Skin Facial Anatomy
Facial anatomy in cutaneous surgery. Nerve endings are inflamed.
 Best Selling The Face Pictorial Atlas Of Clinical Anatomy
Best Selling The Face Pictorial Atlas Of Clinical Anatomy
Facial aging process begins with the surface and subsurface structural changes in multiple facial tissue layers including skin fat muscle and bone.

Skin facial anatomy. The dermis beneath the epidermis contains tough connective tissue hair follicles and sweat. Facial tissue layers age interdependently contributing to the overall facial appearance facial aging is due to changes in several types of tissue including skin fat muscle and bone. We use cookies to offer you a better experience personalize content tailor advertising provide social media features and better understand the use of our services.
Its located between the epidermis and the subcutaneous tissue. In general the facial skin is supported by retaining ligaments that extend from a deep fixed structure to the overlying skin. The skins surface is red and uncomfortable.
The dermis is the middle layer of the three layers of skin. 2 muscles affecting the forehead and eyebrow. It contains connective tissue blood capillaries oil and sweat glands nerve endings and hair follicles.
Yet these lines often but not consistently coincide with natural wrinkle lines of the face. The intrinsic framework which consists of elastin and collagen progressively loosens with age. The subcutaneous layer area below the skin lies underneath the cutaneous layer and is sometimes called the hypodermis or superficial fascia.
These will be discussed later in this chapter. The epidermis the outermost layer of skin provides a waterproof barrier and creates our skin tone. Different anatomic areas of the face have synergistic and antagonist groups of muscles that enable individuals to make varied facial expressions.
It holds most of the bodys fat so it varies in thickness from one person to another. Cleavage lines of skin the path of cleavage lines in the face changes regionally. Skin tension lines cosmetic units and subunits muscles of facial expression skin tension lines stls are the result of a complex interaction between internal and external factors involving the skin.
The uppermost layer is thin and jagged due to lack of water in certain areas of the face. Creases form over joints because the skin always folds the same way as the joints bend. Over time the effects of gravity and age cause relaxation and laxity of facial soft tissues.
 The Face Pictorial Atlas Of Clinical Anatomy Amazon Co Uk
The Face Pictorial Atlas Of Clinical Anatomy Amazon Co Uk
 Skull Head Cut Skin Face Anatomy Stock Vector C Maryvalery
Skull Head Cut Skin Face Anatomy Stock Vector C Maryvalery
 Botox Palm Beach Expert Wrinkle And Age Redution Palm
Botox Palm Beach Expert Wrinkle And Age Redution Palm
 Understanding Facial Aging Skinspirationsskinspirations
Understanding Facial Aging Skinspirationsskinspirations
 Lauren Cooper Facial Anatomy And Skin Tone Studies
Lauren Cooper Facial Anatomy And Skin Tone Studies
 Facial Anatomy Ageing It S Not Only About Your Skin
Facial Anatomy Ageing It S Not Only About Your Skin
 Human Facial Muscular System Art Mark Main Anatomy Human
Human Facial Muscular System Art Mark Main Anatomy Human
 Restylane In 2019 Facial Fillers Facial Bones Dermal Fillers
Restylane In 2019 Facial Fillers Facial Bones Dermal Fillers
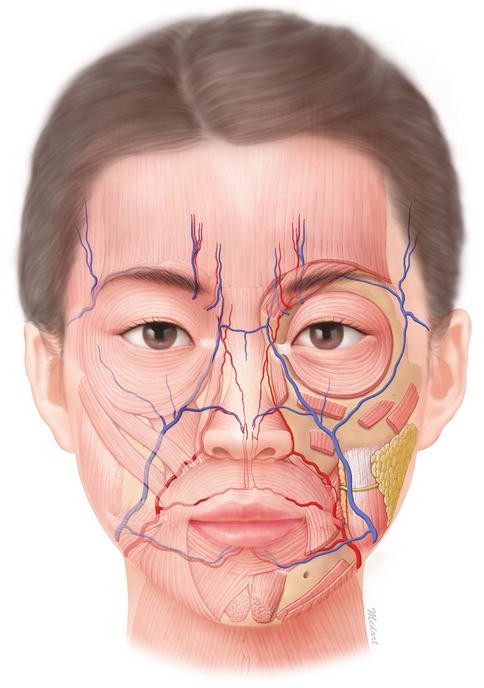 Anatomy Of Face Wiring Diagram Symbols And Guide
Anatomy Of Face Wiring Diagram Symbols And Guide
 Considering Botox Or Fillers Read This First 2oceansvibe Com
Considering Botox Or Fillers Read This First 2oceansvibe Com
 Facial Anatomy Asian Pacific Botox Geras Healthcare
Facial Anatomy Asian Pacific Botox Geras Healthcare
S 417 What Is The Function Of The Skin Skin Anatomy With
 Makeup This Makeup Would Work For All Of The Fraus Mrs
Makeup This Makeup Would Work For All Of The Fraus Mrs
 Facial Anatomy Stock Photos Images Photography Shutterstock
Facial Anatomy Stock Photos Images Photography Shutterstock
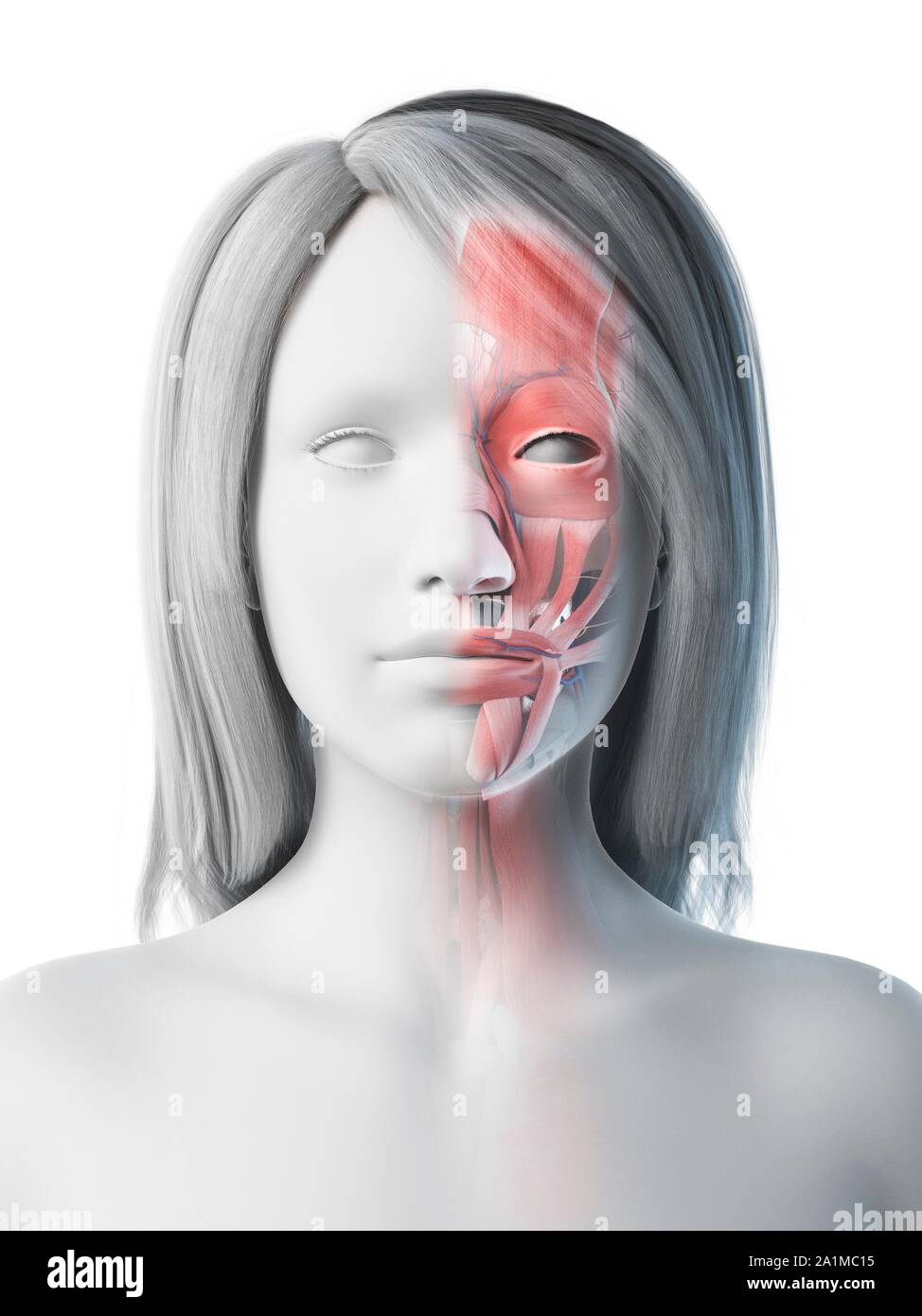 Female Facial Anatomy Computer Illustration Stock Photo
Female Facial Anatomy Computer Illustration Stock Photo
 54 Best Facial Anatomy Images Facial Anatomy Anatomy Facial
54 Best Facial Anatomy Images Facial Anatomy Anatomy Facial
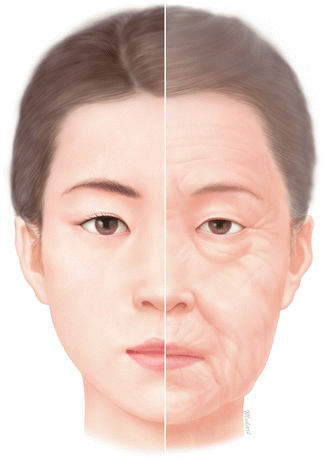 General Anatomy Of The Face And Neck Springerlink
General Anatomy Of The Face And Neck Springerlink
 What Happens To Your Facial Anatomy After Fillers Or Anti
What Happens To Your Facial Anatomy After Fillers Or Anti
 Facial Anatomy Eyes Nose Lips By Naranbaatar Ganbold
Facial Anatomy Eyes Nose Lips By Naranbaatar Ganbold
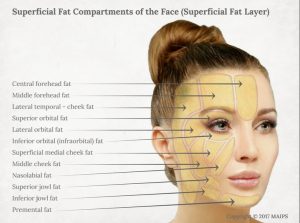 Understanding Facial Aging Skinspirationsskinspirations
Understanding Facial Aging Skinspirationsskinspirations
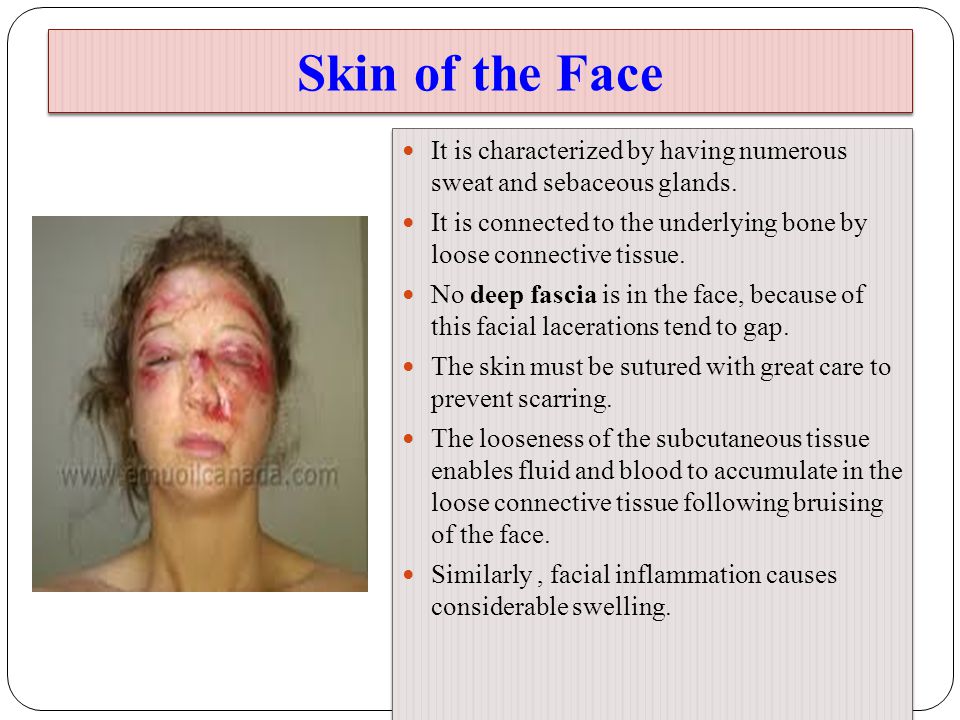 Clinical Anatomy Of The Face Ppt Video Online Download
Clinical Anatomy Of The Face Ppt Video Online Download
 Anatomy Of Face Wiring Diagram Symbols And Guide
Anatomy Of Face Wiring Diagram Symbols And Guide
 Pin On Learning Materials For Cosmetic Acupuncture
Pin On Learning Materials For Cosmetic Acupuncture




Belum ada Komentar untuk "Skin Facial Anatomy"
Posting Komentar