Tracheostomy Anatomy
A tracheostomy is a surgical procedure in which an endotrachealtube is inserted directly into the trachea. A regimented approach to preparation and performance.
 Sagittal Section Showing A Tracheostomy Tube In Position And
Sagittal Section Showing A Tracheostomy Tube In Position And
The superior thyroid notch cricoid and suprasternal notch usually can be easily.
Tracheostomy anatomy. To perfrom a tracheostomy knowledge of the following is required. Trachea anatomy what is the function of the trachea the larynx is a cartilaginous chamber about 4 cm 15 in long figure 1. Average cross sectional area of the male adult trachea is approximately 28 cm2 transverse.
Its primary function is to keep food and drink out of the airway but it evolved the additional role of sound production phonation in many animals. Course of the trachea. The trachea is a tube shaped structure consisting of 15 to 20 d shaped cartilage rings anterolaterally bridged by annular ligaments.
The trachea extends from the inferior margin of the cricoid cartilage. Contains glands small arteries nerves lymph vessels and elastic fibers trachealis. Components of the larynx.
They are the same as a routine open operative tracheostomy with particular. It is used when intubation through the nose or mouth with an endotracheal tube is not possible or when long term ventilator support is needed such as when a person experiences prolonged unconsciousness and coma. Nerves vessels and organs.
Trachea anatomy and structure tracheal tissues and membranes respiratory mucosa. The innermost layer of the trachea consisting of ciliated pseudostratified columnar epithelium and lamina propria a thin layer of connective tissue is covered with a sticky mucus coating produced by the goblet cells present in the region 1. A small hole is cut in the front of the trachea through an incision in the neck.
Hence we colloquially think of it as the voice box. Structure of the tracheal rings. Anatomy of trachea tracheostomy 1.
How a tracheostomy is performed surgical anatomy. U shaped trachea 27. The trachealis muscle encircles the trachea completely but is most prominent posteriorly due to the lack of cartilage 4.
 Care Of The Critically Ill Patient With A Tracheostomy
Care Of The Critically Ill Patient With A Tracheostomy
 Tracheostomy With And Without A Ventilator Newport Beach
Tracheostomy With And Without A Ventilator Newport Beach
 Tracheostomy Pediatrics Clerkship The University Of Chicago
Tracheostomy Pediatrics Clerkship The University Of Chicago
 Chapter 26 Tracheostomy Emergency Medicine Procedures 2e
Chapter 26 Tracheostomy Emergency Medicine Procedures 2e
 Tracheostomy Tubesdiscussion Respiratory Care
Tracheostomy Tubesdiscussion Respiratory Care
 Tracheostomy Operating Technique
Tracheostomy Operating Technique
 Chapter 26 Tracheostomy Emergency Medicine Procedures 2e
Chapter 26 Tracheostomy Emergency Medicine Procedures 2e
 Tracheostomy Care Indications Types Care
Tracheostomy Care Indications Types Care
 Crash Course In Tracheostomies
Crash Course In Tracheostomies
 Airway Medical Malpractice Part Iii Of Iii Failure To
Airway Medical Malpractice Part Iii Of Iii Failure To
 Tracheostomy 4 Supporting Patients Following A Laryngectomy
Tracheostomy 4 Supporting Patients Following A Laryngectomy
 Crash Course In Tracheostomies
Crash Course In Tracheostomies
 Anatomy Of The Trachea With Proper Tracheostomy Placement
Anatomy Of The Trachea With Proper Tracheostomy Placement
 Tracheotomy And Tracheostomy Tube How They Help Your Child
Tracheotomy And Tracheostomy Tube How They Help Your Child
 Tracheostomy Epidemiology Indications Timing Technique
Tracheostomy Epidemiology Indications Timing Technique
 Tracheostomy Care Adapted From Various Resources See
Tracheostomy Care Adapted From Various Resources See
 Trach It Til You Make It Types Of Tracheostomy Tubes Sinaiem
Trach It Til You Make It Types Of Tracheostomy Tubes Sinaiem
 Tracheostomy Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock
Tracheostomy Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock
 How A Tracheostomy Is Performed
How A Tracheostomy Is Performed
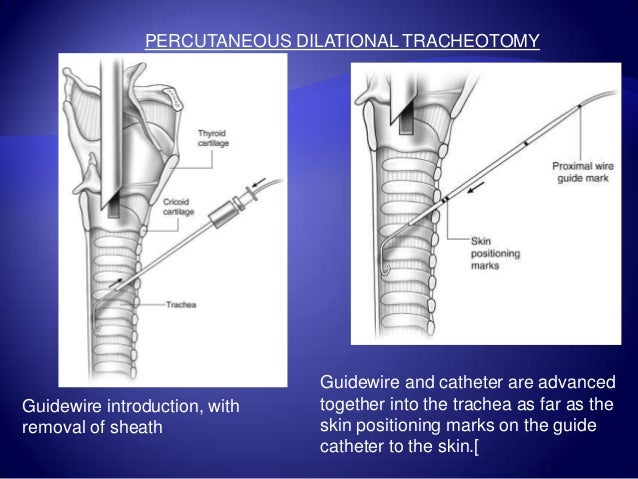
 Percutaneous Tracheostomy Neupsy Key
Percutaneous Tracheostomy Neupsy Key
 Anatomy Of Trachea Tracheostomy
Anatomy Of Trachea Tracheostomy
 Percutaneous Tracheostomy Patient Selection And Complications
Percutaneous Tracheostomy Patient Selection And Complications
 Tracheostomy And Cricothyroidotomy Anesthesia Key
Tracheostomy And Cricothyroidotomy Anesthesia Key
 Tracheostomy Series Normal Anatomy Medlineplus Medical
Tracheostomy Series Normal Anatomy Medlineplus Medical
 Tracheostomy Adult Western New York Urology Associates Llc
Tracheostomy Adult Western New York Urology Associates Llc
 Respiratory Therapy Cave What Is A Tracheostomy
Respiratory Therapy Cave What Is A Tracheostomy
 Emdocs Net Emergency Medicine Educationtrach Travails
Emdocs Net Emergency Medicine Educationtrach Travails




Belum ada Komentar untuk "Tracheostomy Anatomy"
Posting Komentar