Diffusion Anatomy Definition
Integral proteins greatly outnumber peripheral proteins. Simple diffusion is carried out by the actions of hydrogen bonds forming between water molecules and solutes.
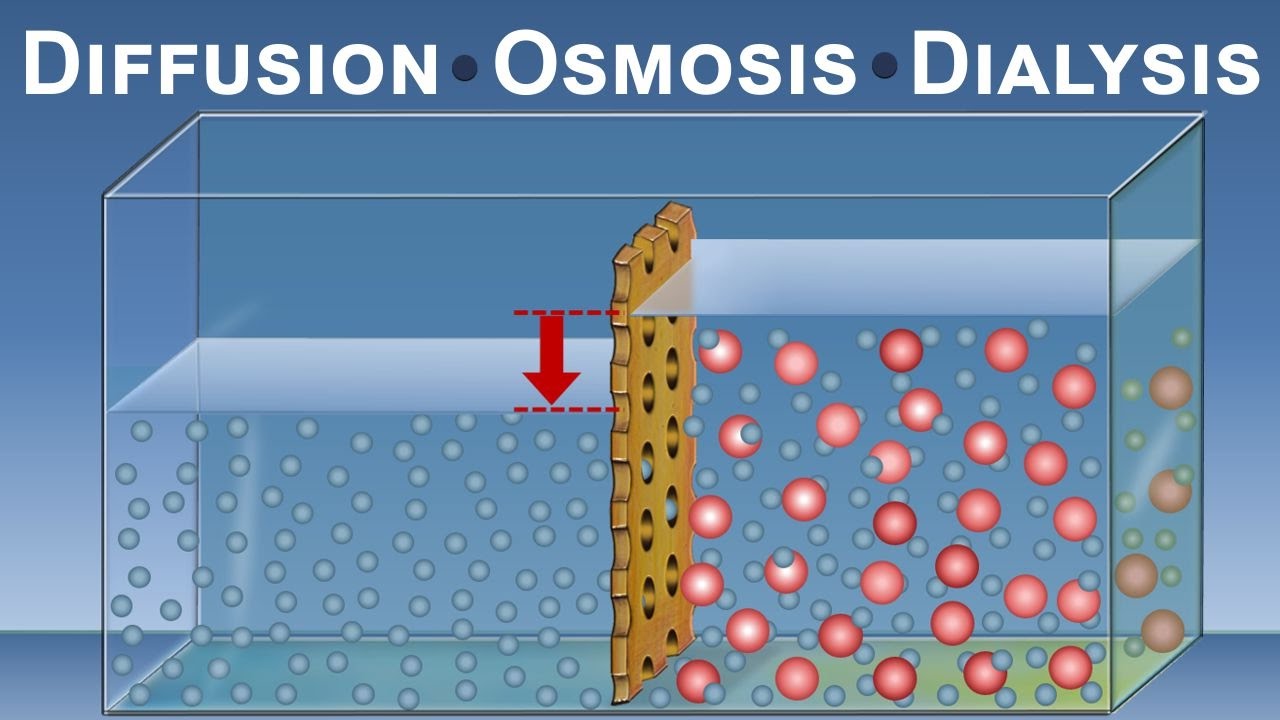 Diffusion Osmosis And Dialysis Iqog Csic
Diffusion Osmosis And Dialysis Iqog Csic
Anatomy physiology diffusion osmosis it moves a specific substrate down its concentration gradient.
Diffusion anatomy definition. Bound to the inner or outer surface of the membrane and are easily separated from it. Steepness of its concentration gradie steepness of concentration gradient measures the vast differe diffusion passive membrane transport where there is net movement of subs equilibrium state in which diffusion is unopposed molecules become even the largest hallow body cavity in humans and many animals. Diffusion by rice university is licensed under a creative commons attribution 40 international license except where otherwise noted.
Passive diffusion is the movement of molecules across a membrane such as a cell membrane. Anatomy physiology plasma membranediffusion osmosis ch. Cell membrane from a region of higher concentration of water to a lower conc.
Diffusion of molecules through a semipermeable membrane from a place of higher concentration to a place of lower concentration until the concentration on both sides is equal. Part of the membrane structure and cannot be removed without damaging or destroying the membrane. For diffusion to occur there must be a concentration gradient.
Share this book powered by pressbooks. Diffusion of only water molecules through the globular protein channels or pores of the cell membrane ie. 3 1 integral proteins.
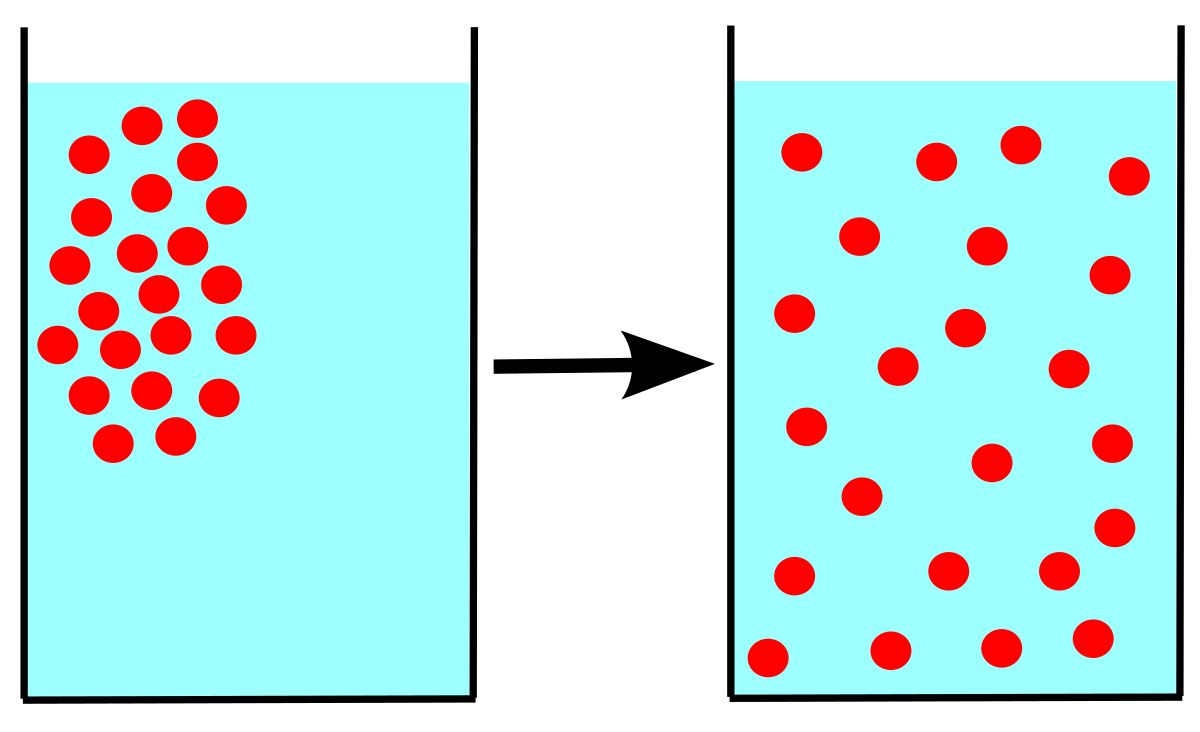
Diffusion definition diffusion is a physical process that refers to the net movement of molecules from a region of high concentration to one of lower concentration. These proteins can move another substrate at the same time without regard to the concentration gradient. Separation of substances in solution by the difference in their rates of diffusion through a semipermeable membrane.
Simple diffusion is the process by which solutes are moved along a concentration gradient in a solution or across a semipermeable membrane. Diffusion is the passive movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. Diffusion is the net passive movement of molecules or particles from regions of higher to regions of lower concentration.
The dissimilarity in the amounts of solutes particles or molecules between two regions will cause them to move between the two regions. One substrates concentration gradient provides the driving force and the other one gets a free ride. Of water until equilibrium of water is reach in an attempt to dilute a particular solute.
The material that diffuses could be a solid liquid or gas.
 Gcse Biology Diffusion Osmosis And Active Transport
Gcse Biology Diffusion Osmosis And Active Transport
 Diffusion Limited And Perfusion Limited Oxygen Transport
Diffusion Limited And Perfusion Limited Oxygen Transport
 What Determines The Direction In Which A Substance Diffuses
What Determines The Direction In Which A Substance Diffuses
 Membrane Functions Physiology And Anatomy Lecture Notes
Membrane Functions Physiology And Anatomy Lecture Notes
Cell Organelles And Cell Transport Thompson Science
 Diffusion Osmosis And Dialysis Iqog Csic Youtube
Diffusion Osmosis And Dialysis Iqog Csic Youtube
 Difference Between Osmosis And Diffusion With Comparison
Difference Between Osmosis And Diffusion With Comparison
Anatomy And Physiology Chapter 3 Proprofs Quiz
Causes Of Restricted Diffusion Questions And Answers In Mri
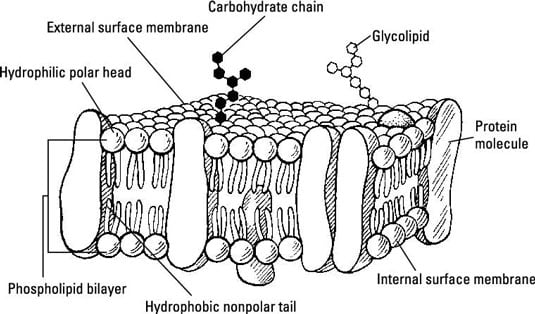 The Cell Membrane Diffusion Osmosis And Active Transport
The Cell Membrane Diffusion Osmosis And Active Transport
 Agar Cell Diffusion Biology Chemistry Science Activity
Agar Cell Diffusion Biology Chemistry Science Activity
 Invention Diffusion And Linear Models Of Innovation The
Invention Diffusion And Linear Models Of Innovation The
 Active And Passive Transport Difference And Comparison
Active And Passive Transport Difference And Comparison
 Diffusion Dictionary Definition Diffusion Defined
Diffusion Dictionary Definition Diffusion Defined
 Facilitated Diffusion Definition Process Examples
Facilitated Diffusion Definition Process Examples
 Mapping The Human Subcortical Auditory System Using
Mapping The Human Subcortical Auditory System Using
 Diffusion Weighted Imaging Radiology Reference Article
Diffusion Weighted Imaging Radiology Reference Article
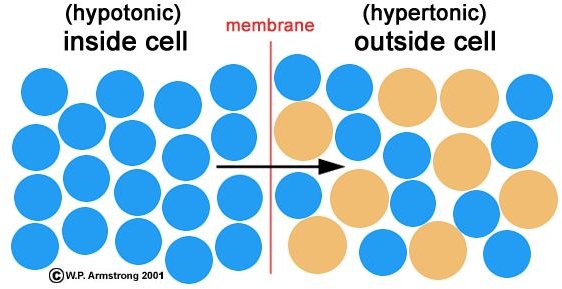 Osmosis And Cells How Osmosis Works In Cell Membrane Functions
Osmosis And Cells How Osmosis Works In Cell Membrane Functions
 Difference Between Osmosis And Diffusion Whyunlike Com
Difference Between Osmosis And Diffusion Whyunlike Com
 Diffusion Definition And Examples Biology Online Dictionary
Diffusion Definition And Examples Biology Online Dictionary
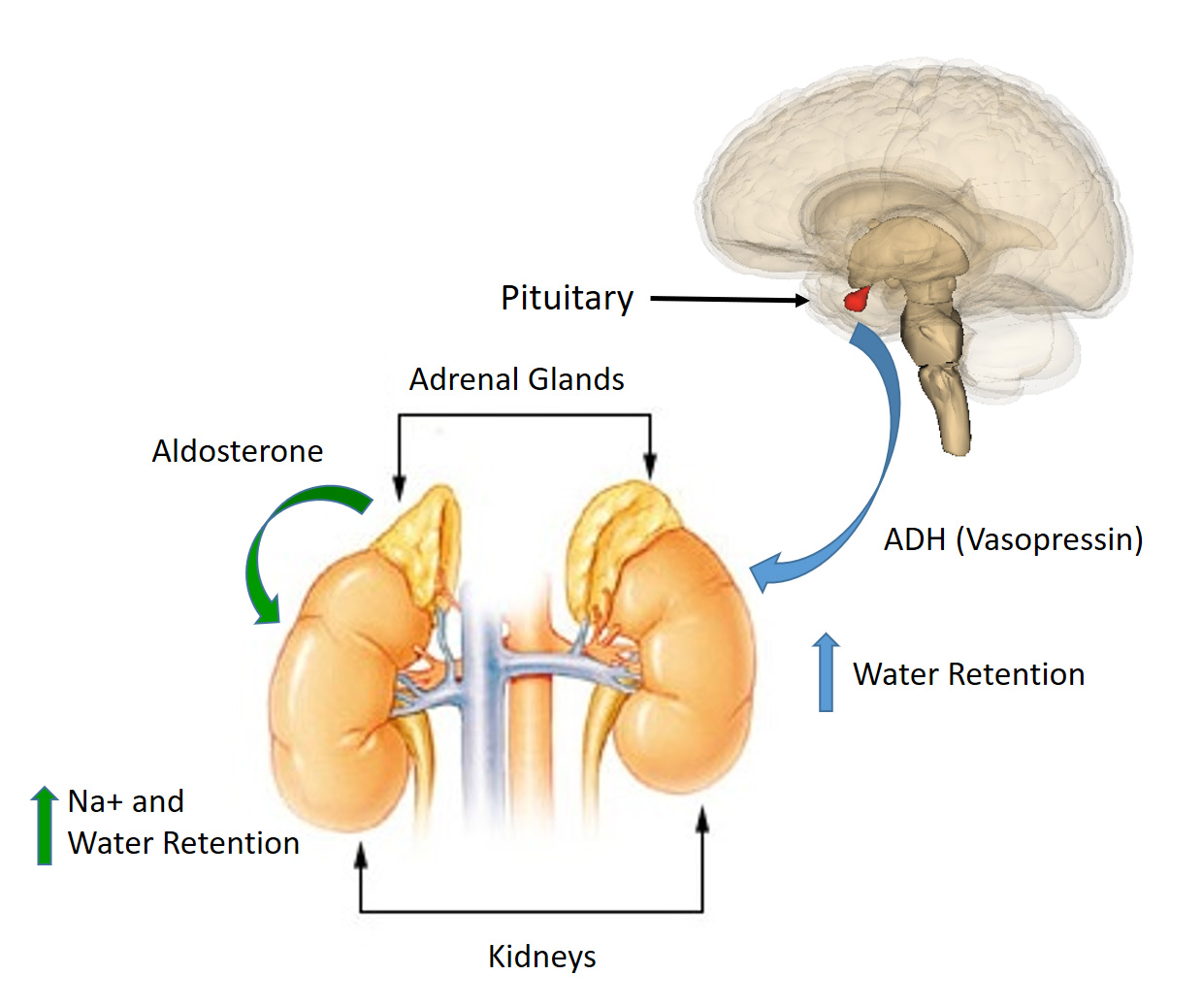 Ch103 Chapter 8 Homeostasis And Cellular Function Chemistry
Ch103 Chapter 8 Homeostasis And Cellular Function Chemistry



:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/gas_exchange_lungs-ca56d9b8ae004cbbb5ab5e33e8723b8b.jpg)
Belum ada Komentar untuk "Diffusion Anatomy Definition"
Posting Komentar