Elbow Ligaments Anatomy
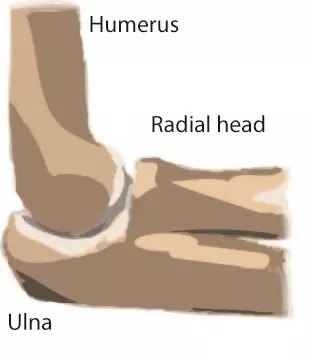
Anatomy of ligaments of elbow joint the elbow joint is a hinge joint formed by the articulation between the lower end of the humerus with the ulna and head of the radius. Humeroulnar joint is the joint between the trochlea on the medial aspect.
The joint capsule of the elbow is strengthened by ligaments medially and laterally.

Elbow ligaments anatomy. Ligaments of the elbow joint. The anatomy of the elbow. Ligaments around the elbow join to form a watertight sac called a joint capsule.
The elbow joint is made up of three articulations 23. Tennis elbow also involves injuries to the annular ligament. Biceps brachii is the main elbow flexor but as a biarticular.
There are a collection of ligaments that connect the bones forming. This capsule surrounds the elbow joint and contains lubricating fluid called synovial fluid. Blood supply and innervation.
The two main ligaments around the elbow are the ulnar collateral ligament ucl and the lateral collateral ligament. When this ligament gets injured it causes pain on the inside of the elbow which can be confused with injury of the medial epicondyle. In full flexion the coronoid process is received by the coronoid fossa and the radial head is received by the radial fossa on the anterior surface of the humerus.
This ligament helps in the flexion of the arm where the elbow joint acts as a pivot. Injury to ulnar collateral ligament. There are four main ligaments in the elbow.
The blood supply to the elbow joint is derived from a number. The radial collateral ligament is found on the lateral side of the joint extending from the lateral epicondyle and blending with the annular ligament of the radius a ligament from the proximal radioulnar joint. The elbow joint is a complex hinge joint formed between the distal end of the humerus in the upper arm and the proximal ends of the ulna and radius in the forearm.
Ligaments are bands of tough elastic tissue around your joints. Brachialis acts exclusively as an elbow flexor and is one of the few muscles in. Brachioradialis acts essentially as an elbow flexor but also supinates during extreme pronation.
The important ligaments of the elbow are the medial collateral ligament on the inside of the elbow and the lateral collateral ligament on the outside of the elbow together these ligaments provide the main source of stability for the elbow holding the humerus and the ulna tightly together. Stability of the elbow joint depends upon the inherent stability of the articulating surfaces strong capsule and collateral ligaments. The elbow allows for the flexion and extension of the forearm relative to the upper arm as well as rotation of the forearm and wrist.
There are three main flexor muscles at the elbow.
 Elbow Ligament Anatomy Musculoskeletal Learning Portfolio
Elbow Ligament Anatomy Musculoskeletal Learning Portfolio
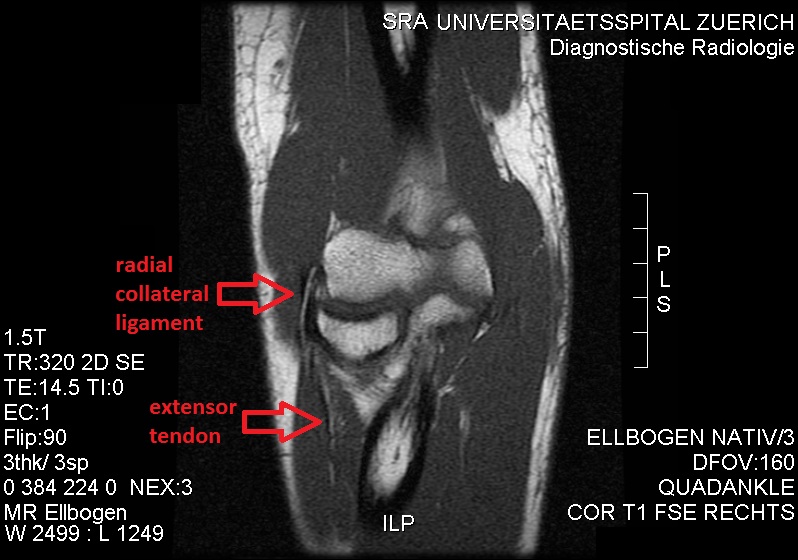 Radial Collateral Ligament Of Elbow Joint Wikipedia
Radial Collateral Ligament Of Elbow Joint Wikipedia
 Elbow Pain Causes And Treatment Bone And Spine
Elbow Pain Causes And Treatment Bone And Spine
 Anatomy Of The Elbow Elbow Pain Treatment
Anatomy Of The Elbow Elbow Pain Treatment
Elbow Fractures In Children Orthoinfo Aaos
 Elbow Anatomy Biomechanics Shoulder Elbow Orthobullets
Elbow Anatomy Biomechanics Shoulder Elbow Orthobullets
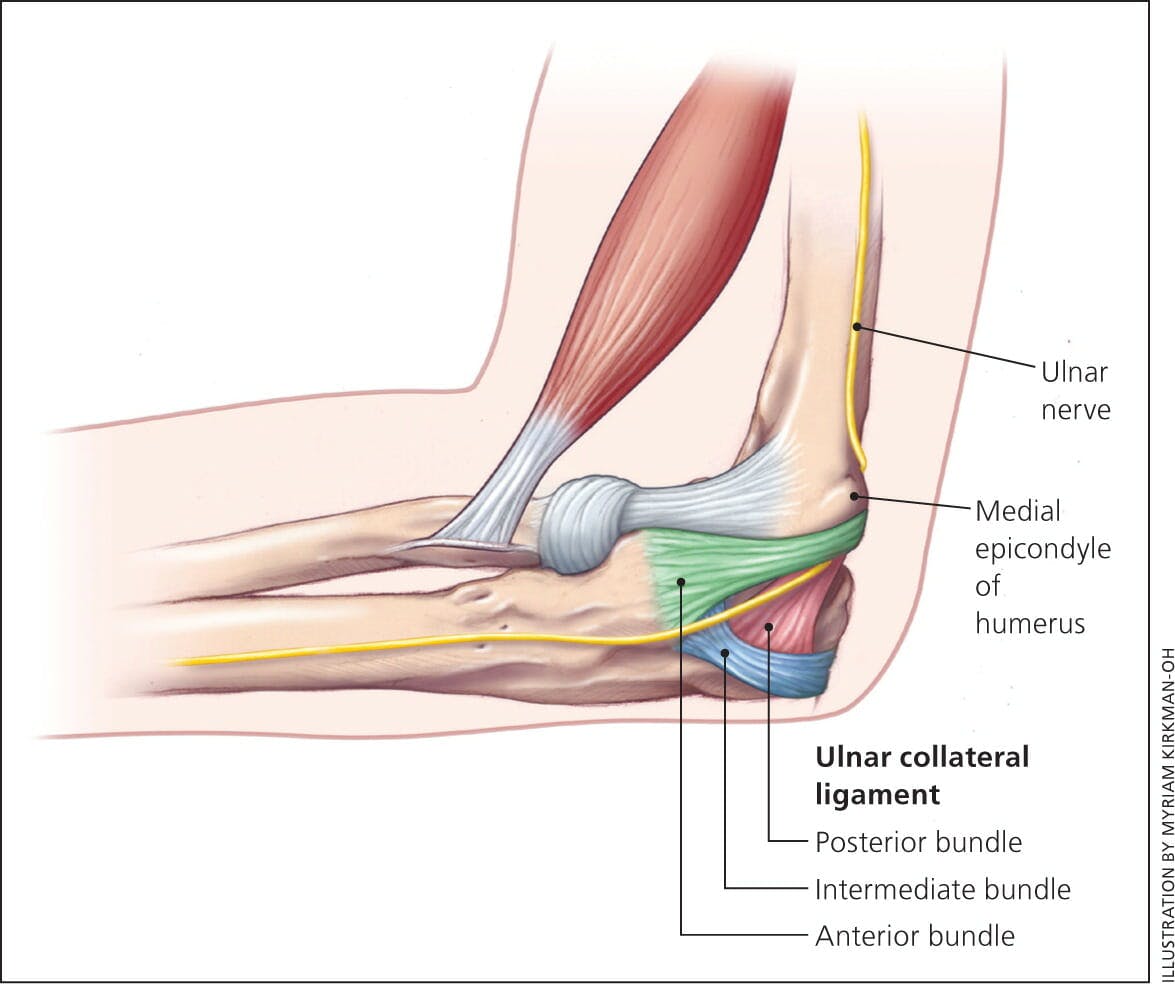 Ulnar Collateral Ligament Injury Archives Park Sports
Ulnar Collateral Ligament Injury Archives Park Sports
 Elbow Anatomy Ligaments Anatomy Americanhighschool
Elbow Anatomy Ligaments Anatomy Americanhighschool
 Elbow Instability Josef Karl Eichinger M D Professor
Elbow Instability Josef Karl Eichinger M D Professor
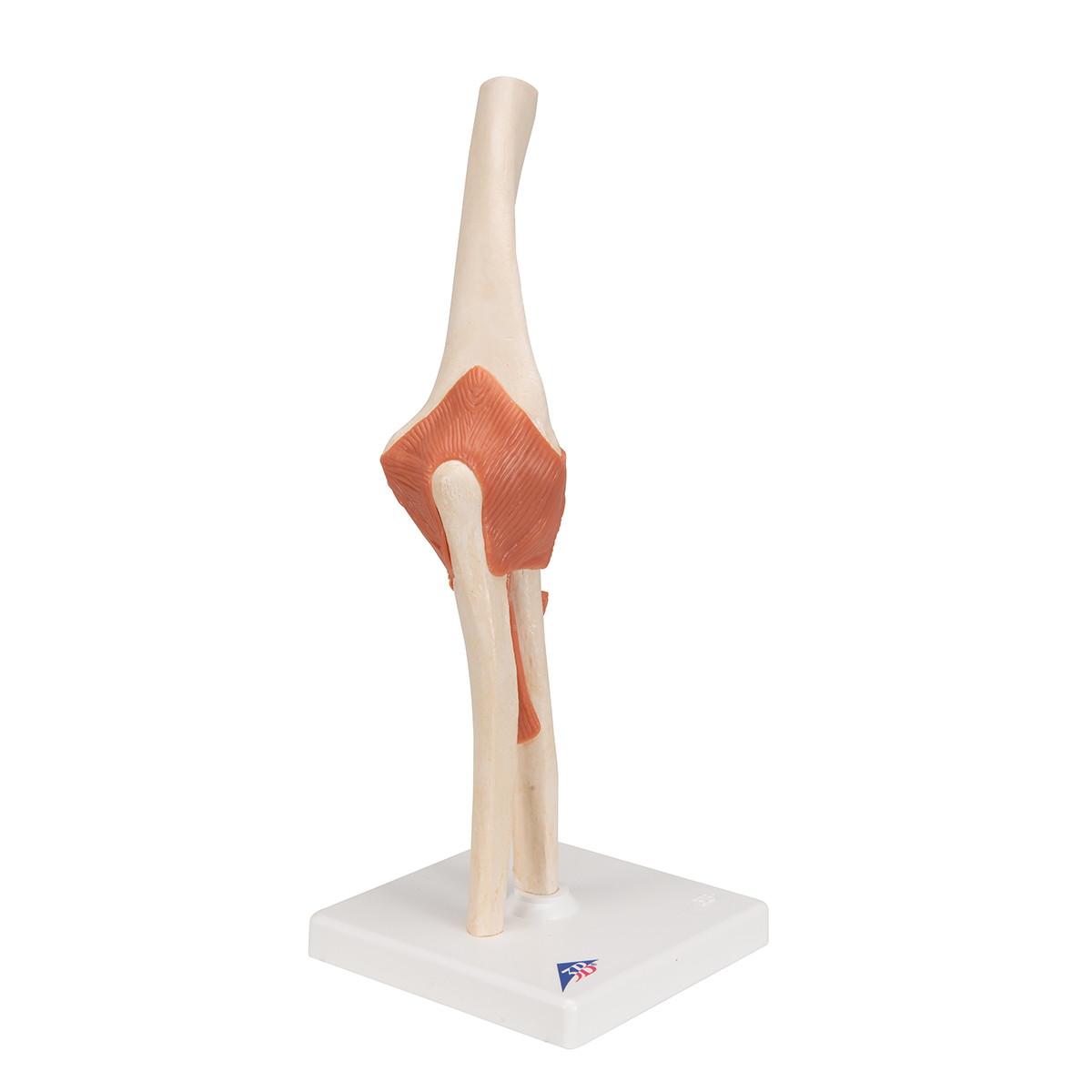 Anatomical Models Human Joint Models Deluxe Functional
Anatomical Models Human Joint Models Deluxe Functional
:watermark(/images/watermark_5000_10percent.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/atlas_overview_image/744/kMQyczxIKCxU5ncr5IqvQ_forearm-bones-and-ligaments_english.jpg) Elbow Joint Anatomy Ligaments Movements Blood Supply
Elbow Joint Anatomy Ligaments Movements Blood Supply
 Anatomy Of The Elbow Elbow Anatomy
Anatomy Of The Elbow Elbow Anatomy
 Figure 1 From Elbow Instability Semantic Scholar
Figure 1 From Elbow Instability Semantic Scholar
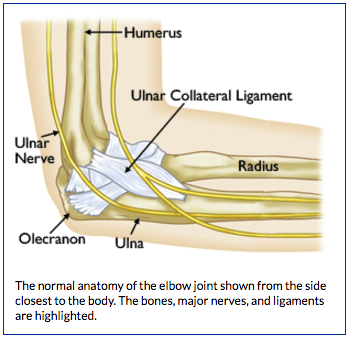 Elbow Overuse Injuries For Throwing Athletes Bouldercentre
Elbow Overuse Injuries For Throwing Athletes Bouldercentre

 Pivot Joint Skeleton Britannica
Pivot Joint Skeleton Britannica
 Elbow Ligaments Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock
Elbow Ligaments Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock
 Anatomical Design Posterior And Radial Collateral Ligament Of
Anatomical Design Posterior And Radial Collateral Ligament Of
 Elbow Anatomy Biomechanics Shoulder Elbow Orthobullets
Elbow Anatomy Biomechanics Shoulder Elbow Orthobullets
 Functional Anatomy Of The Lateral Collateral Ligament
Functional Anatomy Of The Lateral Collateral Ligament
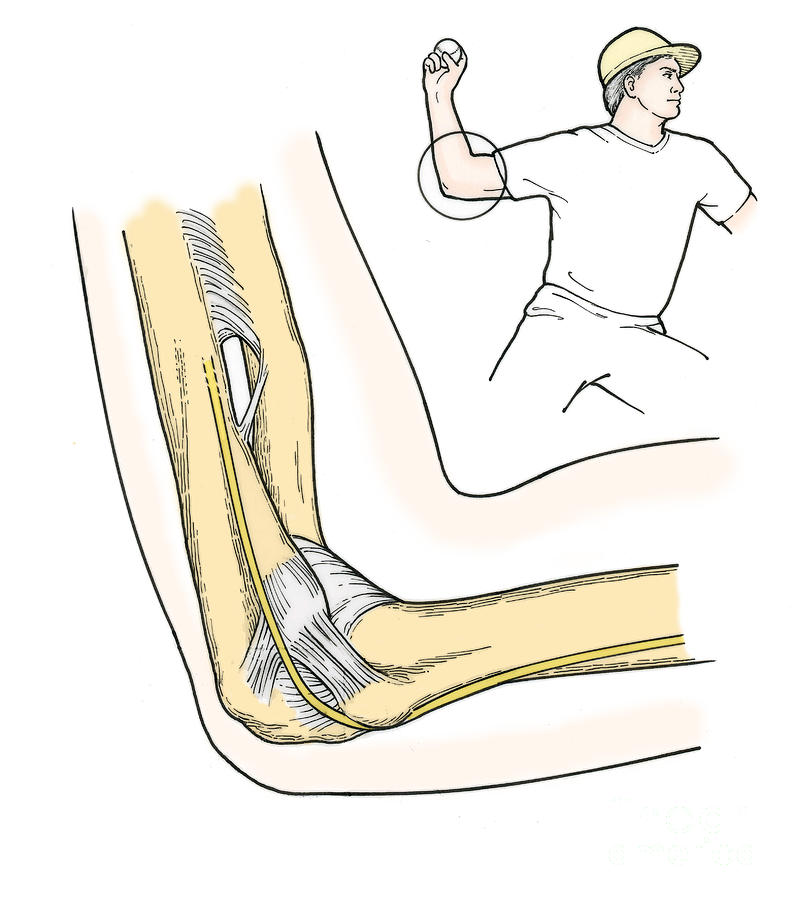 Illustration Of Elbow Ligaments
Illustration Of Elbow Ligaments
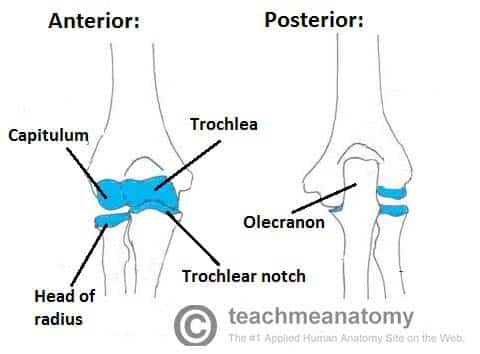 The Elbow Joint Structure Movement Teachmeanatomy
The Elbow Joint Structure Movement Teachmeanatomy
 Ulnar Collateral Ligament Of Elbow Joint Wikipedia
Ulnar Collateral Ligament Of Elbow Joint Wikipedia
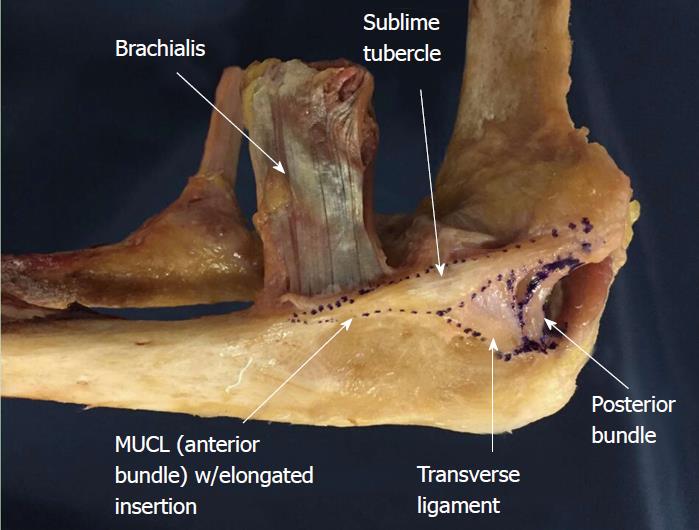 Understanding The Medial Ulnar Collateral Ligament Of The
Understanding The Medial Ulnar Collateral Ligament Of The


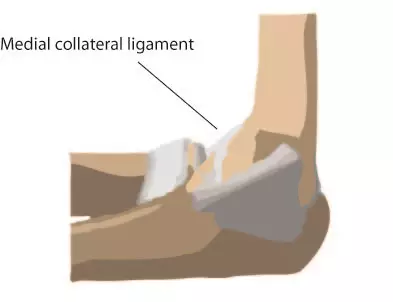
Belum ada Komentar untuk "Elbow Ligaments Anatomy"
Posting Komentar