Diffusion Anatomy
Anatomy physiology diffusion osmosis which results from the random motion and collisions of ions and molecules. 215 the immune response against pathogens.
 3 1 The Cell Membrane Anatomy And Physiology
3 1 The Cell Membrane Anatomy And Physiology
Anatomy physiology plasma membranediffusion osmosis ch.
Diffusion anatomy. 3 1 integral proteins. For diffusion to occur there must be a concentration gradient. Diffusion is one form of passive transport that doesnt require the expenditure of cellular energy.
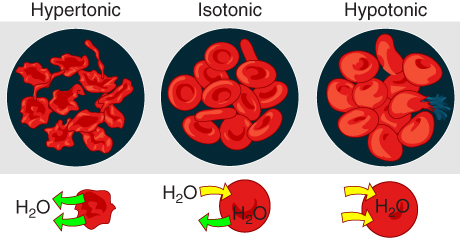
If a membrane is permeable to water though not to a solute water will equalize its own concentration by diffusing to the side of lower water concentration and thus the side of higher solute concentration. Part of the membrane structure and cannot be removed without damaging or destroying the membrane. Osmosis is the diffusion of water through a semipermeable membrane down its concentration gradient.
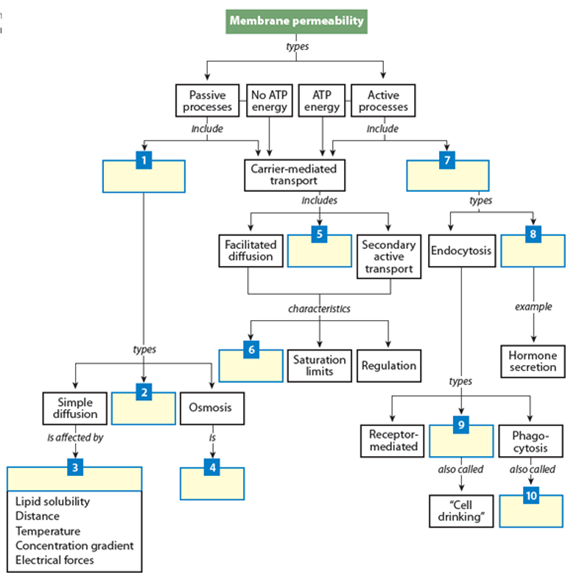
211 anatomy of the lymphatic and immune systems. In facilitated diffusion a molecule is transported across a membrane with the help of a carrier protein. Diffusion diffusion is the net passive movement of molecules or particles from regions of higher to regions of lower concentration.
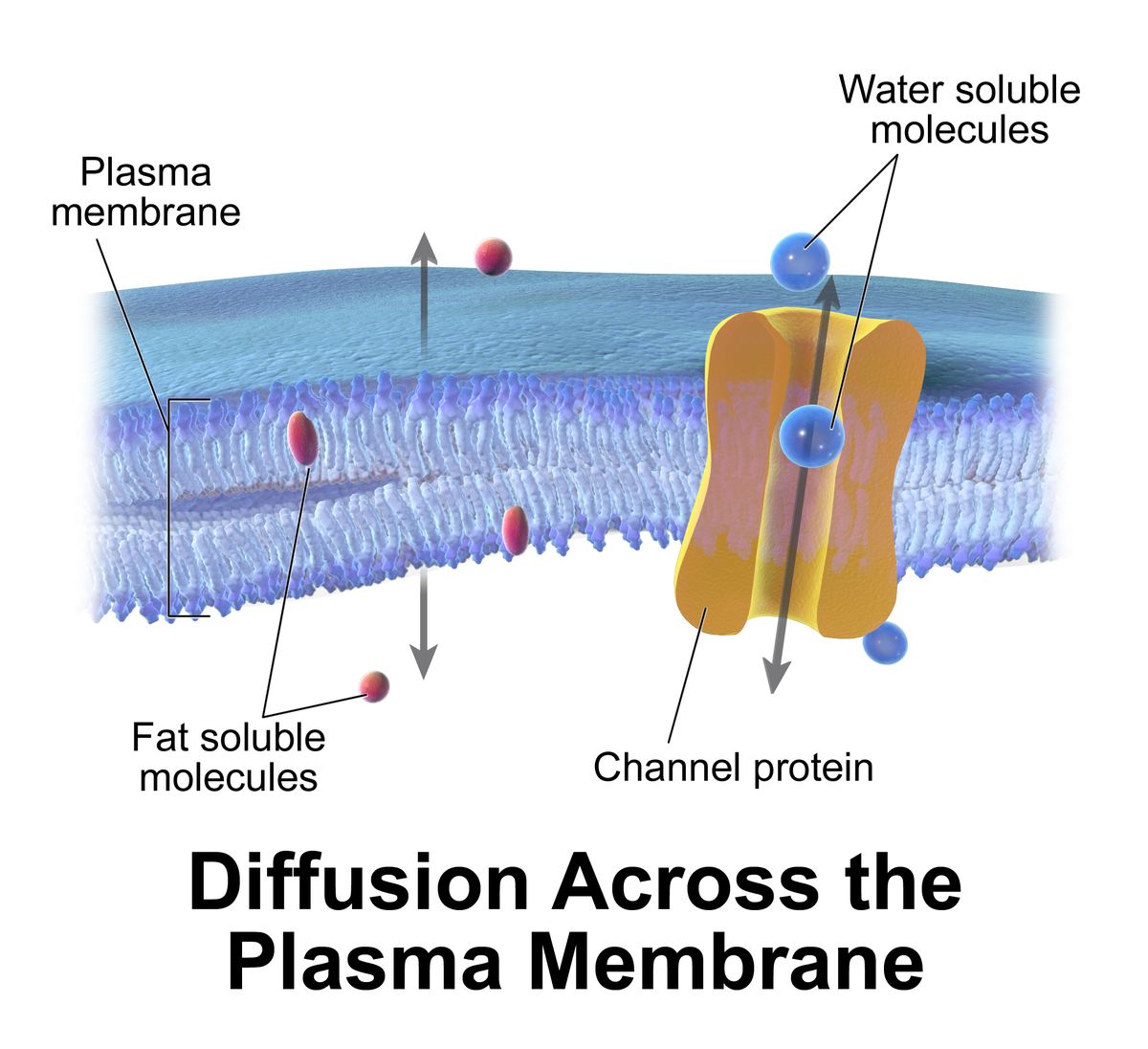
Is a passive process. Separation of substances in solution by the difference in their rates of diffusion through a semipermeable membrane. A molecule can diffuse passively through the cell membrane if its lipid soluble uncharged and very small or if a carrier molecule can assist it.
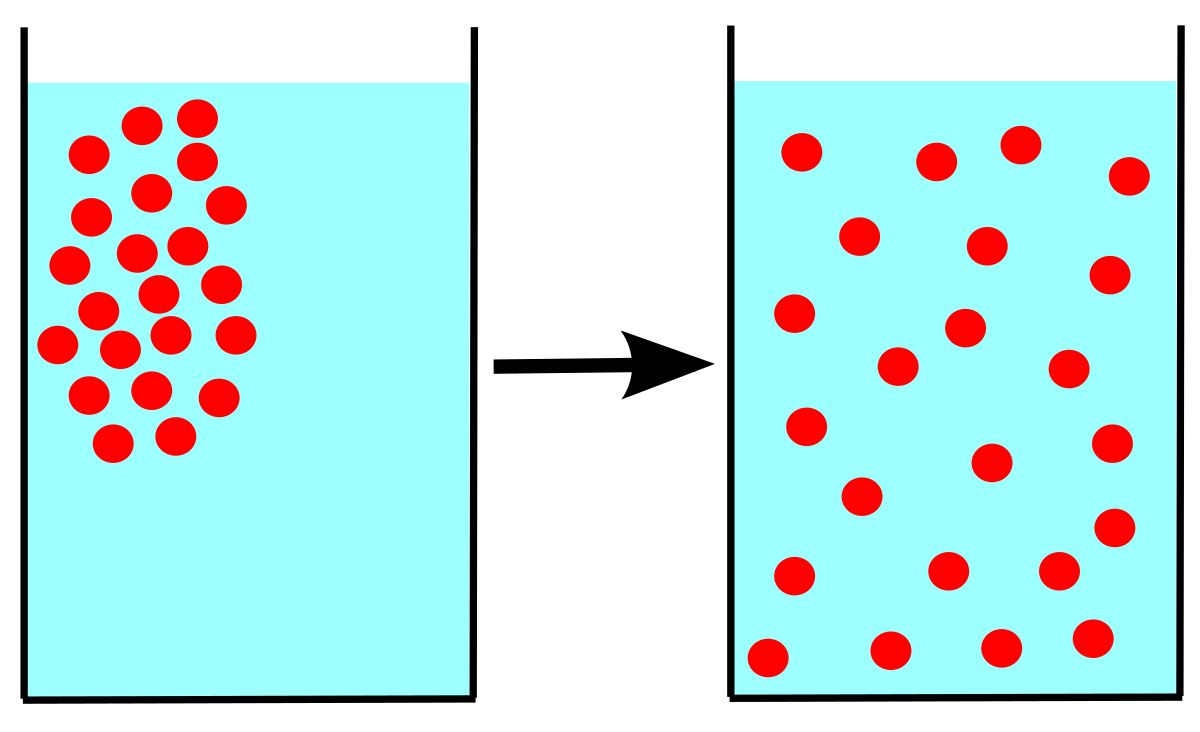
The net movement of a substance from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration. Passive diffusion is the movement of molecules across a membrane such as a cell membrane. The movement does not require energy.
Diffusion is the passive movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. 212 barrier defenses and the innate immune response. 214 the adaptive immune response.
Steepness of its concentration gradie steepness of concentration gradient measures the vast differe diffusion passive membrane transport where there is net movement of subs equilibrium state in which diffusion is unopposed molecules become even the largest hallow body cavity in humans and many animals. Integral proteins greatly outnumber peripheral proteins. Bound to the inner or outer surface of the membrane and are easily separated from it.
T lymphocytes and their functional types. 213 the adaptive immune response. The dissimilarity in the amounts of solutes particles or molecules between two regions will cause them to move between the two regions.
Diffusion of molecules through a semipermeable membrane from a place of higher concentration to a place of lower concentration until the concentration on both sides is equal.
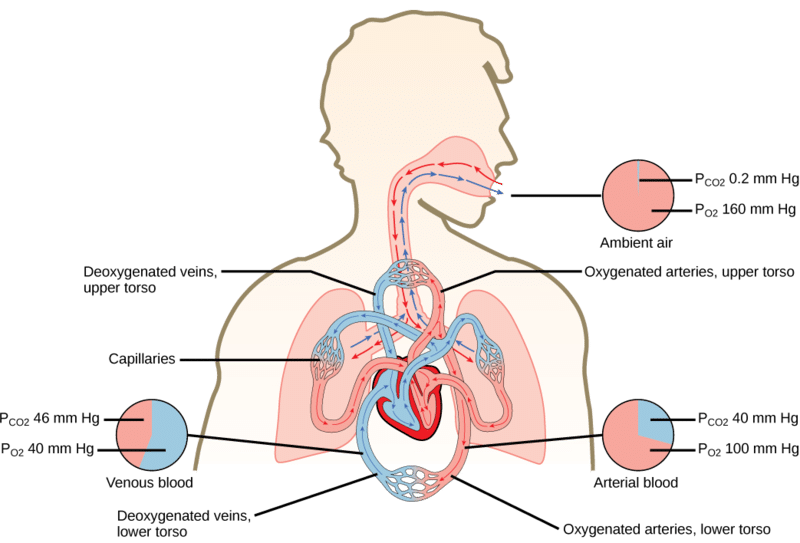 Gas Exchange Physics Diffusion Barrier
Gas Exchange Physics Diffusion Barrier
 Cardio Anatomy Docx Cardio Anatomy Chapter 4 Diffusion Of
Cardio Anatomy Docx Cardio Anatomy Chapter 4 Diffusion Of
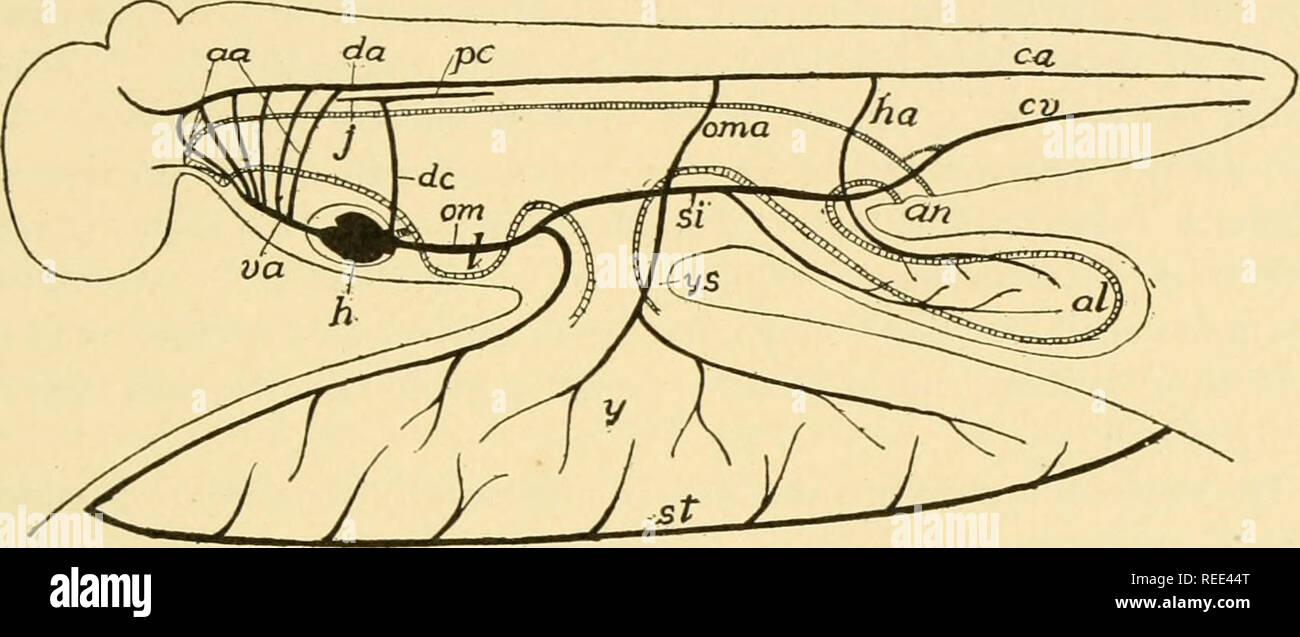 Comparative Anatomy Anatomy Comparative The Vascular
Comparative Anatomy Anatomy Comparative The Vascular
 Diffusion Definition Examples And Types Biology Dictionary
Diffusion Definition Examples And Types Biology Dictionary
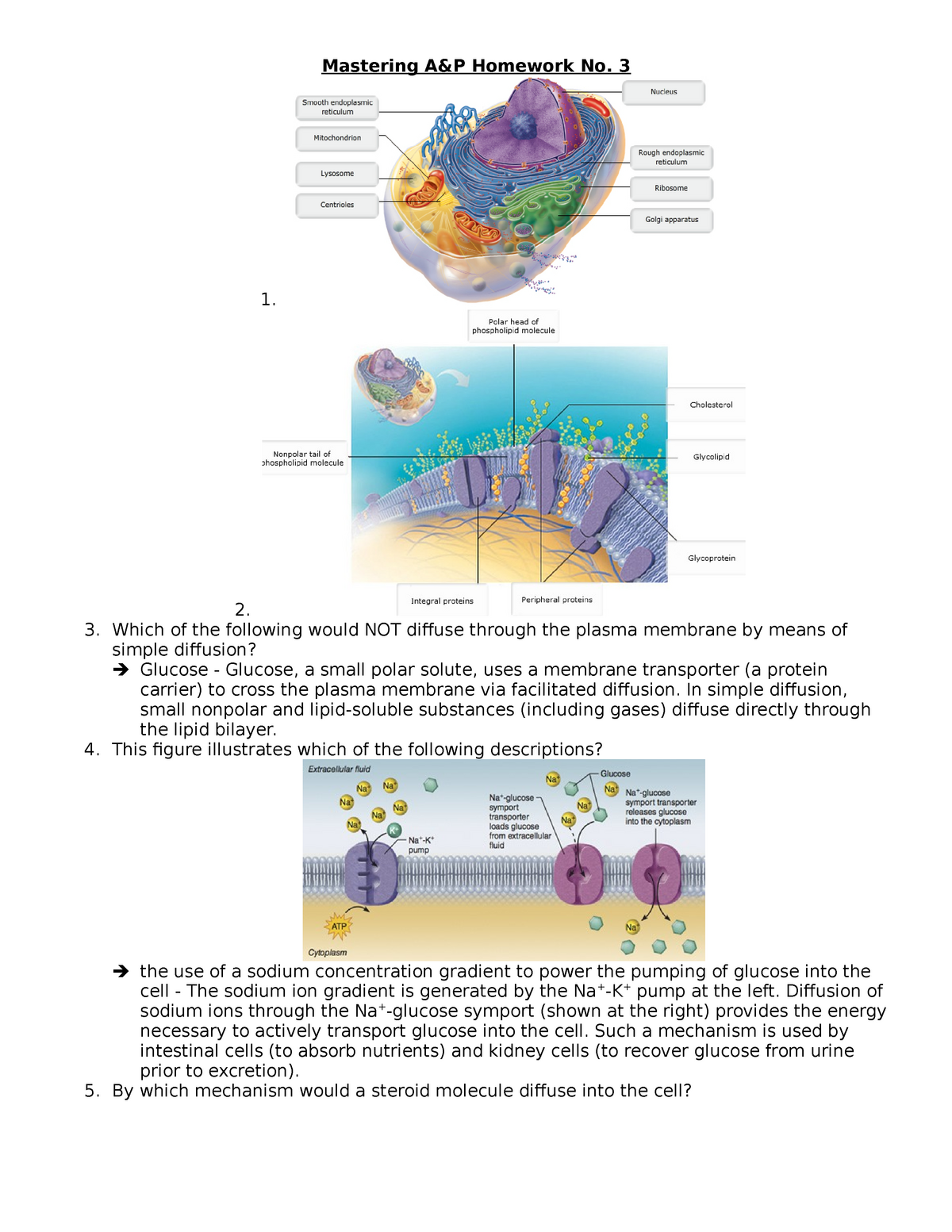 Mastering A P Homework No 3 Aant 316 Human Anatomy Physio
Mastering A P Homework No 3 Aant 316 Human Anatomy Physio
 Chapter 3 3 Solutions Visual Anatomy Physiology 2nd
Chapter 3 3 Solutions Visual Anatomy Physiology 2nd
 Concentration Gradient Definition Example
Concentration Gradient Definition Example
 3 1 The Cell Membrane Anatomy Physiology
3 1 The Cell Membrane Anatomy Physiology
 Anatomy And Physiology Anusha Murali Ppt Download
Anatomy And Physiology Anusha Murali Ppt Download
 Lab Ch 5 Osmosis Diffusion Questions And Study Guide
Lab Ch 5 Osmosis Diffusion Questions And Study Guide
 Johny S Anatomy And Physiology Part 01
Johny S Anatomy And Physiology Part 01
Fig 11 Diffusion Tensor Imaging Of Cerebral White Matter
Figure 1 Helical Structure Of Ventricular Anatomy By
 The New Science Of Sleep Wake Cycles Physiology
The New Science Of Sleep Wake Cycles Physiology
 A P Lab Diffusion Osmosis Flashcards By Proprofs
A P Lab Diffusion Osmosis Flashcards By Proprofs
Passive Transport Anatomy And Physiology I

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/diffusion-58e6ad0a5f9b58ef7e0e1a60.jpg)



:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/gas_exchange_lungs-ca56d9b8ae004cbbb5ab5e33e8723b8b.jpg)
Belum ada Komentar untuk "Diffusion Anatomy"
Posting Komentar