Anatomy Of Echinoderms
Anatomy of a starfish echinoderms. These are microscopic in sea cucumbers.
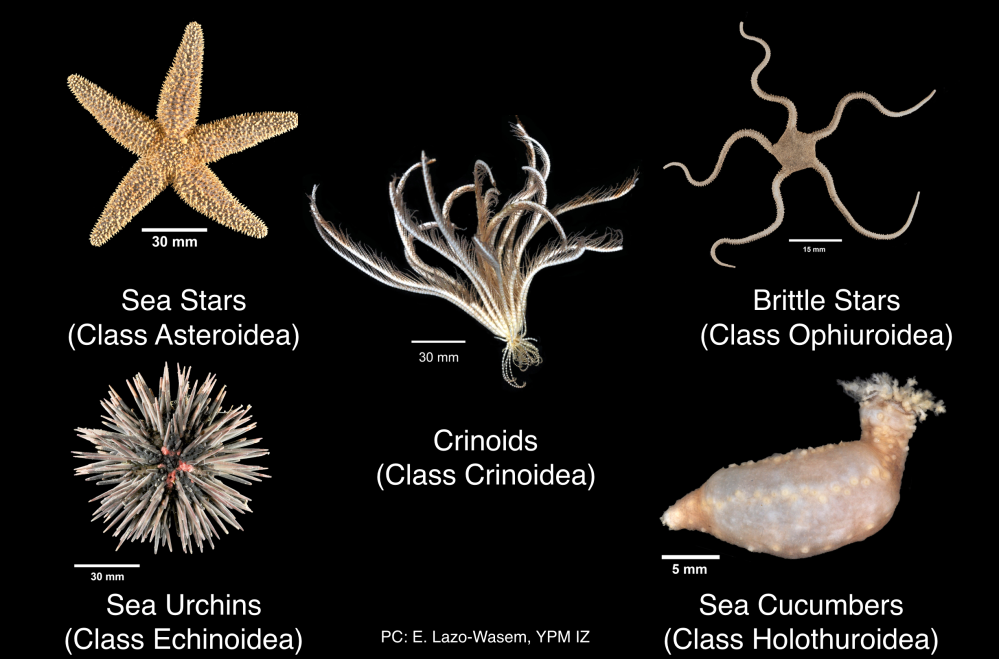 In Focus What S So Great About Echinoderms These 9 Facts
In Focus What S So Great About Echinoderms These 9 Facts
They have a calcite endoskeleton composed of many tiny plates and spines.

Anatomy of echinoderms. Nerves radiate from central rings around the mouth into each arm or along the body wall. Form and function of external features general features. Many of the earliest echinoderms either lacked symmetry or were bilaterally.
This species is also known as sea star. In sea cucumbers the skeleton is made of degenerated calcareous plates buried in the fleshy body. Anatomy is the study of the internal and external structures present in an organism.
Beginning with the dawn of the cambrian period 542 million to 488 million years ago echinoderms have a rich fossil history and are well represented. Like vertebrates and unlike other animal phyla echinoderms are denterostomes meaning the mouth pore forms after the anal pore during early development. This makes them ideal subjects for studies.
Large and centrally located between the mouth and anus is the stomach where food is digested a. Echinoderms have a simple radial nervous system that consists of a modified nerve net consisting of interconnecting neurons with no central brain although some do possess ganglia. The areas with such holes are called ambulacra.
An echinoderm has five fold radial symmetry when its an adult with five arms and spines or bumps all over its body. Echinoderms have a skeleton composed of numerous plates of mineral calcium carbonate. That is why they look softer.
The mouth is on the opposite side of the anus food is taken in here. This forms within the tissues a kind of firm support for the organism. General anatomy echinoderms have radial symmetry which means they are divided into 5 equal sections radiating from a central point.
Starfish are echinoderms and belong to the class asteroidea. The skeleton is dermal but nonetheless. Echinoderm any of a variety of invertebrate marine animals belonging to the phylum echinodermata characterized by a hard spiny covering or skin.
The radially symmetrical body cavity contains a system of water filled canals unique to echinoderms. Symmetry and body form. These are found in the pacific atlantic indian and even the arctic and southern oceans.
The third but the most important characteristic trait is their water vascular system. Similarly the anatomy of the starfish reveals that its skeleton is made from movable calcareous plates thus forming flexible joints. Echinoderms are relatives although distant ones of the vertebrates.
The branches of these nerves coordinate the movements of the organism and the synchronisation of the tube feet. The anus is found on the top of a starfish this is where wastes are removed. In each segment there is an identical set of internal organs.
Called the water vascular or ambulacral system it connects with the tube feet or podia which are extensions of the body wall that generally protrude through holes in the skeleton.
 Echinodermata Chordata Biology 230 With Gerbec At
Echinodermata Chordata Biology 230 With Gerbec At
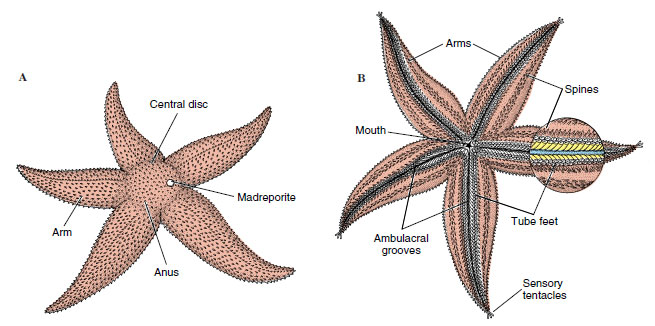 Class Asteroidea Echinoderms The Diversity Of Animal Life
Class Asteroidea Echinoderms The Diversity Of Animal Life
Animal Kingdom Simple Organisms And Echinoderms
 Phylum Echinodermata There Are More Than 5000 Species Of
Phylum Echinodermata There Are More Than 5000 Species Of
 Echinoderms Asteroidea Phylogeny Anatomy Physiology And
Echinoderms Asteroidea Phylogeny Anatomy Physiology And
 End Show Slide 1 Of 37 Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall 28 4
End Show Slide 1 Of 37 Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall 28 4
 Convergent Evolution Of Embryonic Development In Echinoderms
Convergent Evolution Of Embryonic Development In Echinoderms
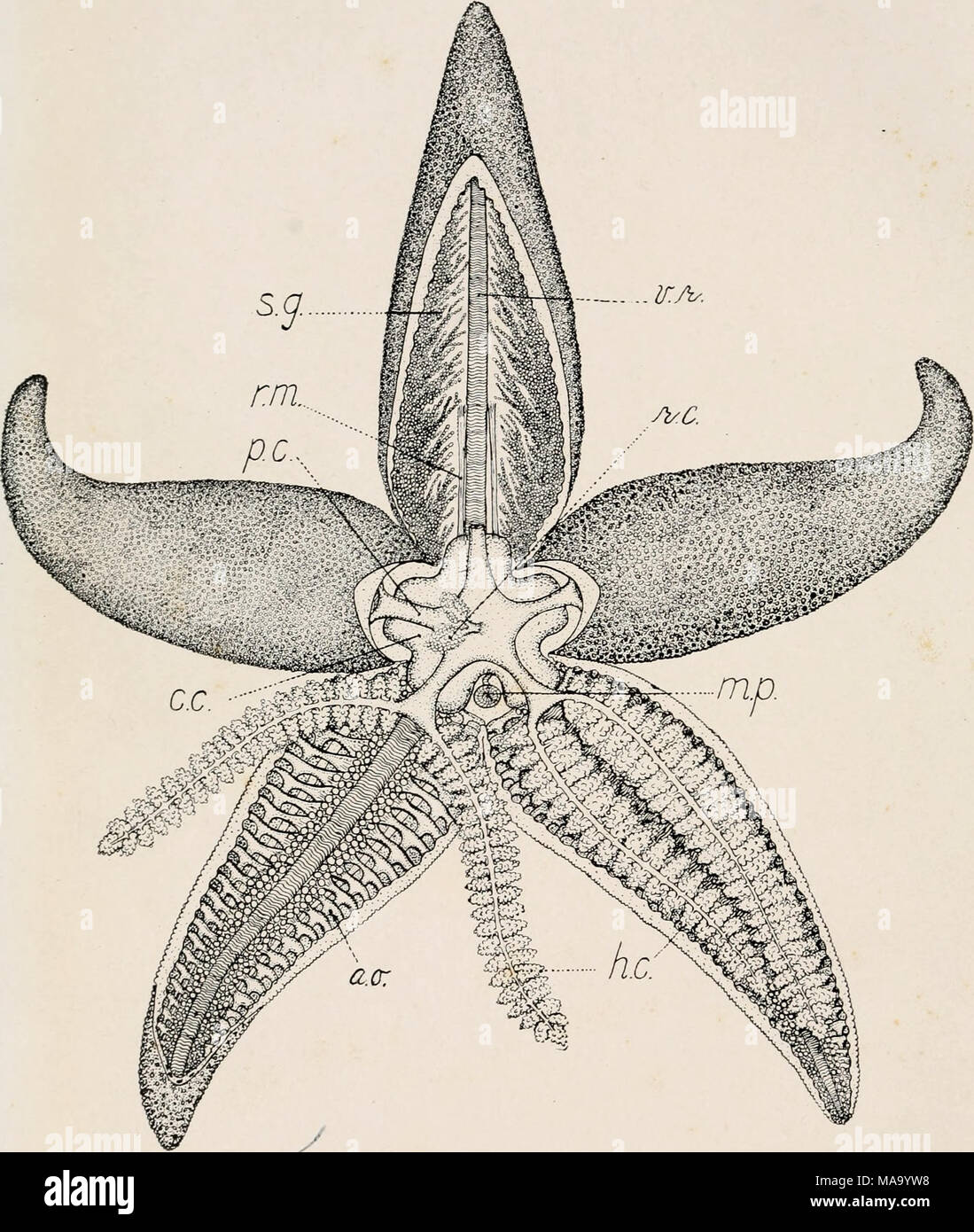 Echinoderms Of Connecticut Plate V Anatomy Of Starfish
Echinoderms Of Connecticut Plate V Anatomy Of Starfish
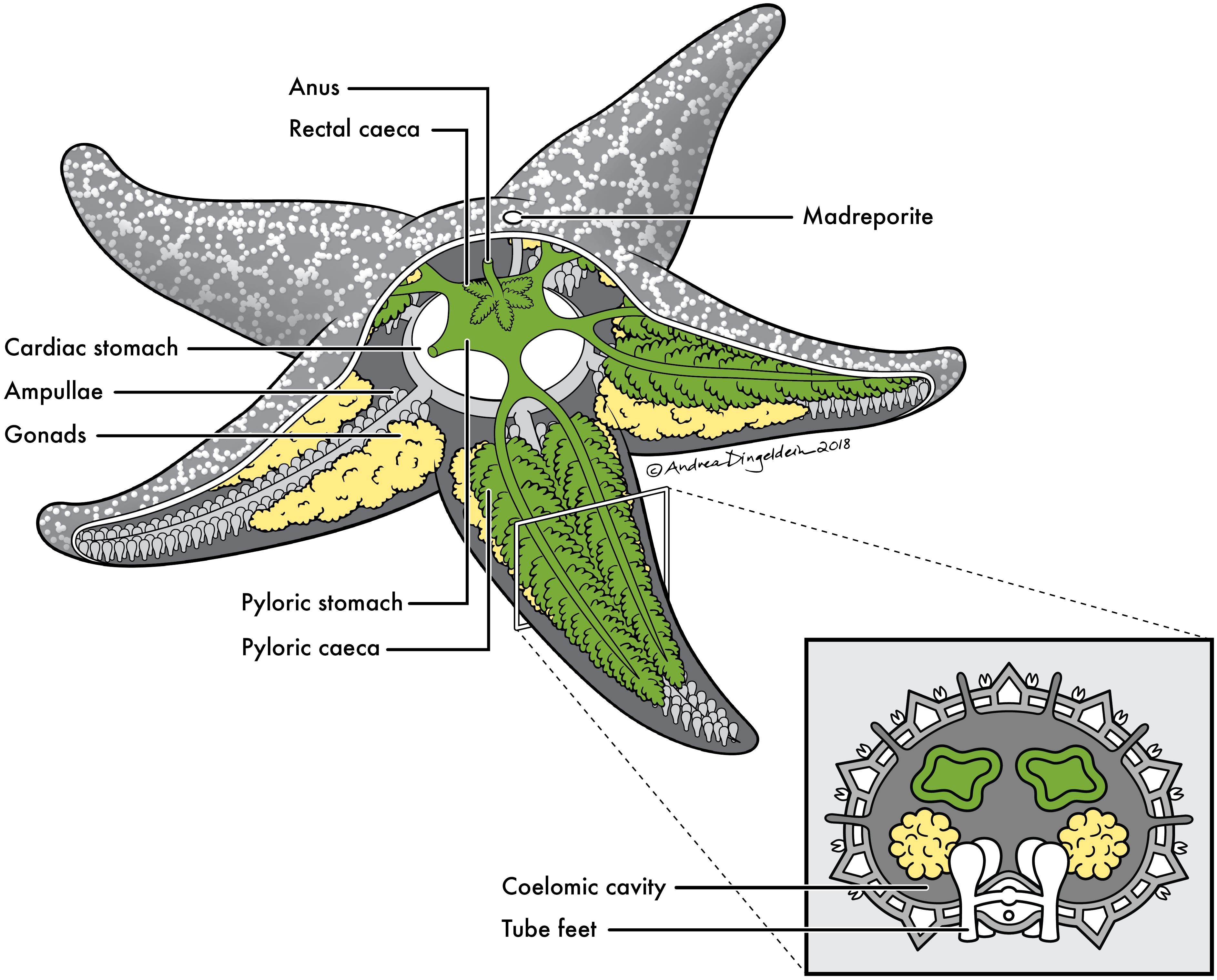 Frontiers The Microbial Landscape Of Sea Stars And The
Frontiers The Microbial Landscape Of Sea Stars And The

 The Two Current Interpretations H1 And H2 Of Stylophoran
The Two Current Interpretations H1 And H2 Of Stylophoran
 Pharmacological And Chemical Properties Of Some Marine
Pharmacological And Chemical Properties Of Some Marine

 Echinodermata Article About Echinodermata By The Free
Echinodermata Article About Echinodermata By The Free
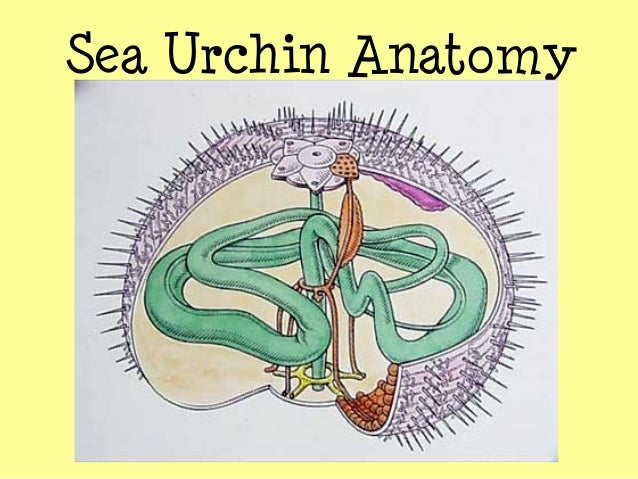
 Echinoderms Asteroidea Phylogeny Anatomy Physiology And
Echinoderms Asteroidea Phylogeny Anatomy Physiology And



/Sea-star-regenerating-Galapagos-Jonathan-Bird-getty-56a5f76f3df78cf7728abeb8.jpg)
Belum ada Komentar untuk "Anatomy Of Echinoderms"
Posting Komentar