Facial Skin Anatomy
The dermis beneath the epidermis contains tough connective tissue hair follicles and sweat. The skins surface is red and uncomfortable.
 Facial Anatomy Ageing It S Not Only About Your Skin
Facial Anatomy Ageing It S Not Only About Your Skin
Cleavage lines of skin the path of cleavage lines in the face changes regionally.

Facial skin anatomy. It is responsible for the skins strength pliability and mechanical resistance and is also involved in the regulation of the body temperature. Lastly sensory branches of the vagus glossopharyngeal and facial nerves innervate the skin of the external auditory canal the concha and the posterior sulcus. Its located between the epidermis and the subcutaneous tissue.
The epidermis the outermost layer of skin provides a waterproof barrier and creates our skin tone. This application allows for the precise and comprehensive labeling of anatomic locations of dermatologic disease thereby reducing biopsy and treatment site ambiguity and providing a rich dataset upon which data mining can be performed. The dermis is the middle layer of the three layers of skin.
The subcutaneous layer area below the skin lies underneath the cutaneous layer and is sometimes called the hypodermis or superficial fascia. It contains connective tissue blood capillaries oil and sweat glands nerve endings and hair follicles. Nerve endings are inflamed.
A web based human surface anatomy mapper was developed to allow labeling of mapped surface anatomy images. The uppermost layer is thin and jagged due to lack of water in certain areas of the face. Yet these lines often but not consistently coincide with natural wrinkle lines of the face.
Creases form over joints because the skin always folds the same way as the joints bend. Facial tissue layers age interdependently contributing to the overall facial appearance facial aging is due to changes in several types of tissue including skin fat muscle and bone. Facial aging process begins with the surface and subsurface structural changes in multiple facial tissue layers including skin fat muscle and bone.
The dermis consists mostly of connective tissue structural tissue and is much thicker than the epidermis. Facial skin the skin is the envelope or canvas of the face revealing the deflation and atrophic changes of the underlying bone and soft tissue compartments as previously discussed. The dermis also provides the epidermis with nutrients by means of its vascular network.
It holds most of the bodys fat so it varies in thickness from one person to another. Awareness of the sensory branches.
 Skull Head Cut Skin Face Anatomy Stock Vector C Maryvalery
Skull Head Cut Skin Face Anatomy Stock Vector C Maryvalery
 Facial Anatomy Ageing It S Not Only About Your Skin
Facial Anatomy Ageing It S Not Only About Your Skin
 Large Eyes Small Nose Mall Face Small Mouth Fairlight Skin V
Large Eyes Small Nose Mall Face Small Mouth Fairlight Skin V
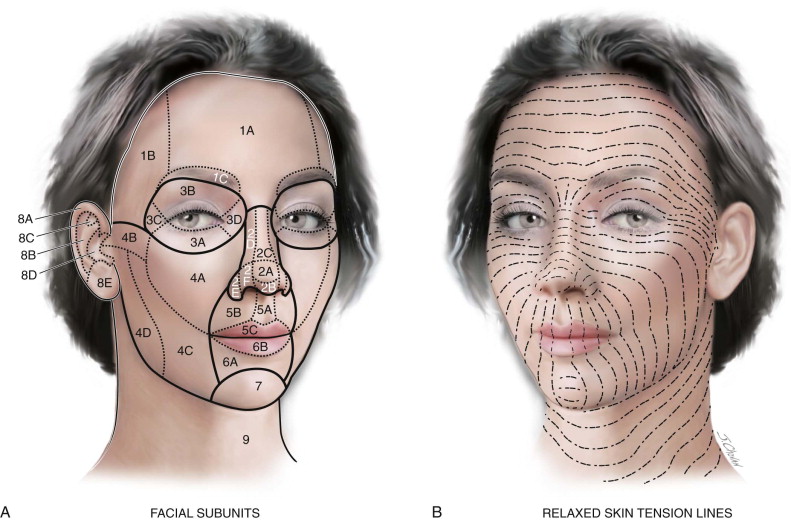 The Anatomy Of The Face Mouth And Jaws Pocket Dentistry
The Anatomy Of The Face Mouth And Jaws Pocket Dentistry
 Understanding Facial Aging Skinspirationsskinspirations
Understanding Facial Aging Skinspirationsskinspirations
 Human Facial Muscular System Art Mark Main Anatomy Human
Human Facial Muscular System Art Mark Main Anatomy Human
 Anatomy Lesson 11 Jamie S Face Or Ye Do It Face To Face
Anatomy Lesson 11 Jamie S Face Or Ye Do It Face To Face

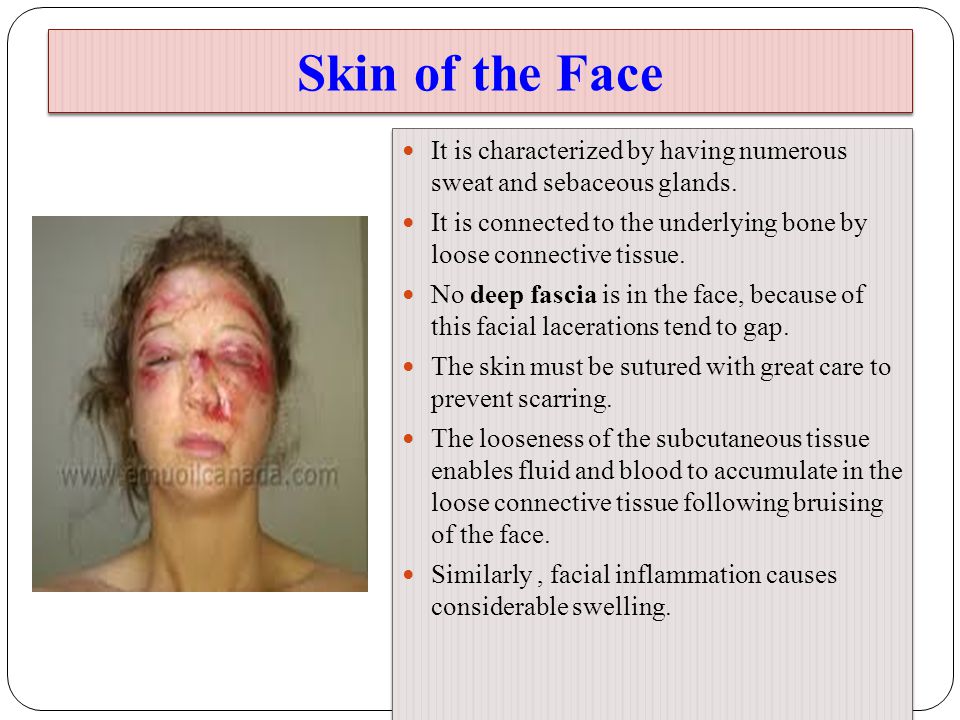 Clinical Anatomy Of The Face Ppt Video Online Download
Clinical Anatomy Of The Face Ppt Video Online Download
 An Approach To Structural Facial Rejuvenation With Fillers
An Approach To Structural Facial Rejuvenation With Fillers
 Skin Skull Facial Skeleton Bone Cosmetics Png Clipart
Skin Skull Facial Skeleton Bone Cosmetics Png Clipart
 Human Facial Muscular System Art Mark Main Anatomy Human
Human Facial Muscular System Art Mark Main Anatomy Human
 Human Anatomy Face Physiology Skin Png 600x600px Anatomy
Human Anatomy Face Physiology Skin Png 600x600px Anatomy
 Sport Sports Teeth Pine Face Skin Eyes Muscles Fantasy Look
Sport Sports Teeth Pine Face Skin Eyes Muscles Fantasy Look
 Surface Anatomy Of The Face And Skin
Surface Anatomy Of The Face And Skin
 Lines Of Incision For Removal Of Skin Tumors Of The Face
Lines Of Incision For Removal Of Skin Tumors Of The Face
 The Anatomy Of An Aging Face Skin Md Dermatologist In
The Anatomy Of An Aging Face Skin Md Dermatologist In
 Face Anatomy Kobe Brynnagraephoto Com
Face Anatomy Kobe Brynnagraephoto Com
 The Five Layers Simple Anatomy Archidemia
The Five Layers Simple Anatomy Archidemia
Book Microcurrent Therapy For Skin Renewal
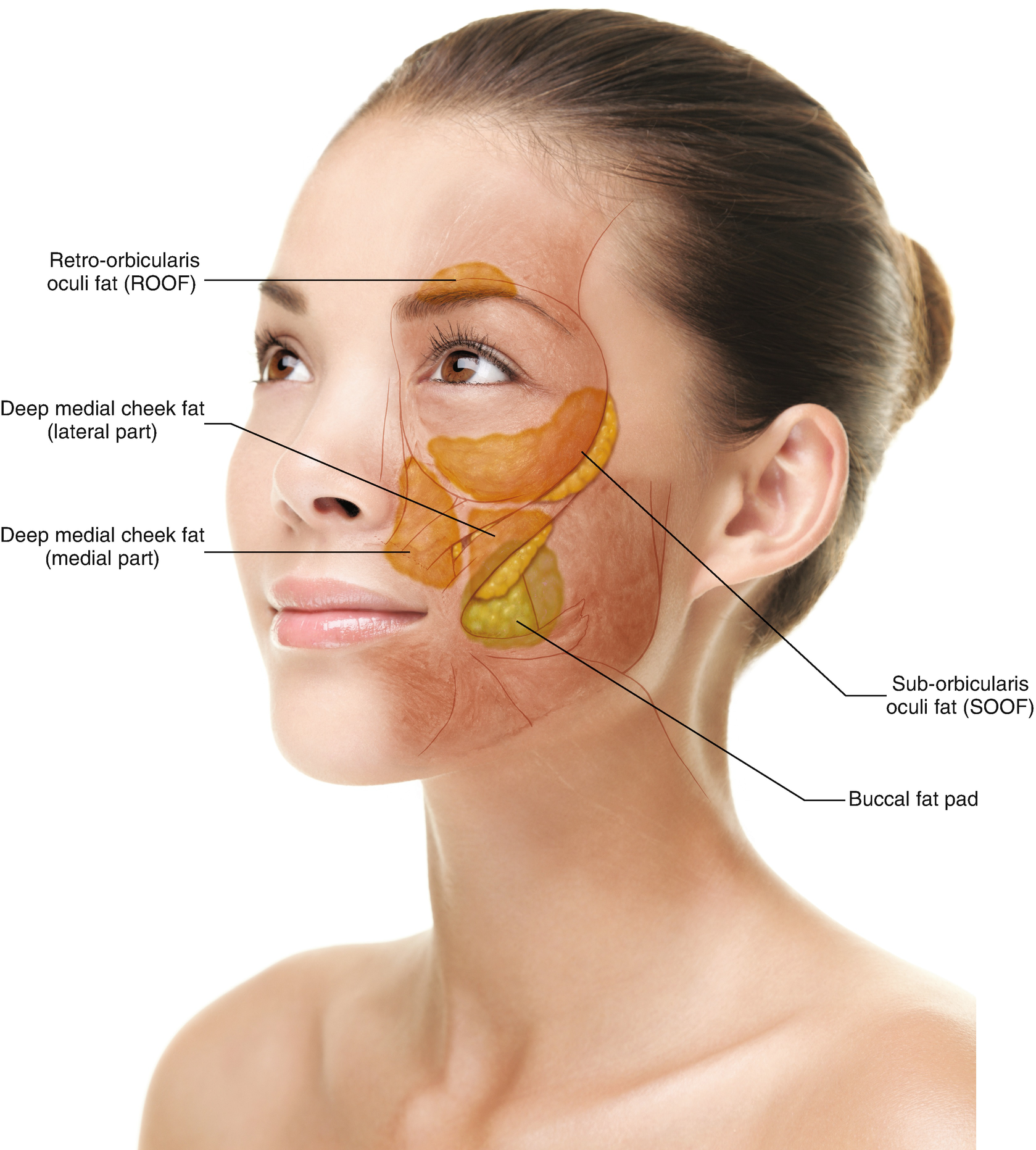 Anatomy For Absorbable Thread Lifting Springerlink
Anatomy For Absorbable Thread Lifting Springerlink



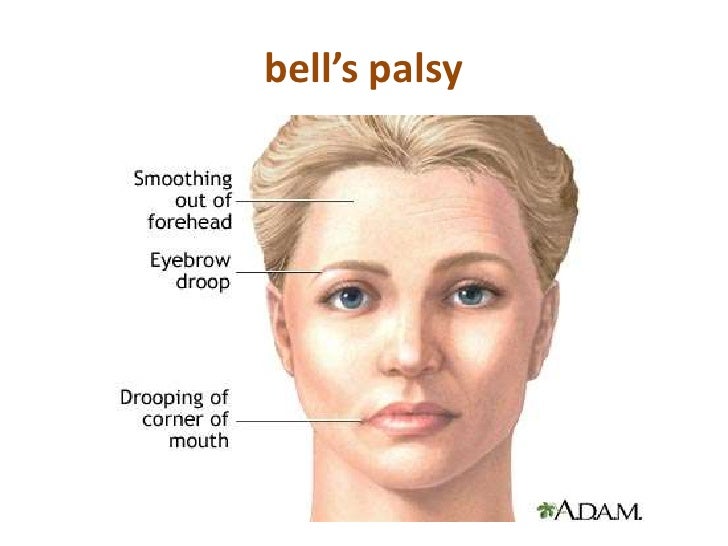
Belum ada Komentar untuk "Facial Skin Anatomy"
Posting Komentar