Homeostasis Anatomy
The body maintains homeostasis for many factors in addition to temperature. Maintaining homeostasis requires that the body continuously monitor its internal conditions.
Maintaining homeostasis requires that the body continuously monitors its internal conditions.

Homeostasis anatomy. The tendency to maintain a stable relatively constant internal environment is called homeostasis. From body temperature to blood pressure to levels of certain nutrients each physiological condition has a particular set point. Homeostasis is the activity of cells throughout the body to maintain the physiological state within a narrow range that is compatible with life.
The biological definition of homeostasis is the tendency of an organism or cell to regulate its internal environment and maintain equilibrium usually by a system of feedback controls so as to stabilize health and functioning. Homeostasis is the dynamic equilibrium that maintains health within the body in spite of the continual changes taking place both internally and in the external environment. A set point is the physiological value around which the normal range fluctuates.
A normal range is the restricted set of values that is optimally healthful and stable. Homeostasis refers to the bodys ability to maintain a stable internal environment regulating hormones body temp water balance etc. Generally the body is in homeostasis when its needs are met and its functioning properly.
For instance the concentration of various ions in your blood must be kept steady along with ph and the concentration of glucose. A set point is the physiological value around which the normal range fluctuates. Homeostasis is regulated by negative feedback loops and much less frequently by positive feedback loops.
From body temperature to blood pressure to levels of certain nutrients each physiological condition has a particular set point. This is achieved by attempting to maintain a constant internal state and all the systems of the body are involved in the effort.

 How Does The Respiratory System Maintain Homeostasis
How Does The Respiratory System Maintain Homeostasis
 Introduction To Anatomy And Physiology
Introduction To Anatomy And Physiology
 Animal And Plant Homeostasis And Physiology Study Guides
Animal And Plant Homeostasis And Physiology Study Guides
 Human Anatomy And Physiology Homeostasis
Human Anatomy And Physiology Homeostasis
 Human Anatomy And Physiology Form Function And
Human Anatomy And Physiology Form Function And
15 06 09 The Role Of Hormones In Homeostasis
 Introduction To Anatomy Physiology Homeostasis Health 01 05
Introduction To Anatomy Physiology Homeostasis Health 01 05
 Biol 3160 Lecture Notes Fall 2017 Lecture 1 Anabolism
Biol 3160 Lecture Notes Fall 2017 Lecture 1 Anabolism
 Gcse Biology The Organs Involved In Homeostasis
Gcse Biology The Organs Involved In Homeostasis
 Anatomy Physiology Ph Balance Homeostasis Activity Acid Base Ph Balance
Anatomy Physiology Ph Balance Homeostasis Activity Acid Base Ph Balance
 Unit 14 Homeostasisfinal Pdf Unit 14 Homeostasis Health
Unit 14 Homeostasisfinal Pdf Unit 14 Homeostasis Health
How Do We Make Sense Of Different Components Of Anatomy And
 Online Workshop 1 Definitions And Homeostasis 102bms
Online Workshop 1 Definitions And Homeostasis 102bms
 Human Anatomy And Physiology Theory
Human Anatomy And Physiology Theory
 Homeostasis Loop Human Anatomy Drawing Physiology Video 4
Homeostasis Loop Human Anatomy Drawing Physiology Video 4
 Anatomy Final Chpt 1 Diagram Quizlet
Anatomy Final Chpt 1 Diagram Quizlet
 03 Homeostasis Anatomy Physiology Biol121 With Morris
03 Homeostasis Anatomy Physiology Biol121 With Morris
 Homeostasis Anatomy Birth Body En Homeostatis Human
Homeostasis Anatomy Birth Body En Homeostatis Human
 Homeostasis Human Physiology Lecture
Homeostasis Human Physiology Lecture
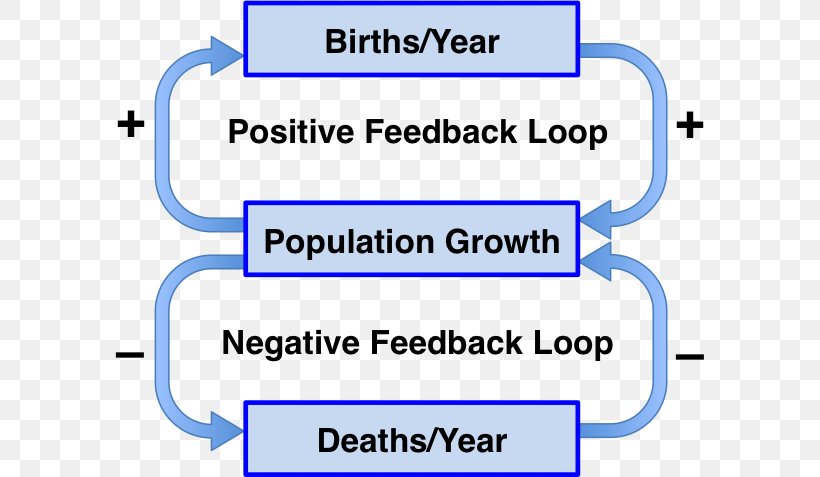 Negative Feedback Positive Feedback Homeostasis Biology Png
Negative Feedback Positive Feedback Homeostasis Biology Png
 Anatomy And Physiology Semester 1 Final Project Group 1
Anatomy And Physiology Semester 1 Final Project Group 1
 Btec Level 3 Health And Social Care Unit 5 Anatomy And Physiology Homeostasis
Btec Level 3 Health And Social Care Unit 5 Anatomy And Physiology Homeostasis
 Chapter 1 Introduction To Anatomy And Physiology
Chapter 1 Introduction To Anatomy And Physiology
 What Is Homeostasis Anatomy And Physiology
What Is Homeostasis Anatomy And Physiology
 Picture Of Homeostasis Picture Of Homeostasis Toxtutor
Picture Of Homeostasis Picture Of Homeostasis Toxtutor
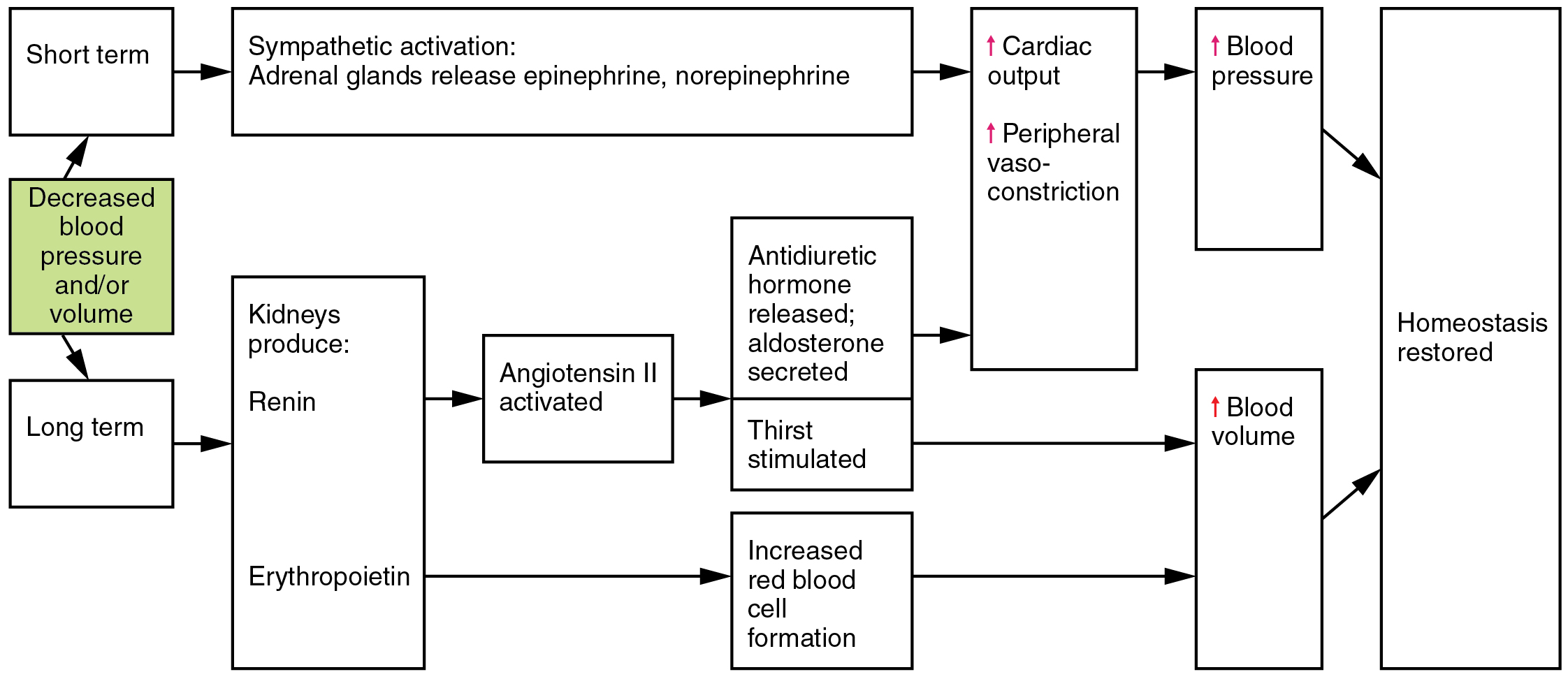 20 4 Homeostatic Regulation Of The Vascular System Anatomy
20 4 Homeostatic Regulation Of The Vascular System Anatomy
Homeostasis And Plant Anatomy Leology


Belum ada Komentar untuk "Homeostasis Anatomy"
Posting Komentar