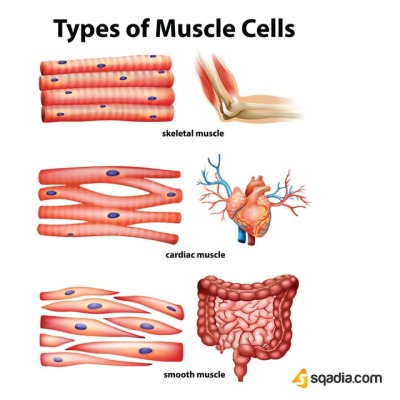
Smooth Muscle Anatomy
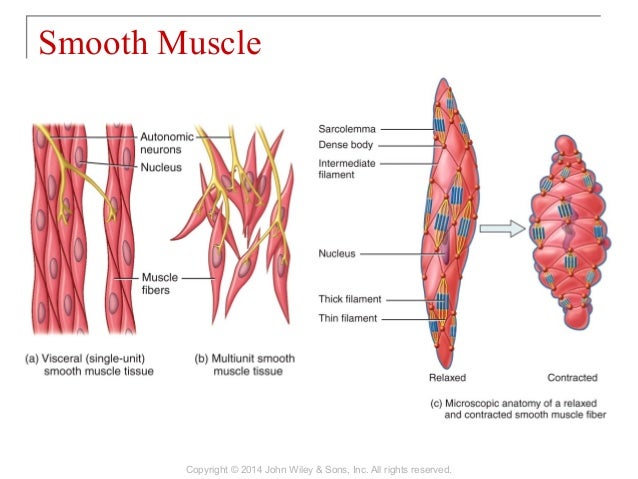
Smooth muscle fibers are spindle shaped wide in the middle and tapered at both ends somewhat like a football and have a single nucleus. Smooth muscle tissue is also known as visceral muscle tissue.
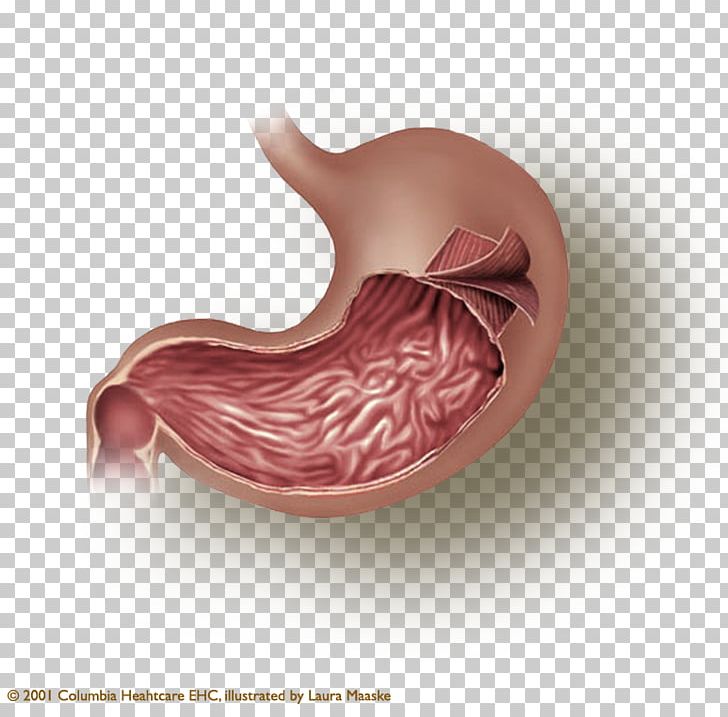 Stomach Smooth Muscle Tissue Muscular Layer Png Clipart
Stomach Smooth Muscle Tissue Muscular Layer Png Clipart
Smooth muscle contracts under certain stimuli as atp is freed for use by the myosin.

Smooth muscle anatomy. These cells have fibers of actin and myosin which run through the cell and are supported by a framework of other proteins. They are designed to contract simultaneously because of their organized muscle layers that are closely interconnected to each other. It is layered in a distinctive pattern of circular layers.
Although they do not have striations and sarcomeres smooth muscle fibers do have actin and myosin contractile proteins and thick and thin filaments. Smooth muscle also called involuntary muscle muscle that shows no cross stripes under microscopic magnification. This smooth muscle can be found surrounding the walls of the blood vessels the bronchioles in the lungs and the sphincter muscles used in the gi tract.
They are also non striated and have no organized myofilaments. Myofibroblasts produce connective tissue proteins such as collagen and elastin. Human anatomy autonomic nervous system smooth muscle.
Smooth muscle is composed of sheets or strands of smooth muscle cells. Smooth muscle cells can undergo hyperplasia mitotically dividing to produce new cells. Smooth muscle is found throughout the body around various organs and tracts.
The smooth muscle around these organs also can maintain a muscle tone when the organ empties and shrinks a feature that prevents flabbiness in the empty organ. Transport chyme through wavelike contractions of the intestinal tube. In general visceral smooth muscle produces slow steady contractions that allow substances such as food in the digestive tract to move through the body.
It consists of narrow spindle shaped cells with a single centrally located nucleus. They range from about 30 to 200 μm thousands of times shorter than skeletal muscle fibers and they produce their own connective tissue endomysium. Smooth muscle cells have a single nucleus and are spindle shaped.
Smooth muscle has different functions in the human body including. The smooth muscle cells are characterized by a single nucleus and a spindle shaped figure. It consists of narrow spindle shaped cells with a single centrally located nucleus.
![]() Icon Of Smooth Muscle Cell Under Microscope Human Anatomy Concept Flat Vector Design Element For Infographic Poster Educational Book Or Flyer Art
Icon Of Smooth Muscle Cell Under Microscope Human Anatomy Concept Flat Vector Design Element For Infographic Poster Educational Book Or Flyer Art
 Royalty Free Smooth Muscle Tissue Stock Images Photos
Royalty Free Smooth Muscle Tissue Stock Images Photos
 Your Muscles For Kids Nemours Kidshealth
Your Muscles For Kids Nemours Kidshealth
 Smooth Muscle Anatomy Stock Vectors Images Vector Art
Smooth Muscle Anatomy Stock Vectors Images Vector Art

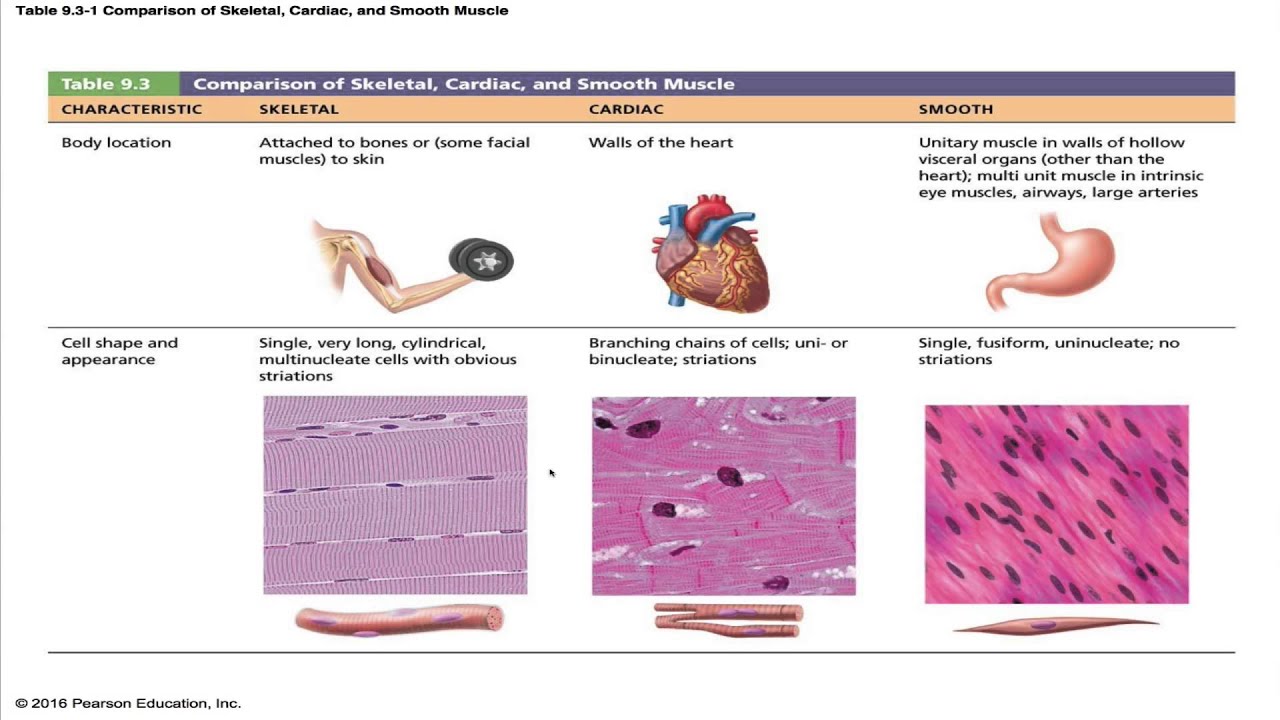 Anatomy Physiology Chapter 9 Part A Lecture Muscles And Muscle Tissue
Anatomy Physiology Chapter 9 Part A Lecture Muscles And Muscle Tissue
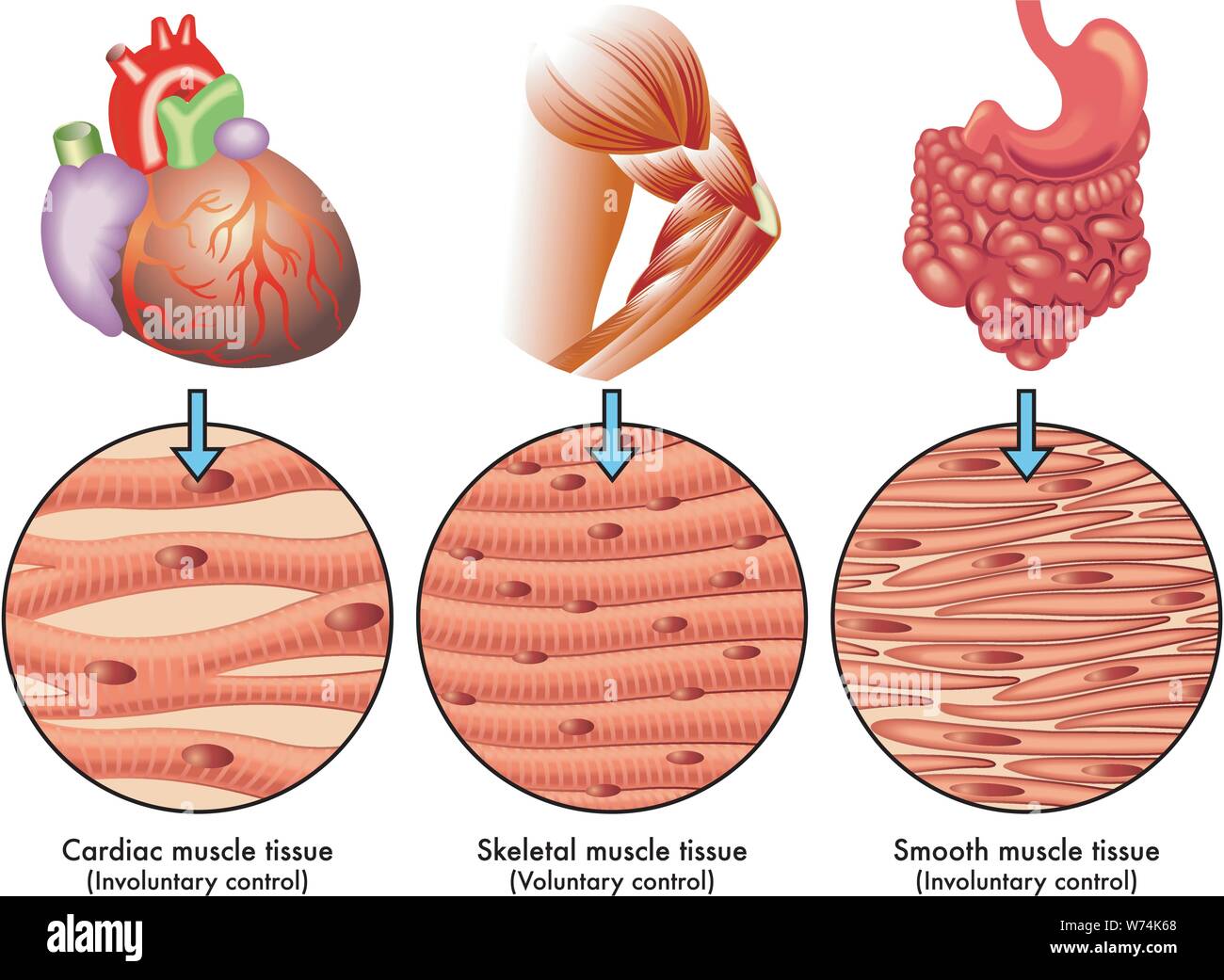 Smooth Muscle Tissue Stock Photos Smooth Muscle Tissue
Smooth Muscle Tissue Stock Photos Smooth Muscle Tissue

 Smooth Muscle Tissue Smooth Muscle Tissue Muscle Anatomy
Smooth Muscle Tissue Smooth Muscle Tissue Muscle Anatomy
 Anatomy And Physiology The Muscular System Smooth Muscle
Anatomy And Physiology The Muscular System Smooth Muscle
 Anatomy And Cell Biology 3319 Lecture Notes Fall 2017
Anatomy And Cell Biology 3319 Lecture Notes Fall 2017
![]() Icon Of Smooth Muscle Cell Under Microscope Human Anatomy Concept
Icon Of Smooth Muscle Cell Under Microscope Human Anatomy Concept
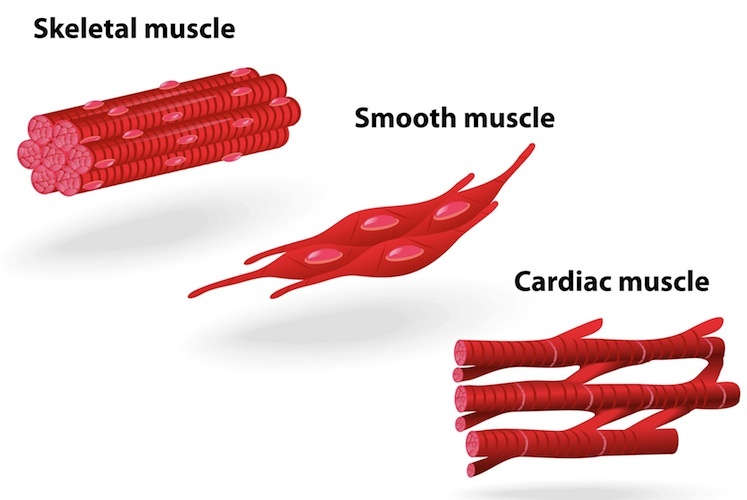 Muscle Structure Muscle Under The Microscope Science
Muscle Structure Muscle Under The Microscope Science
 Skeletal Muscle Smooth Muscle And The Cardiac Muscle Are
Skeletal Muscle Smooth Muscle And The Cardiac Muscle Are
Muscles And Their Types Human Anatomy
 Human Smooth Muscle How Many Smooth Muscles In The Human
Human Smooth Muscle How Many Smooth Muscles In The Human
 Smooth Muscle Physiology Youtube
Smooth Muscle Physiology Youtube
 Smooth Muscle Definition Function And Location Biology
Smooth Muscle Definition Function And Location Biology
 Musculoskeletal System Skeletal Muscle Anatomy
Musculoskeletal System Skeletal Muscle Anatomy
 Contraction Of Skeletal And Smooth Muscles
Contraction Of Skeletal And Smooth Muscles
 Anatomy Of Human Cells Neuron Red And White Blood Cell Columnar
Anatomy Of Human Cells Neuron Red And White Blood Cell Columnar
 Smooth Muscle Anatomy Stock Vectors Images Vector Art
Smooth Muscle Anatomy Stock Vectors Images Vector Art
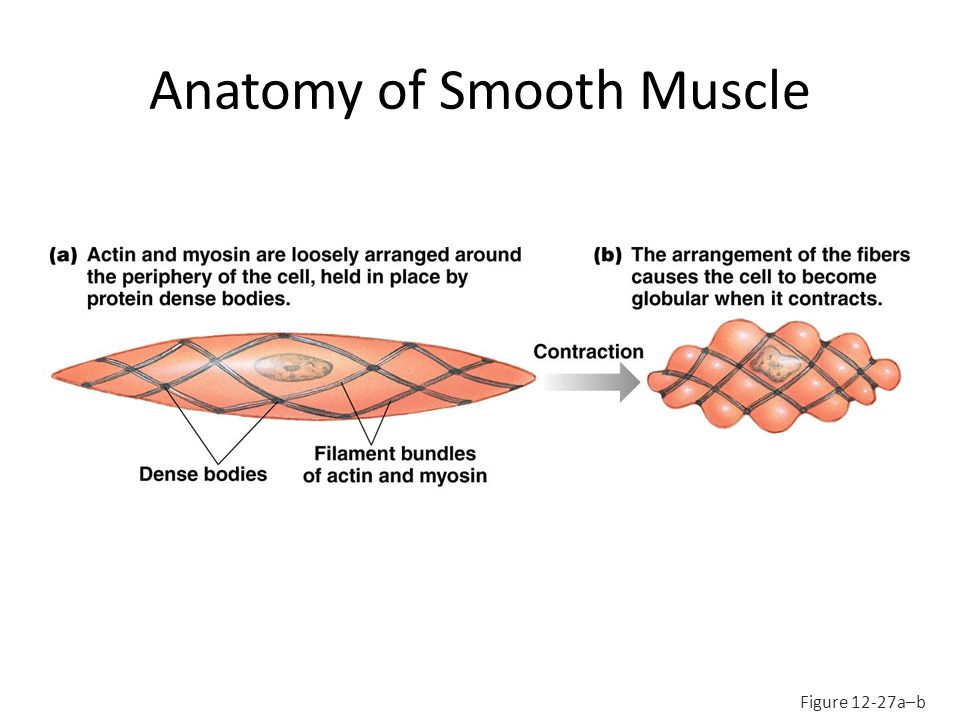 Windsor University School Of Medicine Ppt Download
Windsor University School Of Medicine Ppt Download
 Smooth Muscle Cell Vector Anatomy Relaxed And Contracted
Smooth Muscle Cell Vector Anatomy Relaxed And Contracted
 Smooth Muscle Anatomy Stock Vectors Images Vector Art
Smooth Muscle Anatomy Stock Vectors Images Vector Art
 Smooth Muscle Cell Vector Anatomy Relaxed Royalty Free
Smooth Muscle Cell Vector Anatomy Relaxed Royalty Free
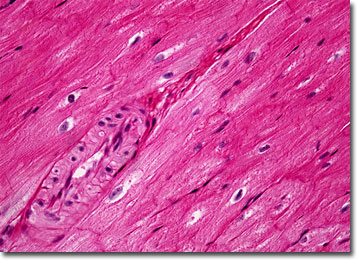 Molecular Expressions Microscopy Primer Anatomy Of The
Molecular Expressions Microscopy Primer Anatomy Of The




Belum ada Komentar untuk "Smooth Muscle Anatomy"
Posting Komentar