Spinal Anesthesia Anatomy
Both spinal and epidural anesthesia have been shown to produce sudden unexplained bradycardia or even asystole 170 1 note. Cardioaccelerators are from t1 4.
 Anesthesia Regional Anesthesia
Anesthesia Regional Anesthesia
Vascular surgery on the legs.

Spinal anesthesia anatomy. The injection is usually made in the lumbar spine below the level at which the spinal cord ends l2. Nephrectomy and cystectomy in combination with. Spinal anaesthesia is induced by injecting small amounts of local anaesthetic into the cerebro spinal fluid csf.
In transverse section the cord comprises a central canal an h shaped zone of grey matter nerve cells and an outer zone of white matter nerve fibers. Spinal anesthesia is performed by placing a needle between the lumbar vertebrae and through the dura to inject anesthetic medication. When locating the midline the following should be noted.
Each limb consists of an short broad anterior column anterior horn. Inevitably what is revealed by dissection even in a living subject. Further work with hyperbaric solutions of ropivacaine in the day case setting is required to demonstrate if this would be a suitable alternative to lidocaine.
If the anesthesia provider is unable to palpate the spinous process identifying the gluteal crease may help identify midline. Below this spinal nerves are numbered according to the vertebral body above. The eighth cervical nerve exits from below the seventh cervical vertebral body.
The spinal nerve roots and spinal cord serve as the target sites for spinal anesthesia. Endovascular aortic aneurysm repair. An agent with a similar recovery profile to lidocaine 5 without neurological complications would be of benefit.
The h shaped grey matter is termed as the transverse commisure. Spinal processes are generally palpable and define midline. Anatomy of the bony spine and vertebrae are discussed in more detail separately figure 1 and figure 2.
Spinal anaesthesia anatomy physiology. Update in anaesthesia. Orthopaedic surgery on the pelvis hip femur knee tibia and ankle.
Surface anatomy is important to help identify the correct area to place a neuraxial block. Pre existing 1st degree block may be a risk factor for progressing to a 2nd or 3rd degree block during spinal anesthesia. Spinal anesthesia also known as subarachnoid blockade or spinal block is a type of regional anesthesia in which the lower half of the body is anesthetized by injecting an anesthetic agent in the subarachnoid space surrounding the spinal cord.
Some old and new findings. Anatomy of spinal anesthesia. Cervical spinal nerves 1 to 7 are numbered according to the vertebral body below.
Also preservation by desiccation or embalming alters the consistency of tissues and death disrupts the balance of pressures in the csf and vessels that hold the spinal contents in position. Hernia inguinal or epigastric. Procedures which use spinal anesthesia include.
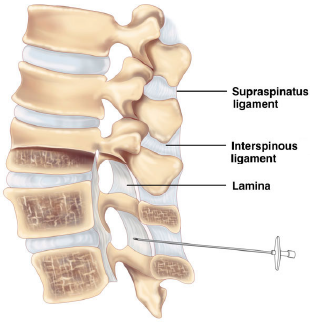 Techniques For Performing Paramedian Approach To Lumbar
Techniques For Performing Paramedian Approach To Lumbar
Regional Anesthesia In The Anticoagulated Patient Nysora
 World S First Ai Powered Ultrasound Guided Automated Spinal
World S First Ai Powered Ultrasound Guided Automated Spinal
Regional Anesthesia In The Anticoagulated Patient Nysora
 Anesthesia Different Types Local Regional Spinal
Anesthesia Different Types Local Regional Spinal
 Level 5 Module 5 The Spinal Cord
Level 5 Module 5 The Spinal Cord
 Lumbar Plexus Block Hadzic S Peripheral Nerve Blocks And
Lumbar Plexus Block Hadzic S Peripheral Nerve Blocks And
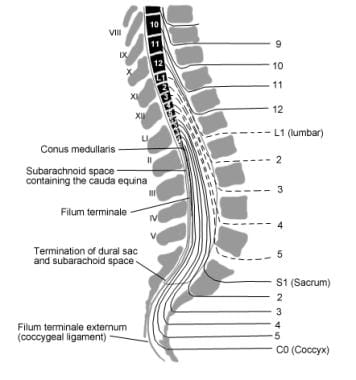 Subarachnoid Spinal Block Overview Periprocedural Care
Subarachnoid Spinal Block Overview Periprocedural Care
 Spinal Epidural And Caudal Anesthesia Anatomy Physiology
Spinal Epidural And Caudal Anesthesia Anatomy Physiology
 Spinal Epidural And Caudal Anesthesia Anatomy Physiology
Spinal Epidural And Caudal Anesthesia Anatomy Physiology
 Spinal Epidural Caudal Blocks Morgan Mikhail S
Spinal Epidural Caudal Blocks Morgan Mikhail S
Lumbar Puncture Oxford Medical Education
 Complications Of Regional Anesthesia In The Pediatric
Complications Of Regional Anesthesia In The Pediatric
 Misconception About Spinal Anaesthesia Doctorsblogging
Misconception About Spinal Anaesthesia Doctorsblogging
 Anatomy And Pathophysiology Of Spinal Cord Injury Associated
Anatomy And Pathophysiology Of Spinal Cord Injury Associated
 Chapter 121 Neuraxial Anesthesia The Anesthesia Guide
Chapter 121 Neuraxial Anesthesia The Anesthesia Guide
 Spinal Anaesthetic Management In Paediatric Surgery Intechopen
Spinal Anaesthetic Management In Paediatric Surgery Intechopen
 Gross Anatomy Of The Spinal Cord Ppt Video Online Download
Gross Anatomy Of The Spinal Cord Ppt Video Online Download
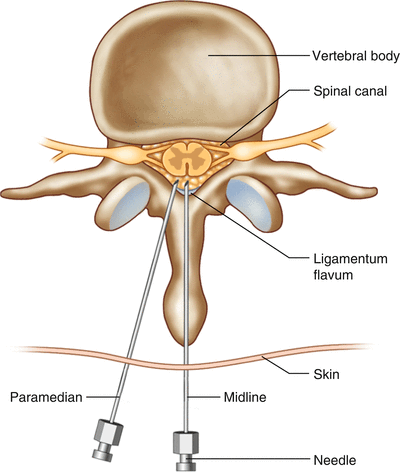 Spinal And Epidural Anesthesia Springerlink
Spinal And Epidural Anesthesia Springerlink
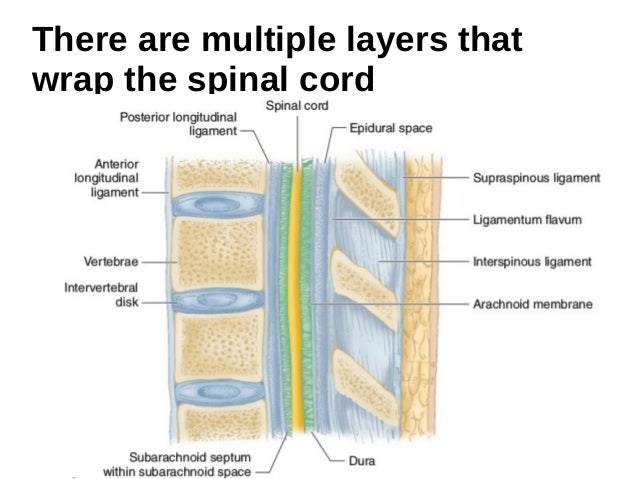 Functional Anatomy Of The Spine For Anesthesia
Functional Anatomy Of The Spine For Anesthesia
 Pdf Real Time Ultrasound Guided Spinal Anesthesia In
Pdf Real Time Ultrasound Guided Spinal Anesthesia In
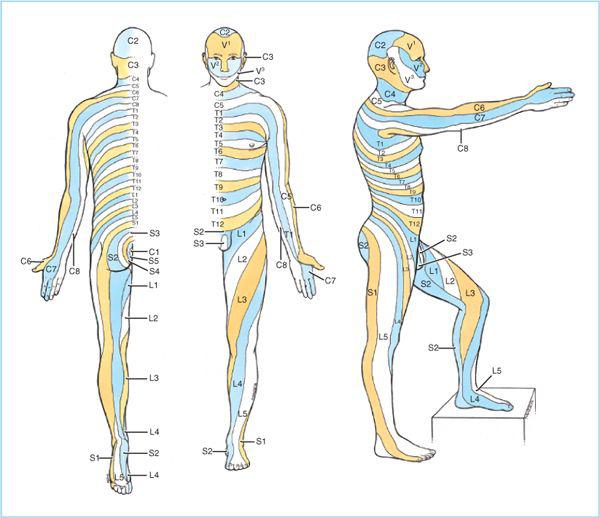 Spinal Anesthesia Anesthesia Key
Spinal Anesthesia Anesthesia Key
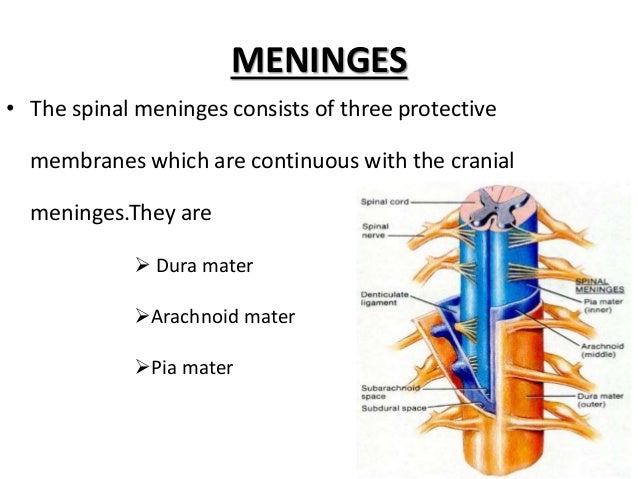 Spinal Anaesthesia Anatomy Physiology
Spinal Anaesthesia Anatomy Physiology
 Spinal Anesthesia Anesthesia Key
Spinal Anesthesia Anesthesia Key
 Medical Addicts Spinal Anesthesia Anatomy
Medical Addicts Spinal Anesthesia Anatomy
Spinal Anesthesia For Cesarean Section In A Patient With
Difference Between Spinal And Epidural Anesthesia Purpose
 Spinal Anesthesia Anatomy And Pharmacology
Spinal Anesthesia Anatomy And Pharmacology
Internet Scientific Publications
 Epidural Management Epidural Analgesia Epidural Anesthesia
Epidural Management Epidural Analgesia Epidural Anesthesia



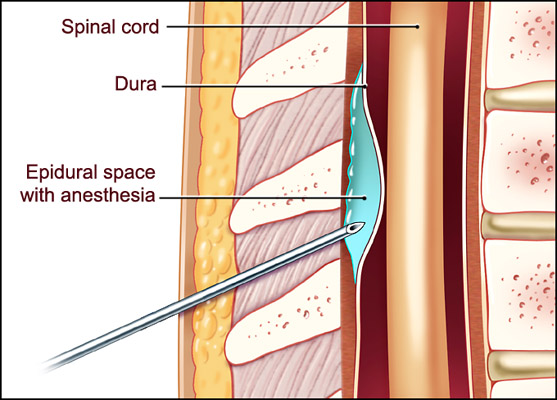
Belum ada Komentar untuk "Spinal Anesthesia Anatomy"
Posting Komentar