Anatomy Of Stem
Adventitious roots may also be produced from the nodes. Vascular bundles ppt structure and classification structure and composition of xylem ppt.
 30 2b Stem Anatomy Biology Libretexts
30 2b Stem Anatomy Biology Libretexts
Internal structure of dicot stem fig.
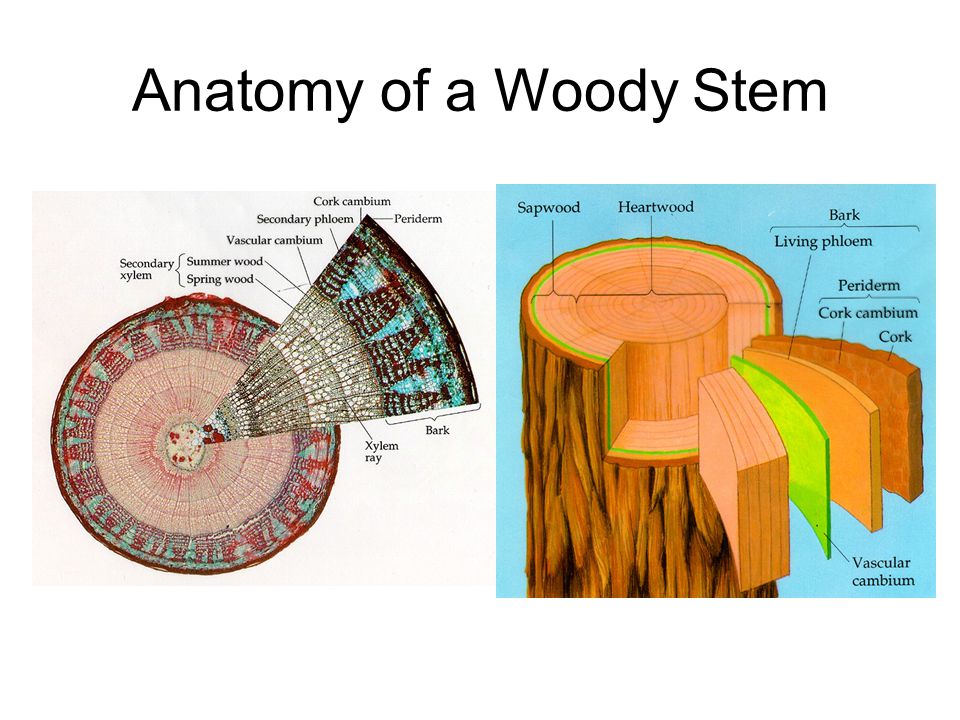
Anatomy of stem. The epidermis is followed by a broad parenchymatous cortex and the vascular tissue in the form of provascular strands is arranged in a ring. It forms the single celled outermost layer of the stem. Anatomy of monocot stems m onocot stems such as corn palms and bamboos do not have a vascular cambium and do not exhibit secondary growth by the production of concentric annual rings.
Simple permanent tissue 1. Anatomy of monocot stem ppt grass and bamboo classification of meristem ppt. Stem cells are the fundamental source of all the bodys tissues the template from which bodily cells are derived.
A young stem of pinus is not circular it shows ridges and furrows due to the surrounding leaves. Parenchyma cells are the most common plant cells. It bears multi cellular hairs and a few stomata.
Stem is the main organ on which the entire weight of plant rests. A stem is one of two main structural axes of a vascular plant the other being the root. They cannot increase in girth by adding lateral layers of cells as in conifers and woody dicots.
Parenchyma collenchyma and sclerenchyma cells. An outline of the internal structure of the stems is given here. The stem and other plant organs are primarily made from three simple cell types.
They are found in the stem the root the inside of the leaf and the pulp of the fruit. As cells die off or are damaged the hundreds of thousands of stem cells in the human body give rise constantly to new tissue. The nodes hold one or more leaves as well as buds which can grow into branches with leaves conifer cones or inflorescences flowers.
Simple permanent tissue 2. The anatomy of stem consists of epidermis hypodermis vascular strands etc. A thin transverse section of a young stem reveals the internal structure when observed under me microscope.
The outer wall of epidermal cells is cutinized. In view of the fact that wide diversities exist as regards the nature of the plants a few common dicotyledons and monocotyledons have been selected for the study of anatomical structures. The stem is normally divided into nodes and internodes.
 The Brain Stem And The Cerebelleum Human Anatomy And
The Brain Stem And The Cerebelleum Human Anatomy And
 3 6 Cellular Differentiation Anatomy And Physiology
3 6 Cellular Differentiation Anatomy And Physiology
 Multilacunar Node Plants Delivered
Multilacunar Node Plants Delivered
 Anatomy Of Stems Botanical Uses
Anatomy Of Stems Botanical Uses
 Anatomy Of Plant Lab Ppt Video Online Download
Anatomy Of Plant Lab Ppt Video Online Download
 The Anatomy Of A Wine Glass Rim Bowl Stem And Base Illustration
The Anatomy Of A Wine Glass Rim Bowl Stem And Base Illustration
 Biology Internal Structure Of Stems Roots Leaves
Biology Internal Structure Of Stems Roots Leaves
 Anatomy Of Dicotyledonous Plants Support And Transport
Anatomy Of Dicotyledonous Plants Support And Transport
 Bulb Anatomy Printout Enchantedlearning Com
Bulb Anatomy Printout Enchantedlearning Com
 File Stem Anatomy Of Cosmos Sulphureus Jpg Wikimedia Commons
File Stem Anatomy Of Cosmos Sulphureus Jpg Wikimedia Commons
 Anatomy Brain Stem Vector Illustration Stock Vector Royalty
Anatomy Brain Stem Vector Illustration Stock Vector Royalty
 Anatomy Of A Dicotyledonous Stem
Anatomy Of A Dicotyledonous Stem
 Stems In Plants Function Types And Anatomy
Stems In Plants Function Types And Anatomy
 Botany Stem Challenge Plant Anatomy Engineering Women S History Activity
Botany Stem Challenge Plant Anatomy Engineering Women S History Activity
 Protostele Plant Anatomy Britannica
Protostele Plant Anatomy Britannica
 Anatomy Of Stems Botanical Uses
Anatomy Of Stems Botanical Uses
 Anatomy Of Stem Cuttings In Relation To Adventitious Rooting
Anatomy Of Stem Cuttings In Relation To Adventitious Rooting
 Horsetails Of Britain And Ireland Terminology Stem Anatomy
Horsetails Of Britain And Ireland Terminology Stem Anatomy
 Dicot Stem Anatomy Plant Science Science Biology
Dicot Stem Anatomy Plant Science Science Biology
 Stems Origin Functions External Anatomy Internal Anatomy
Stems Origin Functions External Anatomy Internal Anatomy
 Anatomy Of Stem Internal Anatomy Of Dicots And Monocots
Anatomy Of Stem Internal Anatomy Of Dicots And Monocots



Belum ada Komentar untuk "Anatomy Of Stem"
Posting Komentar