Anatomy And Physiology Of Bone
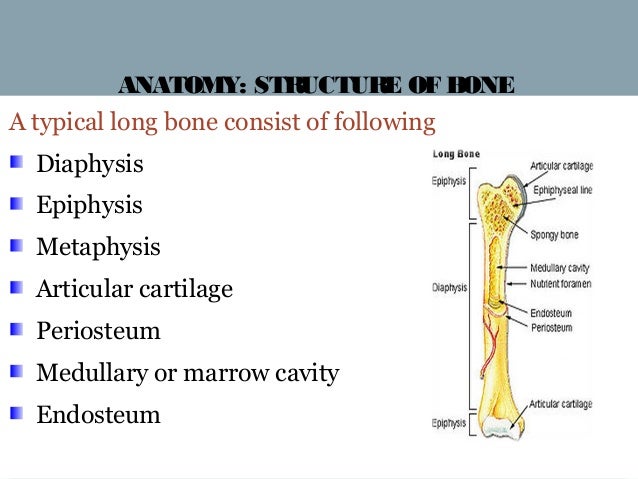
The flat bones of the face most of the cranial bones and the clavicles collarbones are formed via intramembranous ossification. The diaphysis is the tubular shaft that runs between the proximal and distal ends of the bone.
 The Skull Bone Anatomy And Physiology By Er Services In
The Skull Bone Anatomy And Physiology By Er Services In
Biology 121 hacc with professor john sword for lab practical 1 bones skeletal learn with flashcards games and more for free.

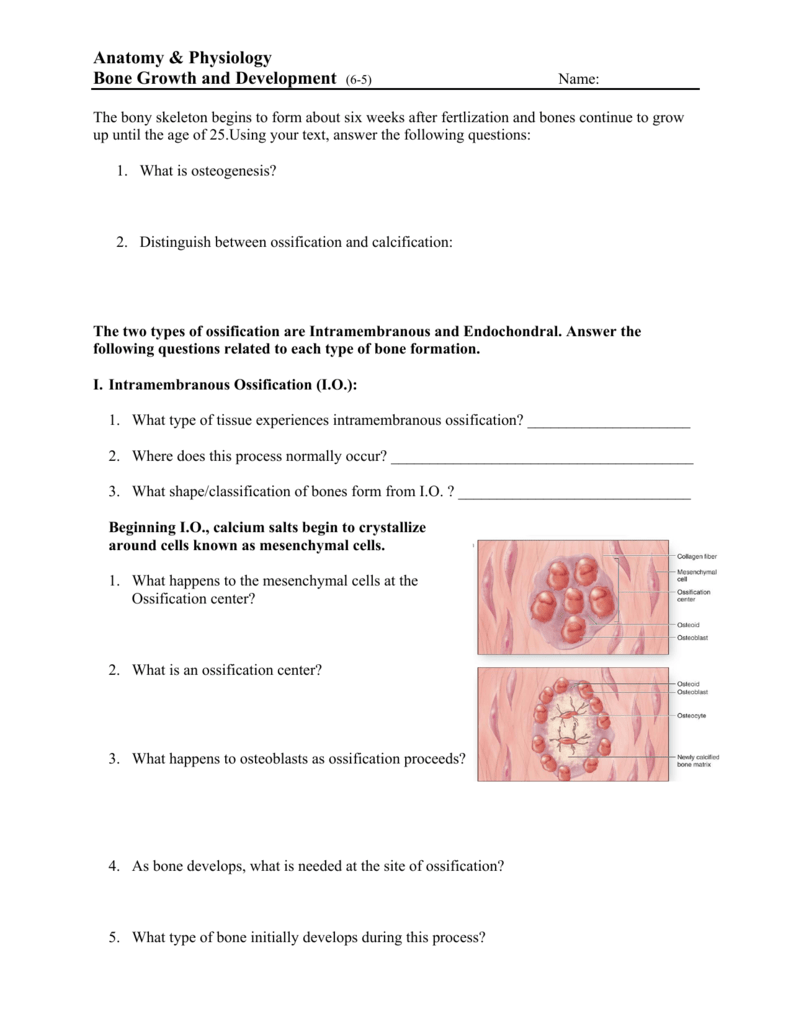
Anatomy and physiology of bone. The scapula is a flat triangular shaped bone that lies adjacent to the posterior surface of ribs. The diaphysis and the epiphysis. During intramembranous ossification compact and spongy bone develops directly from sheets of embryonic mesenchymal undifferentiated connective tissue.
Bone can either be. A long bone has two parts. A spongy has an open meshwork which contains bone marrow or b compact is dense.
The anterior markings of the humerus bone. Gross anatomy of bone. It forms the surface of bones and makes up approximately 80 of the bone mass.
The skeleton is subdivided into two divisions. The structure of a long bone allows for the best visualization of all of the parts of a bone figure 1. Gross anatomy of bone.
A long bone has two parts. Anatomy of the skeletal system. The diaphysis and the epiphysis.
The structure of a long bone allows for the best visualization of all of the parts of a bone link. The bone remodeling process regulates the gain and loss of bone mineral density in the adult skeleton and directly influences bone strength. Bone is relatively hard and lightweight and is primarily made of calcium phosphate.
The normal anatomy and functions of the skeleton are reviewed first followed by a general description of the processes of bone modeling and remodeling. The diaphysis is the tubular shaft that runs between the proximal and distal ends of the bone. The axial skeleton the bones that form the longitudinal axis of the body and the appendicular skeleton the bones of the limbs and girdles.
Seventeen muscles attach to the scapula and it articulates with the clavicle to form the shoulder girdle or pectoral girdle which supports movements of the humerus.
 Introduction To Anatomy And Physiology Online Student
Introduction To Anatomy And Physiology Online Student
Anatomy Gross Anatomy Physiology Cells Cytology Cell
 Anatomy Physiology Skeletal System Bone Tissue Tortora
Anatomy Physiology Skeletal System Bone Tissue Tortora
 Skeletal System Anatomy And Physiology
Skeletal System Anatomy And Physiology
 Long Bone Structure And Bone Markings Table 6 1 Anatomy
Long Bone Structure And Bone Markings Table 6 1 Anatomy
 Bone Remodeling Physiology Britannica
Bone Remodeling Physiology Britannica
 Foot Vertebrate Anatomy Britannica
Foot Vertebrate Anatomy Britannica
Bone Tissue Structure Course Hero
1 Bone Classification And Structure Ehs Anatomy
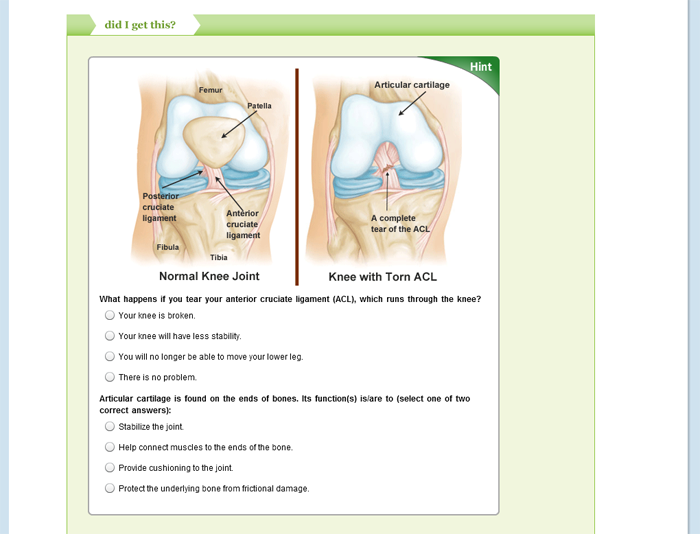 Anatomy Physiology I Ii Open Free Oli
Anatomy Physiology I Ii Open Free Oli
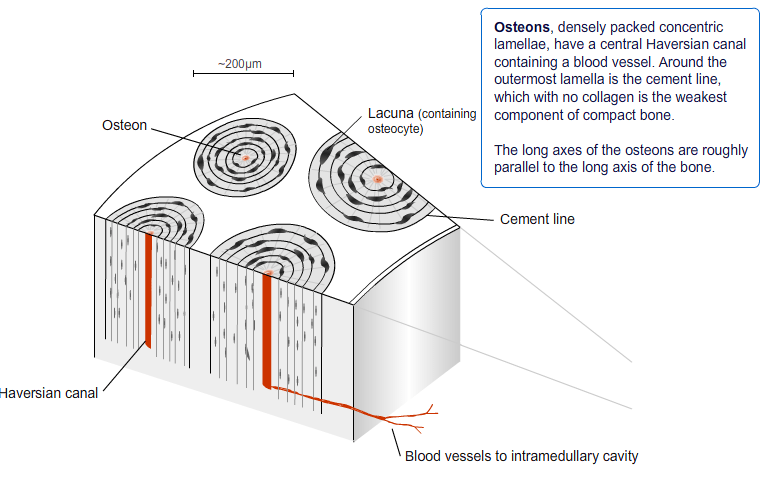 Bone Anatomy And Physiology Bone And Spine
Bone Anatomy And Physiology Bone And Spine
 Scrutinizing The Skeletal System Anatomy Physiology For
Scrutinizing The Skeletal System Anatomy Physiology For
Microscopic Anatomy Of Bone Course Hero
 The Skeletal System Anatomy And Physiology Bone A Connective
The Skeletal System Anatomy And Physiology Bone A Connective
 The Anatomy And Physiology Of The Locomotor System
The Anatomy And Physiology Of The Locomotor System
Synovial Joints Anatomy And Physiology Openstax

Anatomy Of A Long Bone Ms Gallagher S Classroom
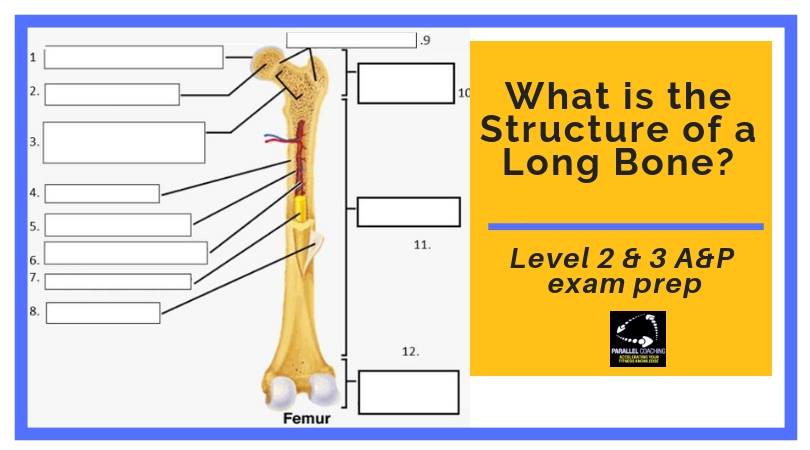 What Is The Structure Of A Long Bone L2 And L3 Anatomy
What Is The Structure Of A Long Bone L2 And L3 Anatomy
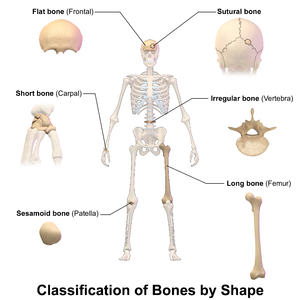
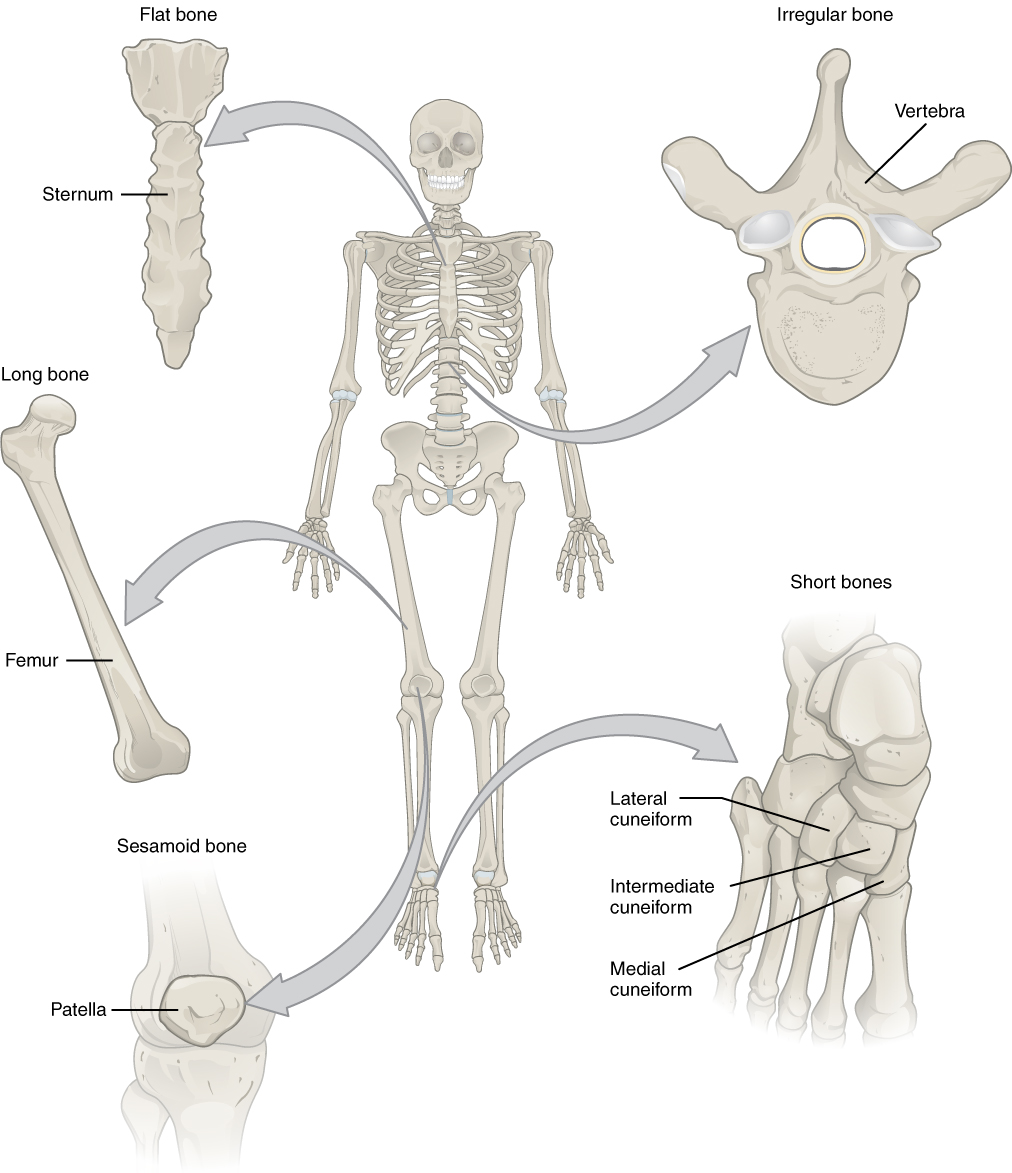 6 2 Bone Classification Anatomy And Physiology
6 2 Bone Classification Anatomy And Physiology
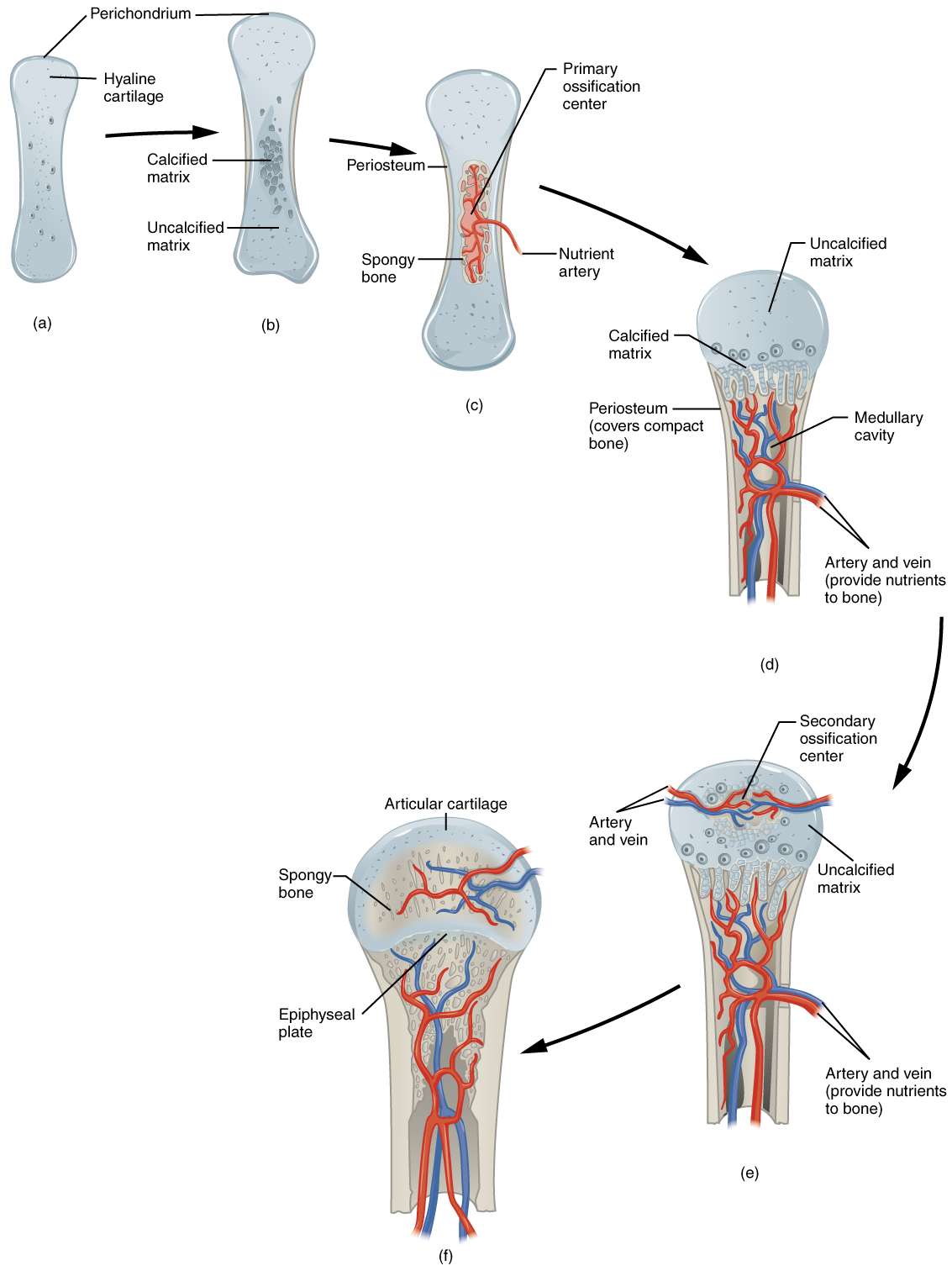 6 4 Bone Formation And Development Anatomy And Physiology
6 4 Bone Formation And Development Anatomy And Physiology
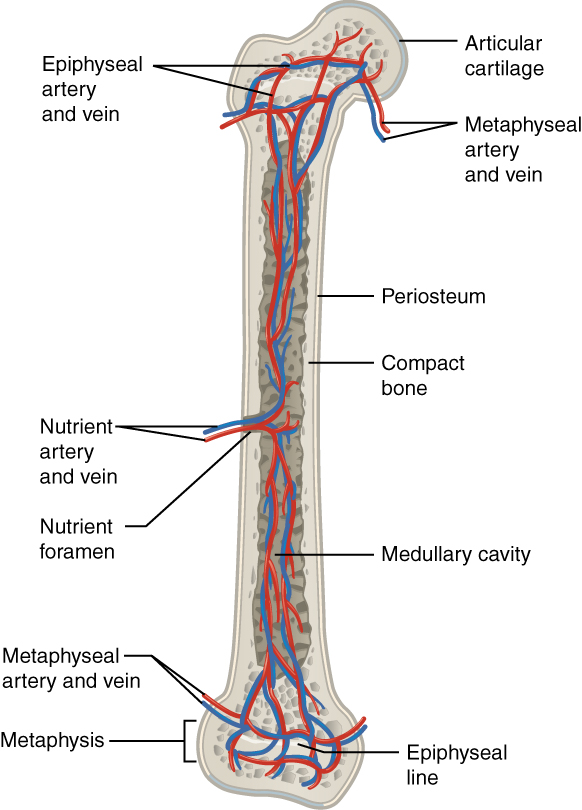 6 3 Bone Structure Anatomy And Physiology
6 3 Bone Structure Anatomy And Physiology
Anatomy Gross Anatomy Physiology Cells Cytology Cell
 Normal Bone Anatomy And Physiology American Society Of
Normal Bone Anatomy And Physiology American Society Of
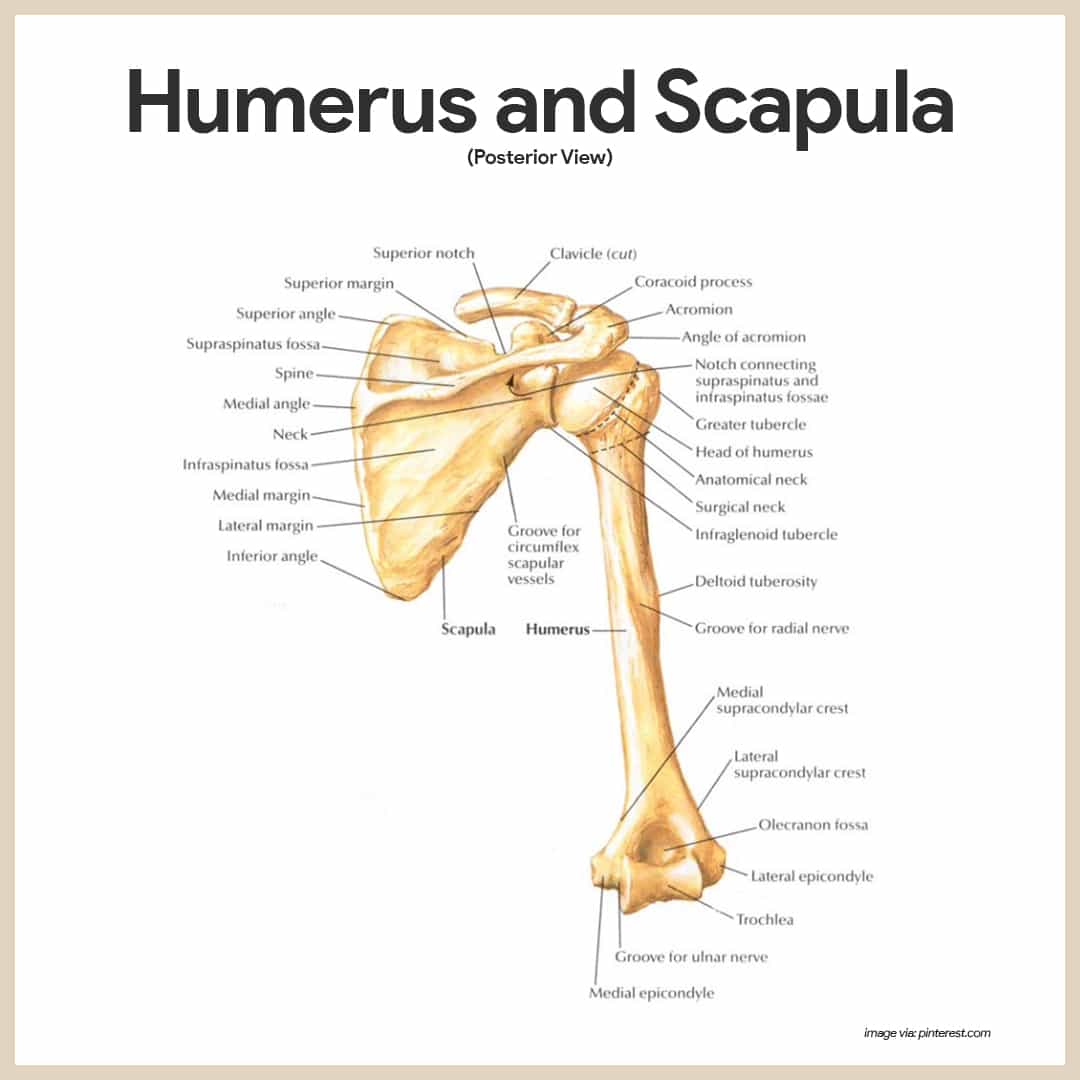 Skeletal System Anatomy And Physiology Nurseslabs
Skeletal System Anatomy And Physiology Nurseslabs
 Human Skeleton And Muscles Anatomy And Physiology
Human Skeleton And Muscles Anatomy And Physiology
 Essentials Of Anatomy Physiology 6e Martini Bartholomew
Essentials Of Anatomy Physiology 6e Martini Bartholomew
 6 3 Bone Structure Anatomy And Physiology
6 3 Bone Structure Anatomy And Physiology



Belum ada Komentar untuk "Anatomy And Physiology Of Bone"
Posting Komentar