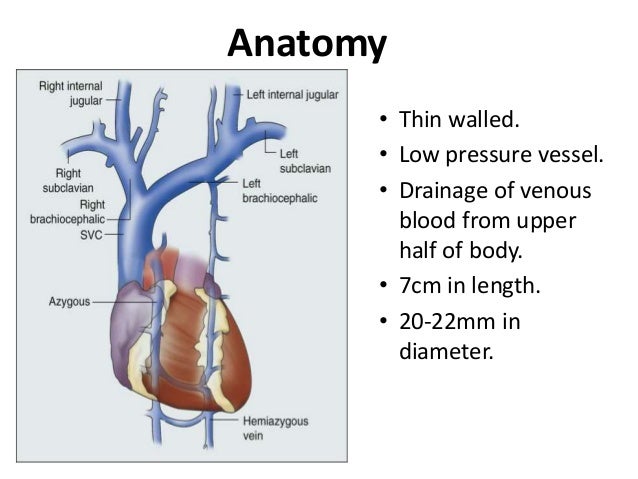
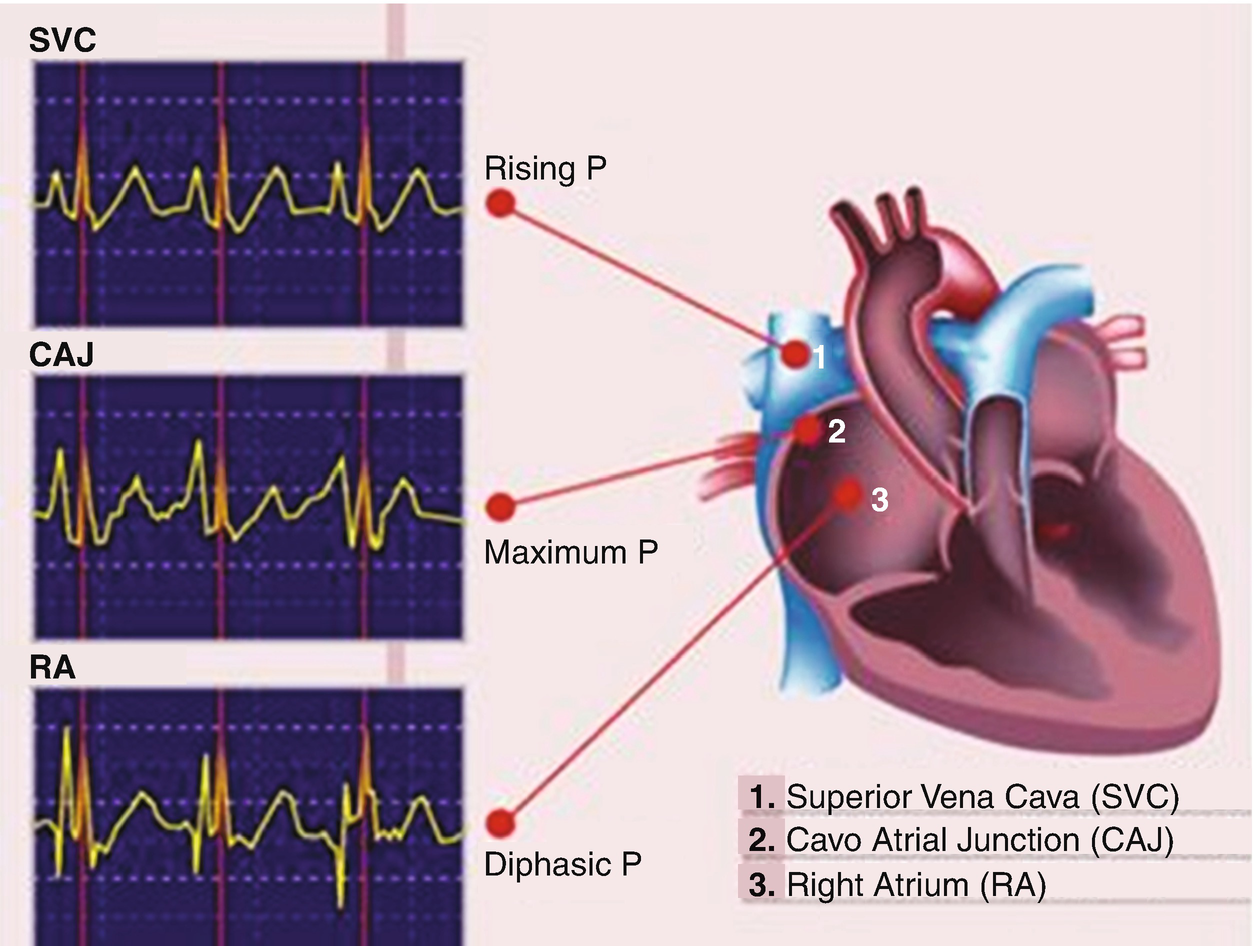
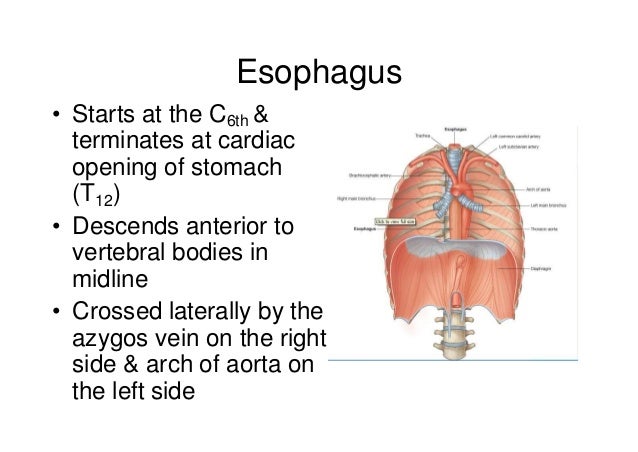
Svc Anatomy
It receives blood from the upper half of the body except the heart and returns it to the right atrium. The anterior vena cava also known as the precava drains the head end of the body while the posterior vena cava or postcava drains the tail or rear end.
 Chapter 140 Resection For Superior Vena Cava Syndrome
Chapter 140 Resection For Superior Vena Cava Syndrome
Thin walls of tissue called fissures separate the.

Svc anatomy. Whereas many mammals including humans have only one anterior vena cava other animals have two. Superior vena cava bcv. The superior vena cava svc is a large valveless vein that conveys venous blood from the upper half of the body and returns it to the right atrium.
The left lung has a superior and inferior lobe while the right lung has superior middle and inferior lobes. Superior vena cava bcv. Gross anatomy the svc be.
It is a large diameter 24 mm short length vein that receives venous return from the upper half of the body above the diaphragm. Created by a team of doctors and medical students each topic combines anatomical knowledge with high yield clinical pearls seamlessly bridging the gap between scholarly learning and. Diagnosis not applicable diagnosis not applicable.
In humans these veins are respectively called the superior and inferior venae cavae. In this article we will look at the anatomy of the superior vena cava its position tributaries and clinical correlations. The superior vena cava svc is a large valveless venous channel formed by the union of the brachiocephalic veins.
Containing over 1000 vibrant full colour images teachmeanatomy is a comprehensive anatomy encyclopaedia presented in a visually appealing easy to read format. The superior vena cava svc also known as the cava or cva is a short but large diameter vein located in the anterior right superior mediastinum. The lung consists of five lobes.
Case contributed by dr omar bashir. Superior vena cavaon left in anatomy a persistent left superior vena cava plsvc is the most common variation of the thoracic venous system 1 2 is prevalent in 03 of the population 3 and an embryologic remnant that results from a failure to involute. The superior vena cava svc is the superior of the two venae cavae the great venous trunks that return deoxygenated blood from the systemic circulation to the right atrium of the heart.
Clinical notes superior vena cava obstruction svco superior vena cava syndrome svcs superior vena cava thrombosis.
 Radiologic Stages Of Vena Cava Obstruction The Stanford
Radiologic Stages Of Vena Cava Obstruction The Stanford
Catheter Interventions For Hemodialysis Fistulas And Grafts
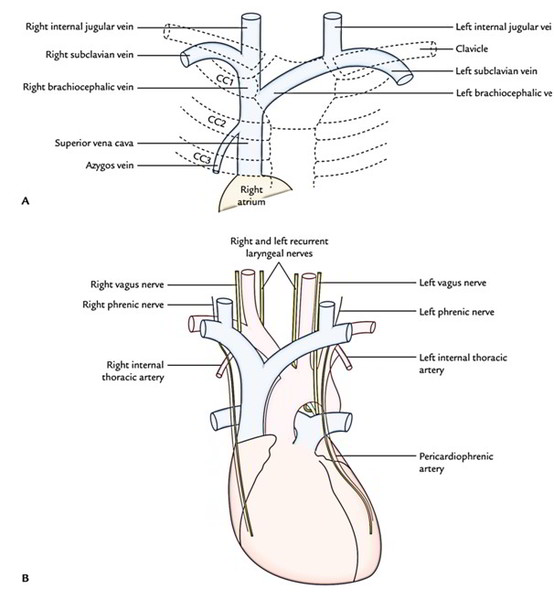 Easy Notes On Superior Vena Cava Learn In Just 3 Minutes
Easy Notes On Superior Vena Cava Learn In Just 3 Minutes
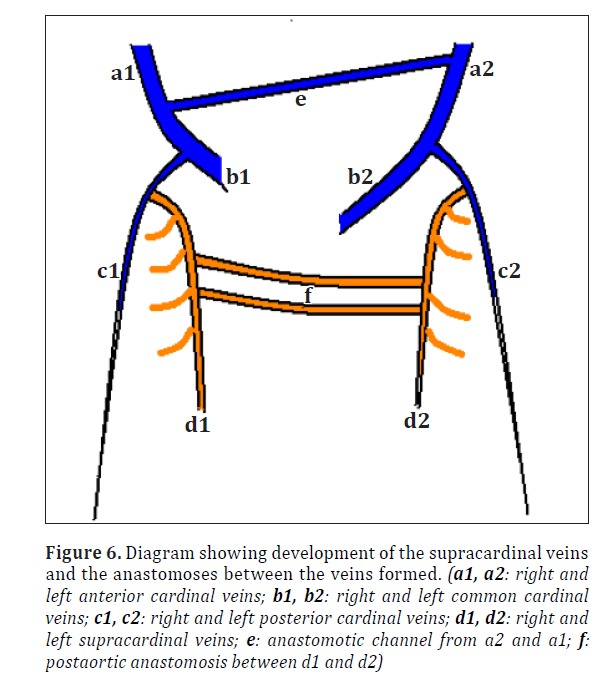
 Cvs 4 Development Of The Innominate Veins S V C
Cvs 4 Development Of The Innominate Veins S V C
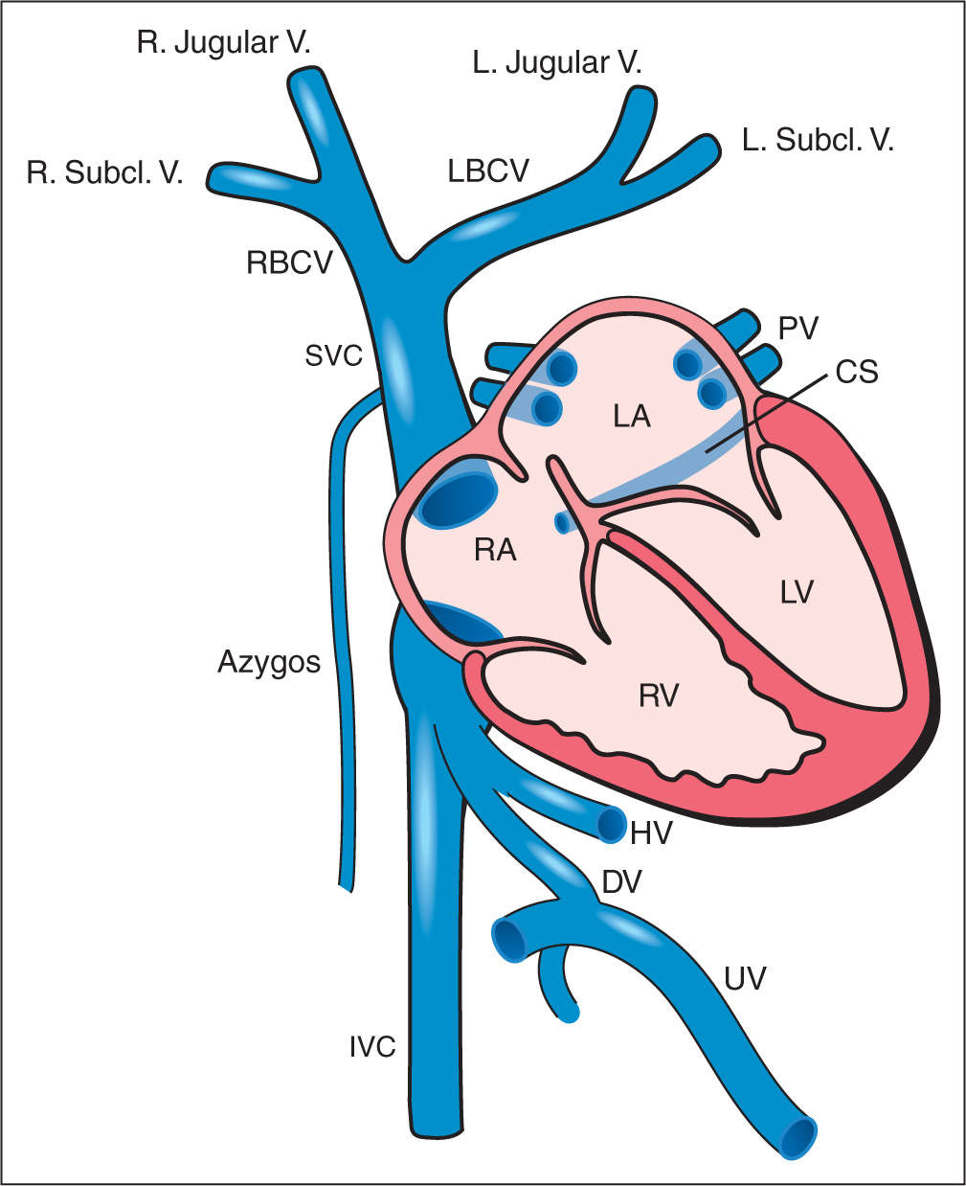
 Atrium Superior Vena Cava Svc Inferior Vena Cava Ivc And
Atrium Superior Vena Cava Svc Inferior Vena Cava Ivc And
 Left Superior Vena Cava With Associated Venous Variations
Left Superior Vena Cava With Associated Venous Variations
 Superior Vena Cava Syndrome Urine Or Urout
Superior Vena Cava Syndrome Urine Or Urout
 Superior Vena Cava Venous And Lymphatic Diseases
Superior Vena Cava Venous And Lymphatic Diseases
 Atrium Superior Vena Cava Svc Inferior Vena Cava Ivc And
Atrium Superior Vena Cava Svc Inferior Vena Cava Ivc And
 Persistent Left Svc Absent Innominate Bridging Vein
Persistent Left Svc Absent Innominate Bridging Vein
 Double Superior Vena Cava Radiology Case Radiopaedia Org
Double Superior Vena Cava Radiology Case Radiopaedia Org
Lab 5 Heart Transplant Coronary Circulation
 Misplaced Central Venous Catheters Applied Anatomy And
Misplaced Central Venous Catheters Applied Anatomy And
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/human-heart-circulatory-system-598167278-5c48d4d2c9e77c0001a577d4.jpg) Superior And Inferior Venae Cavae
Superior And Inferior Venae Cavae
:watermark(/images/watermark_5000_10percent.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/atlas_overview_image/322/6iIuezZLih0fZBxiVSe8uQ_arteries-veins-back-lateral-view_english.jpg) Superior Vena Cava Anatomy Function Clinical Aspects
Superior Vena Cava Anatomy Function Clinical Aspects
 Cardiology Anatomy Embryology Flashcards Quizlet
Cardiology Anatomy Embryology Flashcards Quizlet
:watermark(/images/watermark_only.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/vena-marginalis-sinistra/hAcrjlt8cSBQUW8fhp7aSA_V._marginalis_sinistra_01.png) Superior Vena Cava Anatomy Function Clinical Aspects
Superior Vena Cava Anatomy Function Clinical Aspects
 Heart Anatomy Model 7 Part Model Esophagus Trachea Svc Aorta Front Heart Wall Upper Half Of Heart
Heart Anatomy Model 7 Part Model Esophagus Trachea Svc Aorta Front Heart Wall Upper Half Of Heart
 Systematic Evaluation Of The Venous System Obgyn Key
Systematic Evaluation Of The Venous System Obgyn Key
 Svc Obstruction Chest Fellow Pmk
Svc Obstruction Chest Fellow Pmk
Print Anatomy Of The Veins Of The Trunk Lecture 6


Belum ada Komentar untuk "Svc Anatomy"
Posting Komentar