Ureter Anatomy
Pelvic superior and inferior vesical arteries. Each ureter is about 25 cm 10 inches long and has a diameter of approximately 3mm.
 Transitional Cell Cancer Of The Renal Pelvis And Ureter
Transitional Cell Cancer Of The Renal Pelvis And Ureter
Urine is created in the renal tubules and it is stored in the kidneys renal pelvis.
Ureter anatomy. From the renal pelvis to the pelvic brim. Intravesical or intramural ureter. In the adult the ureters are usually 2530 cm long and around 34 mm in diameter.
The ureter is about 10 to 12 inches long in the average adult. The ureters are a pair of thick walled narrow muscular tubes that drains the urine from the kidney to the urinary bladder by peristaltic contractions of the smooth muscle in their wall. There are two ureters one attached to each kidney.
The ureter is a tube that carries urine from the kidney to the urinary bladder. The ureters have an expansive anastomosing network of arterial supply. Neuronal supply to the ureters.
The ureters are tubes made of smooth muscle fibers that propel urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder. Abdominal renal artery testicularovarian artery and ureteral branches directly from the abdominal aorta. From the pelvic brim to the bladder.
At its termination the ureter passes through the bladder wall in such a way that as the bladder fills with urine this terminal part of the ureter tends to close. The ureter then continues anteriorly on the psoas major muscle crossing under the gonadal vein at the level of the inferior pole of the kidney. Kidneys ureters bladder and urethra.
The tube emerges from each kidney descends behind the abdominal cavity and opens into the bladder. The ureters are a pair of muscular tubular structures responsible for taking urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder for storage prior to excretion. The ureters leave the kidneys posterior to the renal vessels.
The colon and its mesentery are associated anterior to the ureters. The arterial supply to the ureters can be divided into abdominal and pelvic supply. The ureter is 25 30 cm long and has three parts.
Urine builds up in the bladder until it is ejected from the body through the urethra. Ureters gross and histological perspective. The anatomy of the urinary system consist of.
What is the extent and parts of ureter. The upper half of the ureter is located in the abdomen and the lower half is located in the pelvic area. The ureters are collapsible s shaped channels.
The ureter is lined by urothelial cells a type of transitional epithelium and has an additional smooth muscle layer in the more distal one third to assist with peristalsis. They are collapsible s shaped channels. Urine flows from the kidneys passing through the ureters to the bladder.
The ureters course medial to the sacroiliac joint and then curve laterally in the pelvis. Within the bladder wall.
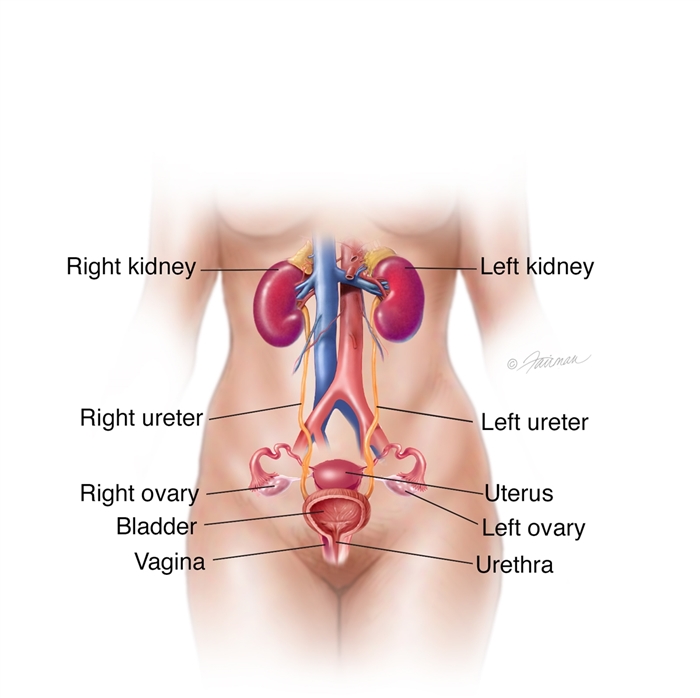 Megaureter Symptoms Diagnosis Treatment Urology Care
Megaureter Symptoms Diagnosis Treatment Urology Care
 Surgical Anatomy Of The Ureter Frober 2007 Bju
Surgical Anatomy Of The Ureter Frober 2007 Bju
 Ureter Anatomy Function Ectopic Ureter Ureter Pain
Ureter Anatomy Function Ectopic Ureter Ureter Pain
Case Study S A Medical Graphics
 Surgical Anatomy Of The Ureter Frober 2007 Bju
Surgical Anatomy Of The Ureter Frober 2007 Bju
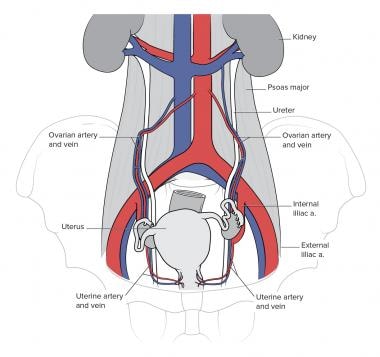 Ureter Anatomy Overview Gross Anatomy Microscopic Anatomy
Ureter Anatomy Overview Gross Anatomy Microscopic Anatomy
Urology Notes 2012 Ureter Anatomy With Illustrations
Urinary Tract Injury And Repair
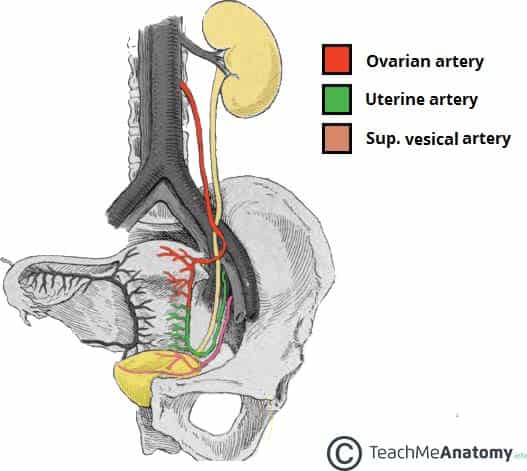 The Ureters Anatomical Course Neurovascular Supply
The Ureters Anatomical Course Neurovascular Supply
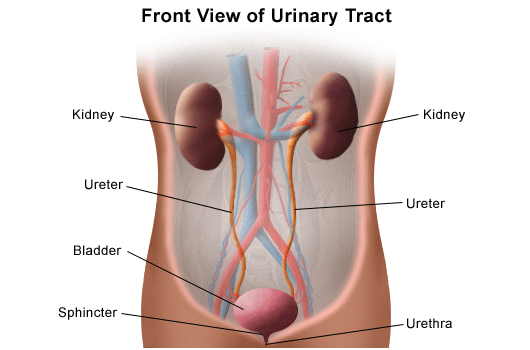
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/12418/Kidneys_in_situ.png) Ureters Anatomy Innervation Blood Supply Histology Kenhub
Ureters Anatomy Innervation Blood Supply Histology Kenhub
021a Pelvis Viscera 1 Urinary Bladder And Rectum Anatomy
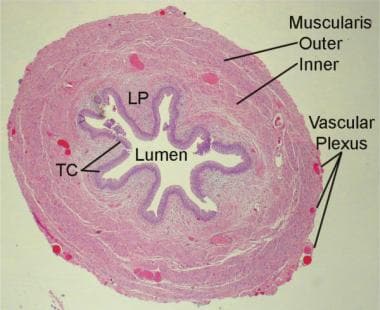 Ureter Anatomy Overview Gross Anatomy Microscopic Anatomy
Ureter Anatomy Overview Gross Anatomy Microscopic Anatomy
 Anatomy Of The Kidney And Ureter Sciencedirect
Anatomy Of The Kidney And Ureter Sciencedirect
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/11902/renal-cortex_english.jpg) Kidneys Ureters Suprarenal Glands Anatomy Location Kenhub
Kidneys Ureters Suprarenal Glands Anatomy Location Kenhub
 Water Runs Under The Bridge Ureter Under Neath Uterine
Water Runs Under The Bridge Ureter Under Neath Uterine
 Ureters Anatomy Physiology Wikivet English
Ureters Anatomy Physiology Wikivet English
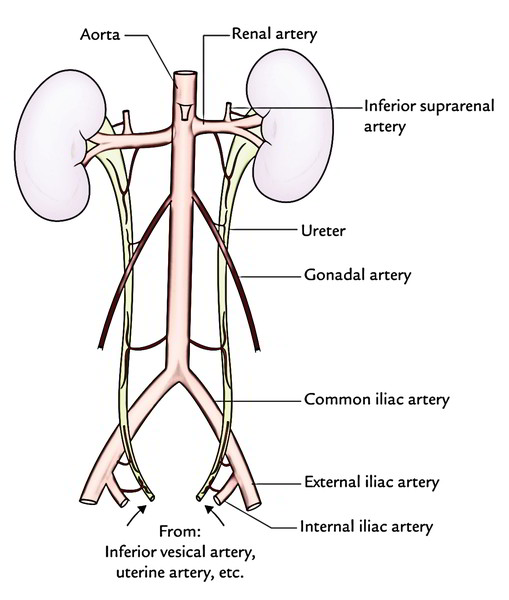 Easy Notes On Ureter Learn In Just 4 Minutes Earth S Lab
Easy Notes On Ureter Learn In Just 4 Minutes Earth S Lab
 Kidney Excretory System Anatomy Ureter Renal Medulla Png
Kidney Excretory System Anatomy Ureter Renal Medulla Png
 Innervation Of The Kidneys And The Proximal Part Of The
Innervation Of The Kidneys And The Proximal Part Of The
 Anatomy Of The Human Kidney Cut To Show Internal Structures
Anatomy Of The Human Kidney Cut To Show Internal Structures
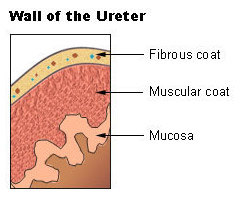



Belum ada Komentar untuk "Ureter Anatomy"
Posting Komentar