Anatomy Of The Hip Area
Anatomy of the hip. The round head of the femur rests in a cavity the acetabulum that allows free rotation of the limb.
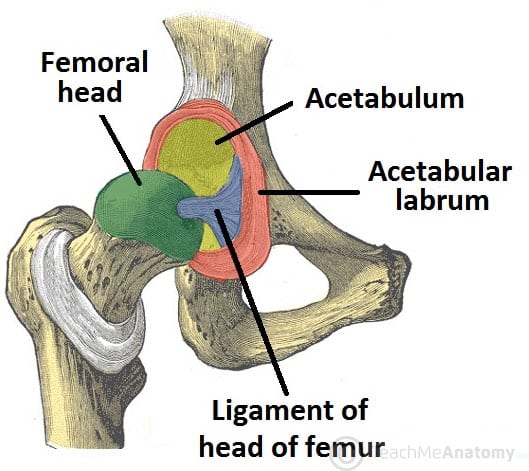 The Hip Joint Articulations Movements Teachmeanatomy
The Hip Joint Articulations Movements Teachmeanatomy
The hip joint is a ball and socket synovial joint formed between the os coxa hip bone and the femur.
Anatomy of the hip area. The medial muscles of the hip are the adductor muscles of the hip joint. Hip pain may result from inflammation degeneration or injury to structures and tissues within the hip joint. Also the area adjacent to this joint.
Hip bones there are two hip bones one on the left side of the body and the other on the right. Hip ligaments and tendons tough fibrous tissues that bind bones to bones and muscles to bones. It is a ball and socket joint at the juncture of the leg and pelvis.
The rounded head of the femur thighbone forms the ball which fits into the acetabulum a cup shaped socket in the pelvis. Hip in anatomy the joint between the thighbone femur and the pelvis. Rectus femoris muscle one of the quadriceps muscles on the front of your thigh.
The hip bones join to the upper. Hip problems occur when any one of these components starts to degenerate or is in some way compromised or irritated. The hip is the bodys second largest weight bearing joint after the knee.
Together they form the part of the pelvis called the pelvic girdle. Adductor muscles on the inside of your thigh. A round cup shaped structure on the os coxa known as the acetabulum forms the socket for the hip joint.
The hip joint is the uppermost part of the leg where the head of the thigh bone femur fits into the socket of the pelvis. Its the need for such a high degree of stabilization of the joint that limits movement. And synovial membrane and fluid which encapsulates the hip joint and lubricates it respectively.
This joint allows a wide range of movements of the lower limbs and is used when walking running climbing lunging and bending. The hip joint is a ball and socket joint. Some of the other muscles in the hip are.
Amphibians and reptiles have relatively weak pelvic girdles and the femur extends horizontally. If you think of the hip joint in layers the deepest layer is bone then ligaments of the joint capsule and the tendons and muscles are on top. Iliopsoas muscle a hip flexor muscle that attaches to the upper thigh bone.
Anatomy of the hip the hip is a major ball and socket joint connecting the long bones of the lower limbs femur to the pelvis. The adductor longus the adductor brevis the adductor magnus and the gracilis pectineus muscles are the four basic muscles that provide the hip with adduction. Muscles play an important role in the health and well being.
Nerves and vessels supply the muscles and bones of the hip.
 Acetabulum An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Acetabulum An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
 Hip Anatomy Pictures Function Problems Treatment
Hip Anatomy Pictures Function Problems Treatment
 Why People Have To Squat Differently The Movement Fix
Why People Have To Squat Differently The Movement Fix
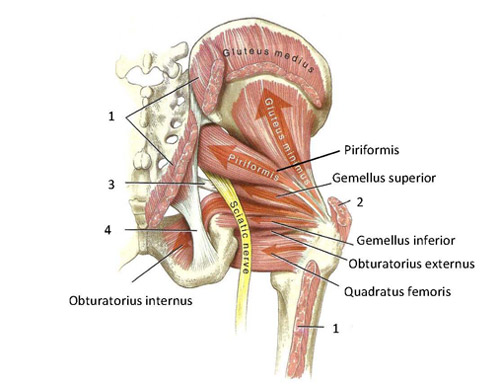 Functional Anatomy Of The Small Pelvic And Hip Muscles
Functional Anatomy Of The Small Pelvic And Hip Muscles
 Hip Abduction Exercises Anatomy Benefits Effectiveness
Hip Abduction Exercises Anatomy Benefits Effectiveness
 Hip Picture Image On Medicinenet Com
Hip Picture Image On Medicinenet Com
Hip Labral Tear Cleveland Clinic
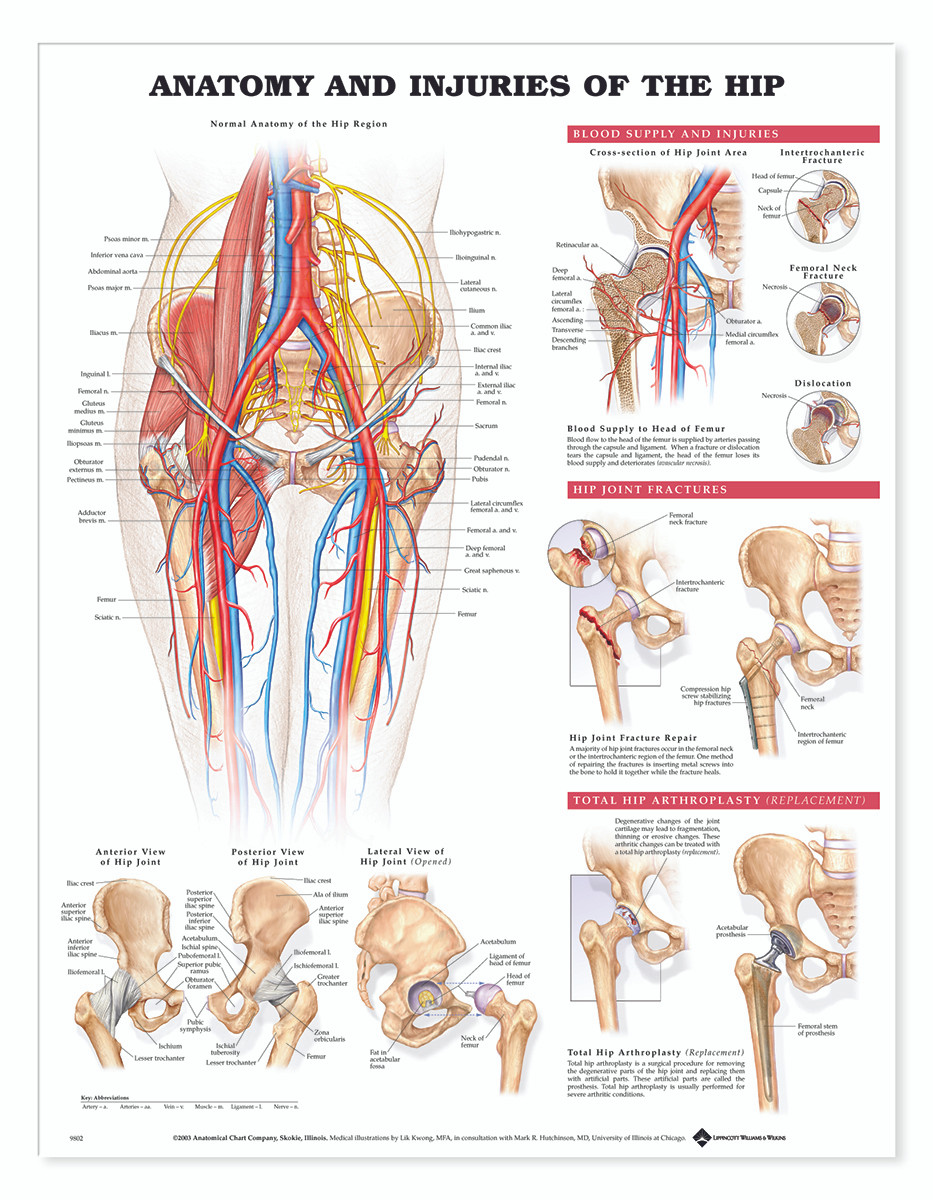 Reference Chart Anatomy And Injuries Of The Hip
Reference Chart Anatomy And Injuries Of The Hip
Transient Osteoporosis Of The Hip Orthoinfo Aaos
 Hip Anatomy Pictures Function Problems Treatment
Hip Anatomy Pictures Function Problems Treatment
 The Truth About Cracking Popping Joints Yoga Journal
The Truth About Cracking Popping Joints Yoga Journal
 Joints Ligaments And Connective Tissues Advanced Anatomy
Joints Ligaments And Connective Tissues Advanced Anatomy
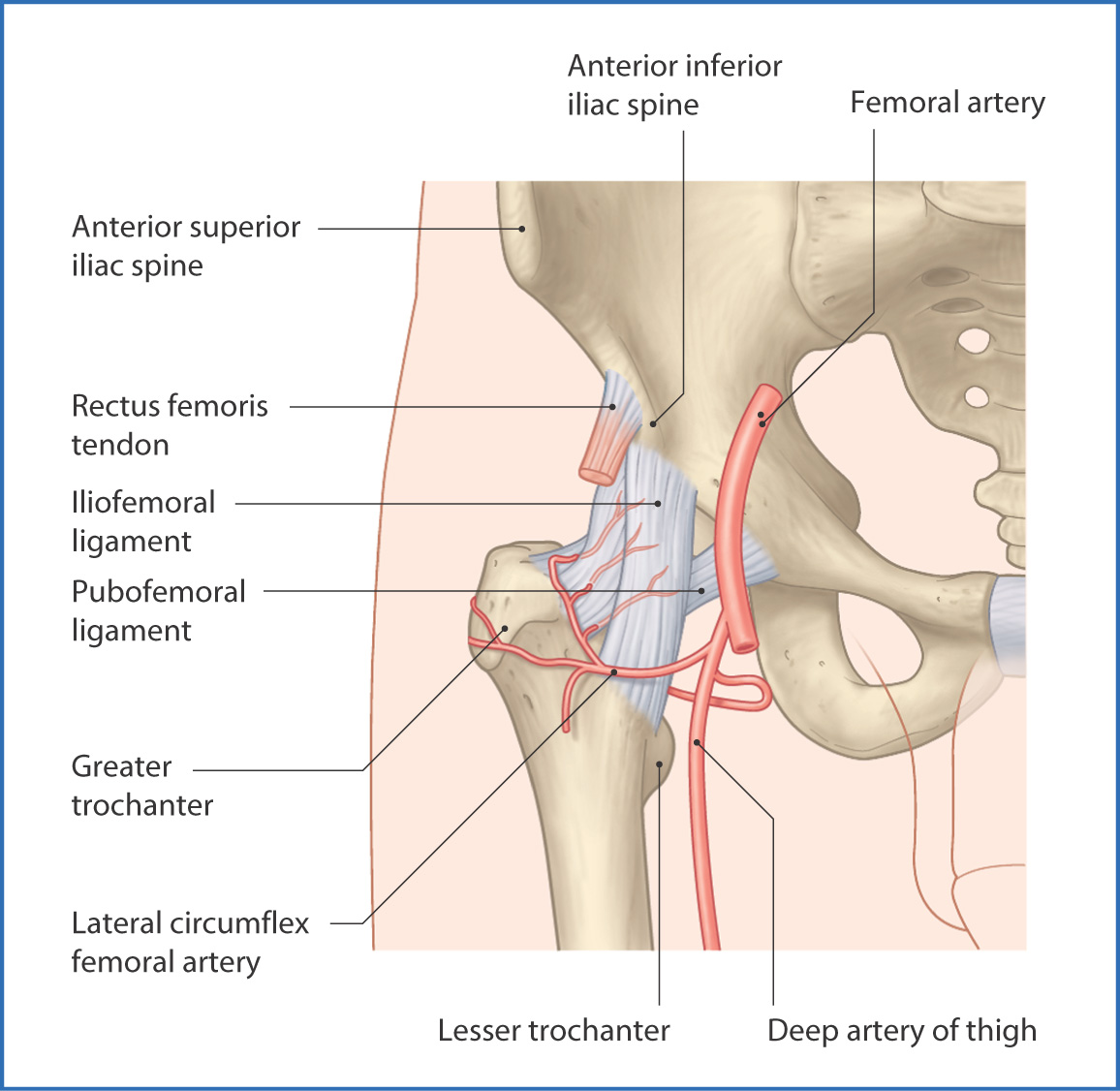 Hip Anatomy Recon Orthobullets
Hip Anatomy Recon Orthobullets
:watermark(/images/watermark_5000_10percent.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/atlas_overview_image/987/xSiX0lUlLxEIjBI8malVw_bones-pelvis-femur_english.jpg) Hip Joint Ligaments Movements Muscles Kenhub
Hip Joint Ligaments Movements Muscles Kenhub
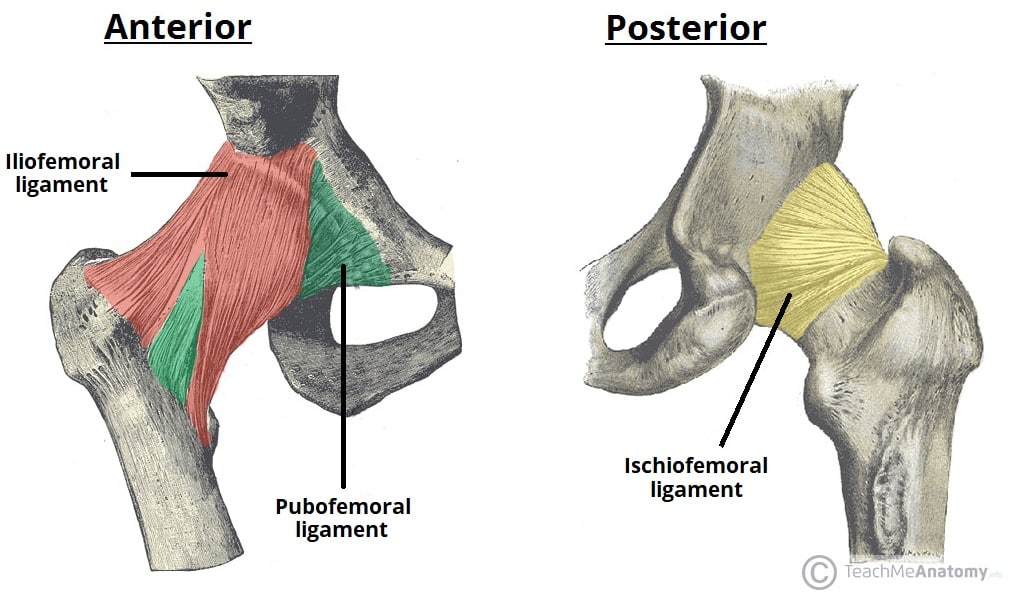 The Hip Joint Articulations Movements Teachmeanatomy
The Hip Joint Articulations Movements Teachmeanatomy
Hip Anatomy Orthopedic Surgery Algonquin Il Barrington
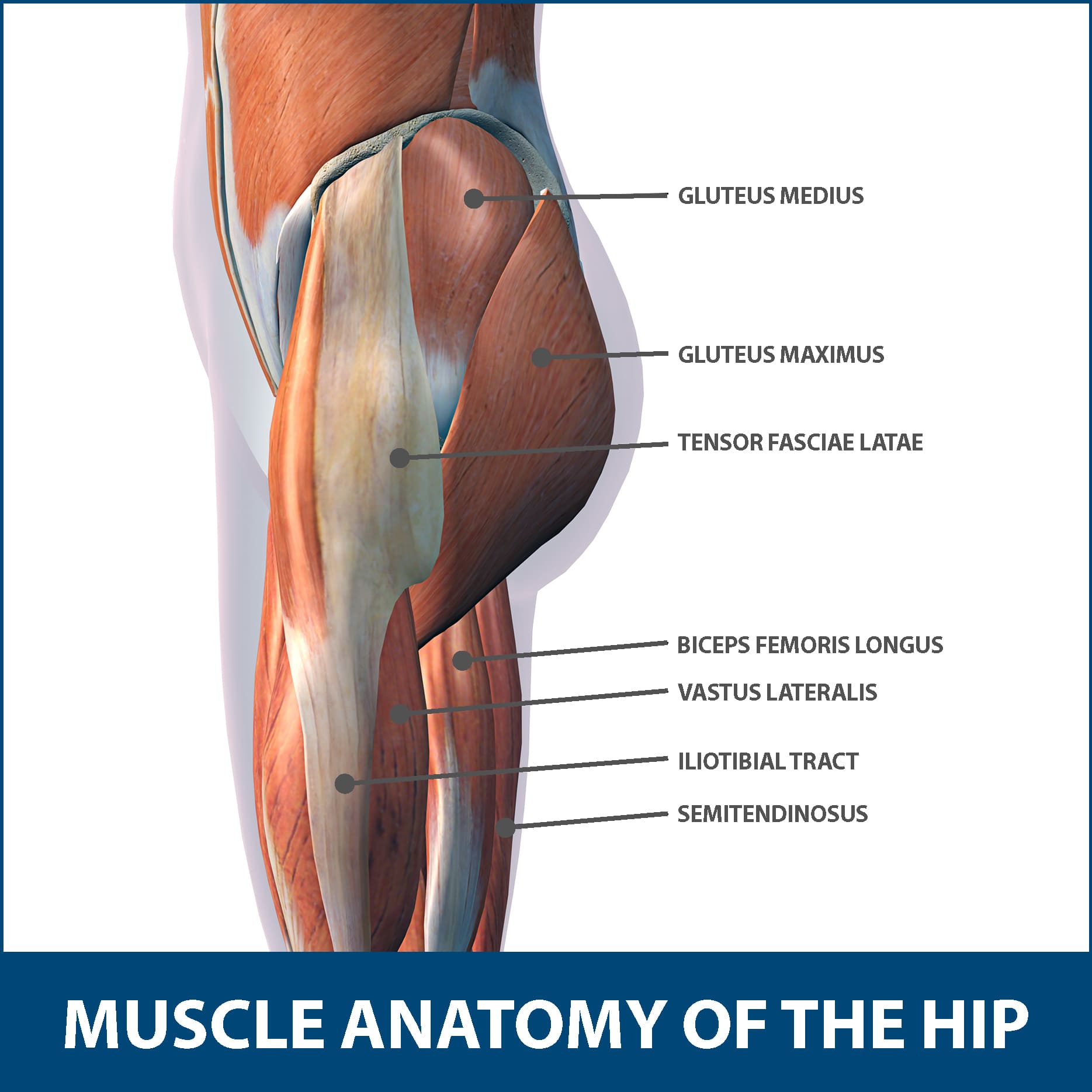 Hip Muscle Strains Info Florida Orthopaedic Institute
Hip Muscle Strains Info Florida Orthopaedic Institute
 Hip Pain Symptoms Treatment Causes Exercises Relief
Hip Pain Symptoms Treatment Causes Exercises Relief
 Mr Miles Callahan Anatomy Of The Hip
Mr Miles Callahan Anatomy Of The Hip





Belum ada Komentar untuk "Anatomy Of The Hip Area"
Posting Komentar