Anatomy Of Hip
The 2 hip bones form the bony pelvis along with the sacrum and the coccyx and are united anteriorly by the pubic symphysis. Adductor muscles on the inside of your thigh.
 Amazon Com Anatomy Hip Femur Joint Print Sra3 12x18
Amazon Com Anatomy Hip Femur Joint Print Sra3 12x18
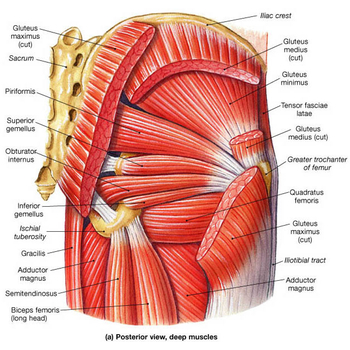
Some of the other muscles in the hip are.
Anatomy of hip. And synovial membrane and fluid which encapsulates the hip joint and lubricates it respectively. Muscles of the hip. The adult os coxae or hip bone is formed by the fusion of the ilium the ischium and the pubis which occurs by the end of the teenage years.
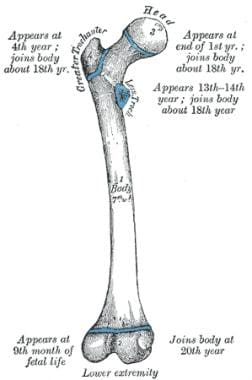
Femoral head a ball shaped piece of bone located at the top of your thigh bone or femur. Rectus femoris muscle one of the quadriceps muscles on the front of your thigh. It is a ball and socket joint at the juncture of the leg and pelvis.
The hip joint consists of two main parts. The hip joint is a ball and socket joint. Lateral or external rotation 30 with the hip extended 50 with the hip flexed.
One of the bodys largest weight bearing joints the hip is where the thigh bone meets the pelvis to form a ball and socket joint. Acetabulum a socket in your pelvis into which the femoral head fits. Hip ligaments and tendons tough fibrous tissues that bind bones to bones and muscles to bones.
Amphibians and reptiles have relatively weak pelvic girdles and the femur extends horizontally. The stability of the hip is increased by the strong ligaments that encircle the hip. The movements of the hip joint is thus performed by a series of muscles which are here presented in order of importance with the range of motion from the neutral zero degree position indicated.
Hip problems occur when any one of these components starts to degenerate or is in some way compromised or irritated. The rounded head of the femur thighbone forms the ball which fits into the acetabulum a cup shaped socket in the pelvis. The hip joint is a ball and socket type joint.
The muscles of the thigh and lower back work together to keep the hip stable. The hip is the bodys second largest weight bearing joint after the knee. The round head of the femur rests in a cavity the acetabulum that allows free rotation of the limb.
Anatomy of the hip the hip joint. Iliopsoas muscle a hip flexor muscle that attaches to the upper thigh bone.
 Pelvis Bones And The Ligaments Front On And Rear View
Pelvis Bones And The Ligaments Front On And Rear View
 Hip Joint Bones Ligaments Blood Supply And Innervation Anatomy Kenhub
Hip Joint Bones Ligaments Blood Supply And Innervation Anatomy Kenhub
 Hip Flexors An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Hip Flexors An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
 Hip Osteoarthritis Physiopedia
Hip Osteoarthritis Physiopedia
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/11162/anatomy-hip-joint_english.jpg) Hip And Thigh Bones Joints Muscles Kenhub
Hip And Thigh Bones Joints Muscles Kenhub
 The Hip Anatomy And Physiology
The Hip Anatomy And Physiology
 Laminated Anatomy And Injuries Of The Hip Poster Hip Joint Anatomical Chart 18 X 27
Laminated Anatomy And Injuries Of The Hip Poster Hip Joint Anatomical Chart 18 X 27
 Hip Joint Anatomy Overview Gross Anatomy
Hip Joint Anatomy Overview Gross Anatomy
 Hip Anatomy Femur And Pelvis Bones That Make Up The Hip
Hip Anatomy Femur And Pelvis Bones That Make Up The Hip
 Femoroacetabular Impingement Orthoinfo Aaos
Femoroacetabular Impingement Orthoinfo Aaos
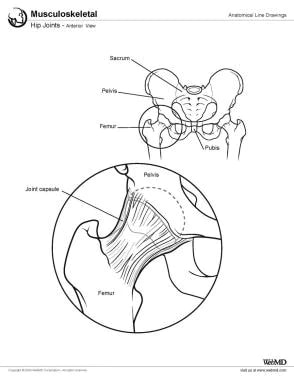 Hip Joint Anatomy Overview Gross Anatomy
Hip Joint Anatomy Overview Gross Anatomy
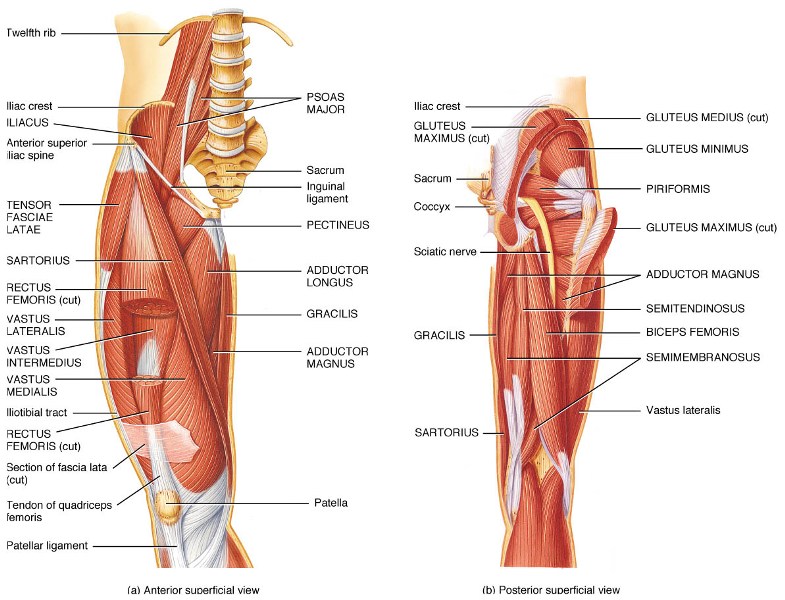 Hip Joint Anatomy Bone And Spine
Hip Joint Anatomy Bone And Spine
 Yoga For Hip Stability Understanding Hypermobility
Yoga For Hip Stability Understanding Hypermobility
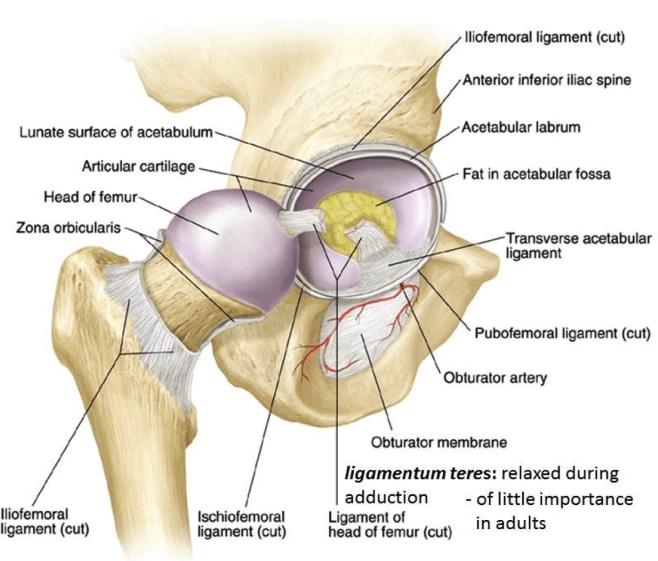 Hip Anatomy Recon Orthobullets
Hip Anatomy Recon Orthobullets
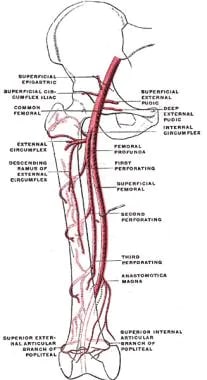 Hip Joint Anatomy Overview Gross Anatomy
Hip Joint Anatomy Overview Gross Anatomy
:watermark(/images/watermark_only.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/hip-joint-3/viwpOeWZpKjfLaqqpsJJw_Hip_Joint_01.png) Hip Joint Ligaments Movements Muscles Kenhub
Hip Joint Ligaments Movements Muscles Kenhub
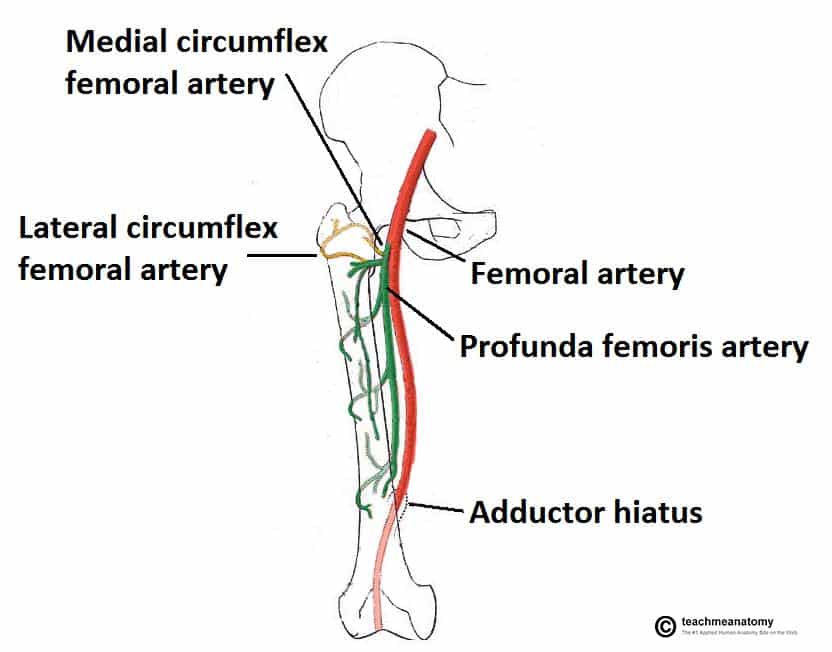
 The Hip Joint Articulations Movements Teachmeanatomy
The Hip Joint Articulations Movements Teachmeanatomy
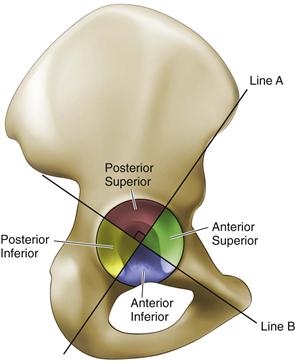 Hip Anatomy Recon Orthobullets
Hip Anatomy Recon Orthobullets
 Hip Anatomy Yoga Understanding The Hips For Yoga Jason
Hip Anatomy Yoga Understanding The Hips For Yoga Jason
 Hip Flexors An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Hip Flexors An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
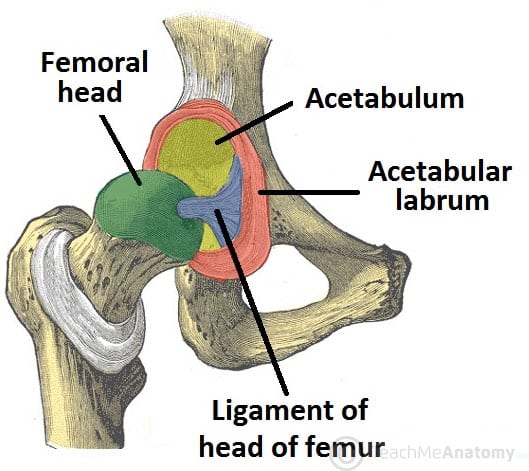 The Hip Joint Articulations Movements Teachmeanatomy
The Hip Joint Articulations Movements Teachmeanatomy


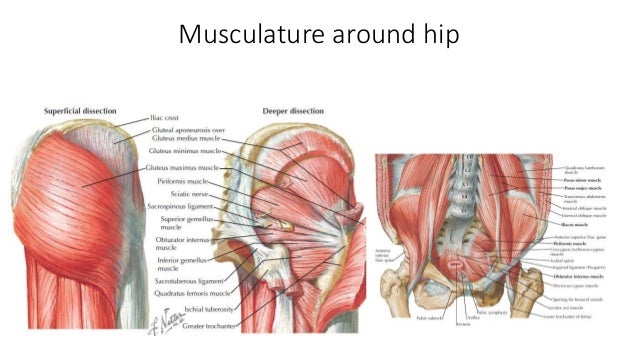



Belum ada Komentar untuk "Anatomy Of Hip"
Posting Komentar