Femoral Hernia Anatomy
Femoral hernias protrude inferior to the course of the inferior epigastric vessels. The estimated time for bowel viability survival is about 8 12 hours.
 Femoral Hernia Repair Tipp Technique Webop E Learning
Femoral Hernia Repair Tipp Technique Webop E Learning
Get a printable copy pdf file of the complete article 11m or click on a page image below to browse page by page.

Femoral hernia anatomy. Overall femoral hernias are not common. Scanning below the inguinal ligament assessing the space medial to. A femoral hernia occurs in the mid thigh area where the femoral canal is located.
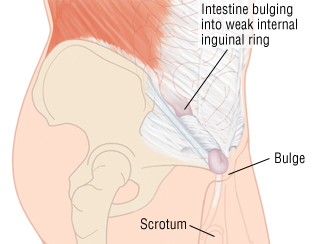
Examples of these are the canals inguinal and femoral which allow passage of vessels down to the scrotum and the legs respectively. If a loop or knuckle of intestine is within the hernia sac it requires immediate emergency surgery. When a femoral hernia is experienced a portion of the intestine has moved into the canal.
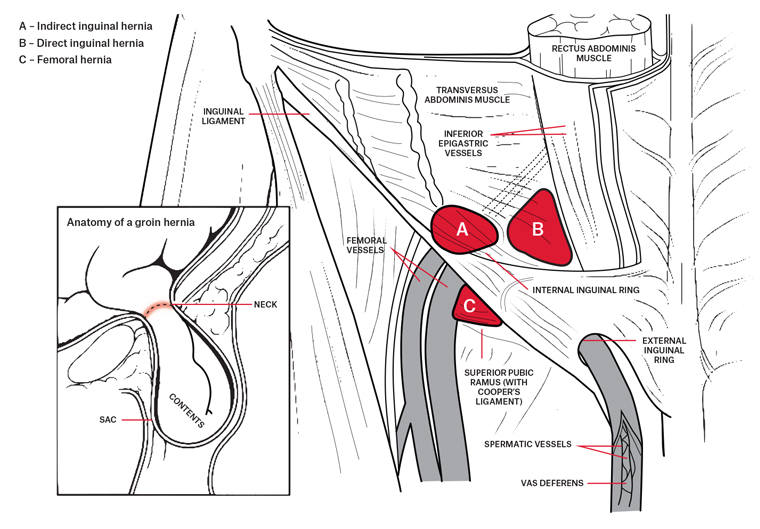
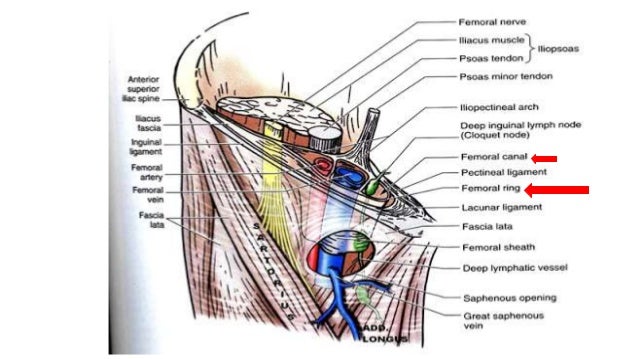
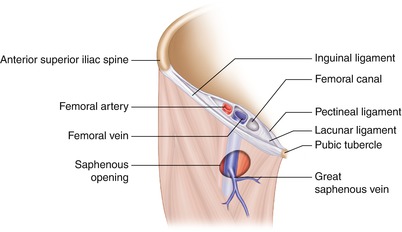
A strangulated femoral hernia occurs when a constriction of the hernia limits or completely obstructs blood supply to part of the bowel involved in the hernia. A femoral hernia that gets stuck or incarcerated on the way to strangulation can cause severe local and abdominal pain nausea and vomiting. The orifice of the femoral hernia called the femoral ring is bordered laterally by the femoral vein anteriorly by the iliopubic tract and medially by coopers ligament 5 figure 2.
The iliopubic tract represents a thickening of the transversalis fascia and the transversalis fascia should extend to the femoral canal and further to coo. Full text full text is available as a scanned copy of the original print version. However they can occasionally lead to severe problems if the hernia obstructs and blocks blood flow to your intestines.
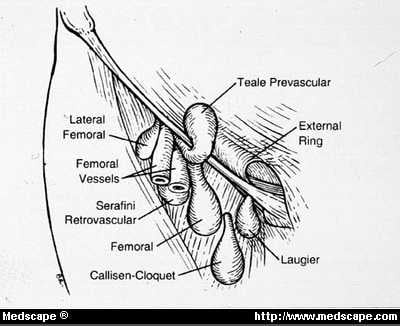
Most hernias that affect the groin are inguinal hernias and fewer than 3 percent of all hernias are femoral. Most femoral hernias do not cause symptoms. The anatomy of the femoral canal is that the anterior border is the inguinal ligament the posterior border is the pectineal ligament the medial border is the lacunar ligament and the lateral border is the femoral vein.
There may be an increased right sided predilection 23. The femoral artery vein and nerve travel through this path. Strangulation can occur in all hernias but is more common in femoral and inguinal hernias due to their narrow weaknesses in the abdominal wall.
Whilst a femoral hernia is usually asymptomatic aside from the lump at presentation due to the anatomy of the femoral canal around 30 of femoral hernia cases will present as an emergency either obstruction or strangulation. The umbilical area navel is another area of natural weakness frequently prone to hernia. The femoral canal is a path that leads from the abdominal cavity to the thigh.
Femoral hernias will commonly present as a small lump in the groin.
 Csa Surgical Center Groin Inguinal Or Femoral Hernia Repair
Csa Surgical Center Groin Inguinal Or Femoral Hernia Repair
 Hernias Gastrointestinal Medbullets Step 1
Hernias Gastrointestinal Medbullets Step 1
 Repair Of Femoral Hernia With Mesh Zollinger S Atlas Of
Repair Of Femoral Hernia With Mesh Zollinger S Atlas Of
 Femoral Triangle Sheath Canal Hernia
Femoral Triangle Sheath Canal Hernia
 Inguinal Canal An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Inguinal Canal An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
 Abdominal Hernias Practice Essentials Background Anatomy
Abdominal Hernias Practice Essentials Background Anatomy
Laparoscopic View Of Surgical Anatomy Of The Groin Bittner R
Laparoscopic Repair Of Inguinal Femoral Hernias
Femoral Hernia Holistic Hernia Remediation
Anatomy Of Inguinal And Femoral Hernias Inguinal And
 Hernias Types Of Hernias Symptoms And Treatment Of Hernias
Hernias Types Of Hernias Symptoms And Treatment Of Hernias
Anatomy Essentials For Laparoscopic Inguinal Hernia Repair
 Racgp General Practitioner Primer On Groin Hernias
Racgp General Practitioner Primer On Groin Hernias
 1000 Hernia Stock Images Photos Vectors Shutterstock
1000 Hernia Stock Images Photos Vectors Shutterstock
 Inguinal Hernia Harvard Health
Inguinal Hernia Harvard Health
 Abdominal Wall Hernias Gastrointestinal Medbullets Step 2 3
Abdominal Wall Hernias Gastrointestinal Medbullets Step 2 3
 1000 Hernia Stock Images Photos Vectors Shutterstock
1000 Hernia Stock Images Photos Vectors Shutterstock
 Hernia Symptoms Signs Types Treatment Surgery Pictures
Hernia Symptoms Signs Types Treatment Surgery Pictures
 Clinical Correlations Abdomical Anatomy Biology
Clinical Correlations Abdomical Anatomy Biology
 Inguinal Hernia Anatomy And Management
Inguinal Hernia Anatomy And Management
 Types Of Hernias The Hernia Clinic
Types Of Hernias The Hernia Clinic
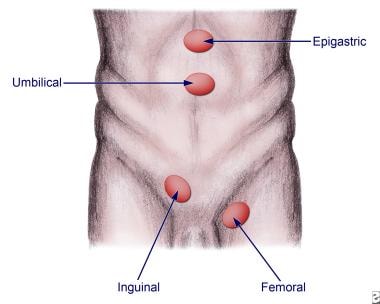
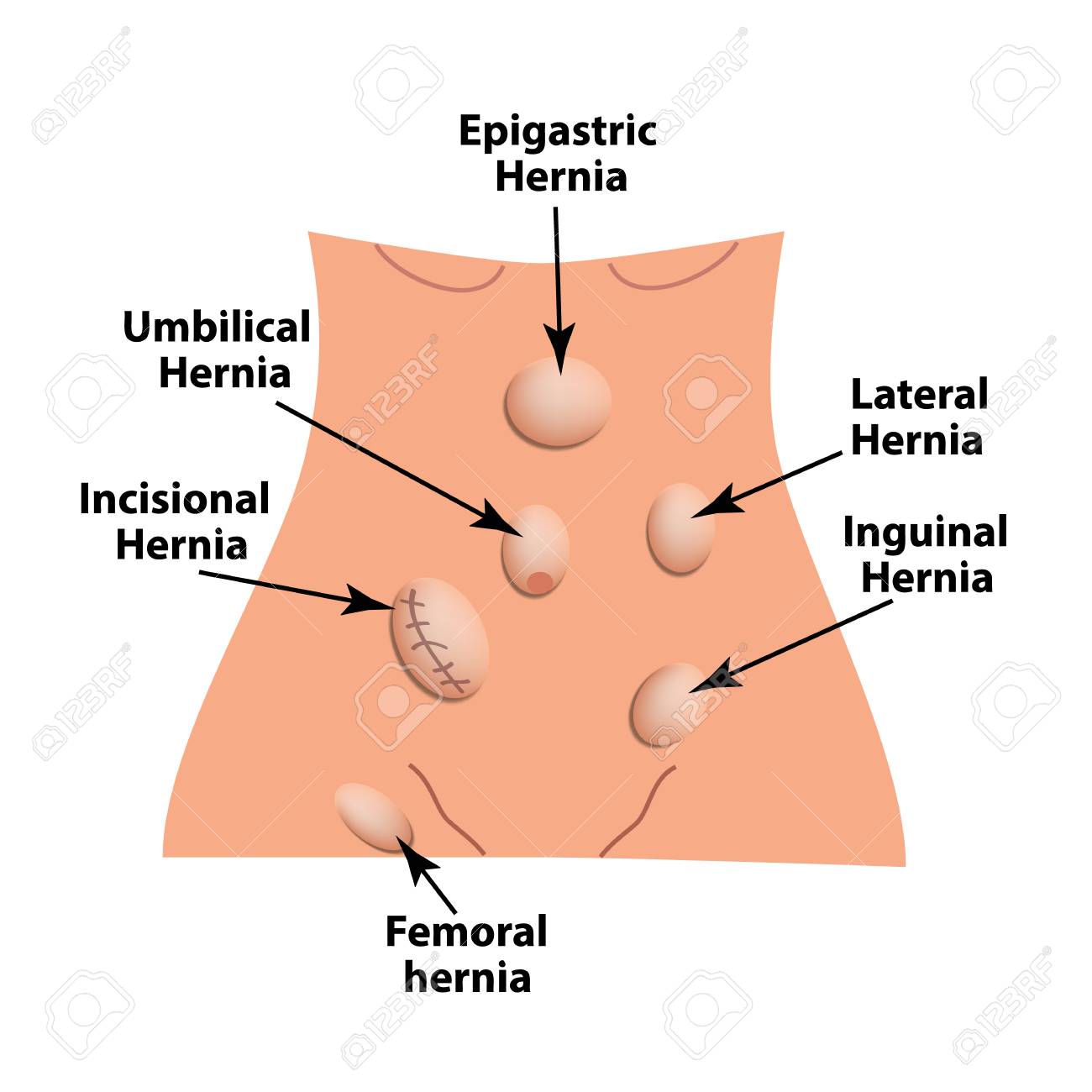 Types Of Hernia Epigastric Lateral Umbilical Inguinal Femoral
Types Of Hernia Epigastric Lateral Umbilical Inguinal Femoral
 Femoral Hernia Repair Healthdirect
Femoral Hernia Repair Healthdirect
 Laparoscopic Repair Of An Incarcerated Femoral Hernia
Laparoscopic Repair Of An Incarcerated Femoral Hernia
Belum ada Komentar untuk "Femoral Hernia Anatomy"
Posting Komentar