Cheeks Anatomy
House and protect the sense organs of smell sight and taste. Our prominent cheeks are created by the zygomatic bones.
It includes several distinct areas of which the main features are.

Cheeks anatomy. In this article we shall look at the anatomical course of the nerve and the motor sensory and parasympathetic functions of its terminal branches. Bones of the face nose. Ethmoidal frontal lacrimal palatine parietal temporal and zygomatic bones mandible maxilla sphenoid vomer.
Lips cheeks and palate anatomy. The two bones that sit side by side and form the bridge of the nose are called. The facial skeleton serves to protect the brain.
The inside of the cheek is lined with a mucous membrane buccal mucosa part of the oral mucosa. The eyes sitting in the orbit and protected by eyelids and eyelashes. The slightly concave temple area at the side of our eyes has the temporal.
How to visualize anatomic labels. Deep face spaces anatomy based on mdct. Face front part of the head that in vertebrates houses the sense organs of vision and smell as well as the mouth and jaws.
The mucosa is rich in mucus secreting glands which together with saliva ensure adequate lubrication for the purposes of speech and mastication. And provide a frame on which the soft tissues of the face can act to facilitate eating facial expression breathing and speech. The horizontal menu allows access to the groups of anatomical structures.
Subcutaneous fat creates the bulk of the cheeks which is then covered with an outer layer of skin. The majority of them originate from bones of the skull and are added into the skin. The distinctive human nose shape nostrils and nasal septum.
The lateral walls of the oral cavity are created by the cheeks. In human digestive system. The facial nerve cn vii is the seventh paired cranial nerve.
Temporal space parotid space prevertebral space retropharyngeal space masticator space. In humans it extends from the forehead to the chin. The forehead comprising the skin beneath the hairline bordered laterally by.
During the course of evolution from the prehuman australopithecus to modern humans homo sapiens the face became smaller in relation to the overall size of the head. Cheeks are fleshy in humans the skin being suspended by the chin and the jaws and forming the lateral wall of the human mouth visibly touching the cheekbone below the eye. Under the fat are facial muscles which are adept at assisting in the manipulation of food in the mouth and creating facial expressions.
Anatomy of the head and neck. The primary bones of the face are the mandible maxilla frontal bone nasal bones and zygoma. Muscles of facial expressions the muscles of facial expression are embedded in the superficial fascia of the face.
The lips and cheeks the lips two fleshy folds that surround the mouth are composed externally of skin and internally of mucous membrane or mucosa. Consists of the upper jaw area made.
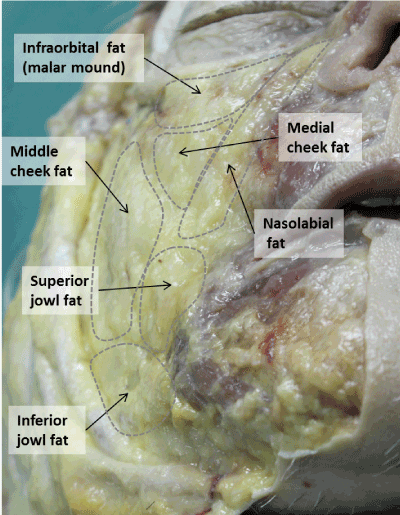 Anatomy And Aging Of Cheek Fat Compartments
Anatomy And Aging Of Cheek Fat Compartments
Lips Cheeks And Palate Human Anatomy Organs
 Buccal Fat Pad Reduction Bristol Uk
Buccal Fat Pad Reduction Bristol Uk
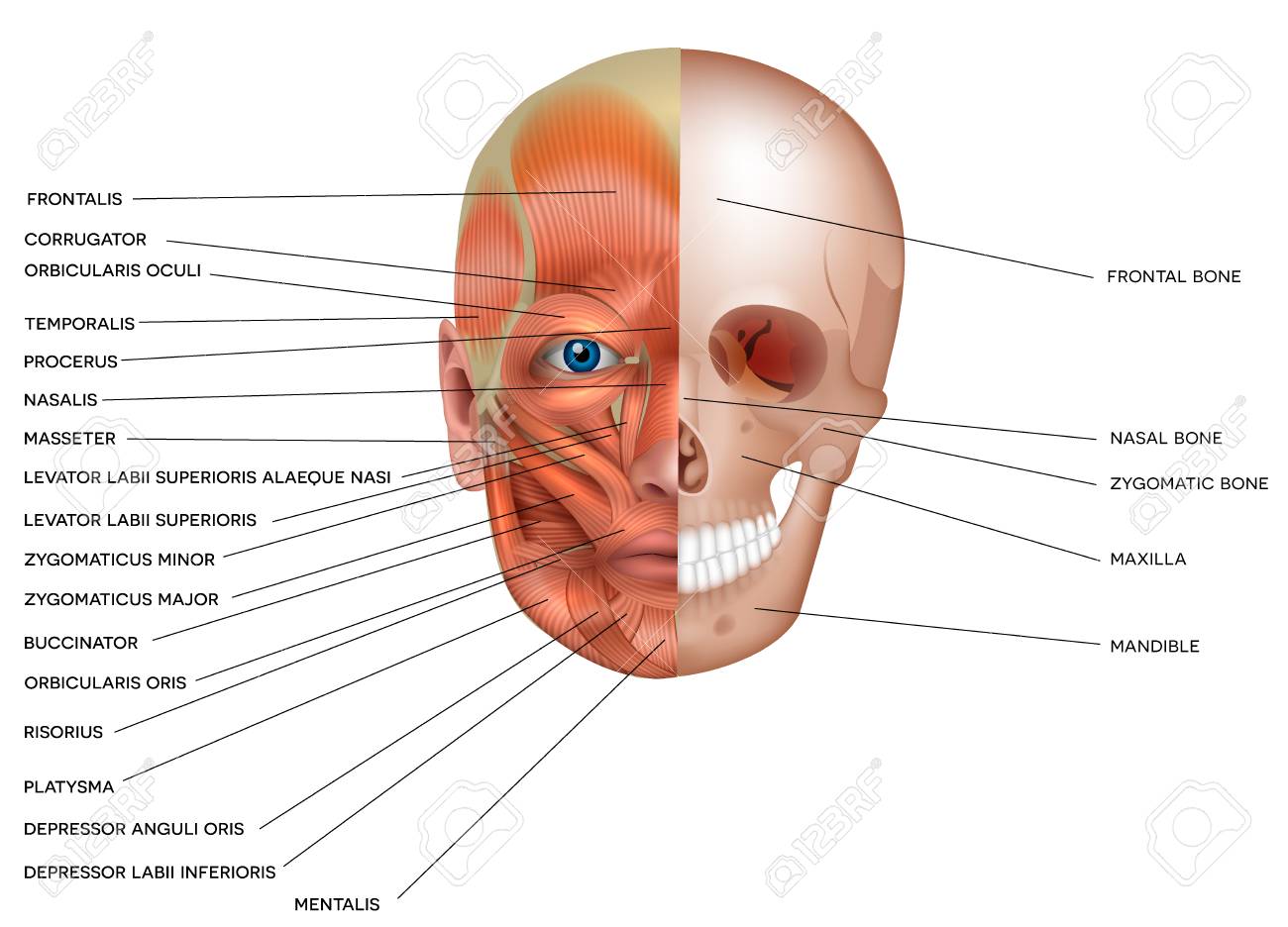 Muscles And Bones Of The Face Detailed Bright Anatomy Isolated
Muscles And Bones Of The Face Detailed Bright Anatomy Isolated
 Oral Cavity Oropharynx Outlander Anatomy
Oral Cavity Oropharynx Outlander Anatomy
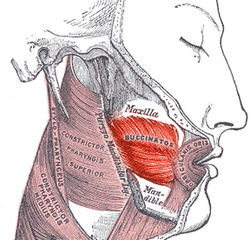
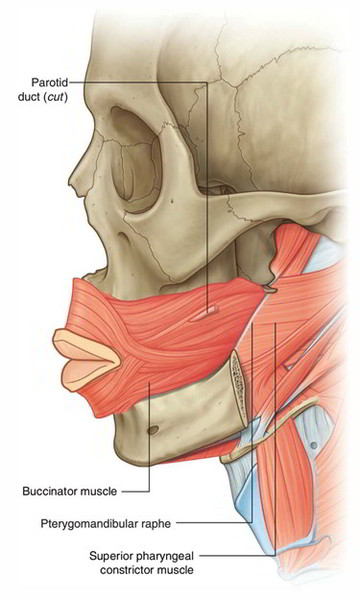 Easy Notes On Buccinator Muscle Learn In Just 4 Minutes
Easy Notes On Buccinator Muscle Learn In Just 4 Minutes
 Figure Anatomy Of The Oral Cavity Pdq Cancer
Figure Anatomy Of The Oral Cavity Pdq Cancer
 Sports Related Facial Trauma Facial Injuries Basic Anatomy
Sports Related Facial Trauma Facial Injuries Basic Anatomy
 Did Plant Eating Dinosaurs Have Cheeks Science Connected
Did Plant Eating Dinosaurs Have Cheeks Science Connected
 Facial Muscles Eyes Google Search In 2019 Facial Anatomy
Facial Muscles Eyes Google Search In 2019 Facial Anatomy
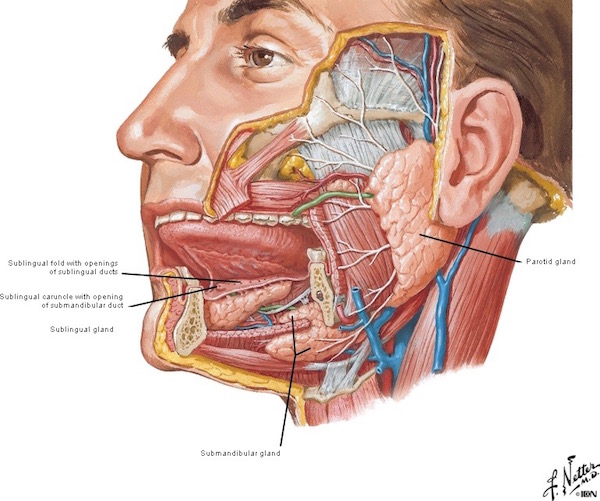
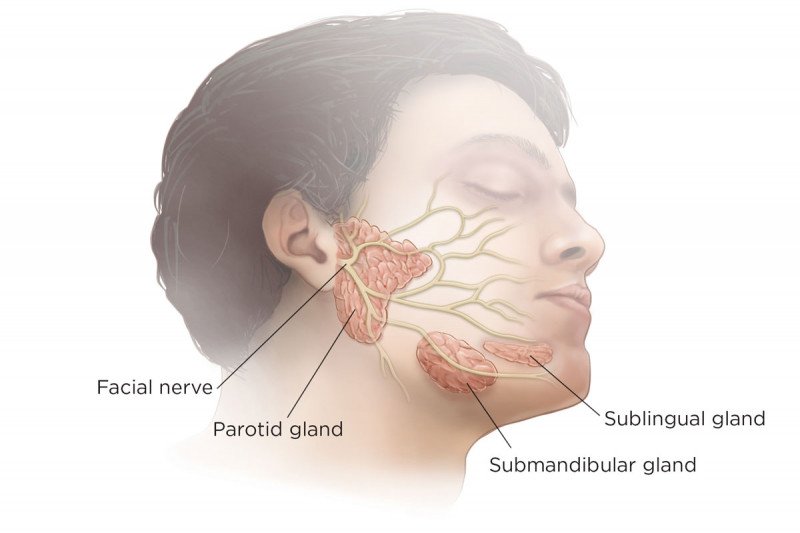 Salivary Glands Anatomy Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center
Salivary Glands Anatomy Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center
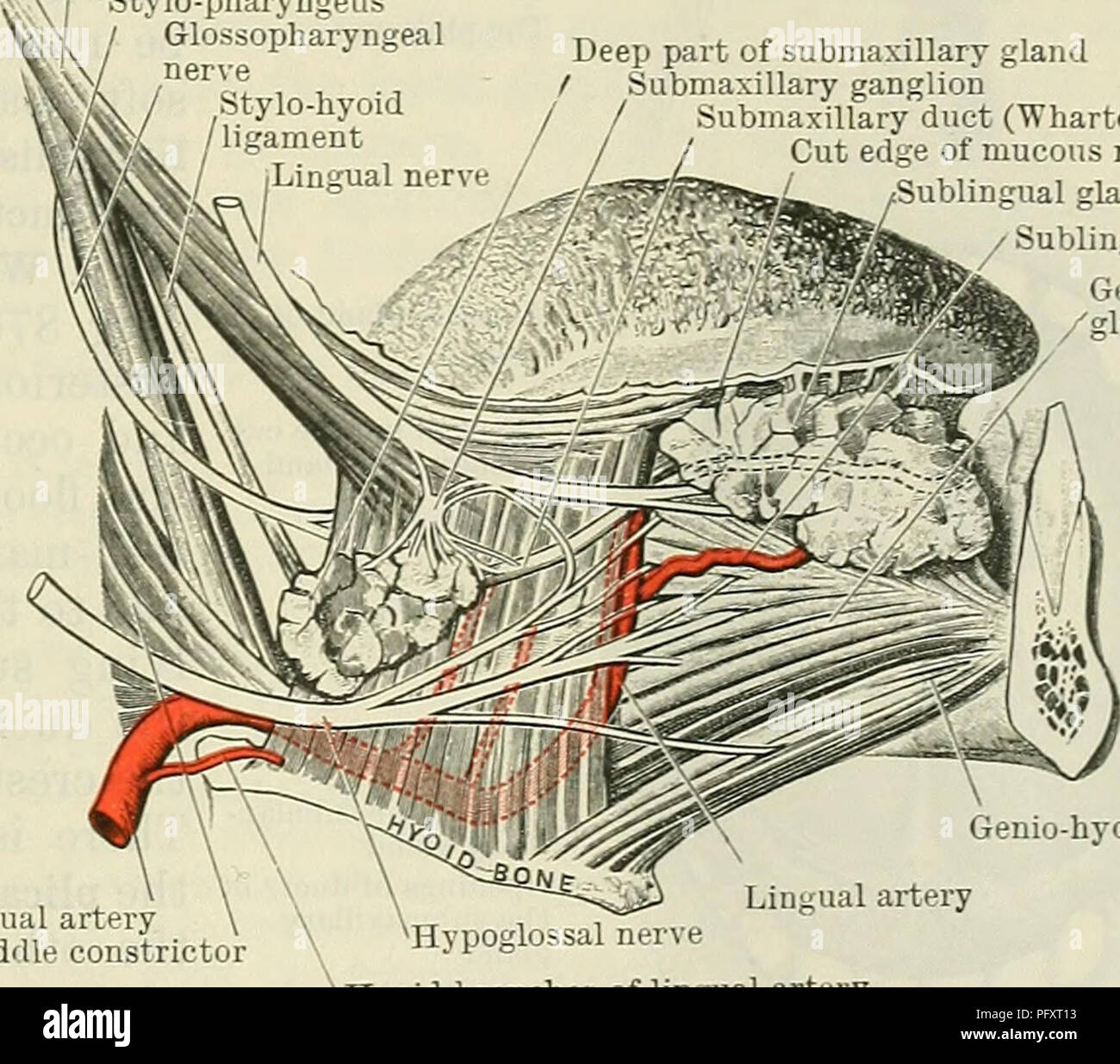 Cunningham S Text Book Of Anatomy Anatomy The Mouth 1107
Cunningham S Text Book Of Anatomy Anatomy The Mouth 1107
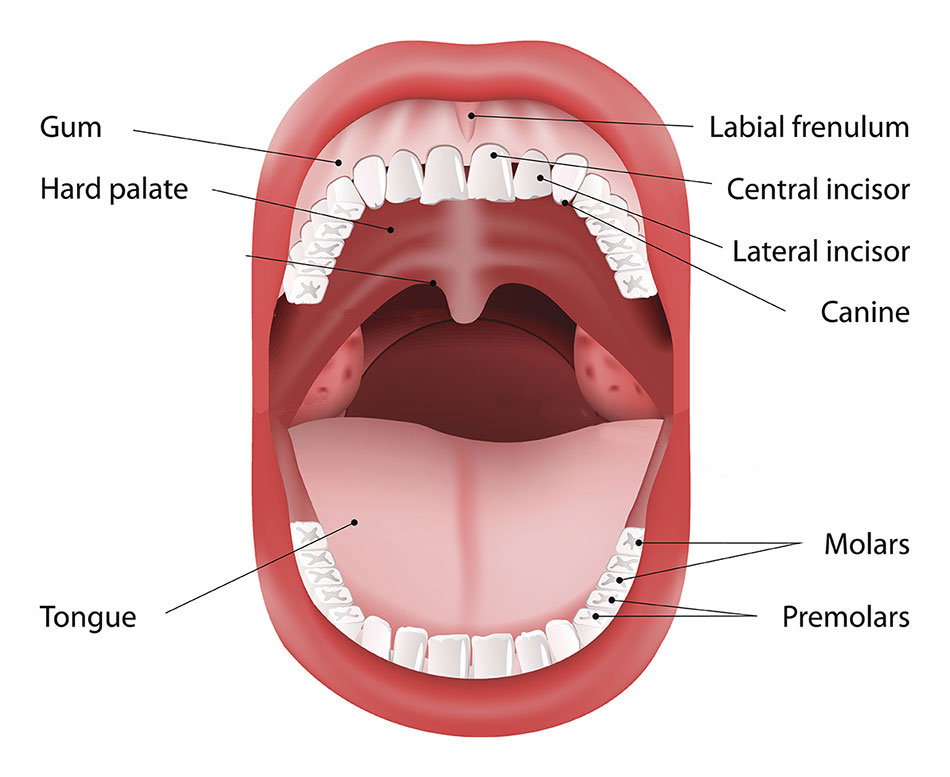 Cancer Of The Tongue Mouth Cheeks And Lips
Cancer Of The Tongue Mouth Cheeks And Lips
 Archive Image From Page 920 Of The Cyclopaedia Of Anatomy And
Archive Image From Page 920 Of The Cyclopaedia Of Anatomy And
 Best Dermal Filler For Cheeks Facial Fillers Facial Bones
Best Dermal Filler For Cheeks Facial Fillers Facial Bones
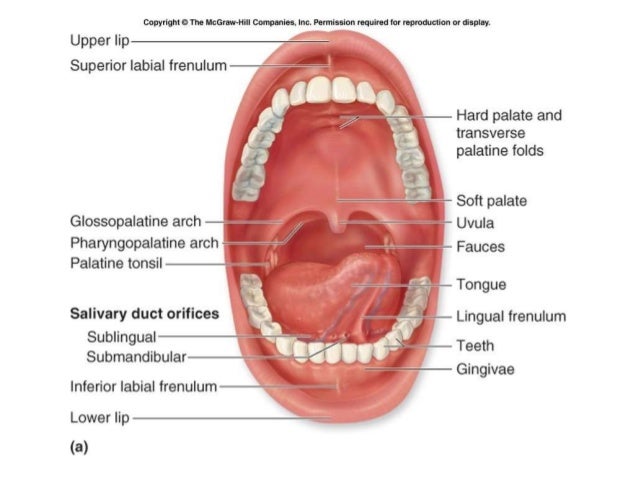 Carcinoma Buccal Mucosa Anatomy To Management
Carcinoma Buccal Mucosa Anatomy To Management
 Structures In The Oral Cavity The Teeth Anatomy And
Structures In The Oral Cavity The Teeth Anatomy And
 Face Muscles And Arteries Illustration Stock Image C047
Face Muscles And Arteries Illustration Stock Image C047
 Anatomy Of Buccal Cancer Mouth Cancer
Anatomy Of Buccal Cancer Mouth Cancer
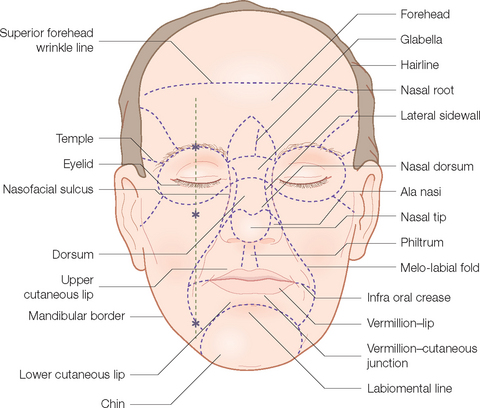
Face Anatomy For Makeup Understanding Technical Terms Of
 Digestive Cheeks Lips Palate Diagram Quizlet
Digestive Cheeks Lips Palate Diagram Quizlet





Belum ada Komentar untuk "Cheeks Anatomy"
Posting Komentar