Mandibular Bone Anatomy
Other mandibular fracture areas include the body the angle the. Movement of the lower jaw opens and closes the mouth and also allows for the chewing of food.
 Understanding Orthognathic Anatomy And Problems Medcor
Understanding Orthognathic Anatomy And Problems Medcor
Alveolar bone resorption occurs when the teeth are lost.

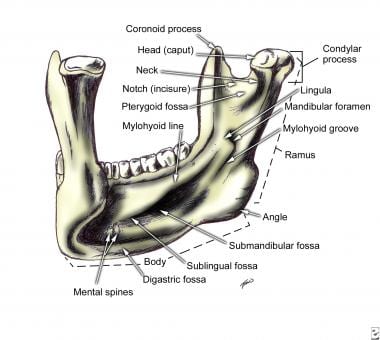
Mandibular bone anatomy. It forms the lower jaw and holds the lower teeth in place. It is the only movable bone of the skull discounting the ossicles of the middle ear. Four different muscles connect.
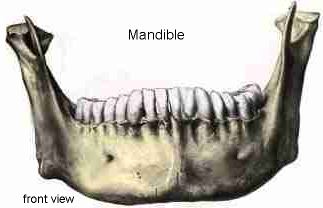
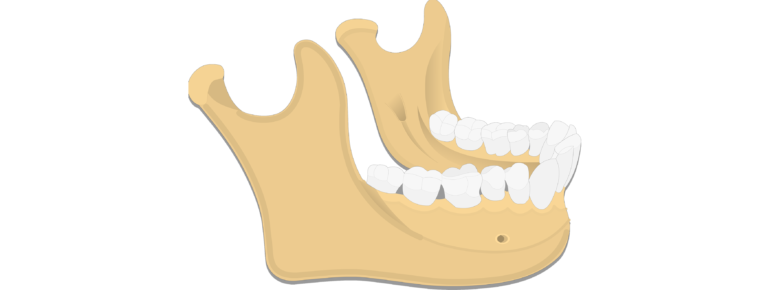
The anterior portion of the mandible called the body is horseshoe shaped and runs horizontally. The mandible is the single midline bone of the lower jaw. The mandible or lower jaw is the bone that forms the lower part of the skull and along with the maxilla upper jaw forms the mouth structure.
It consists of right and left halves that fuse together early in life. The tooth sockets called alveoli open onto this surface. It articulates with both temporal bones at the mandibular fossa at the temporomandibular joints tmj.
There is a lack. Anteriorly the two halves of the mandible fuse at the mandibular symphysis. Head situated posteriorly and articulates with the temporal bone to form the temporomandibular joint.
The mandible sits beneath the maxilla. The lower set of teeth in the mouth is rooted in the lower jaw. Coronoid process site of attachment of the.
It consists of a curved horizontal portion the body and two perpendicular portions the rami which unite with the ends of the body nearly at right angles angle of the jaw. Its superior border is the alveolar process. The body of the mandible anchors the lower teeth and forms the chin.
Each ramus contains the following bony landmarks. Here the most common bony disturbances have been noted. Introduction to mandible bone anatomy.
The mandible is composed of the body and the ramus and is located inferior to the maxilla. Neck supports the head of the ramus and site of attachment of the lateral pterygoid muscle. The mandible lower jaw or jawbone is the largest strongest and lowest bone in the human face.
It is formed by intramembranous ossification. The body is a horizontally curved portion that creates the lower jawline. Intra and extracapsular condylar fractures are the most frequent mandibular fractures.
The mental protuberance at this junction forms the chin. The mandible l mandere to chew is the facial bone that forms the lower jaw and contains the lower teeth. It holds the lower teeth in place it assists in mastication and forms the lower jawline.
The mandible is the largest bone in the human skull. The mandible is composed of 2 hemimandibles joined at the midline by a vertical symphysis. It is the only mobile bone of the facial skeleton and since it houses the lower teeth its motion is essential for mastication.
The mandible is a u shaped bone.
 Skull Definition Anatomy Function Britannica
Skull Definition Anatomy Function Britannica

 The Temporal Bone Human Anatomy
The Temporal Bone Human Anatomy
 Teeth And Jaw Bone Anatomy Print
Teeth And Jaw Bone Anatomy Print
 Anatomy Of The Jaw And Teeth High Impact Visual
Anatomy Of The Jaw And Teeth High Impact Visual
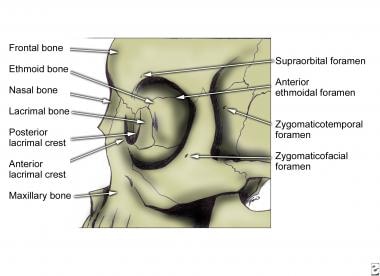 Facial Bone Anatomy Overview Mandible Maxilla
Facial Bone Anatomy Overview Mandible Maxilla
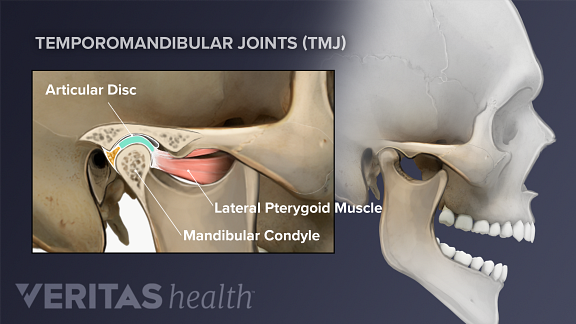 Temporomandibular Joint Tmj Disorders An Overview
Temporomandibular Joint Tmj Disorders An Overview
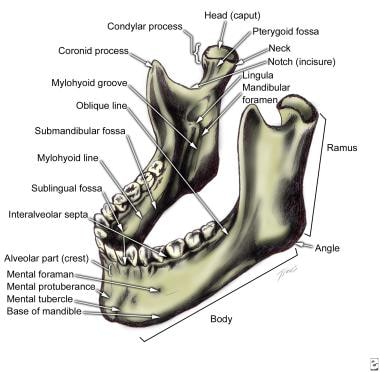 Facial Bone Anatomy Overview Mandible Maxilla
Facial Bone Anatomy Overview Mandible Maxilla

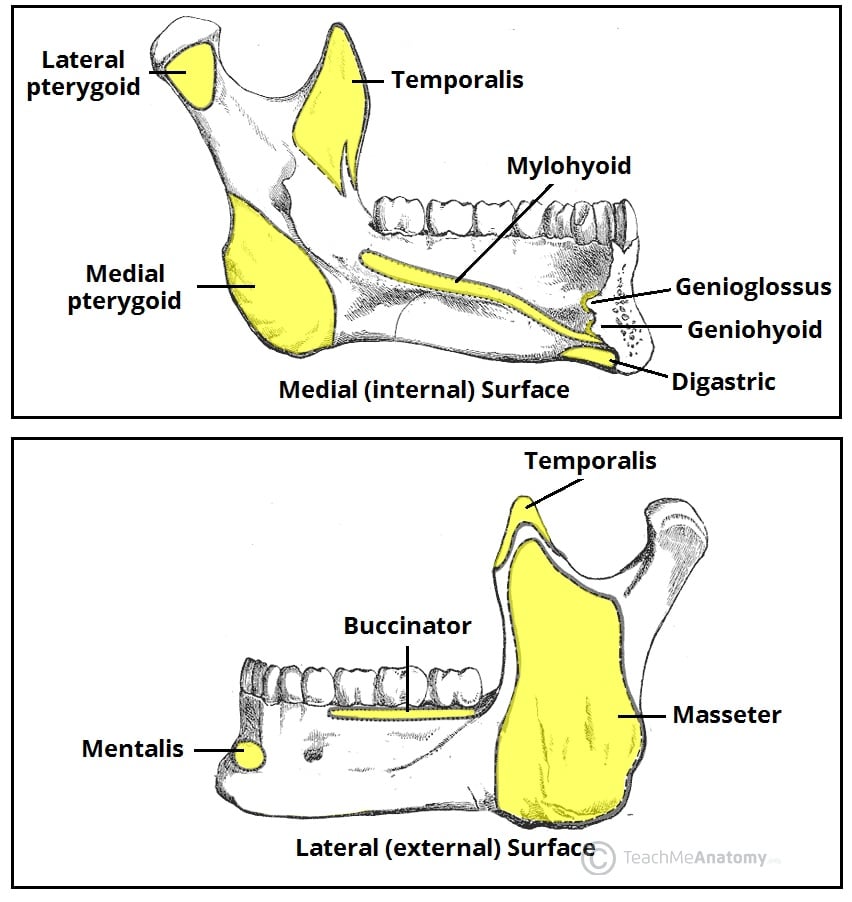 The Mandible Structure Attachments Fractures
The Mandible Structure Attachments Fractures
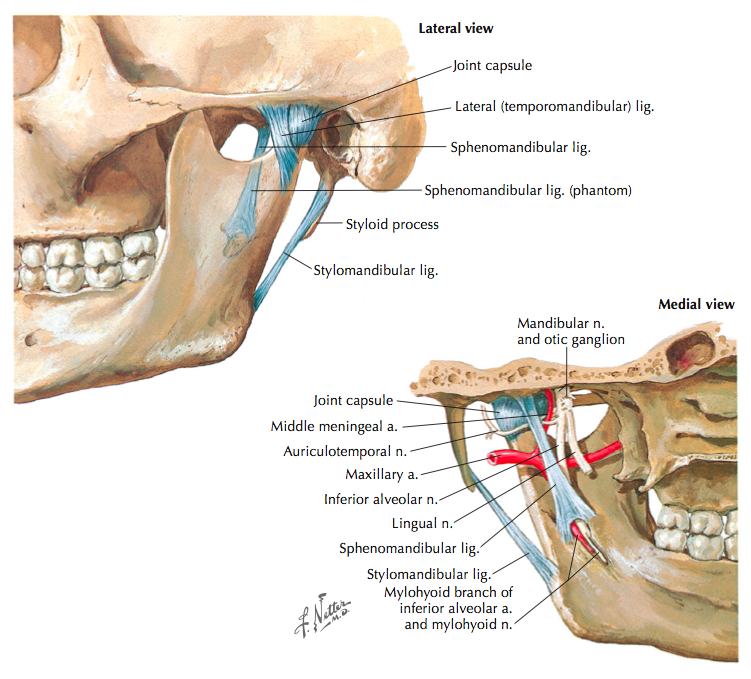 Temporomandibular Joint Disorders Clinical Anatomy
Temporomandibular Joint Disorders Clinical Anatomy
 Maxilla Mandible Anatomy Human Body Bone Png Clipart
Maxilla Mandible Anatomy Human Body Bone Png Clipart
 Mandible Bone Anatomy Images Stock Photos Vectors
Mandible Bone Anatomy Images Stock Photos Vectors
 The Bones Of The Skull Human Anatomy And Physiology Lab
The Bones Of The Skull Human Anatomy And Physiology Lab
 Mandible Anatomy Jaw Skull Infratemporal Fossa Png
Mandible Anatomy Jaw Skull Infratemporal Fossa Png
 Pin By Renee Mccarty On Diagnostic Imaging Dental Anatomy
Pin By Renee Mccarty On Diagnostic Imaging Dental Anatomy
 Jaw Mandible Facial Skeleton Bone Anatomy Png Clipart
Jaw Mandible Facial Skeleton Bone Anatomy Png Clipart
 Front Anatomical View Of Human Skull Bone With Mandible And The
Front Anatomical View Of Human Skull Bone With Mandible And The
 Facial Bone Anatomy Overview Mandible Maxilla
Facial Bone Anatomy Overview Mandible Maxilla
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/7639/IkZJJPMujD6IQ2e7r8yiNA_mandible_latin.jpg) The Mandible Anatomy Structures Fractures Kenhub
The Mandible Anatomy Structures Fractures Kenhub
Human Being Anatomy Skeleton Lateral View Of Skull




Belum ada Komentar untuk "Mandibular Bone Anatomy"
Posting Komentar