Hand Nerve Anatomy
As major sensory components of the body the hands are the destination for a majority of the nerves in the upper limb. The median nerve enters the hand through the carpal tunnel which is a passageway between the tubercles of the scaphoid and trapezium bones laterally and by the pisiform and the hook of the hamate on the medial side.
 Hand Anatomy And Function Nerve Anatomy Median Nerve
Hand Anatomy And Function Nerve Anatomy Median Nerve
This plexus is formed from the combination of the anterior branches of the 5th to 8th cervical spinal nerves and the first thoracic one.

Hand nerve anatomy. Hypothenar muscles a group of muscles associated with the little finger. Nerves of the hand. The ulnar nerve c8 t1 supplies all of the intrinsic muscles of the hand apart from the muscles of the thenar eminence and the radial two lumbricals these muscles are supplied by the median nerve c5 t1.
The median nerve supplies sensation to the radial 3 and a half fingers on the palmar aspect as well as the nail beds. The hand is innervated by the radial median and ulnar nerves. It gives nerve supply to the thenar muscles and the first two lumbricals plus it sends sensory fibers to the skin on the lateral part of the palm and to the sides and distal portions of the first three digits.
In the hand the median nerve supplies the thenar eminence the muscles at the base of the thumb with nerves. It also supplies nerves to the lumbrical muscles to the index and middle fingers. A major nerve of the upper extremity.
The connection point between the arm and the hand the wrist enables hand movements. In humans the fibers of the radial nerve originate in the lower cervical and upper thoracic spinal cord usually c5 to t1 travel via the posterior cord of the brachial plexus and supply motor innervation to extensor muscles of the arm and cutaneous sensory fibers to extensor regions of the arm and hand. These nerves control the muscles of the forearm and hand and give us the sensations of touch temperature and pain.
The majority of the intrinsic hand muscles are innervated by the deep branch of the ulnar nerve. The nerves innervating the muscles of the hand originate higher up from a structure called the brachial plexus. Each hand consists of 19 bones.
Along the anterior of the forearm the median and ulnar nerves supply nerve signals to the skin and to the flexor muscles of the hand and fingers. Hand nerves the median radial and ulnar nerves are the three major nerves that run the length of the entire arm. The palm includes five metacarpals and each finger except the thumb.
The radial nerve supplies the finger extensors and the thumb abductor thus the muscles that extends at the wrist and metacarpophalangeal joints knuckles. The median nerve provides sensation to the thumb side of the palm the thumb index middle and half of the ring finger.
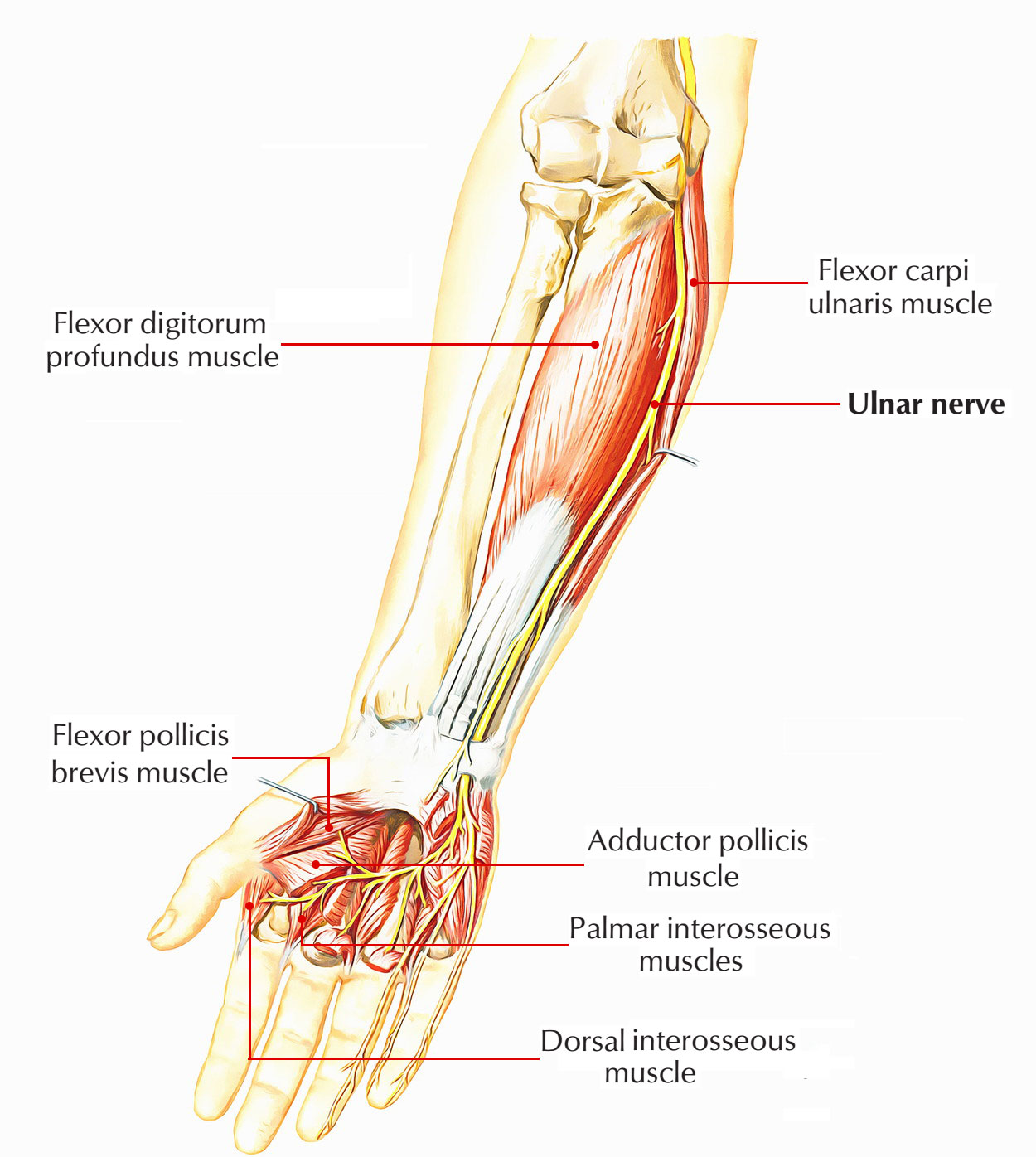 Easy Notes On Ulnar Nerve Learn In Just 4 Minutes
Easy Notes On Ulnar Nerve Learn In Just 4 Minutes
 Hand Vessel Hand Tendon Hand Nerve Anatomy
Hand Vessel Hand Tendon Hand Nerve Anatomy
 Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Vs Cervical Radiculopathy
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Vs Cervical Radiculopathy
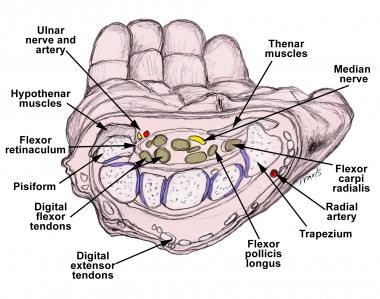 Median Nerve Block Overview Indications Contraindications
Median Nerve Block Overview Indications Contraindications
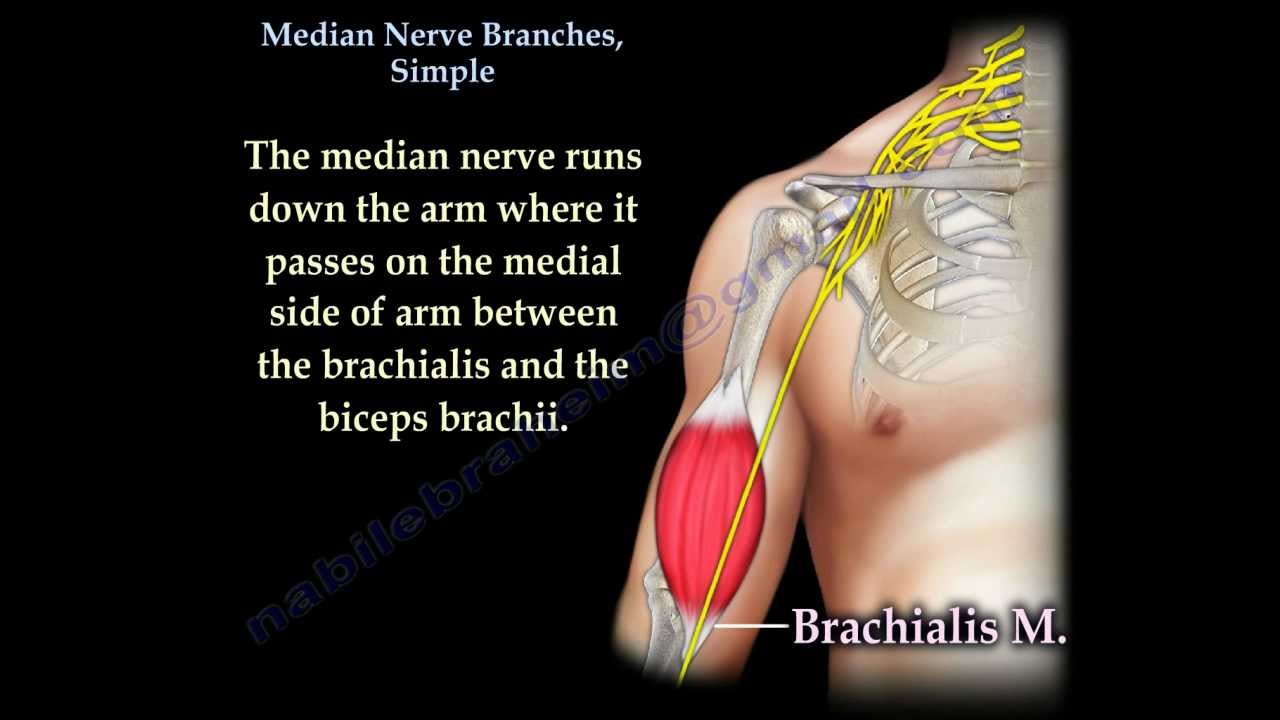 Median Nerve Branches Simple Everything You Need To Know Dr Nabil Ebraheim
Median Nerve Branches Simple Everything You Need To Know Dr Nabil Ebraheim
 Extensor Muscle Anatomy Britannica
Extensor Muscle Anatomy Britannica
 Lateral Antebrachial Cut Nerve Anatomy Orthobullets
Lateral Antebrachial Cut Nerve Anatomy Orthobullets
 Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Symptoms And Treatment Orthoinfo
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Symptoms And Treatment Orthoinfo
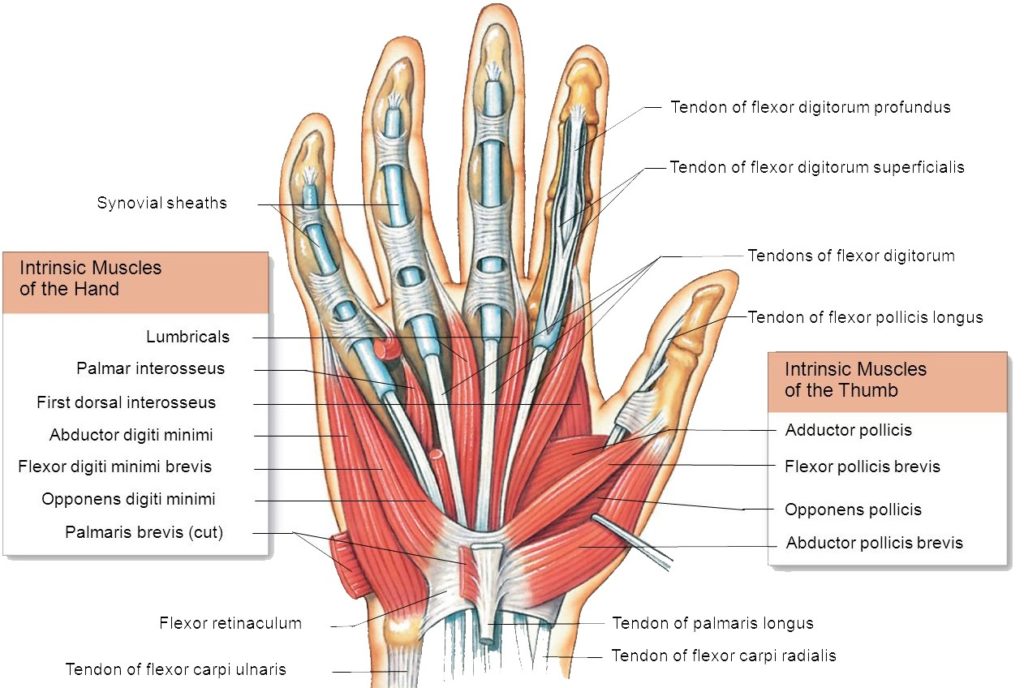 Hand Muscles Attachment Nerve Supply Action Anatomy Info
Hand Muscles Attachment Nerve Supply Action Anatomy Info
 Nerves Blood Vessels And Lymph Advanced Anatomy 2nd Ed
Nerves Blood Vessels And Lymph Advanced Anatomy 2nd Ed
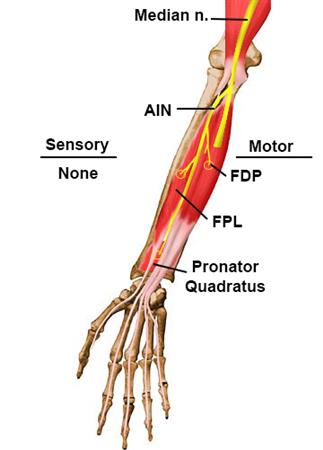 Anterior Interosseous Nerve Anatomy Orthobullets
Anterior Interosseous Nerve Anatomy Orthobullets
 Injuries To The Hand And Digits Tintinalli S Emergency
Injuries To The Hand And Digits Tintinalli S Emergency
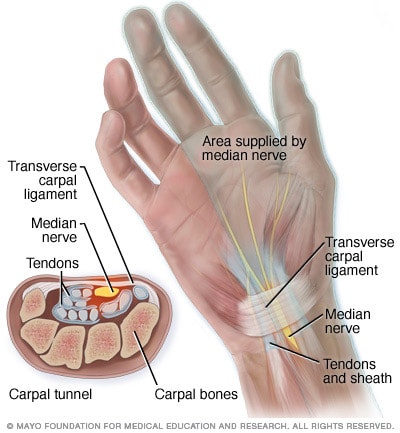 Carpal Tunnel Anatomy Mayo Clinic
Carpal Tunnel Anatomy Mayo Clinic
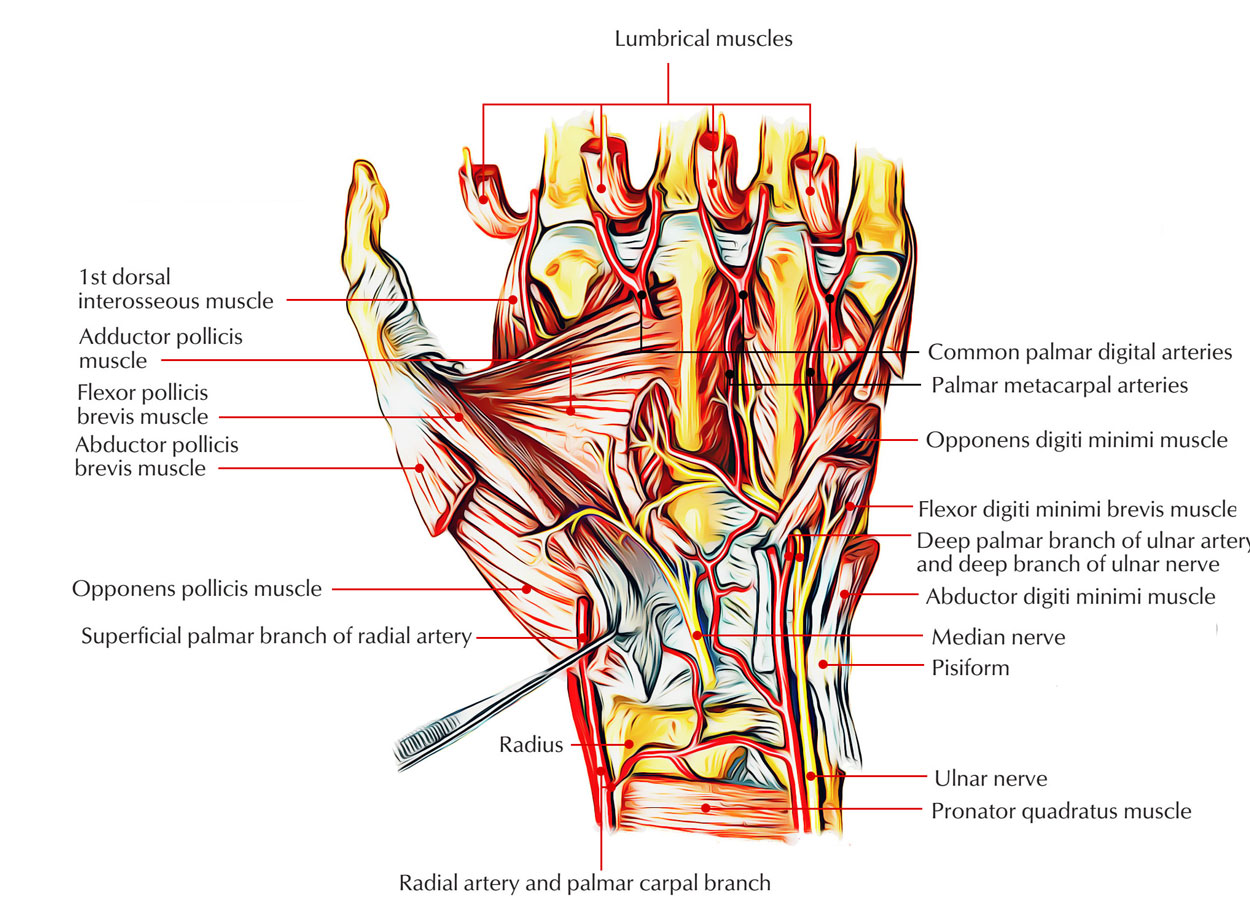 Easy Notes On Intrinsic Muscles Of The Hand Learn In Just
Easy Notes On Intrinsic Muscles Of The Hand Learn In Just
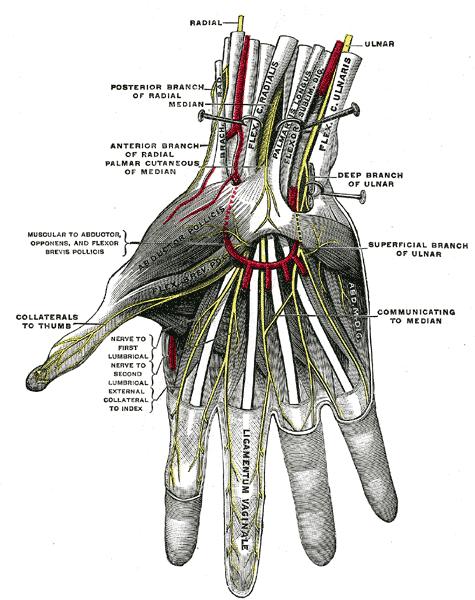 Ulnar Nerve Anatomy Orthobullets
Ulnar Nerve Anatomy Orthobullets
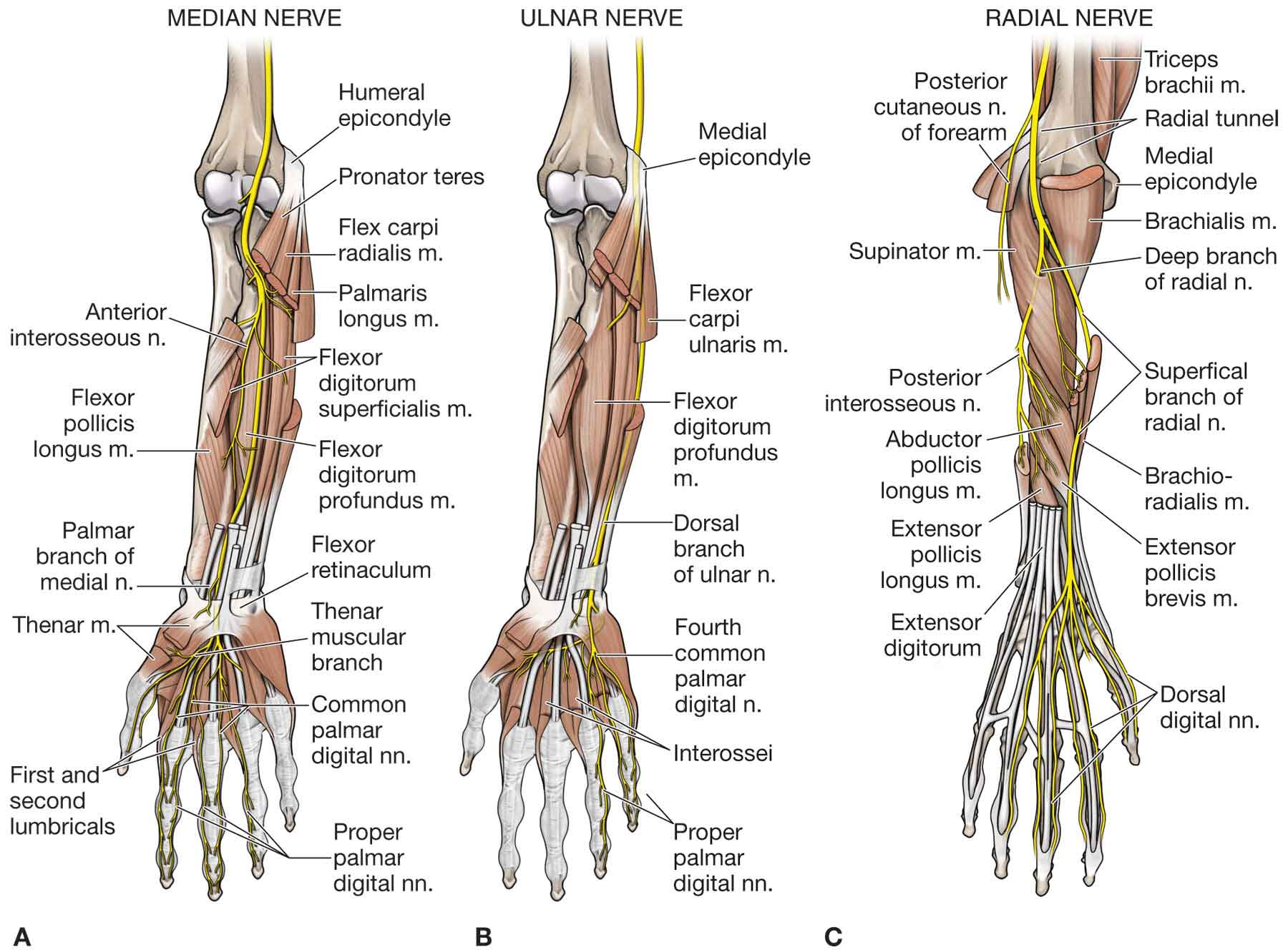 The Forearm Wrist And Hand Musculoskeletal Key
The Forearm Wrist And Hand Musculoskeletal Key
 Posterior Interosseous Nerve Anatomy Orthobullets
Posterior Interosseous Nerve Anatomy Orthobullets
 Magnetic Resonance Imaging Of The Digital Nerves Of The Hand
Magnetic Resonance Imaging Of The Digital Nerves Of The Hand
 Cutaneous Innervation Of Hand Anatomy Qa
Cutaneous Innervation Of Hand Anatomy Qa
 Us 260 0 Hand Sectional Anatomy Of Nerves And Blood Vessels Model Palm Anatomical Model Hand Anatomy Model Anatomical Model Gasen Gl030 In Medical
Us 260 0 Hand Sectional Anatomy Of Nerves And Blood Vessels Model Palm Anatomical Model Hand Anatomy Model Anatomical Model Gasen Gl030 In Medical

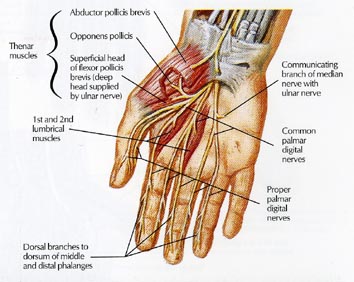

Belum ada Komentar untuk "Hand Nerve Anatomy"
Posting Komentar