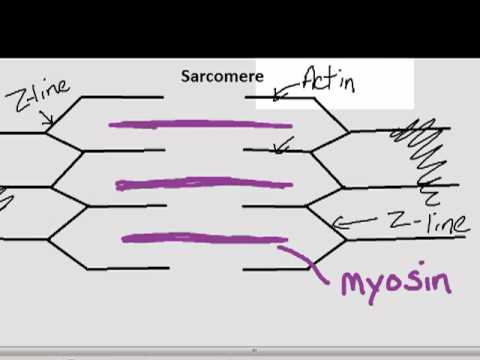
Z Line Definition Anatomy
A fine line in the center of the a band of the sarcomere of striated muscle myofibrils. Z a new york city subway service.
 Structure And Position Of Titin In A Sarcomere Human
Structure And Position Of Titin In A Sarcomere Human
Thick filaments myosin.

Z line definition anatomy. Z line definition is any of the dark thin bands across a striated muscle fiber that mark the junction of actin filaments in adjacent sarcomeres. Thin filaments extended from z line anchor to the z line a. The gastroesophageal junction that joins the esophagus to the stomach.
Z line can refer to. Occasionally it can be irregular and protrude more into the esophagus and not have the typical appearance. The borders that separate and link sarcomeres within a skeletal muscle a ban on a users ip address for the purposes of blocking their access to internet relay chat.
In the center of each i band is a dark transverse membrane the z line. The z line is a zig zag line where these 2 different type tissues meet. Irregular z lines in the esophagus are displacements of the stratified squamous epithelium and the columnar epithelium in the tube that connects the stomach to the throat.
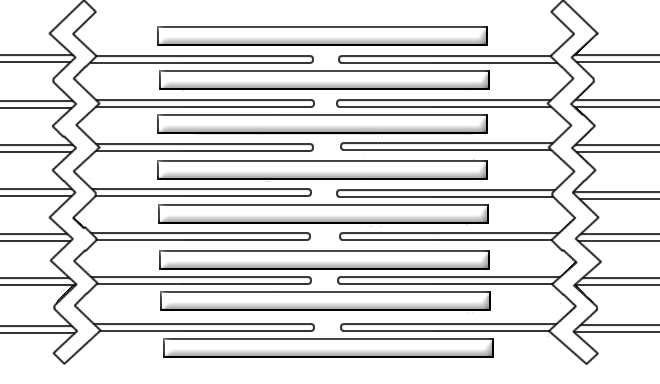
H zone light zone in the centre of the a band where the thick filaments are not overlapped by the thin filaments the sarcomere consist of two lines. The body of the esophagus is approximately 1825 cm in length extending from the upper esophageal sphincter c5 c6 vertebral space to the lower esophageal sphincter t10 level. The a bands are formed by thick myosin filaments and the i bands by thin actin filaments.
Anatomy muscle tissue. Z line forms periphery of sarcomere where thin actin filaments attach m line found inside h zone and forms the middle of the sarcomere. H zone with m line in its middle are located in the middle of the a band.
The national institutes of health state that irregular z lines typically lead to a diagnosis of barretts esophagus. The area between 2 adjacent z lines is called a sarcomere. The esophagus serves as a conduit between the pharynx and the stomach.
Any of the dark thin protein bands to which actin filaments are attached in a striated muscle fiber and that mark the boundaries of adjoining contractile units. Actin forms a twisted helix 2 perl necklaces wrapped around each other 2 proteins that attach called tropomyosin troponin 2. This is generally a benign condition but can occasionally represent mild barretts esophagus a precancerous change caused by reflux.
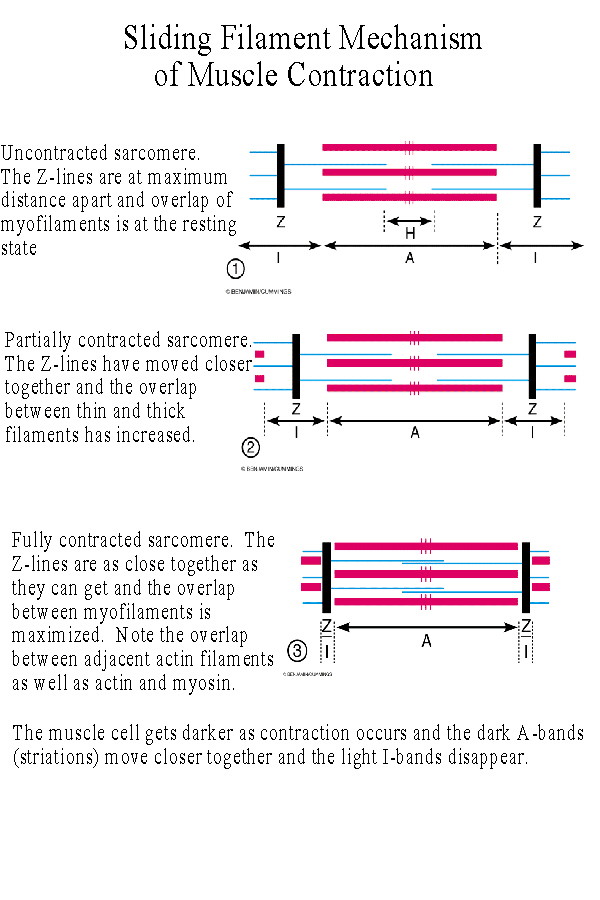 Biol 237 Class Notes Muscle Cells Muscle Physiology
Biol 237 Class Notes Muscle Cells Muscle Physiology
 Muscle Biochemistry Structure And Function
Muscle Biochemistry Structure And Function
 Difference Between A Band And I Band Sarcomere
Difference Between A Band And I Band Sarcomere
 Muscle Biochemistry Structure And Function
Muscle Biochemistry Structure And Function
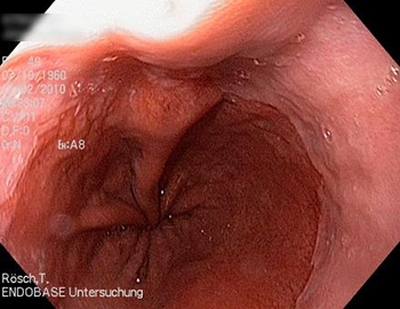 Endoscopy Campus When The Z Line Is Not Completely Normal
Endoscopy Campus When The Z Line Is Not Completely Normal
 Sarcomere Definition Structure Function And Quiz
Sarcomere Definition Structure Function And Quiz
 Muscles Ii Microscopic Anatomy And Contraction Ppt Download
Muscles Ii Microscopic Anatomy And Contraction Ppt Download
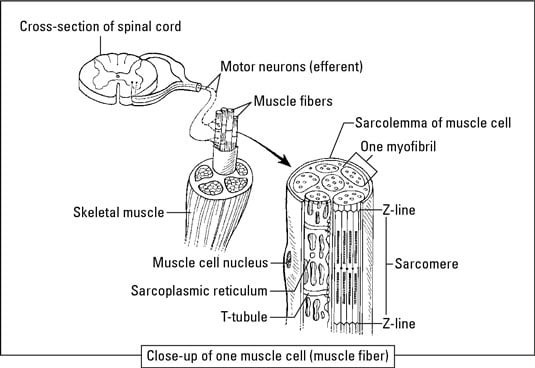 Biology Basics The Basics Of Muscles Dummies
Biology Basics The Basics Of Muscles Dummies
 Endoscopy Campus When The Z Line Is Not Completely Normal
Endoscopy Campus When The Z Line Is Not Completely Normal
 Chapter 9 Muscular System Ppt Video Online Download
Chapter 9 Muscular System Ppt Video Online Download
 Endoscopy Campus When The Z Line Is Not Completely Normal
Endoscopy Campus When The Z Line Is Not Completely Normal
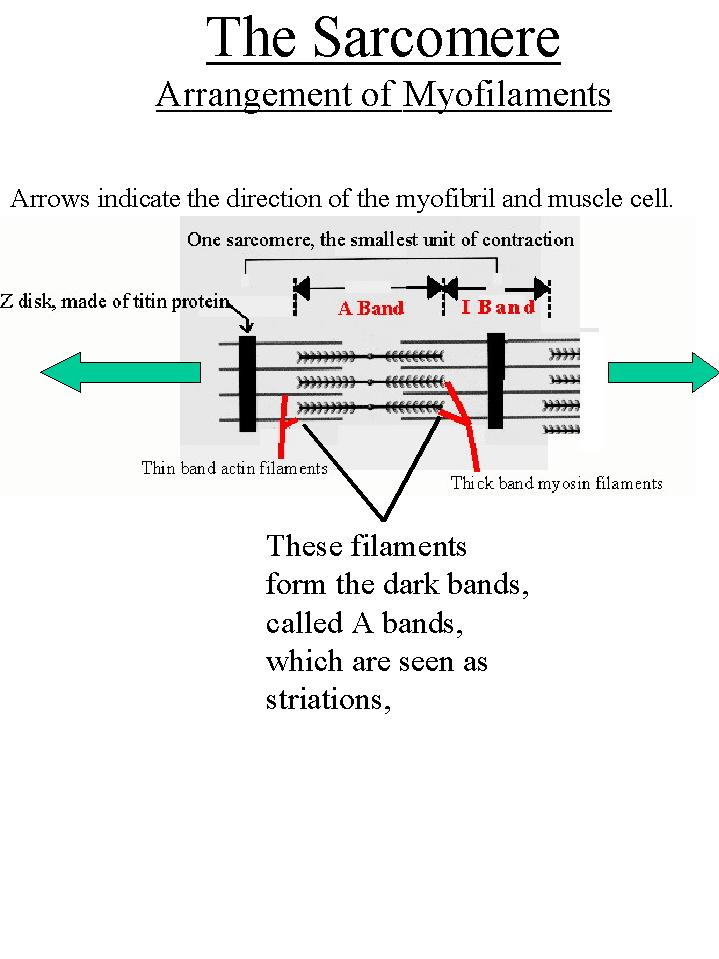 Biol 237 Class Notes Muscle Cells Muscle Physiology
Biol 237 Class Notes Muscle Cells Muscle Physiology
Question Feed What Happens To A Band I Band Z Line M
 Mcat Question Of The Day Sarcomere Anatomy I Band A Band M Line Z Line And H Zone
Mcat Question Of The Day Sarcomere Anatomy I Band A Band M Line Z Line And H Zone
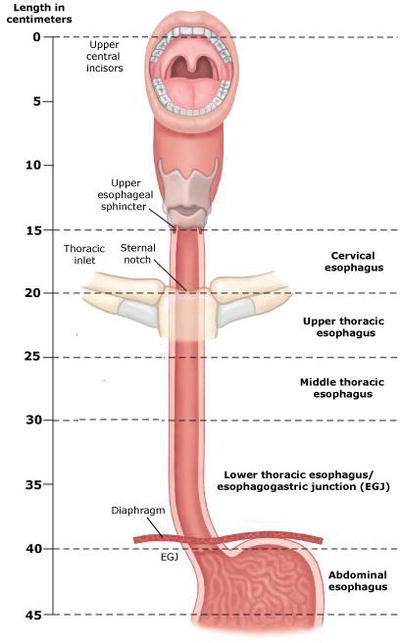 Anatomy Of Esophagus Intechopen
Anatomy Of Esophagus Intechopen
 Muscular Levels Of Organization Anatomy And Physiology I
Muscular Levels Of Organization Anatomy And Physiology I
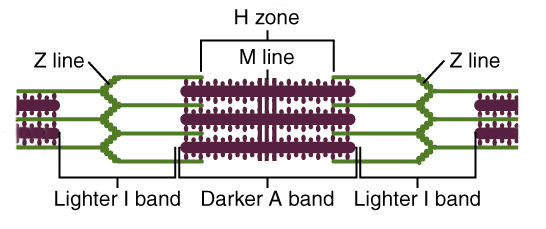 Ultrastructure Of Muscle Skeletal Sliding Filament
Ultrastructure Of Muscle Skeletal Sliding Filament
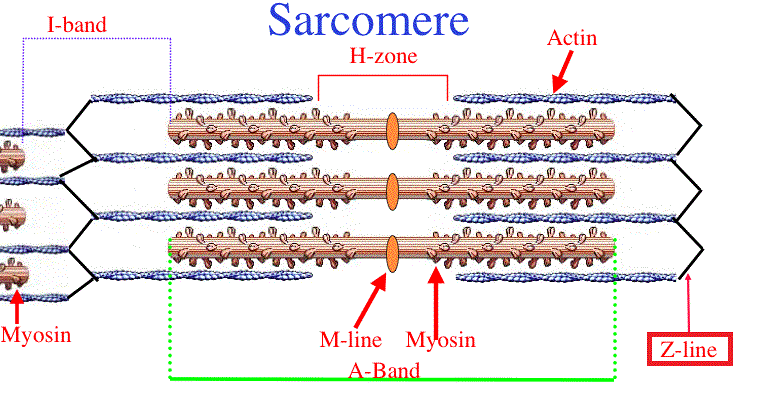
 Microscopic Anatomy Of Skeletal Muscle At Cuesta College
Microscopic Anatomy Of Skeletal Muscle At Cuesta College
 What Is The Structure Of The Muscular System Socratic
What Is The Structure Of The Muscular System Socratic
 Barrett S Esophagus Symptoms Causes Treatment
Barrett S Esophagus Symptoms Causes Treatment





Belum ada Komentar untuk "Z Line Definition Anatomy"
Posting Komentar