Anatomy Of Arthropods
All members have four pairs of walking legs two body sections and no antennae. Comparing the anatomy of arthropods coloring then the reading focuses on specific groups.
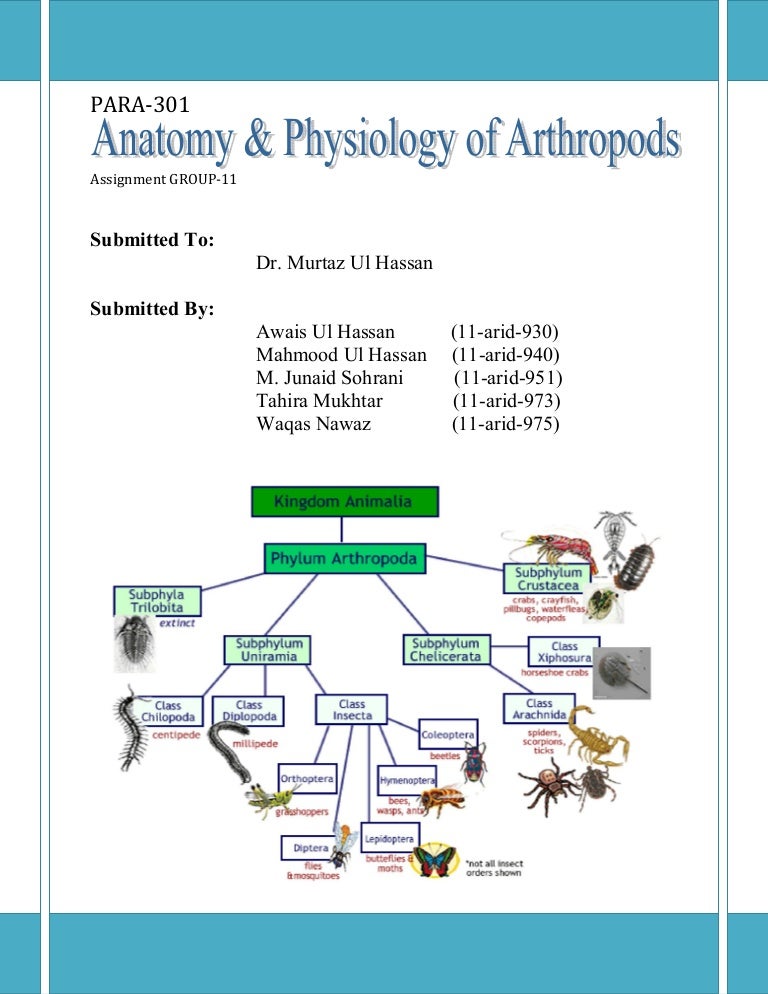 Anatomy Physiology Of Arthropods
Anatomy Physiology Of Arthropods
Students are directed to color each insect according to the directions so that they can see that in each plan the abdomen thorax and head are consistent.

Anatomy of arthropods. Hemolymph enters the heart from the surrounding pericardial sinusthrough pairs of lateral openings the ostiaostia are one way valves. Insects arachnids crustaceans and centipedes. They include claws antennae wings flippers and etc.
All of the appendages in an arthropod have evolved into structures that benefit them in their environment. Wikimedia commons has media related to arthropoda anatomy. ποδός is an invertebrate animal having an exoskeleton a segmented body and paired jointed appendages.
A member of a major arthropod group chelicerata that includes spiders scorpions ticks and mites. The sub phyla of arthropods that contains all extinct members. This category is for articles about the anatomy of arthropods.
Compare the anatomy of arthropods. This category has the following 8 subcategories out of 8 total. Arachnids spiders mites scorpions.
Arthropods form the phylum euarthropoda which includes insects arachnids myriapods and crustaceans. When the heart contracts ostia close forcing hemolymph anteriorly into the arteries and finally into a system of tissue spaces or sinuses. 4 similarly the coelom lost its primary function as a hydrostatic skeleton for locomotion as in annelids and nematodes.
Characteristics anatomy groups description. Arthropods definition an arthropod is an invertebrate animal that has an exoskeleton a segmented body and jointed appendages. As body segments are lost so are appendages.
The word arthropod literally translates into jointed foot. There are three main groups within the phylum arthropoda. Hence many arthropods exhibit a loss or fusion of body segments into distinct body regions eg head thorax and abdomen.
Arthropods are a group of animals belonging to the animal kingdom that have a hard exoskeleton body segments and jointed appendages. The following families of an arthropod is an invertebrate animal that has an exoskeleton a segmented body and jointed appendages. An arthropod ˈ ɑːr θ r ə p ɒ d from greek ἄρθρον arthron joint and πούς pous foot gen.
They have two to three main segments a head a thorax and an abdomen. Anatomy physiology of arthropods. You have probably seen many different types of arthropodsjust in the last day.
Some have evolved into only having an abdomen and a cephalothorax. Insects have three body segments the head thorax middle region and the abdomen. The coelom of arthropods became greatly reduced until the major body.
 Arthropod Definition Characteristics Examples And Types
Arthropod Definition Characteristics Examples And Types
 10 Best Phylum Arthropoda Images Pictures Of Insects
10 Best Phylum Arthropoda Images Pictures Of Insects
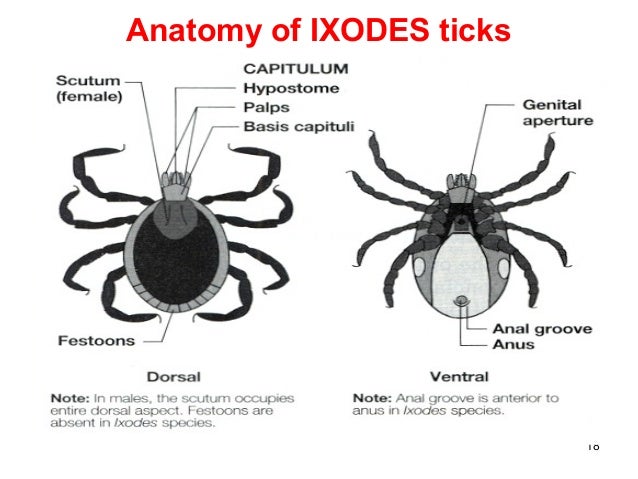 Phylum Arthropoda As Causative Agents
Phylum Arthropoda As Causative Agents
 Anatomy Of Arthropoda P Gogoi 9788182930278 Amazon Com
Anatomy Of Arthropoda P Gogoi 9788182930278 Amazon Com
 Specializations Of The External Anatomy Of Arthropods Is Due
Specializations Of The External Anatomy Of Arthropods Is Due
 Ilustraciones Imagenes Y Vectores De Stock Sobre Arthropod
Ilustraciones Imagenes Y Vectores De Stock Sobre Arthropod
 Anatomy Physiology Of Arthropods
Anatomy Physiology Of Arthropods
 Subphylums Of Arthropoda Biology For Majors Ii
Subphylums Of Arthropoda Biology For Majors Ii
 Internal Anatomy Of A Female Cricket Typical Arthropod
Internal Anatomy Of A Female Cricket Typical Arthropod
Body Plan Of Arthropods Biology 4 Kids By Kids
 Arthropod Structure And Function Advanced Ck 12 Foundation
Arthropod Structure And Function Advanced Ck 12 Foundation
 Arthropods Characteristics Anatomy Groups Study Com
Arthropods Characteristics Anatomy Groups Study Com
 Arthropods Introduction To The Arthropoda The Real
Arthropods Introduction To The Arthropoda The Real
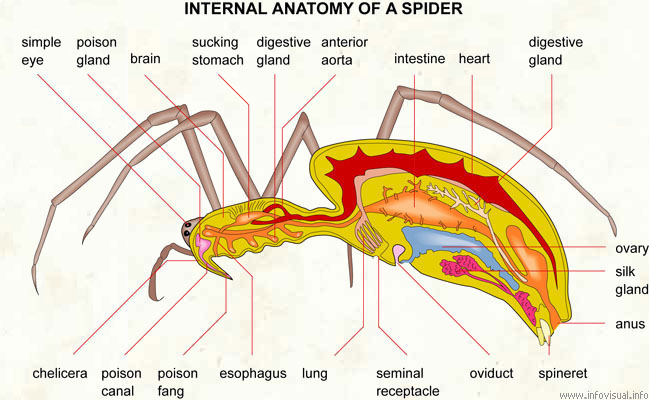 Internal Anatomy Of A Spider Visual Dictionary
Internal Anatomy Of A Spider Visual Dictionary
Insects Beetles Spiders Wireworms Ants Caterpillars
 Biology Life Takes To The Land Shmoop Biology
Biology Life Takes To The Land Shmoop Biology
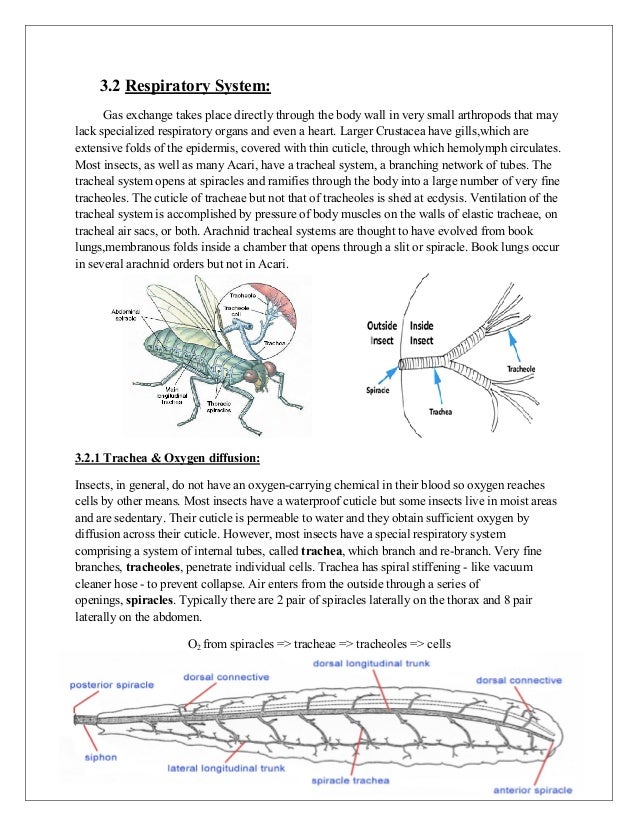 Anatomy Physiology Of Arthropods
Anatomy Physiology Of Arthropods
 Insect External Anatomy Courses Cit Cornell Edu
Insect External Anatomy Courses Cit Cornell Edu
Arthropods Body Cavity Digestive System And Life History
Arthropoda Ms Anderson S Zoology Class
 Outlines Of The Comparative Physiology And Morphology Of
Outlines Of The Comparative Physiology And Morphology Of
 Comparative Anatomy Of Two Arthropods
Comparative Anatomy Of Two Arthropods
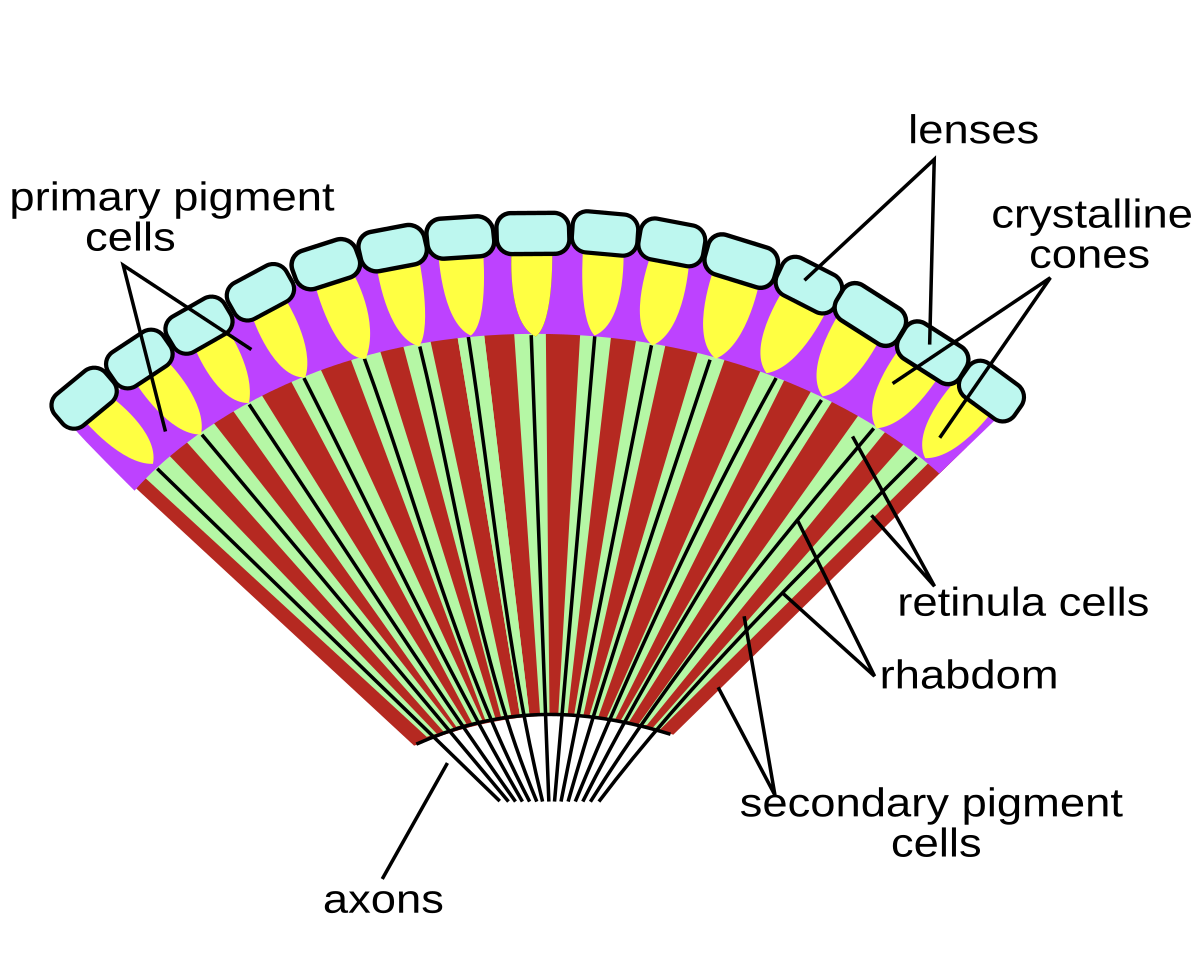

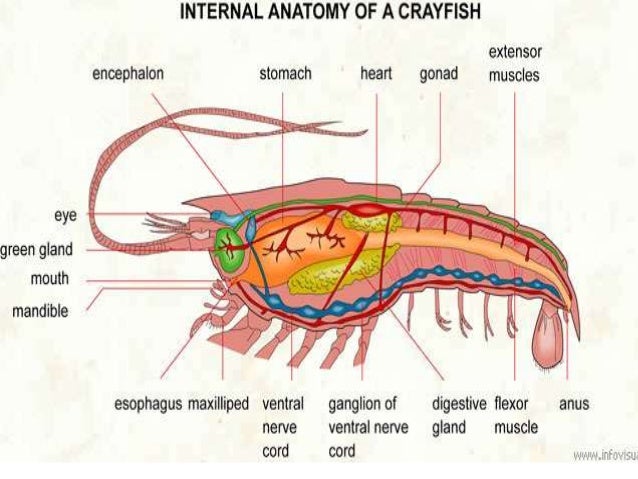
Belum ada Komentar untuk "Anatomy Of Arthropods"
Posting Komentar