Anatomy Of Normal Heart
The heart is made up of the two atria which receive blood and two ventricles which are the actual pumps of the heart. Exercise emotions fever and some medications can cause your heart to beat faster sometimes to well over 100 beats per minute.
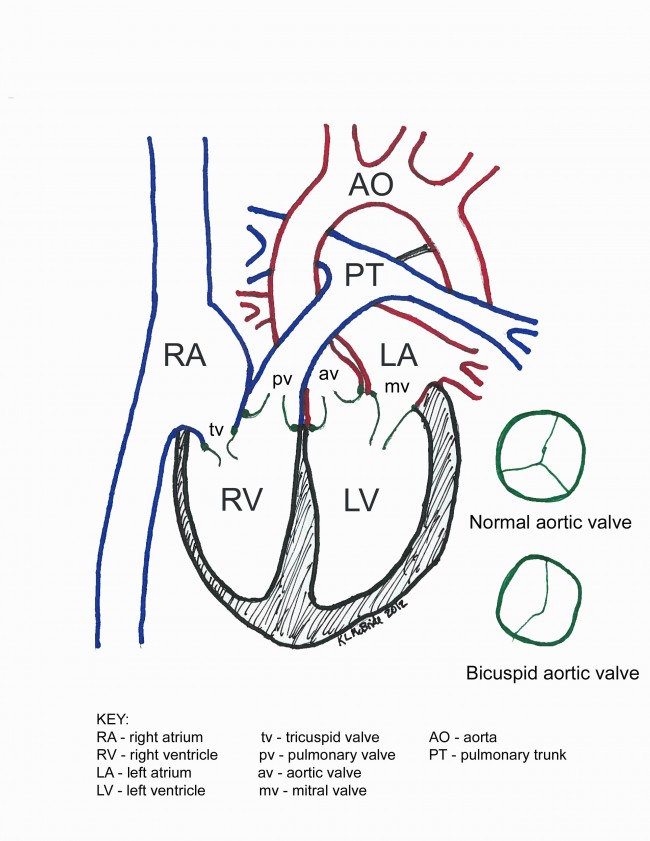 Normal Heart Anatomy Pediacast
Normal Heart Anatomy Pediacast
The shape of the heart is similar to a pinecone rather broad at the superior surface and tapering to the apex.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/heart_electrical_system-597907ca03f4020010e78125.jpg)
Anatomy of normal heart. The right atrium ra and the right ventricle rv pump deoxygenated blood to the lungs where it becomes oxygenated. Epicardium protective layer mostly made of connective tissue. The lv is the main pump that delivers the newly oxygenated blood to the rest of the body.
The two lower chambers are known as the ventricles and the two upper chambers are the atria. Myocardium the muscles of the heart. The left ventricle pumps blood into the aorta sending oxygenated blood to the rest of the body.
This oxygen rich blood returns to the left atrium la and then enters the left ventricle lv. Basic anatomy of the heart. Shape and size of the heart.
De oxygenated blood returns to the right side of the heart via the venous circulation. Endocardium lines the inside of the heart and protects the valves and chambers. The heart itself is made up of 4 chambers 2 atria and 2 ventricles.
At rest a normal heart beats around 50 to 99 times a minute. A typical heart is approximately the size of your fist. 12 cm 5 in in length 8 cm 35 in wide and 6 cm 25 in in thickness.
The heart pumps blood through the network of arteries and veins called the. Heart disease is very common disrupting the normal function of this important organ and often causing death. The wall of the heart consists of three layers of tissue.
A beginners guide to normal heart function sinus rhythm common cardiac arrhythmias. Normal heart anatomy the main function of the heart is to deliver oxygen rich blood to every cell in the body. The average heart can push around 5 to 55 liters per minute at rest.
Normal heart anatomy and physiology. Heart rate is the number of heartbeats per minute. The hearta hollow musclehas four chambers that are kept in place by thick walls of tissue known as the septum.
The arteries are the passageways through which the blood is delivered and the veins are the passageways through which the blood is collected and returned to the heart. The heart is a muscular organ about the size of a fist located just behind and slightly left of the breastbone.

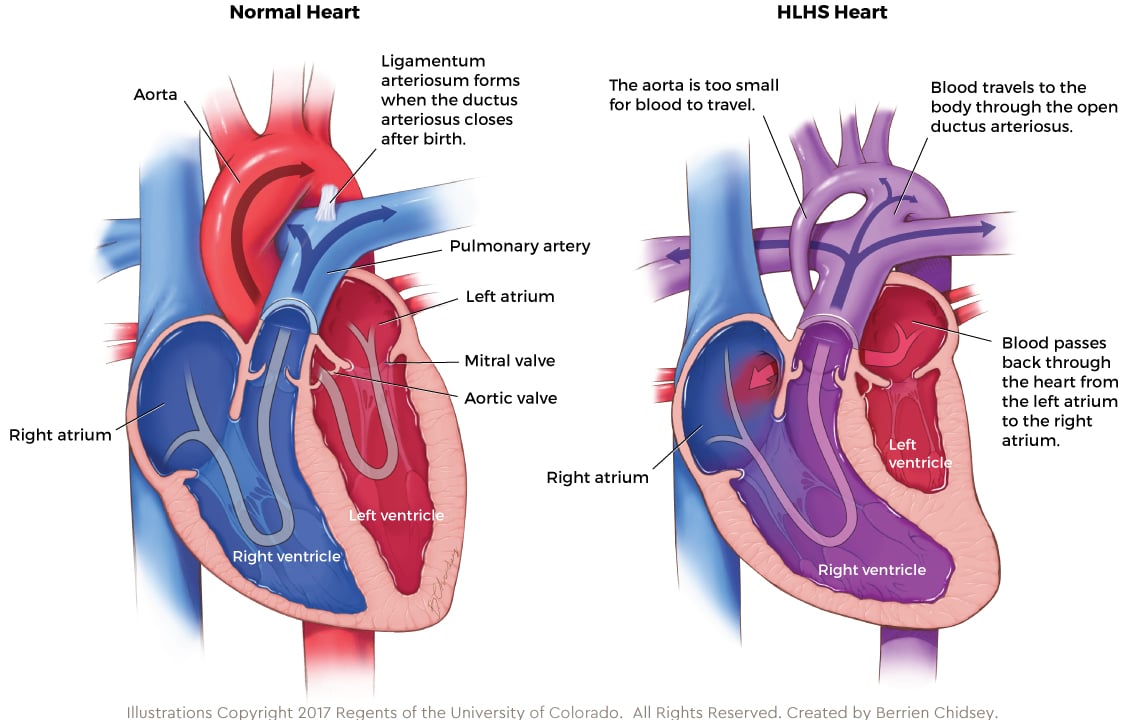 Single Ventricle Surgery Children S Hospital Colorado
Single Ventricle Surgery Children S Hospital Colorado
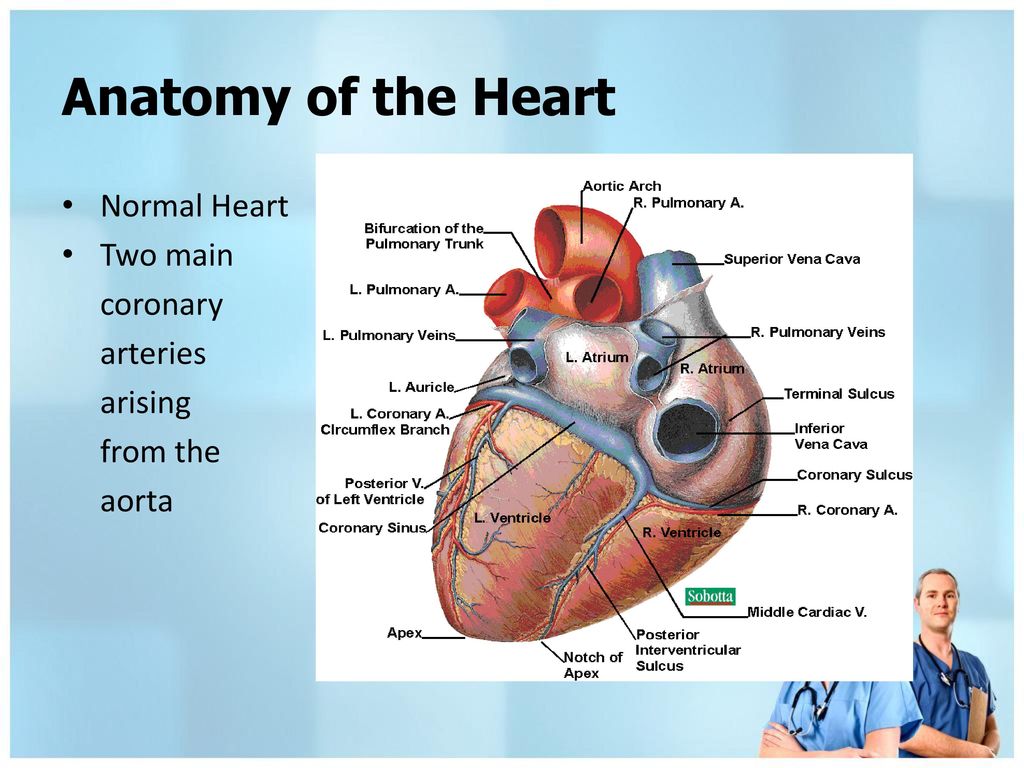 Anatomy Of The Heart And Lungs And Thoracic Surgery Ppt
Anatomy Of The Heart And Lungs And Thoracic Surgery Ppt
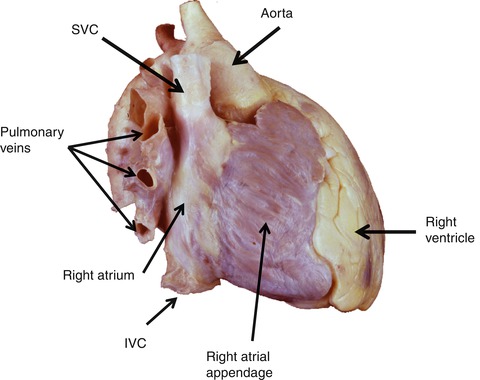 Normal Cardiac Anatomy And Clinical Evaluation Springerlink
Normal Cardiac Anatomy And Clinical Evaluation Springerlink
 Normal Heart Electrical Conduction And Atrial Fibrillation
Normal Heart Electrical Conduction And Atrial Fibrillation
Innocent Heart Murmur Congenital Children S Heart Centre
 Science Source Normal Heart Exterior And Interior
Science Source Normal Heart Exterior And Interior
 Normal Heart Anatomy La Left Atrium Lv Left Ventricle
Normal Heart Anatomy La Left Atrium Lv Left Ventricle
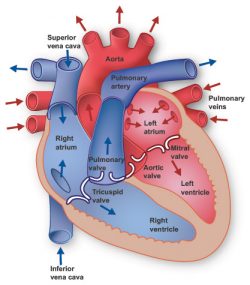 Heart Information Center Heart Anatomy Texas Heart Institute
Heart Information Center Heart Anatomy Texas Heart Institute
 Cross Section Of A Normal Heart License Download Or Print
Cross Section Of A Normal Heart License Download Or Print
 Science Source Normal Heart And Artery Illustration
Science Source Normal Heart And Artery Illustration
 Structure Of The Heart A Anatomy Of A Normal Healthy Heart
Structure Of The Heart A Anatomy Of A Normal Healthy Heart
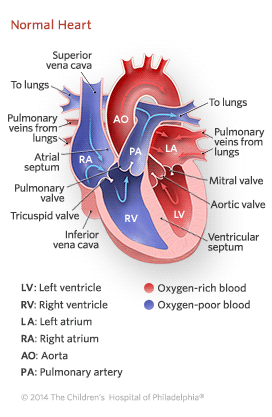 How The Normal Heart Works Children S Hospital Of Philadelphia
How The Normal Heart Works Children S Hospital Of Philadelphia
 Science Source Normal Heart Exterior And Interior
Science Source Normal Heart Exterior And Interior
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/heart_electrical_system-597907ca03f4020010e78125.jpg) Overview Of Sinoatrial And Atrioventricular Heart Nodes
Overview Of Sinoatrial And Atrioventricular Heart Nodes
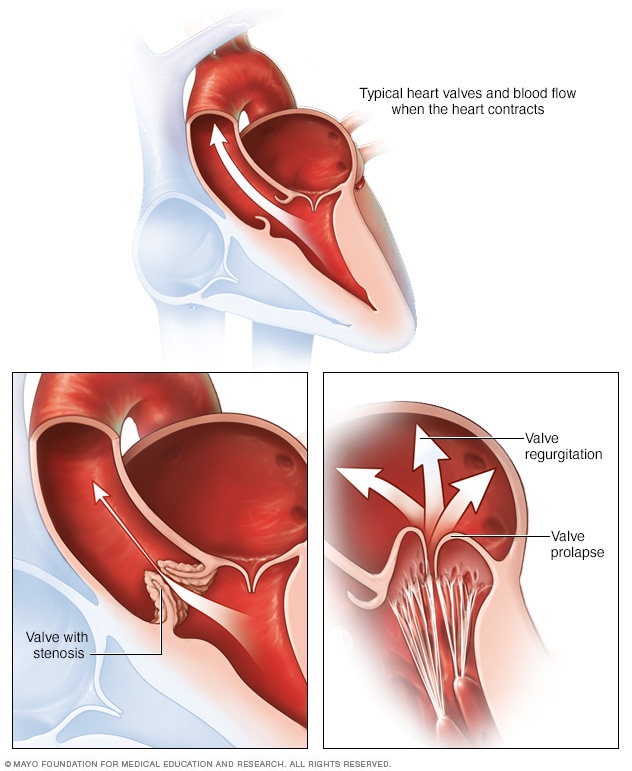 A Normal Heart And Heart Valve Problems Mayo Clinic
A Normal Heart And Heart Valve Problems Mayo Clinic
 Ce Article Diagnosis And Treatment Of The Patient With
Ce Article Diagnosis And Treatment Of The Patient With
 The Heart Anatomy Physiology And Function
The Heart Anatomy Physiology And Function
 Normal Heart Anatomy Vs Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome Hlhs Anatomy
Normal Heart Anatomy Vs Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome Hlhs Anatomy
Congenital Defects Tutorial Congenital Heart Defects
 Normal Cardiac Anatomy The Blue Arrows Give The Flow Of
Normal Cardiac Anatomy The Blue Arrows Give The Flow Of
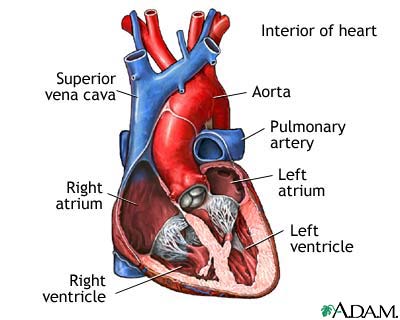 Normal Heart Anatomy Cut Section Medlineplus Medical
Normal Heart Anatomy Cut Section Medlineplus Medical
 Acls Normal Heart Anatomy And Physiology
Acls Normal Heart Anatomy And Physiology
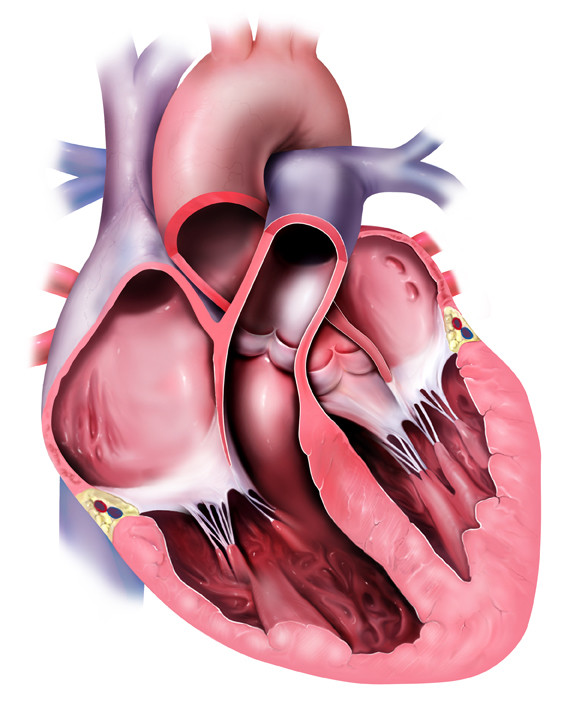 Normal Heart In Cross Section And Pulmonary Outflow Tract
Normal Heart In Cross Section And Pulmonary Outflow Tract
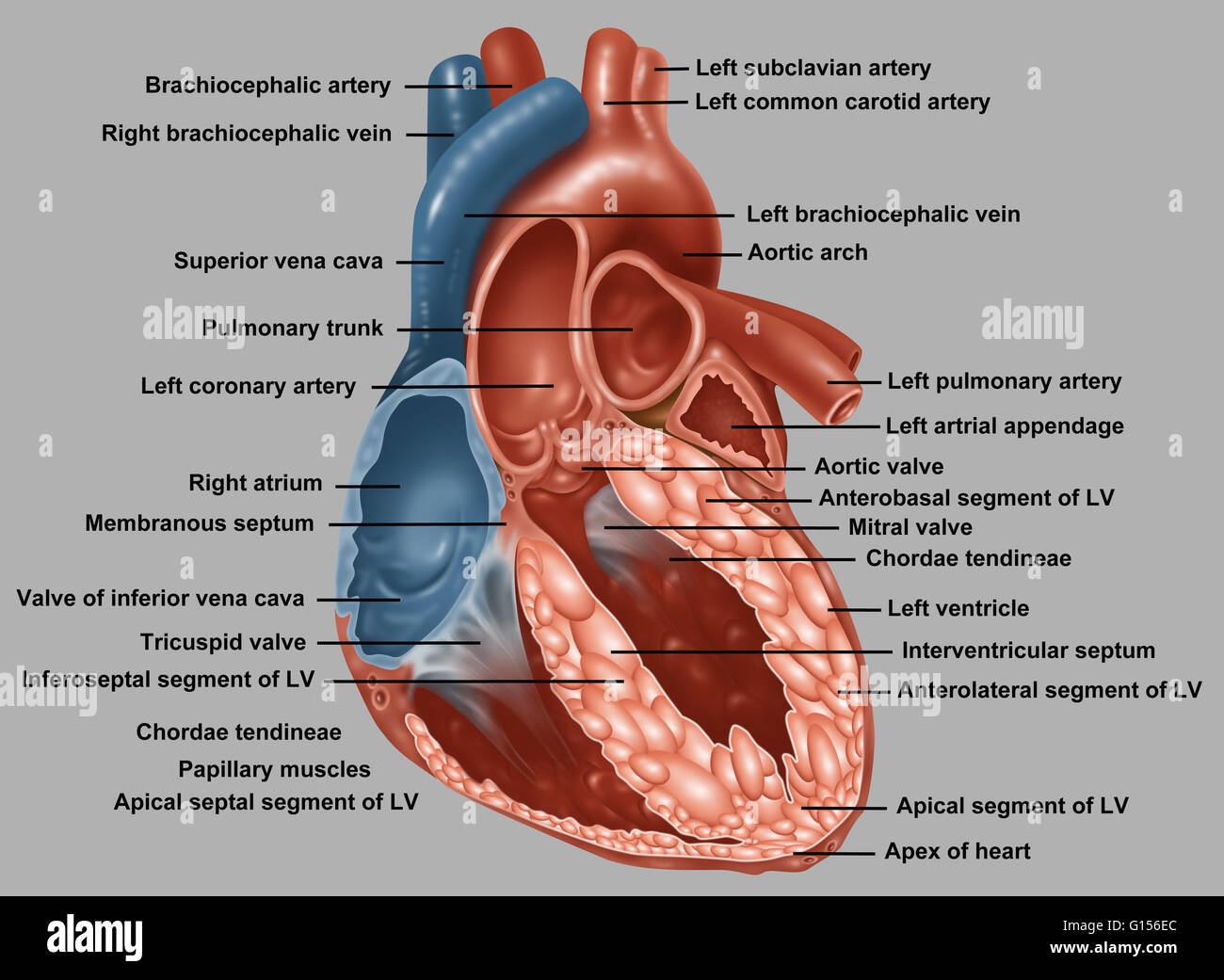 Anatomy Normal Human Heart Everything Stock Photos Anatomy
Anatomy Normal Human Heart Everything Stock Photos Anatomy
 Human Heart Normal Rhythm And Heart Anatomy
Human Heart Normal Rhythm And Heart Anatomy


Belum ada Komentar untuk "Anatomy Of Normal Heart"
Posting Komentar