Facial Anatomy Skin
The bones involved in shaping the face are mainly the maxilla mandible nasal bone and zygomatic bone. These will be discussed later in this chapter.
 Facelift Dallas Neck Lift Park Cities
Facelift Dallas Neck Lift Park Cities
The dermis beneath the epidermis contains tough connective tissue hair follicles and sweat.

Facial anatomy skin. Our face shape is created by the underlying bone and muscle structure. Facial tissue layers age interdependently contributing to the overall facial appearance facial aging is due to changes in several types of tissue including skin fat muscle and bone. Over time the effects of gravity and age cause relaxation and laxity of facial soft tissues.
Rather than inserting into bones or tendons all of the muscles of facial expression originate from or insert into the skin. Its health and surface appearance are determined by environmental factors as well as the function of the components that comprise the layers below. Yet these lines often but not consistently coincide with natural wrinkle lines of the face.
They are all derived from the second embryonic branchial arch and are. Facial anatomy in cutaneous surgery. The epidermis the outermost layer of skin provides a waterproof barrier and creates our skin tone.
Cleavage lines of skin the path of cleavage lines in the face changes regionally. The shape of the face is influenced by the bone structure of the skull and each face is unique through the anatomical variation present in the bones of the viscerocranium and neurocranium. Clinical anatomy of the face clin dermatol j clinical anatomy of the face.
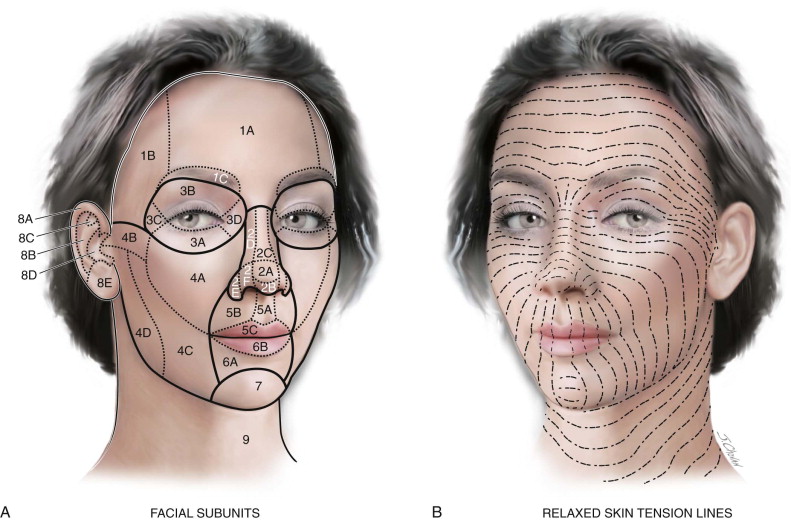
Facial aging process begins with the surface and subsurface structural changes in multiple facial tissue layers including skin fat muscle and bone. Thickness skin on top of the subcutaneous adipose lar oculi muscles and origin of the greater zygomatic muscle on the zygomatic bone prominence 124. Skin tension lines cosmetic units and subunits muscles of facial expression skin tension lines stls are the result of a complex interaction between internal and external factors involving the skin.
Skin anatomy physiology the skin is the bodys largest organ and it serves as a protective barrier. The intrinsic framework which consists of elastin and collagen progressively loosens with age. In general the facial skin is supported by retaining ligaments that extend from a deep fixed structure to the overlying skin.
The boundary between the orbital the nasal and the buccal regions is the nasolacrimal. A makeup artist should understand facial anatomy and proportions to be able to enhance a persons features to create the makeup and character look required or to make an actor or stunt double look like someone else.
 The Anatomy Of The Face Mouth And Jaws Pocket Dentistry
The Anatomy Of The Face Mouth And Jaws Pocket Dentistry
 Lauren Cooper Facial Anatomy And Skin Tone Studies
Lauren Cooper Facial Anatomy And Skin Tone Studies
 Juvederm Toronto Dr Martin Jugenburg
Juvederm Toronto Dr Martin Jugenburg
 Facial Anatomy Volumizing Injection
Facial Anatomy Volumizing Injection
 Figure 1 From I Basic Concepts In Facial Anatomy And Facial
Figure 1 From I Basic Concepts In Facial Anatomy And Facial
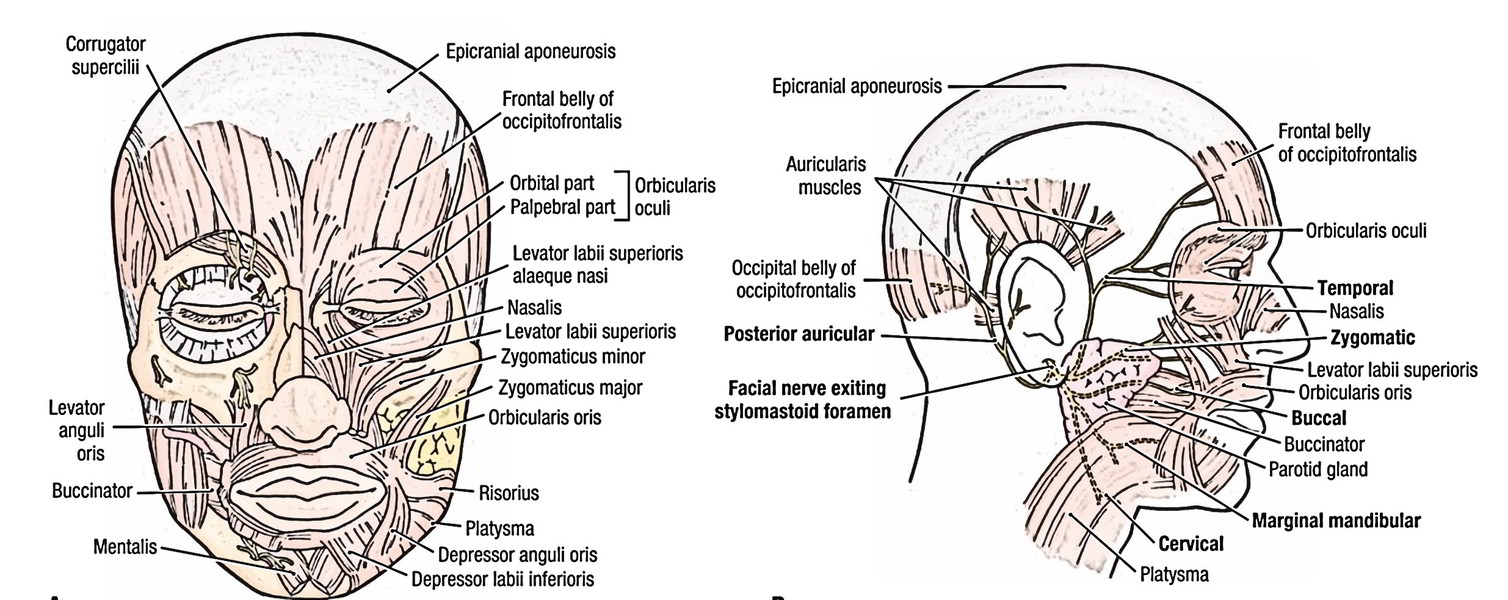 Easy Notes On Face Anatomy Learn In Just 4 Minutes
Easy Notes On Face Anatomy Learn In Just 4 Minutes
 Anatomy Of The Face Scalp Docsity
Anatomy Of The Face Scalp Docsity
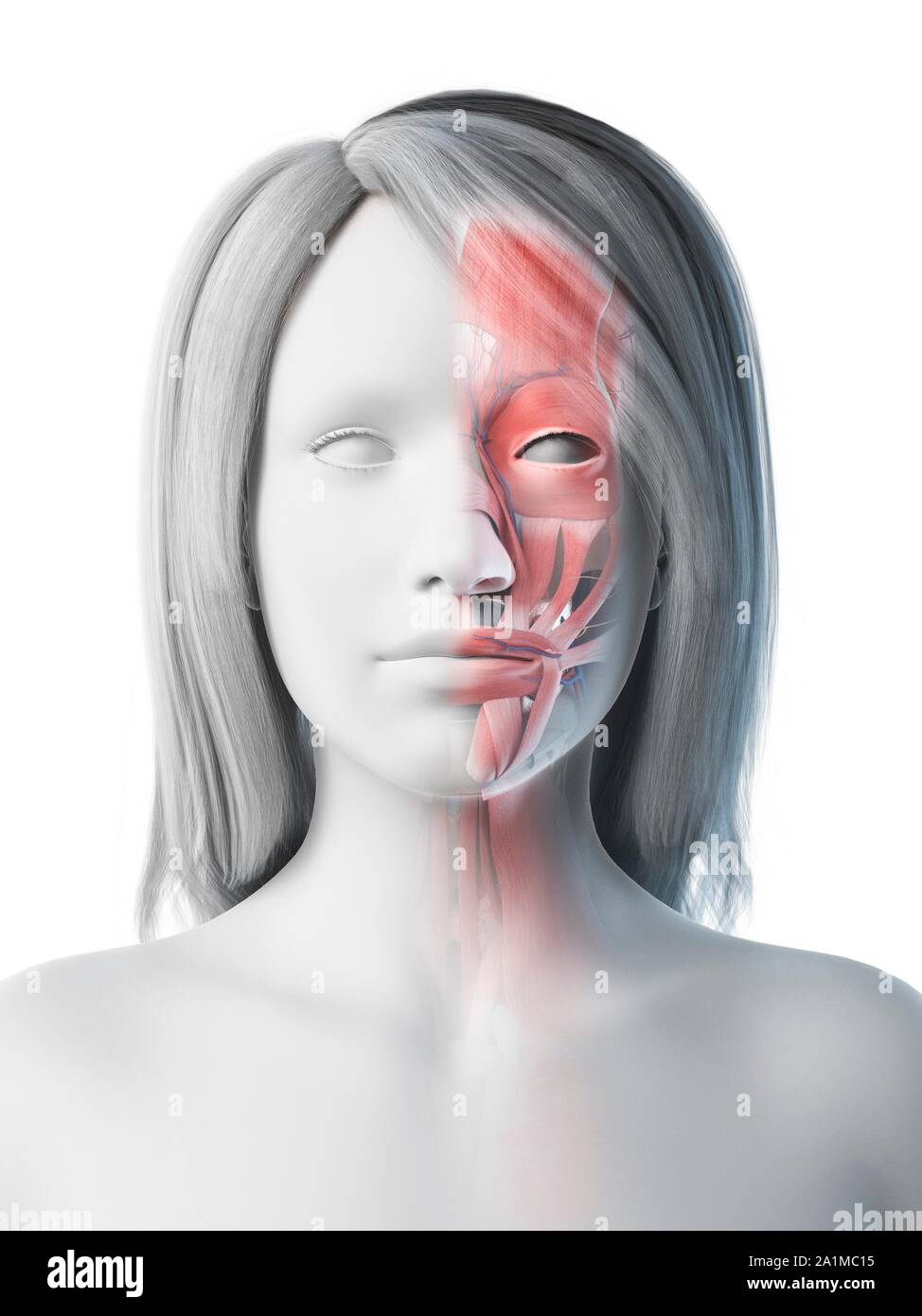 Female Facial Anatomy Computer Illustration Stock Photo
Female Facial Anatomy Computer Illustration Stock Photo
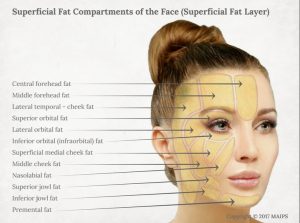 Understanding Facial Aging Skinspirationsskinspirations
Understanding Facial Aging Skinspirationsskinspirations
 Drawings Understanding Facial Anatomy
Drawings Understanding Facial Anatomy
 An Illustrator S Guide To Facial Anatomy
An Illustrator S Guide To Facial Anatomy
 Face Anatomy Skin Google Search In 2019 Face Anatomy
Face Anatomy Skin Google Search In 2019 Face Anatomy
 Applied Facial Anatomy Plastic Surgery Key
Applied Facial Anatomy Plastic Surgery Key
 Portraiture And Facial Anatomy For Artists Scott Eaton
Portraiture And Facial Anatomy For Artists Scott Eaton
 Human Facial Muscular System Art Mark Main Anatomy Human
Human Facial Muscular System Art Mark Main Anatomy Human
 Understanding Facial Aging Skinspirationsskinspirations
Understanding Facial Aging Skinspirationsskinspirations
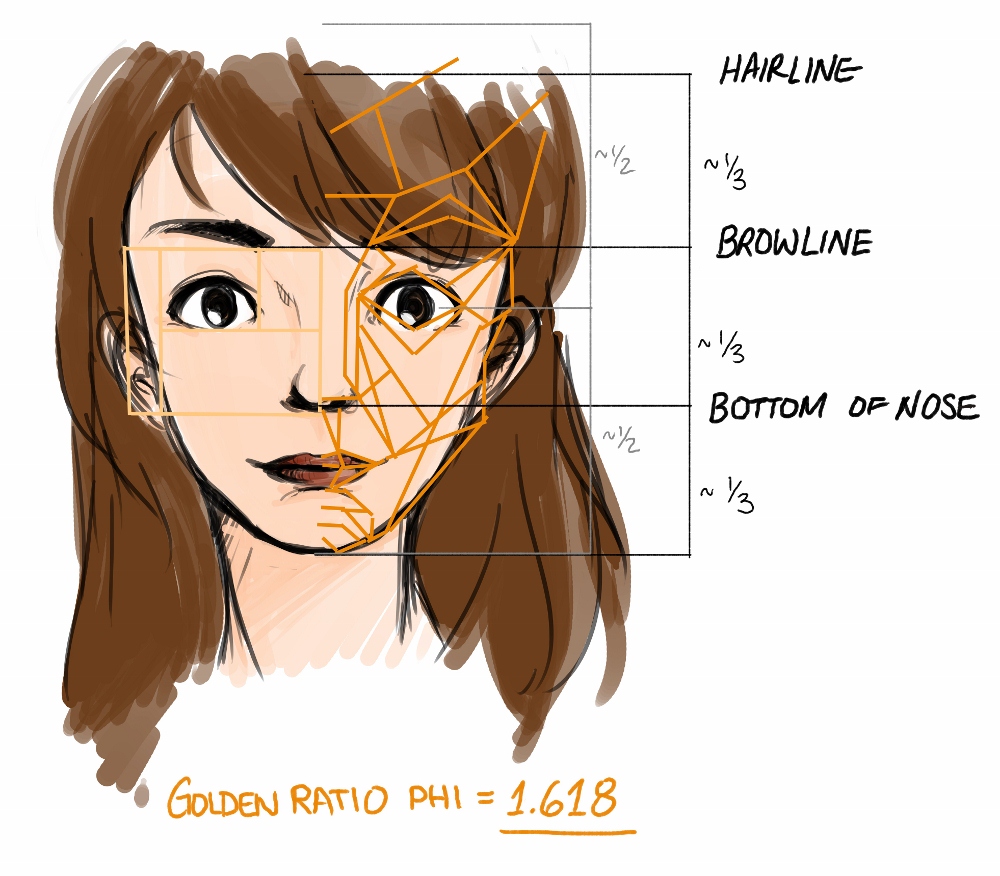 The Science Of Beauty Anatomy Of Beauty Think Skin
The Science Of Beauty Anatomy Of Beauty Think Skin

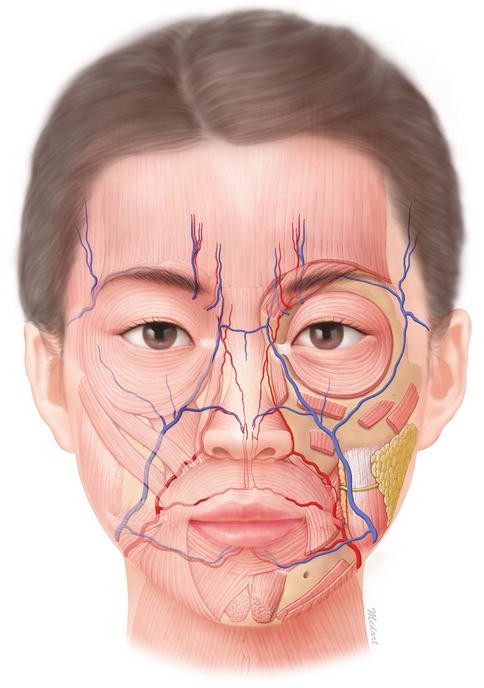 Anatomy Of Face Wiring Diagram Symbols And Guide
Anatomy Of Face Wiring Diagram Symbols And Guide
 Facial Anatomy Nov 3 2019 In Miami Cge Medical
Facial Anatomy Nov 3 2019 In Miami Cge Medical
 Liquid Facelift The Clinic For Plastic Surgery
Liquid Facelift The Clinic For Plastic Surgery
 What Happens To Your Facial Anatomy After Fillers Or Anti
What Happens To Your Facial Anatomy After Fillers Or Anti
 Lines Of Incision For Removal Of Skin Tumors Of The Face
Lines Of Incision For Removal Of Skin Tumors Of The Face
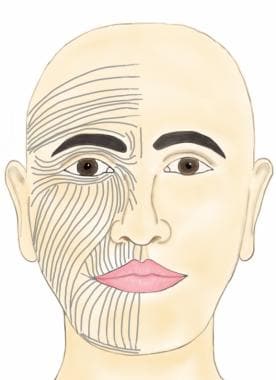 Sports Related Facial Trauma Facial Injuries Basic Anatomy
Sports Related Facial Trauma Facial Injuries Basic Anatomy
 Facial Anatomy In Cutaneous Surgery Skin Tension Lines
Facial Anatomy In Cutaneous Surgery Skin Tension Lines

Belum ada Komentar untuk "Facial Anatomy Skin"
Posting Komentar