Reptiles Anatomy
Reptiles are the longest lived species on the planet. We told you that amphibians have legs on the sides.
Those four subclasses were.

Reptiles anatomy. In non crocodilian reptiles some mixing of blood occurs in the single ventricle however functional separation of venous and arterial blood is largely maintained thanks to a muscular ridge in the ventricle termed the intraventricular septum or vertical septum. The anatomy of the snakes head has a number of adaptations that allow it to swallow large prey. Snakes however do not have legs.
They also lack a pectoral girdle shoulder bones and with the exception of the boids which retain a vestigial pelvis and external spurs they also lack a pelvic girdle rear leg support. Most reptiles have four legs. Reptiles body is covered in scales or they have a bony external plate called shell.
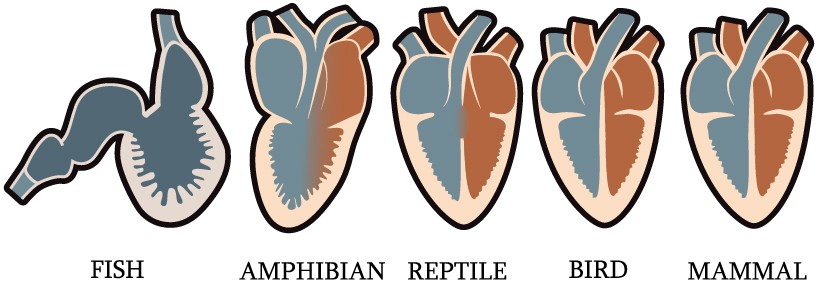
In addition the snake has no temporomandibular joint. All reptiles have both pulmonary and systemic circulations ie similar to mammals. That change in direction allows reptiles to pick their bellies off the ground and helps them move more efficiently.
Caudal autotomy is found in many species of reptiles and in two species of spiny mouse of the genus acomys. A small piece of cartilage just inside the glottis vibrates when the snake forcefully expels air from its lungs. Reptiles facts reptiles are ectothermic which means they get their body heat from external sources.
They have color vision with the visual depth perception being much more advanced than amphibians and many mammals. Euryapsida one high fenestra above the postorbital and squamosal protorosaurs small. Reptiles cannot chew their food they can only tear it.
Basically the legs of reptiles shifted to the bottom of the body. Unlike what mammals have the reptile glottis is always closed forming a vertical slit unless the snake takes a breath. Reptiles legs are directed down towards the ground.
Snakes have a small opening just behind the tongue called the glottis which opens into the trachea or windpipe. Reptile anatomy the reptile anatomy clipart gallery provides 63 illustrations of reptile body parts skeletons organs and other internal and external anatomical views. In reptiles we can find caudal autotomy in lacertids geckos skinks and tuataras.
Reptile anatomy most reptiles are unable to see properly during nighttime as their vision is mainly adapted to the daylight conditions. In all snakes the two halves of lower jaw are loosely held together rostrally and the mandibular symphysis can separate. Autotomy or self amputation is defined as a behaviour in which the animal can shed off one or more body parts.
Synapsida one low fenestra pelycosaurs and therapsids the mammal like reptiles. Anapsida no fenestrae cotylosaurs and chelonia turtles and relatives.

 Lizard Animal Medicine Animal Doctor Veterinary Medicine
Lizard Animal Medicine Animal Doctor Veterinary Medicine
 Scientific Illustration Reptiles And Amphibians Tagged
Scientific Illustration Reptiles And Amphibians Tagged
 Text Book Of Vertebrate Zoology Vertebrates Anatomy
Text Book Of Vertebrate Zoology Vertebrates Anatomy
 Turtle Species Classification Facts Britannica
Turtle Species Classification Facts Britannica
 Lizard On White Background A Beige Lizard That Lies On Its
Lizard On White Background A Beige Lizard That Lies On Its
 Clinical Anatomy And Physiology Of Exotic Species Structure
Clinical Anatomy And Physiology Of Exotic Species Structure
 Scientific Illustration Reptiles And Amphibians Tagged
Scientific Illustration Reptiles And Amphibians Tagged
Reptiles Anatomy Snake Mouth Powerpoint Template Background

 Reptiles Anatomy And Physiology All You Need Is Biology
Reptiles Anatomy And Physiology All You Need Is Biology
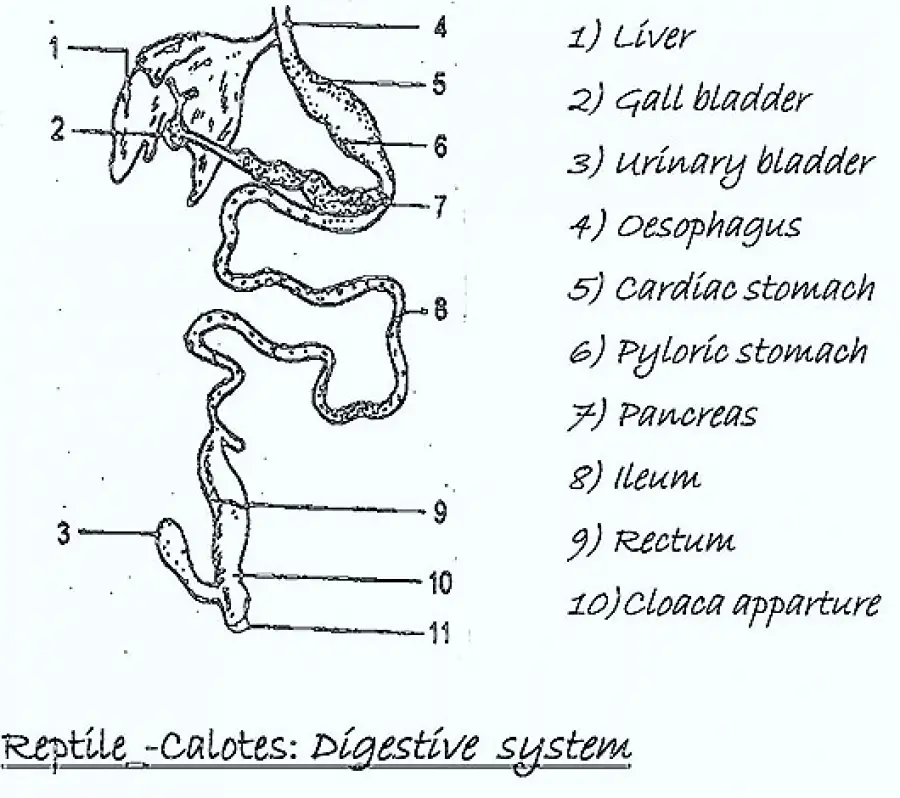 Comparative Anatomy Digestive System Of Bird Mammal And
Comparative Anatomy Digestive System Of Bird Mammal And
 Mr Nussbaum Reptiles And Amphibians Interactive Online
Mr Nussbaum Reptiles And Amphibians Interactive Online
 On The Anatomy Of Vertebrates Fishes And Reptiles
On The Anatomy Of Vertebrates Fishes And Reptiles
 Understanding Reptile Dental Anatomy Clinical Applications
Understanding Reptile Dental Anatomy Clinical Applications
 Leopard Gecko Anatomy Reptiles Amphibians Reptiles
Leopard Gecko Anatomy Reptiles Amphibians Reptiles
 Figure 7 From Approach To Reptile Emergency Medicine
Figure 7 From Approach To Reptile Emergency Medicine
 Episode 3 Field Guide What S A Reptile Past Time Paleo
Episode 3 Field Guide What S A Reptile Past Time Paleo
Respiratory System Reptiles Anatomy Our Reptile Forum
 Herps Explorers Anatomy Caecilians Crocs 6 Week Online
Herps Explorers Anatomy Caecilians Crocs 6 Week Online
Belum ada Komentar untuk "Reptiles Anatomy"
Posting Komentar