Nerve Anatomy Of Foot
The nerves of the foot help move the body and keep balance both while its moving and at rest. This nerve is a branch of the femoral nerve and runs down the medial portion of the leg to the medial part of the foot and innervates the skin on the medial side of the ankle and foot.
A viral infection in the sole of the foot that can form a callus with a central dark spot.

Nerve anatomy of foot. As such when the sciatic nerve is impaired it can lead to muscle weakness andor numbness or tingling in the leg ankle foot andor toes. The sural nerve branches from the tibial and common fibular nerves and is responsible for feeling on the outside of the foot and the small toe. Pain swelling redness and bruising may be signs of a fracture.
Many times an injured nerve will cause intense pain and heat felt within the foot. Terminal branches supply skin on the medial side of the proximal foot and enter the foot in superficial fascia on the medial part of the ankle. Nerves act as a network communicating important information from the foot to the brain.
Problems with nerves in the feet are very common. Lumbircals to 2nd and 3rd toes. Branches of the tibial nerve.
Medial calcaneal nerve innervates plantar medial heel. Saphenous nerve the saphenous nerve is a cutaneous branch of the femoral nerve that originates in the thigh. It innervates the skin on the lateral side of the leg and foot.
At risk proper branch of medial plantar nerve at risk with medial plantar approach to the tibial sesamoid. All of these nerves extend as branches of nerves in the leg that pass through the ankle and into the foot. The sural nerve branches from the tibial and common fibular nerves and is responsible for feeling on the outside of the foot and the small toe.
All of these nerves extend as branches of nerves in the leg that pass through the ankle and into the foot. The anatomy of the nerves of the foot and ankle is complex and familiarity with the normal anatomy and course of these nerves as well as common anatomic variants is essential for correct identifi. It connects the spinal cord with the outside of the thigh the hamstring muscles in the back of the thighs and muscles in the lower leg and feet.
The nerves of the foot help move the body and keep balance both while its moving and at rest. On the sole the nerves of the foot are the medial and lateral plantar nerves which arise from the tibial nerve in the heel. The metatarsal bones are the most frequently broken bones in the feet either from injury or repetitive use.
Medial plantar nerve innervates abductor hallucis. The dorsal digital nerves are those nerves of the foot that cross the top surface and insert in the digits or toes. Clinical anatomy for dummies.
 Axis Scientific 9 Part Foot With Muscles Ligaments Nerves And Arteries
Axis Scientific 9 Part Foot With Muscles Ligaments Nerves And Arteries
 Chapter 38 Foot The Big Picture Gross Anatomy
Chapter 38 Foot The Big Picture Gross Anatomy
 Uncommon Injuries Sural Nerve Neuropathy
Uncommon Injuries Sural Nerve Neuropathy
 Common Fibular Nerve An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Common Fibular Nerve An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
 Foot Nerves Anatomy Pictures Diagram Of Nerves In Foot
Foot Nerves Anatomy Pictures Diagram Of Nerves In Foot
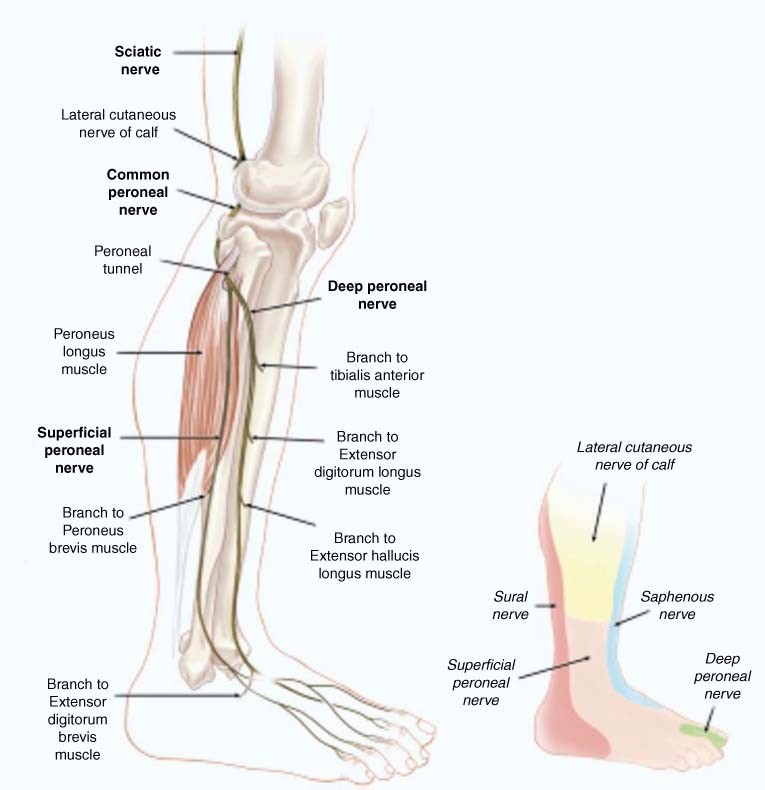 Nerve Entrapments Of The Lower Leg Ankle And Foot In Sport
Nerve Entrapments Of The Lower Leg Ankle And Foot In Sport
:watermark(/images/watermark_only.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/nervi-digitales-dorsales-pedis/7L0lagpXJaemKG5Yi07QOA_Nervi_digitales_dorsales_pedis_01.png) Tibial Nerve Anatomy And Pathology Kenhub
Tibial Nerve Anatomy And Pathology Kenhub
 Ankle Block Landmarks And Nerve Stimulator Technique Nysora
Ankle Block Landmarks And Nerve Stimulator Technique Nysora
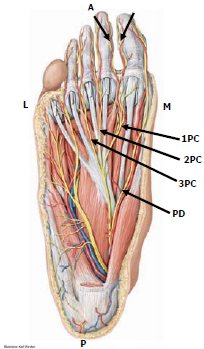
 Ankle Block Landmarks And Nerve Stimulator Technique Nysora
Ankle Block Landmarks And Nerve Stimulator Technique Nysora
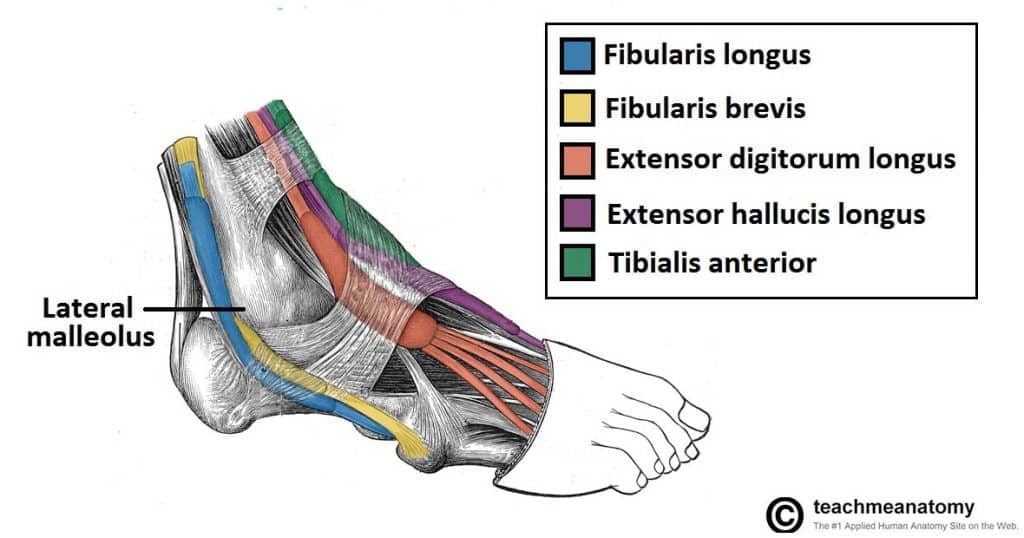 Muscles In The Lateral Compartment Of The Leg Teachmeanatomy
Muscles In The Lateral Compartment Of The Leg Teachmeanatomy
 Dorsal Digital Nerves Of Foot Wikipedia
Dorsal Digital Nerves Of Foot Wikipedia
 The Foot And Ankle Practical Office Orthopedics
The Foot And Ankle Practical Office Orthopedics
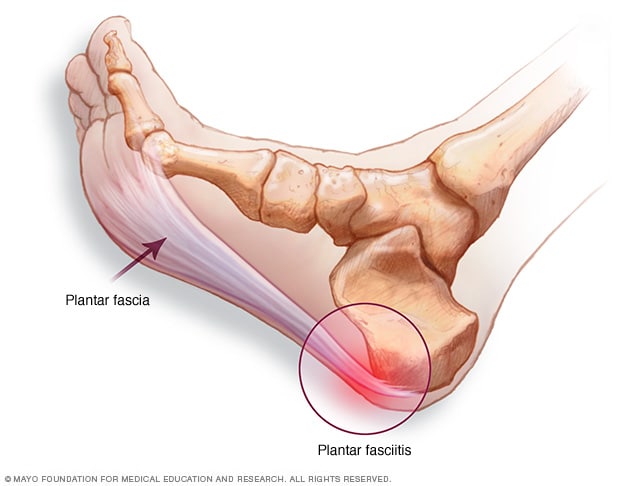 Plantar Fasciitis Symptoms And Causes Mayo Clinic
Plantar Fasciitis Symptoms And Causes Mayo Clinic
 Reasons You Feel Burning In Your Feet
Reasons You Feel Burning In Your Feet
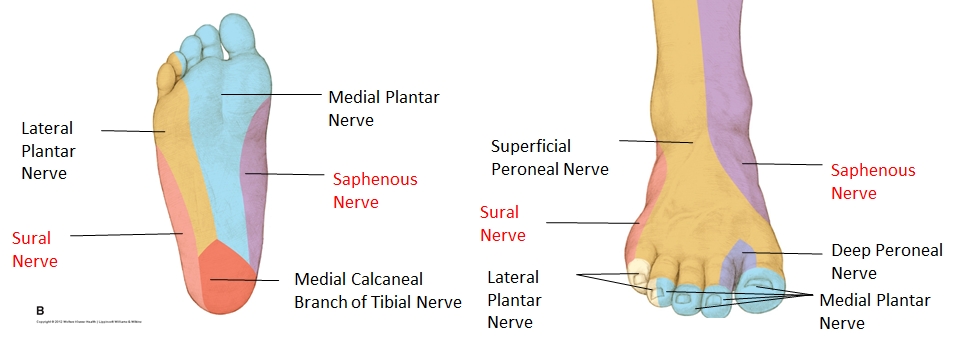

Foot Drop The Causes And Anatomy
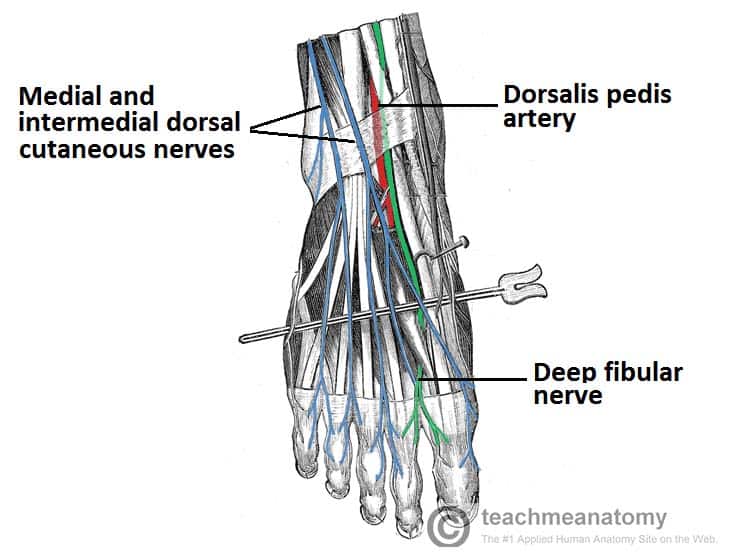 The Deep Fibular Nerve Course Motor Sensory
The Deep Fibular Nerve Course Motor Sensory
 A Anatomy Of Plantar Muscles Digital Nerves And Arteries
A Anatomy Of Plantar Muscles Digital Nerves And Arteries
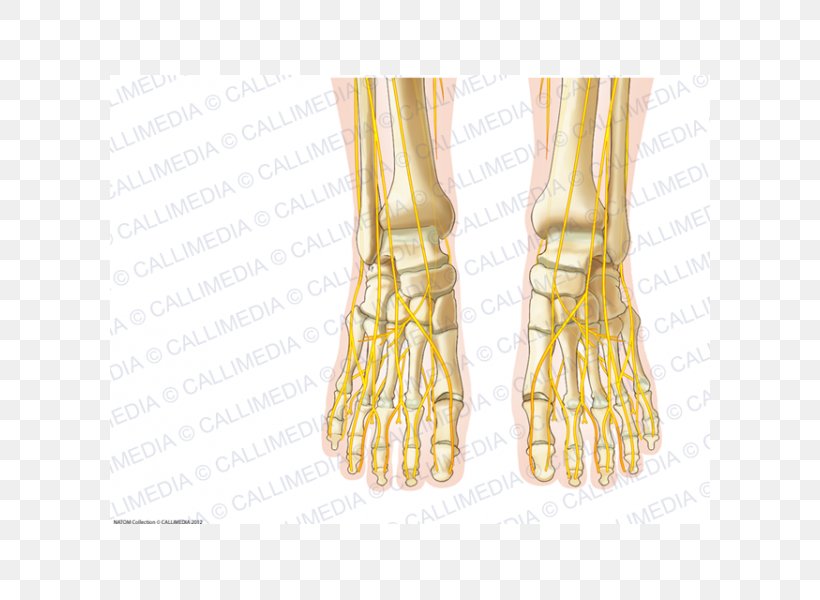 Human Anatomy Foot Nerve Nervous System Png 600x600px
Human Anatomy Foot Nerve Nervous System Png 600x600px
 Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome Foot Ankle Orthobullets
Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome Foot Ankle Orthobullets
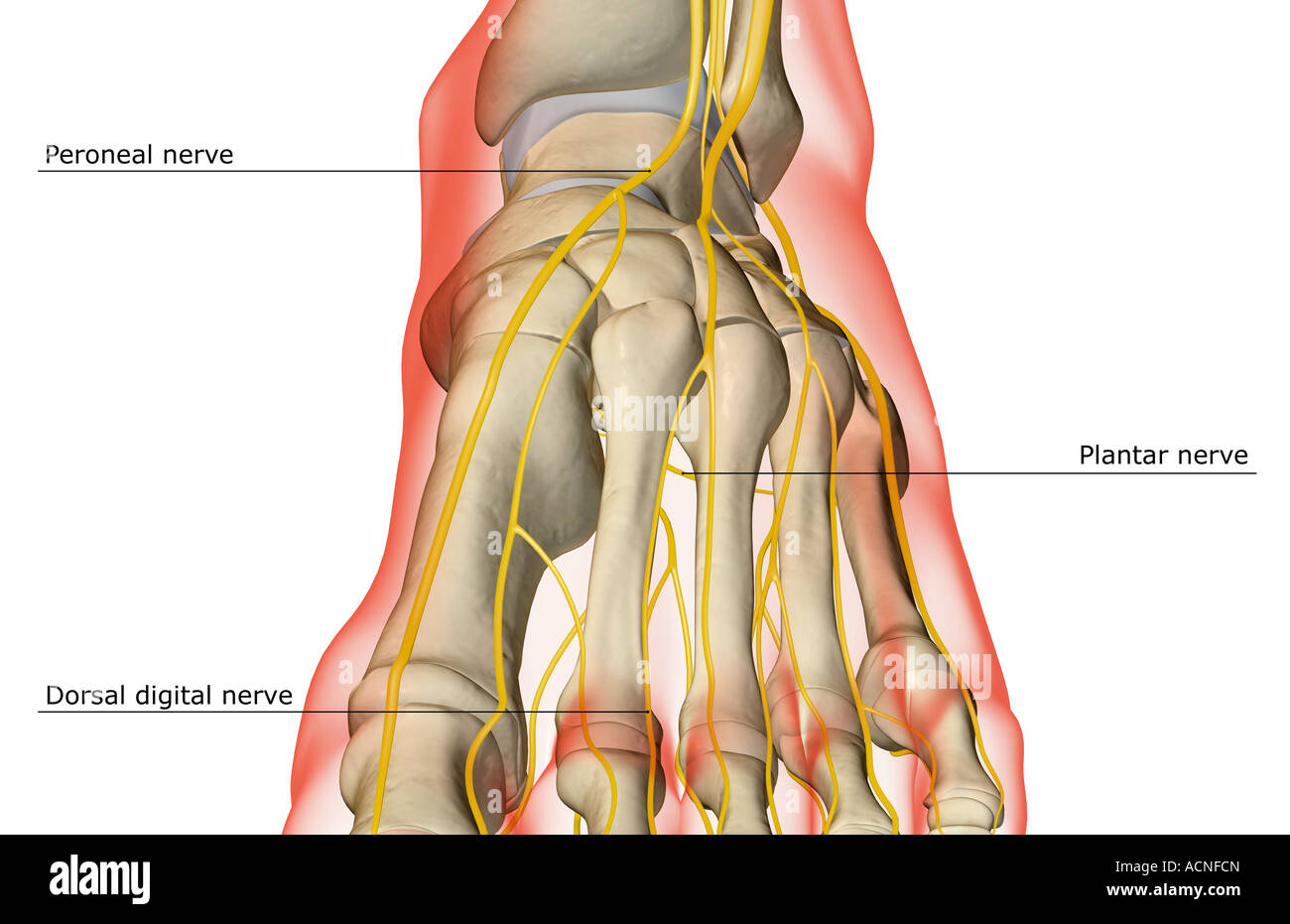 The Nerves Of The Foot Stock Photo 13198340 Alamy
The Nerves Of The Foot Stock Photo 13198340 Alamy
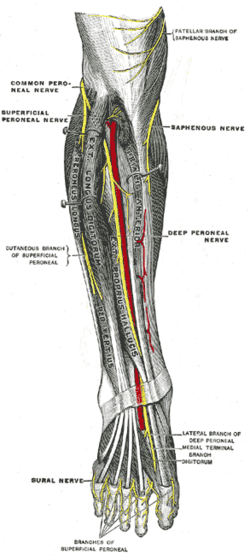 Superficial Peroneal Nerve Wikipedia
Superficial Peroneal Nerve Wikipedia

Belum ada Komentar untuk "Nerve Anatomy Of Foot"
Posting Komentar