomy Over 600 Human Skeletal
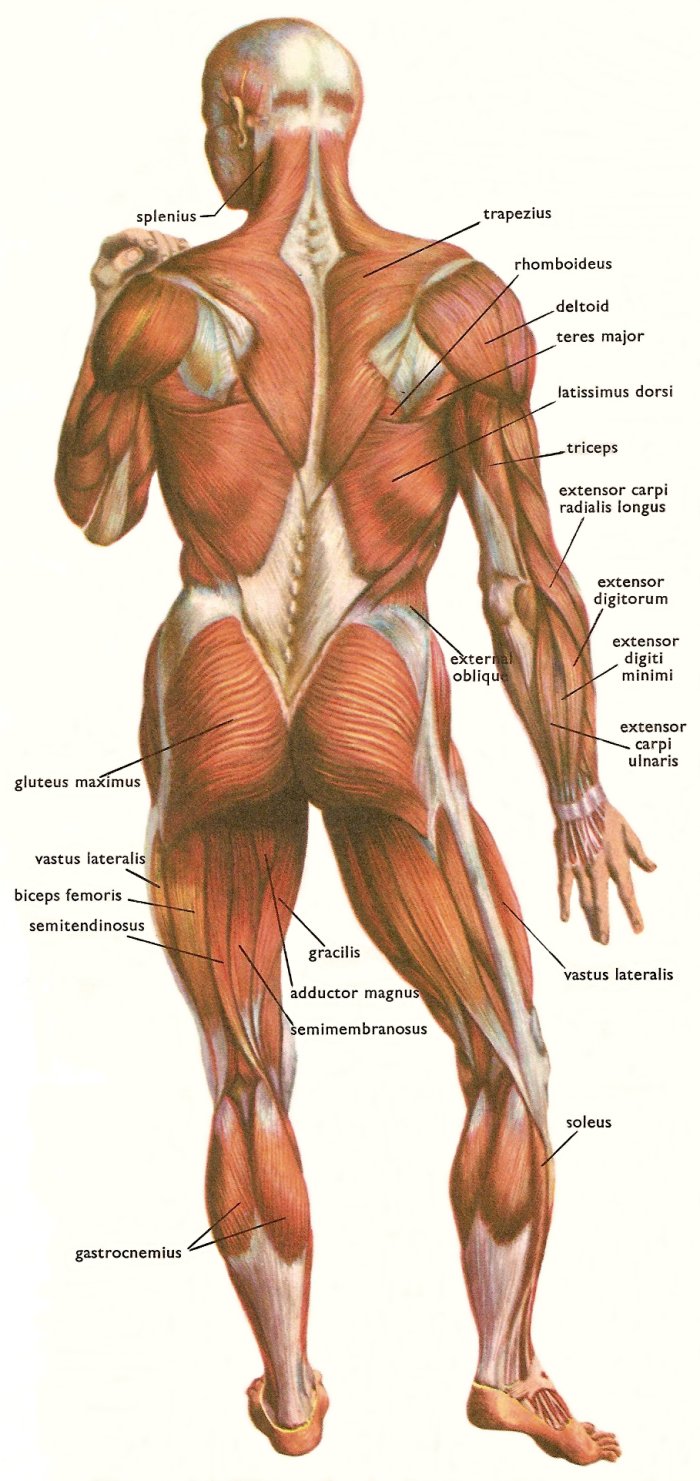 Skeletal Muscles And Muscle Groups
Skeletal Muscles And Muscle Groups
 Gross Anatomy Of Skeletal Muscle The Muscular System Micro
Gross Anatomy Of Skeletal Muscle The Muscular System Micro
 Skeletal Muscle Anatomy Of Weddell Seals Biopsy Samples
Skeletal Muscle Anatomy Of Weddell Seals Biopsy Samples
 Ultrastructure Of Muscle Skeletal Sliding Filament
Ultrastructure Of Muscle Skeletal Sliding Filament
 1 Gross Anatomical Structure Of Mature Mammalian Skeletal
1 Gross Anatomical Structure Of Mature Mammalian Skeletal
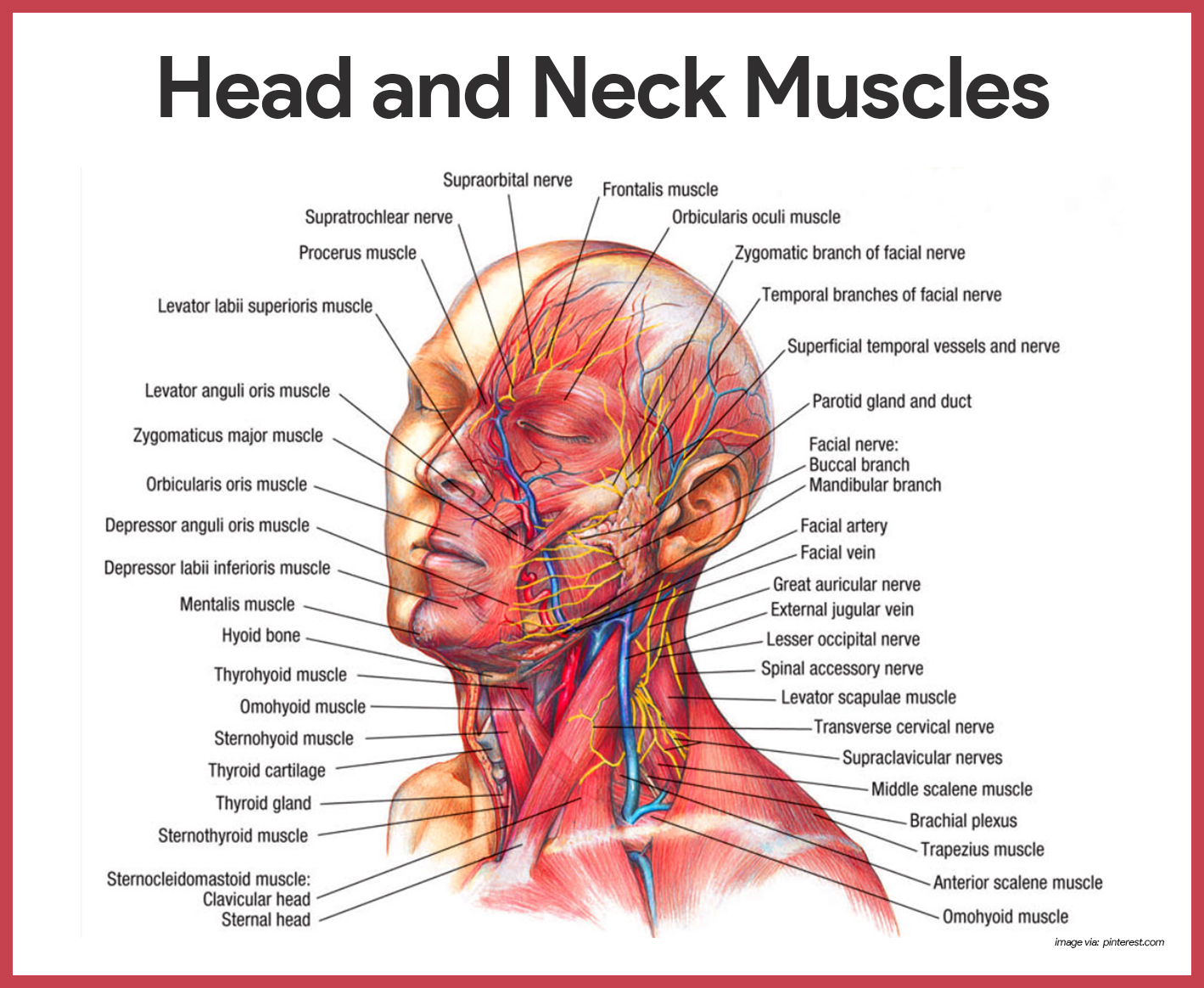 Muscular System Anatomy And Physiology Nurseslabs
Muscular System Anatomy And Physiology Nurseslabs
 Human Muscle System Functions Diagram Facts Britannica
Human Muscle System Functions Diagram Facts Britannica
 9 Skeletal Muscle Anatomy At University Of Michigan Ann
9 Skeletal Muscle Anatomy At University Of Michigan Ann
 Ch 09 Gross Anatomy Of Skeletal Muscle
Ch 09 Gross Anatomy Of Skeletal Muscle
Notes Microscopic Anatomy Of Skeletal Muscle
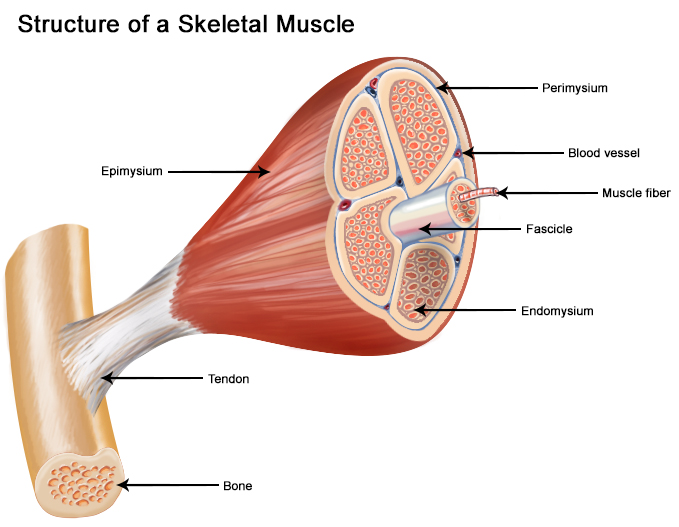 Seer Training Structure Of Skeletal Muscle
Seer Training Structure Of Skeletal Muscle
 Human Body Skeletal Muscle Tissue Anatomy Others Png
Human Body Skeletal Muscle Tissue Anatomy Others Png
Skeletal Muscles And Muscle Groups

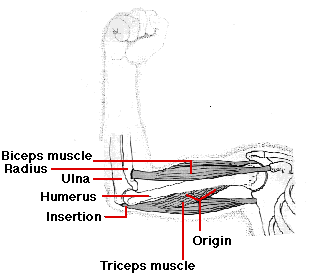
Belum ada Komentar untuk "Anatomy Of Skeletal Muscle"
Posting Komentar