Hair Strand Anatomy
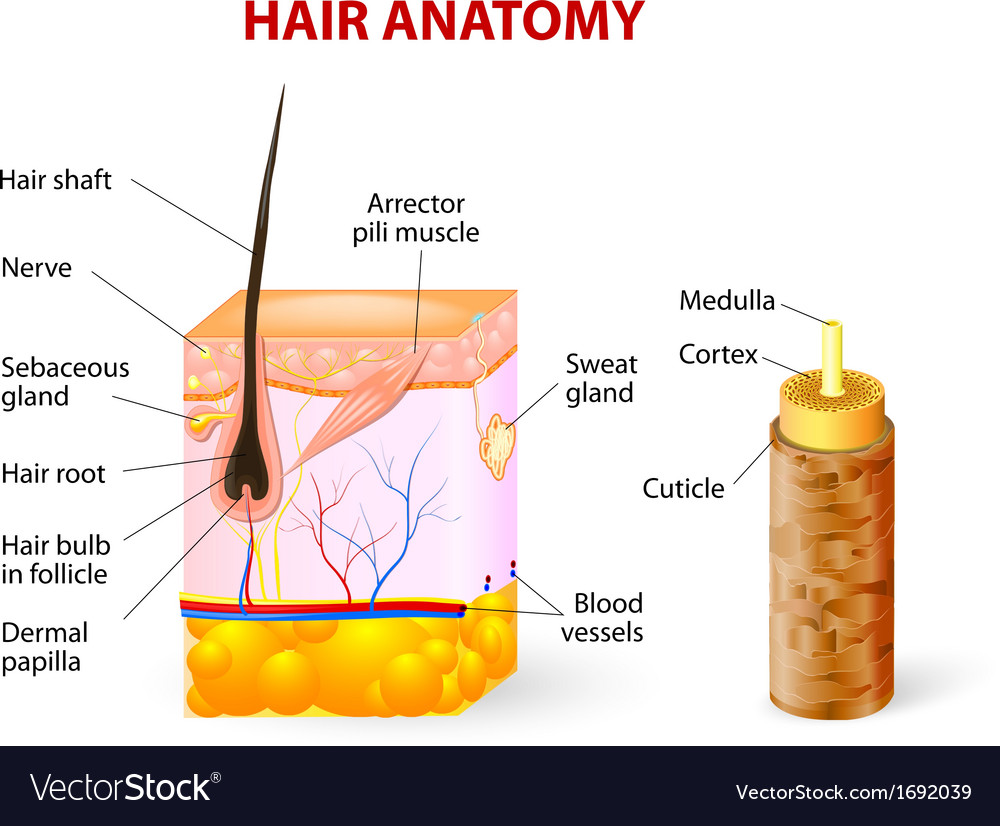
Strands of hair originate from the base of the downward extension of living epithelial cells into the dermis that is called the hair follicle. Pigment granules can be found in small gaps between these cells.
It is present only in large thick hairs like the ones on our scalps.

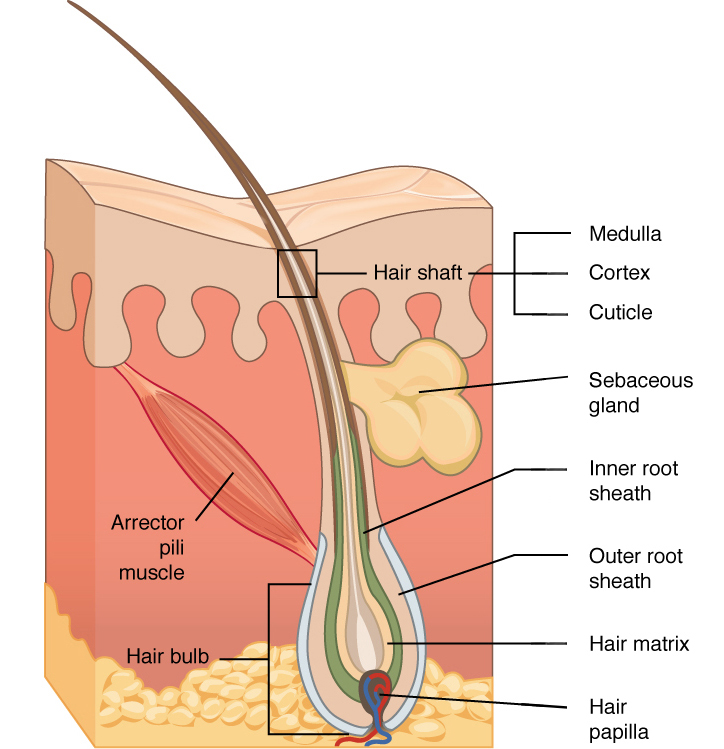
Hair strand anatomy. The innermost region the medulla is not always present and is an open unstructured region. The innermost layer is called the medulla. Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools.
A hair follicle anchors each hair into the skin. Strands of curly or kinky hair are flat. Hair follicles are surrounded by the dermis but the cells are part of the epidermis and are separated from the dermis by basal lamina layer.
The flatter the shaft the curlier the hair. In the hair bulb living cells divide and grow. Surrounding the medulla is the cortex elongated cells which form the main fibrous structure and strength of the hair.
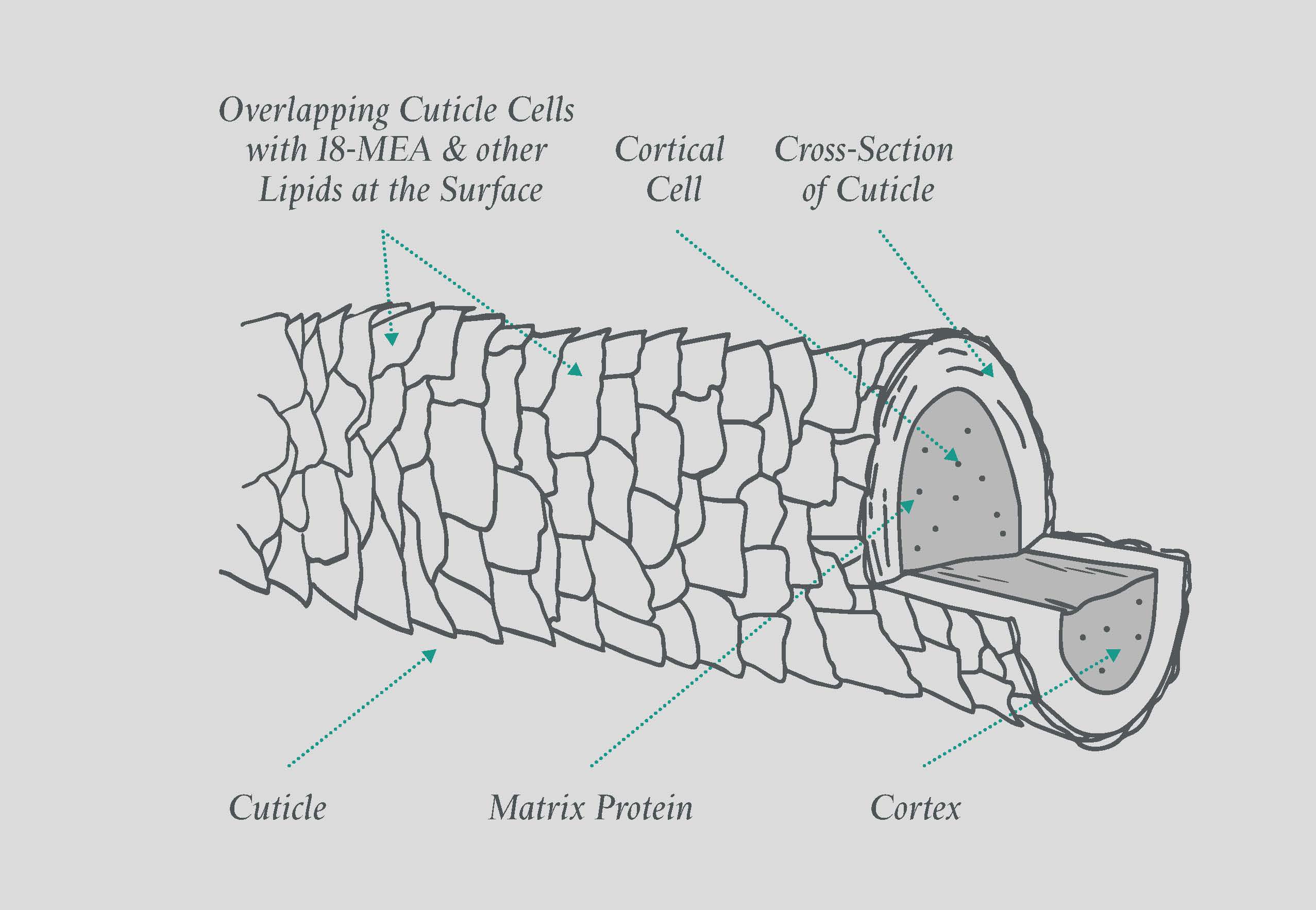
Cuticle cortex and medulla. Hair is made of a tough protein called keratin. The more circular the hair shaft the straighter the hair.
Hair is a derivative of the epidermis and consists of two distinct parts. Each strand of hair is made up of the medulla cortex and cuticle. The highly structural and organized cortex or second of three layers of the hair is the primary source of mechanical strength and water uptake.
Anatomy of human hair shaft consists of 3 layers. Cuticle a narrow band of epidermis extending from the nail wall onto the nail surface. The amount of natural curl that a hair has is determined by its cross sectional shape.
Start studying anatomy chapter 4 integumentary system. The follicle is the essential unit for the generation of hair. Straight hair has a mostly circular circumference.
Flexible strand of dead keratinized cells found projecting outside from the epidermis. As the cortex cells move outwards toward the external layer of hair they become thin and scale like forming the cuticle of the hair strand. Hair follicle has a continuous growth and rest sequence named hair cycle.
The hair bulb forms the base of the hair follicle. The follicle and the hair shaft. The natural appearance of hair is attributed to the shape of the hair.
Hair shaft sebaceous gland arrector pili muscle hair follicle sweat gland sweat gland duct pore of sweat gland duct. The hair shaft consists of a cortex and cuticle cells and a medulla for some types of hairs.
 Human Hair Anatomy Infographics With Cross Section Of Skin Layers
Human Hair Anatomy Infographics With Cross Section Of Skin Layers
Learn The Science Of Curly Hair Paramount Beauty
 Structure And Composition Of The Hair Activilong
Structure And Composition Of The Hair Activilong
 Human Hair Structure Anatomy Help You To Know About Your Hair
Human Hair Structure Anatomy Help You To Know About Your Hair
 Determining Your Hair Type How To Care For It Have A
Determining Your Hair Type How To Care For It Have A
 Human Hair Structure Anatomy Help You To Know About Your Hair
Human Hair Structure Anatomy Help You To Know About Your Hair
 Hair Follicle Function Anatomy And Conditions
Hair Follicle Function Anatomy And Conditions
 Human Hair Structure Anatomy Help You To Know About Your Hair
Human Hair Structure Anatomy Help You To Know About Your Hair
Strand And Science Hair Anatomy
 What Is Hair Made Of Hair Structure And Anatomy 101 L
What Is Hair Made Of Hair Structure And Anatomy 101 L
 The Integumentary System Skin Hair And Nails This Pic Is
The Integumentary System Skin Hair And Nails This Pic Is
 Hair Growth Cycle Skin Follicle Anatomy Anagen
Hair Growth Cycle Skin Follicle Anatomy Anagen
Pictures 7 Things Your Should Know About Hair Growth
 Hair Shaft Thickness And Hair Transplants Chicago Il
Hair Shaft Thickness And Hair Transplants Chicago Il
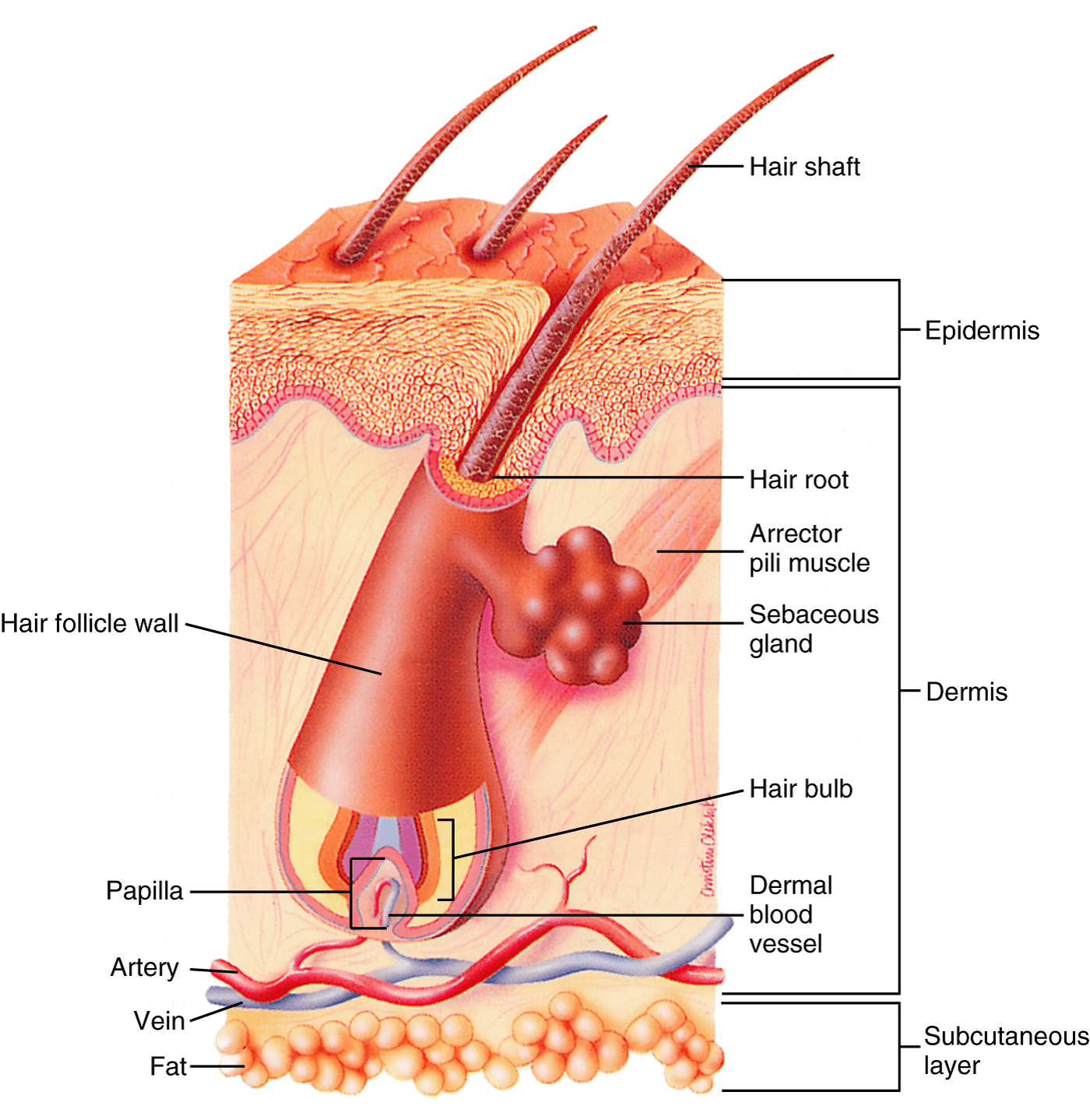 Hair And Hair Types Boldbarber Com
Hair And Hair Types Boldbarber Com
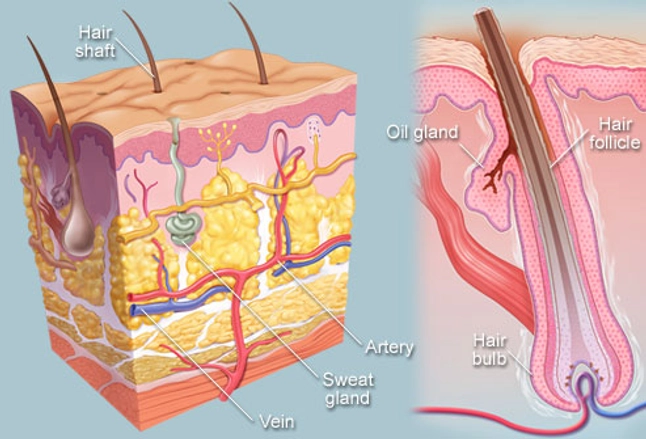 Hair Human Anatomy Image Parts Follicle Growth
Hair Human Anatomy Image Parts Follicle Growth
 Human Hair Cross Section Art Print Anatomy Art Hair Follicle
Human Hair Cross Section Art Print Anatomy Art Hair Follicle
 Hair Facts Hair Growth Facts Hair Histology Hair
Hair Facts Hair Growth Facts Hair Histology Hair
 Hair And Nails Anatomy And Physiology I
Hair And Nails Anatomy And Physiology I
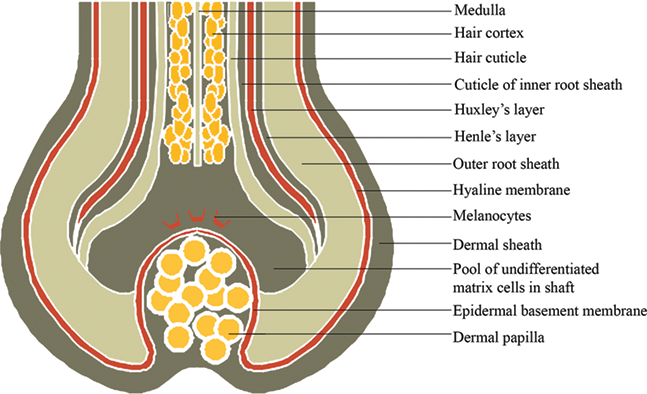 Anatomy And Physiology Of Hair Intechopen
Anatomy And Physiology Of Hair Intechopen
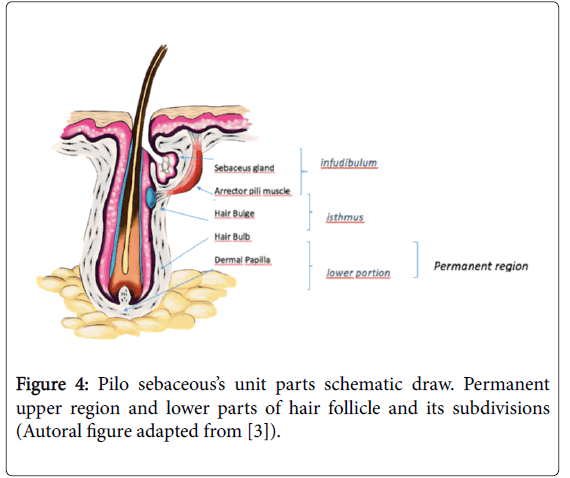 Revisiting Hair Follicle Embryology Anatomy And The
Revisiting Hair Follicle Embryology Anatomy And The



Belum ada Komentar untuk "Hair Strand Anatomy"
Posting Komentar