Labrum Anatomy
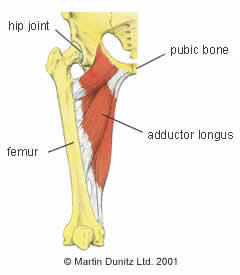
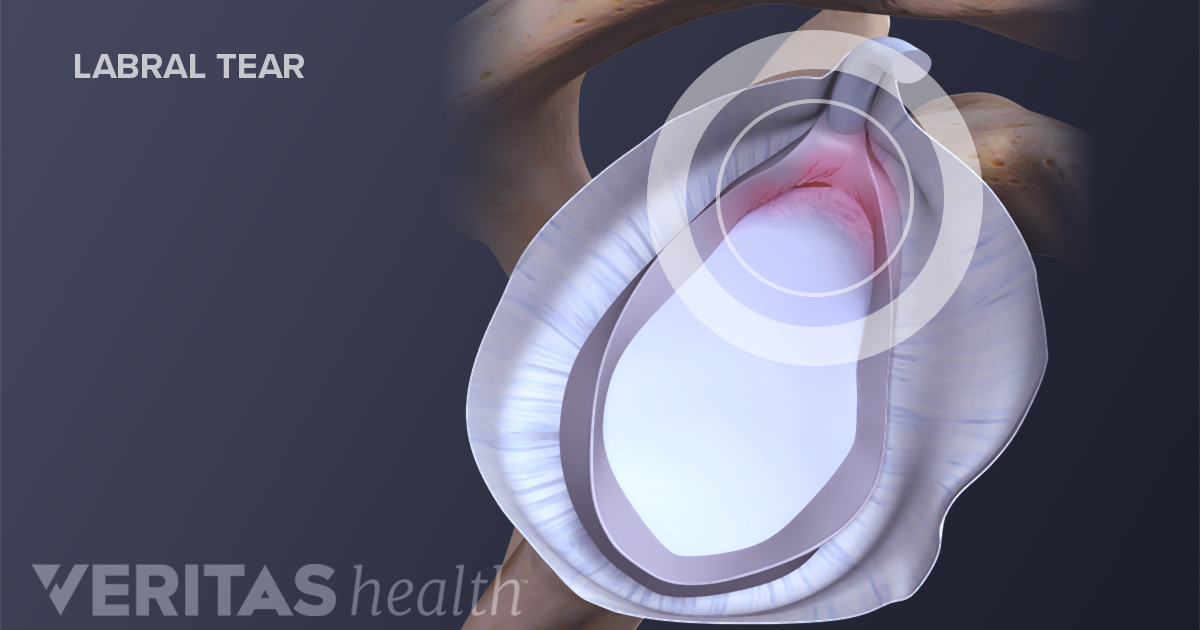
A labral tear occurs when the cartilage is torn. It provides an articulating surface for the acetabulum allowing the head of the femur to articulate with the pelvis.
 Hip Labrum Tear Acetabular Labrum Tear In Depth Hip Thigh
Hip Labrum Tear Acetabular Labrum Tear In Depth Hip Thigh
The shoulder joint is considered a ball and socket joint.
Labrum anatomy. The term labrum is used in anatomy to designate a lip edge or brim. The outer glenoid is vascular and the inner glenoid is avascular 4. The anterior portion is most vulnerable when the labrum tears.
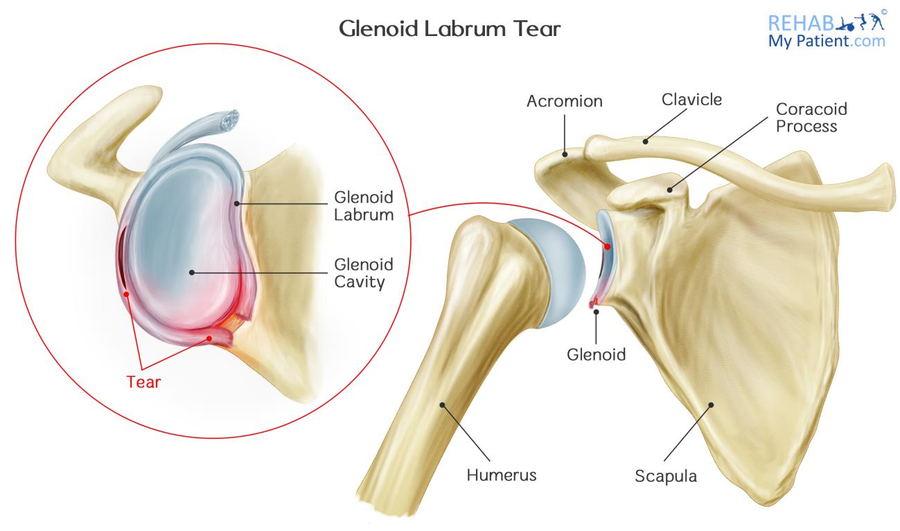
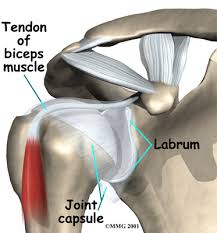
The labrum surrounding the shoulder socket is called the the glenoid labrum. The glenoid labrum is approximately 4 mm thick and is round or triangular in cross section. It contributes to shoulder stability and when torn can lead to partial or complete shoulder dislocation.
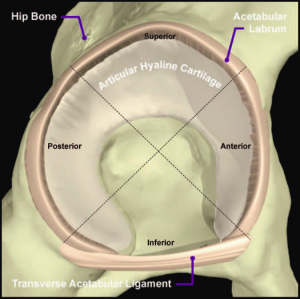
It is triangular in cross section. The acetabular labrum is a ring of cartilage that surrounds the acetabulum of the hip. Circumferentially orientated layer with radial reinforcing filaments.
Keeping joint fluid inside the hip joint capsule joint fluid. One arm of the biceps tendon long head also attaches to the shoulder labrum at its top. Helping maintain alignment between the hips ball and socket.
Glenoid labrum gross anatomy. It acts and looks almost like a washer sealing the two sides of the joint together. It is a fibro cartilaginous rubbery structure which encircles the glenoid cavity deepening the socket providing static stability to the glenohumeral joint.
The labrum is the attachment site for the ligaments and supports the ball and socket joint along with the rotator cuff tendons and muscles. The labrum is a thick fibrous ring that surrounds the glenoid. It helps provide stability to the shoulder by deepening the socket and serving as a firm attachment point for the ligaments that connect the humerus to the glenoid.
It coats the surface of the socket area with a soft cartilage enabling the shoulder to move more freely and painlessly. The glenoid labrum is similar to the meniscus of the knee. The labrum serves several purposes including.
The labrum is thickest posterosuperiorly and widest anterosuperiorly. The term labrum is used in anatomy to designate a lip edge or brim. The glenoid labrum glenoid ligament is a fibrocartilaginous structure not a fibrocartilage as previously thought rim attached around the margin of the glenoid cavity in the shoulder blade.
In anatomy and physiology the term labrum is used to refer to an edge or a brim. Deepening the joint and increasing the surface area of the hip socket by 21 1. Anatomy of the shoulder featuring the humerus upper arm bone and the labrum.
Blood supply and innervation. The fibrocartilage is is arranged in three distinct layers. In medicine a ring of fibrocartilage fibrous cartilage around the edge of the articular joint surface of a bone.
Allowing for a significant range of motion.
 About Hip Labrum Tears And Injuries Ortopedic Hip Service
About Hip Labrum Tears And Injuries Ortopedic Hip Service
 Slap Tear Shoulder Injury And Treatment
Slap Tear Shoulder Injury And Treatment
 Shoulder Dislocation And Instability Labrum Tear Huang
Shoulder Dislocation And Instability Labrum Tear Huang
 Labral Tears Of The Shoulder Orthonorcal
Labral Tears Of The Shoulder Orthonorcal
 Glenoid Labrum Tear Rehab My Patient
Glenoid Labrum Tear Rehab My Patient
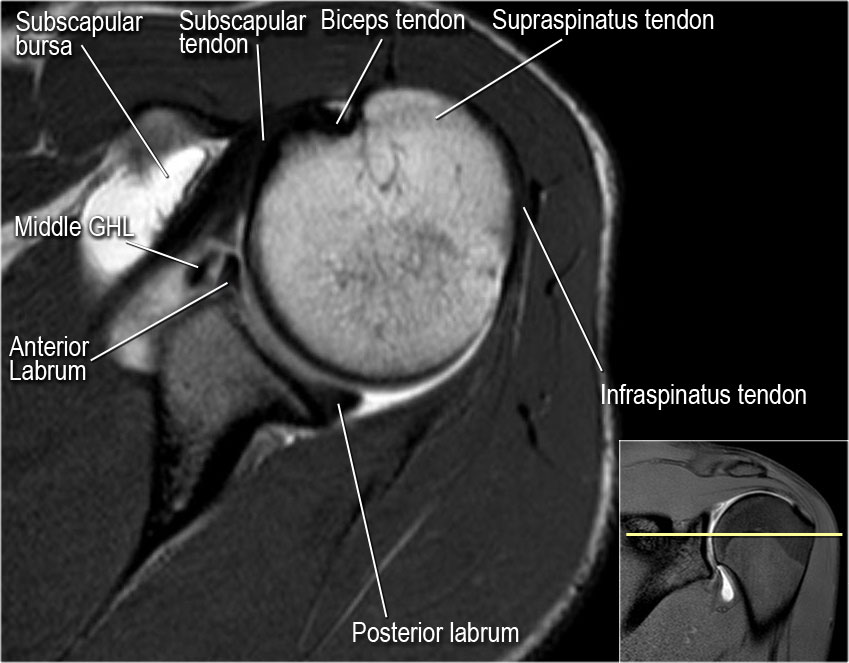 The Radiology Assistant Shoulder Mr Anatomy
The Radiology Assistant Shoulder Mr Anatomy
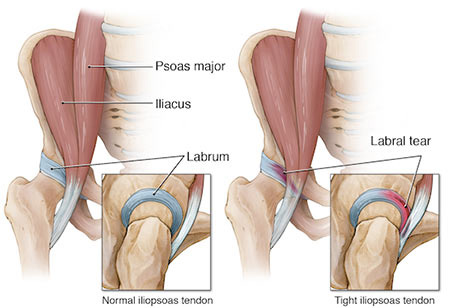 Nyc Labral Tear Treatment Doctor Specialist Sports Pain
Nyc Labral Tear Treatment Doctor Specialist Sports Pain
 The Hip Labrum What Is It What Happens When It Tears How
The Hip Labrum What Is It What Happens When It Tears How
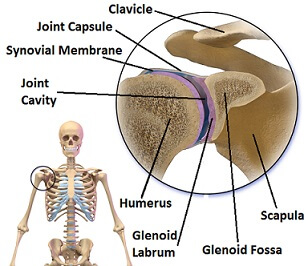 Bankart Lesion Causes Symptoms Treatment
Bankart Lesion Causes Symptoms Treatment
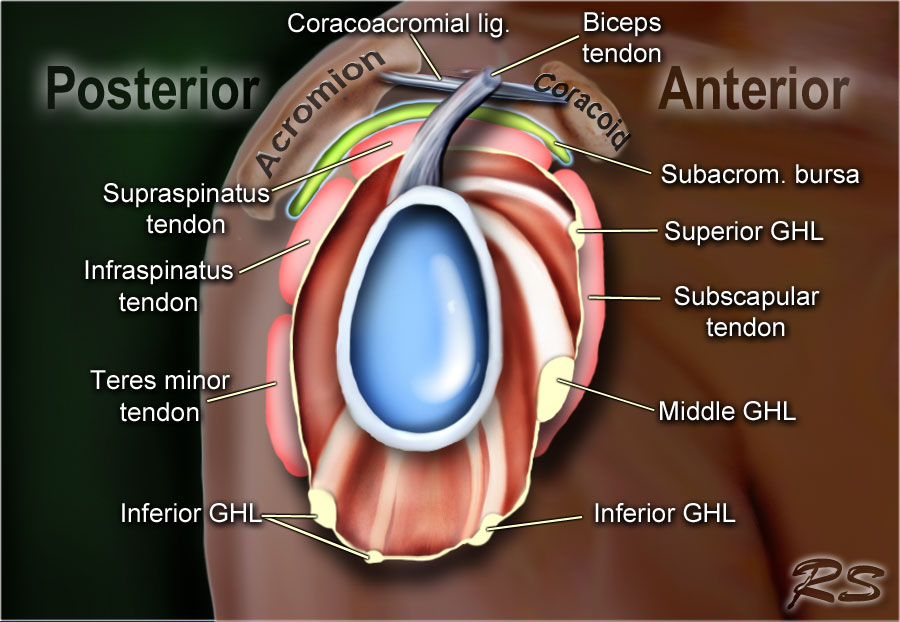 The Radiology Assistant Shoulder Mr Anatomy
The Radiology Assistant Shoulder Mr Anatomy
 Hip Labral Disorders Physiopedia
Hip Labral Disorders Physiopedia
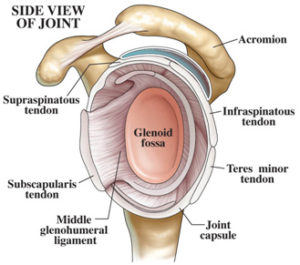 Glenoid Labrum Anatomy Shoulder Joint Anatomy Shoulder
Glenoid Labrum Anatomy Shoulder Joint Anatomy Shoulder
 Glenoid Labrum An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Glenoid Labrum An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
 Anatomy Of Shoulder Impingement Rotator Cuff And Labral Tears
Anatomy Of Shoulder Impingement Rotator Cuff And Labral Tears
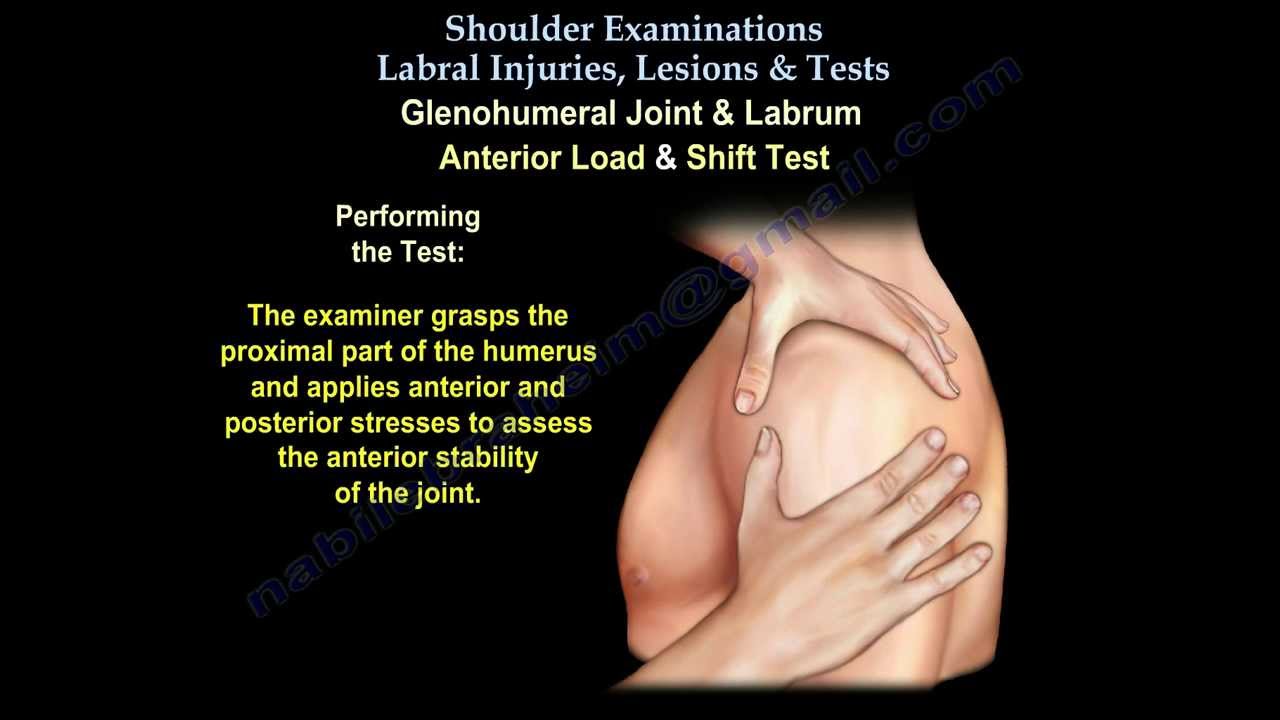 Shoulder Examinations Labral Tear Tests Everything You Need To Know Dr Nabil Ebraheim
Shoulder Examinations Labral Tear Tests Everything You Need To Know Dr Nabil Ebraheim
Playing With Pain Bear S Kyle Long Postpones Shoulder
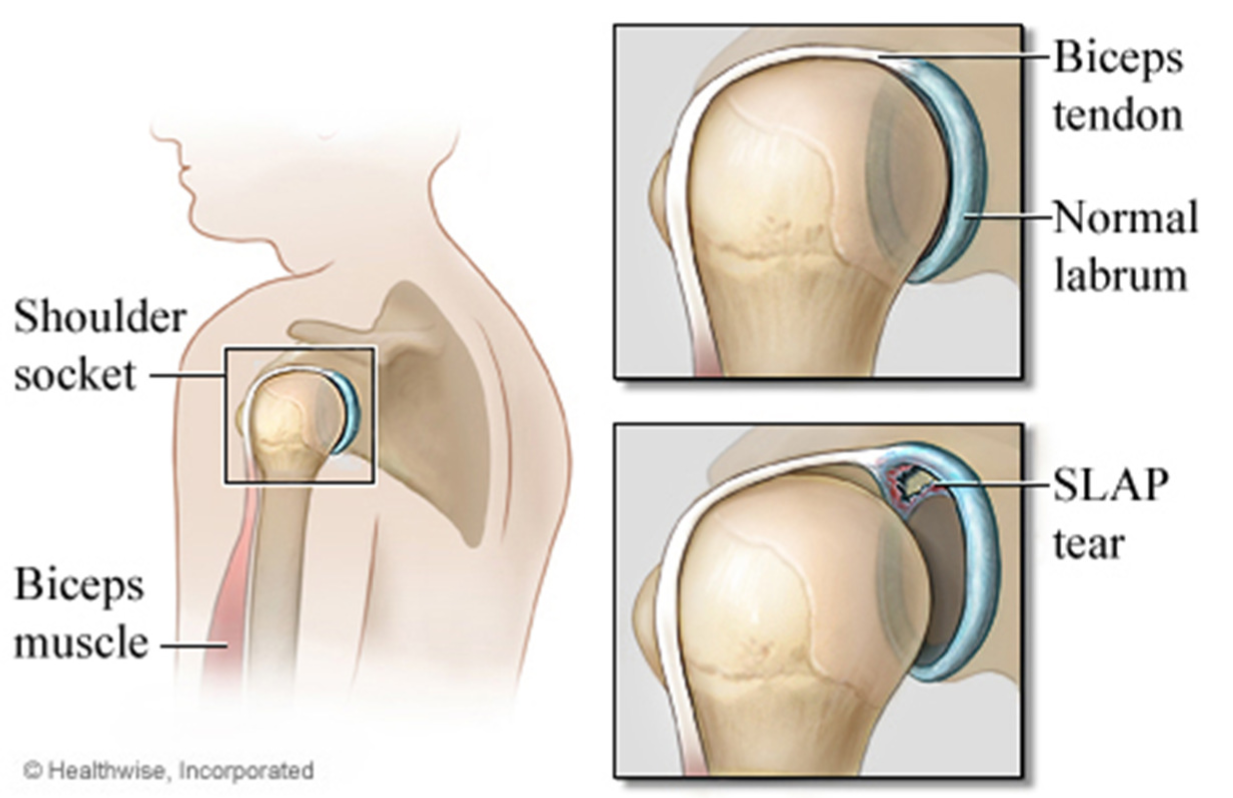 Slap Tear Brisbane Knee And Shoulder Clinic Dr
Slap Tear Brisbane Knee And Shoulder Clinic Dr
 Labral Tear University Of Utah Health
Labral Tear University Of Utah Health
 Physical Therapy In Sioux Falls For Shoulder Pain Labral Tears
Physical Therapy In Sioux Falls For Shoulder Pain Labral Tears
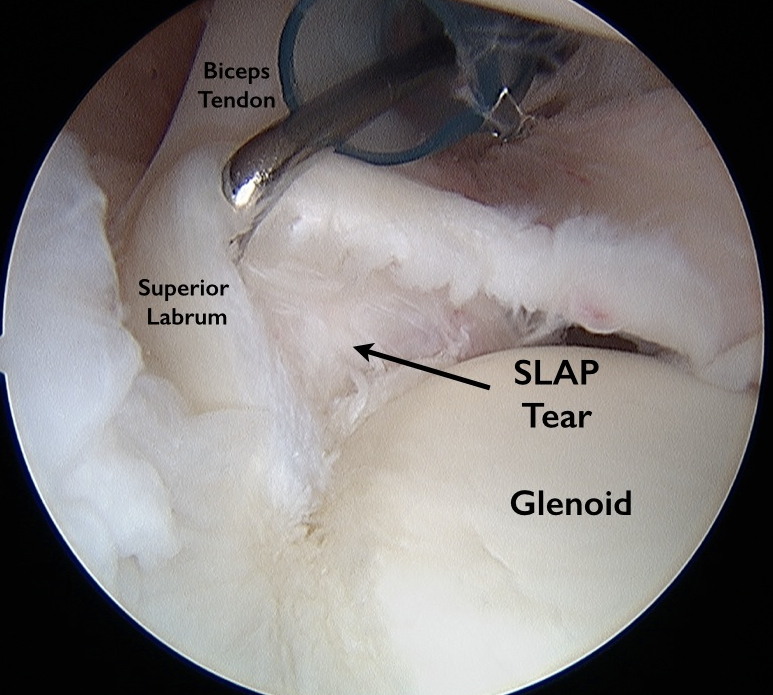 Labral Tears Of The Shoulder Anatomy And Causes Video
Labral Tears Of The Shoulder Anatomy And Causes Video
 Shoulder Anatomy And Normal Variants
Shoulder Anatomy And Normal Variants


Belum ada Komentar untuk "Labrum Anatomy"
Posting Komentar