Anatomy Of The Index Finger
Fingers are constructed of ligaments strong supportive tissue connecting bone to bone tendons attachment tissue from muscle to bone and three phalanges bones. The thumb has two.
 Left Index Finger A Crucial Anatomy For Ge14 New Straits
Left Index Finger A Crucial Anatomy For Ge14 New Straits
This finger often possesses the largest amount of sensitivity and greatest dexterity of any of the fingers.

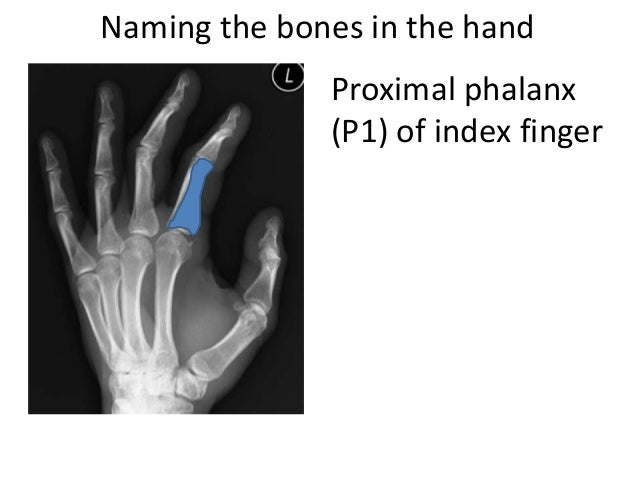
Anatomy of the index finger. Distal interphalangeal dip proximal interphalangeal pip and metacarpophalangeal mcp. The index finger has three phalanges. The thumb has two.
Fingers have a complex anatomy. Basic anatomy of the finger. The index finger is composed of three bones.
A digit includes the hand bones but these bones are not separated into individual appendages like a finger. Each finger has 3 phalanges bones and 3 hinged joints. Each finger has three phalanges the distal middle and proximal.
Picture of finger anatomy. The index middle ring and fifth digits have proximal middle and distal phalanges and three hinged joints. The index finger does not contain any muscles but is controlled by muscles in the hand by attachments of tendons to the bones.
There are no muscles in the fingers. It is also called the index finger or the forefinger. The little finger and index finger both have an extra muscle.
Ligaments connect finger bones and help keep them in place. The phalanges singular phalanx the 14 narrow bones that make up the fingers of each hand. And fingers move by the pull of forearm muscles on the tendons.
Finger movement is controlled by muscles in the forearms that pull on finger tendons. Anatomy of the fingers the human finger is mainly a bony structure with multiple joints giving it strength and flexibility. The extensor indicis extends the index finger while the palmar interosseus adducts it.
The thumb has two of each. Oxygenated blood arrives at the finger through the common palmar artery which extends off of the palmar arch connecting the ulnar and radial arteries. The thumb has a distal and proximal phalanx as well as an interphalangeal and mcp joint.
Each finger has three phalanges the distal middle and proximal. The median nerve innervates the fingers skin. Tendons connect muscles to bones.
The distal phalanx intermediate phalanx and proximal phalanx.
 Tactilus Compression Force Sensing Resistor Fsr Force
Tactilus Compression Force Sensing Resistor Fsr Force
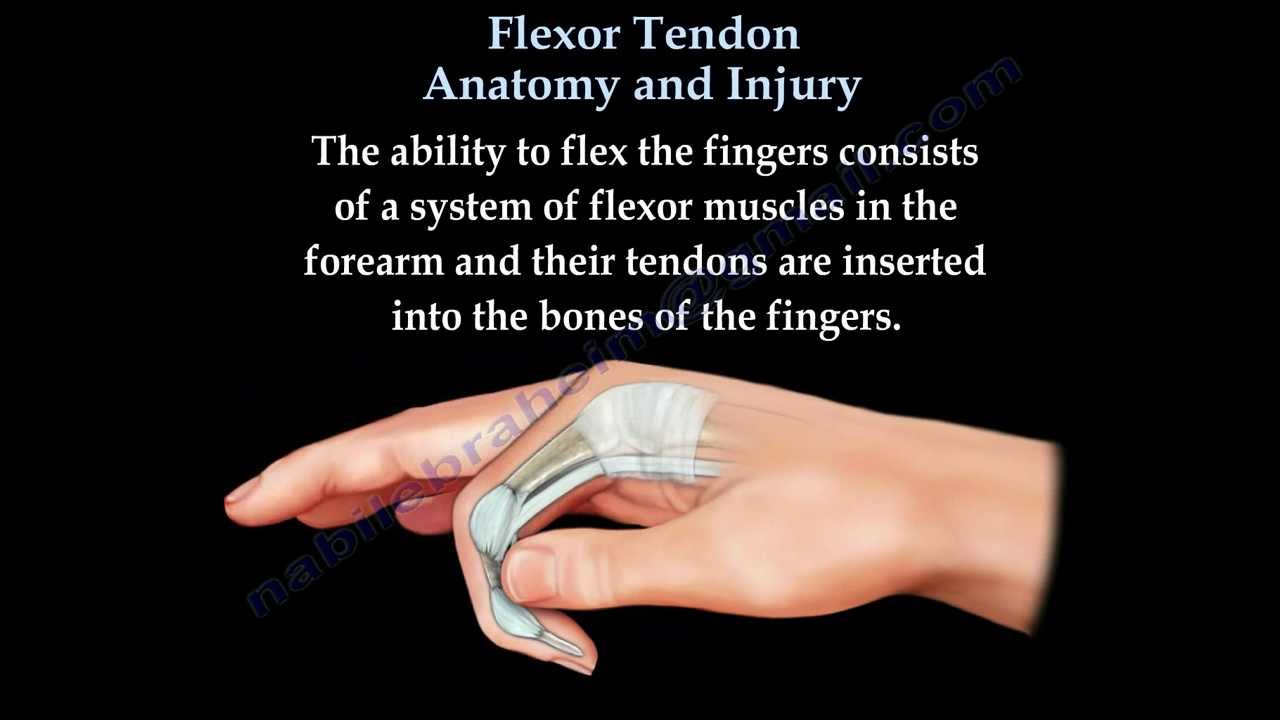 Flexor Tendon Anatomy And Injury Everything You Need To Know Dr Nabil Ebraheim
Flexor Tendon Anatomy And Injury Everything You Need To Know Dr Nabil Ebraheim
Pollicization Boston Children S Hospital
Hand Anatomy Midwest Bone Joint Institute Elgin Illinois
 Extensor Tendon Injuries Florida Bone And Joint
Extensor Tendon Injuries Florida Bone And Joint
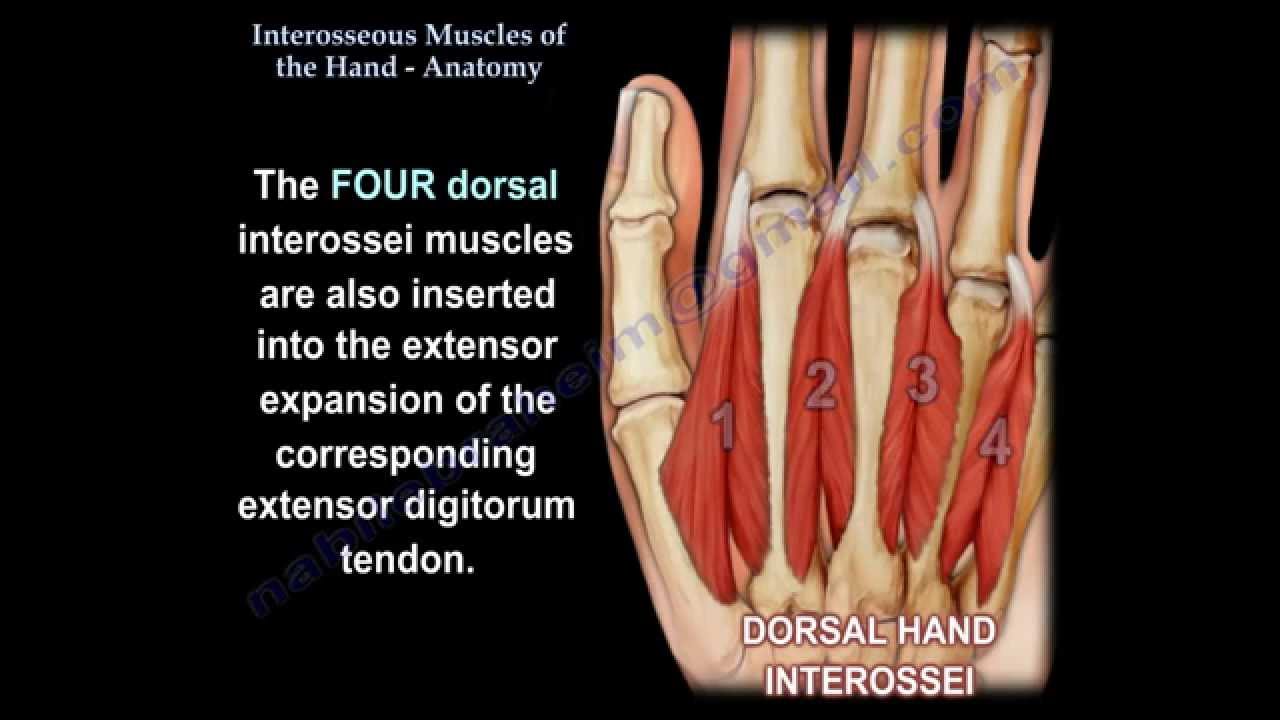 Interosseous Muscles Of The Hand Anatomy Everything You Need To Know Dr Nabil Ebraheim
Interosseous Muscles Of The Hand Anatomy Everything You Need To Know Dr Nabil Ebraheim
 Hand And Finger Bones Kirkland Wa Evergreenhealth
Hand And Finger Bones Kirkland Wa Evergreenhealth
 Outstretched Index Finger Pointing To Something Illustration
Outstretched Index Finger Pointing To Something Illustration
Patient Education Concord Orthopaedics
25 Hands Anatomy Mar 30 Flashcards Memorang
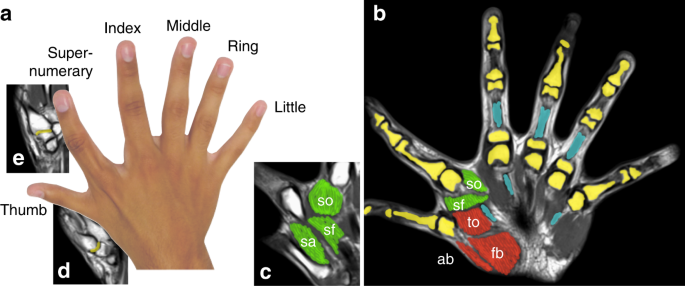 Augmented Manipulation Ability In Humans With Six Fingered
Augmented Manipulation Ability In Humans With Six Fingered
 The Cyclopaedia Of Anatomy And Physiology Anatomy
The Cyclopaedia Of Anatomy And Physiology Anatomy

I Cut My Index Finger With A Knife Can I Save It From Death
 Surface Anatomy Hand Surgery Source
Surface Anatomy Hand Surgery Source
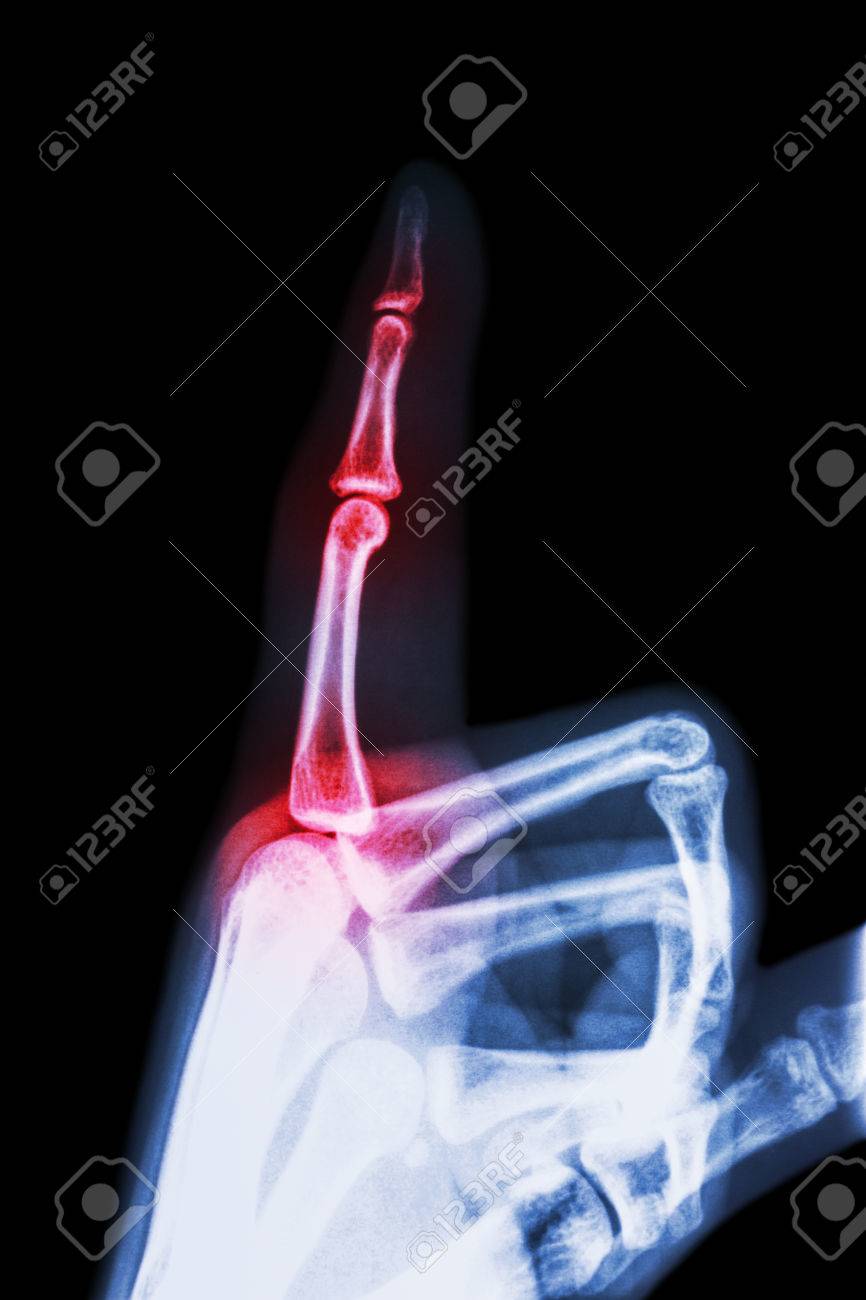 Rheumatoid Arthritis Gouty Arthritis Film X Ray Index Finger
Rheumatoid Arthritis Gouty Arthritis Film X Ray Index Finger
 Little Finger Anatomy Yahoo Image Search Results Finger
Little Finger Anatomy Yahoo Image Search Results Finger
 Anatomy Of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Everything You Need To Know Dr Nabil Ebraheim
Anatomy Of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Everything You Need To Know Dr Nabil Ebraheim
 Human Anatomy Archives Health Linear
Human Anatomy Archives Health Linear
 Hand Finger Anatomy Hand Anatomy Hand Surgery Human Anatomy
Hand Finger Anatomy Hand Anatomy Hand Surgery Human Anatomy
 The Muscles And Fasciae Of The Forearm Human Anatomy
The Muscles And Fasciae Of The Forearm Human Anatomy
 Gifts Delight Laminated 36x24 Inches Poster Hand Middle Finger X Ray Radiation Finger Gesture Anatomy Bone Finger Thumb Index Finger Pinkie Finger
Gifts Delight Laminated 36x24 Inches Poster Hand Middle Finger X Ray Radiation Finger Gesture Anatomy Bone Finger Thumb Index Finger Pinkie Finger

Belum ada Komentar untuk "Anatomy Of The Index Finger"
Posting Komentar