Dog Paws Anatomy
These pads act as a cushion for the load bearing limbs of the animal. Their front and rear paws are very similar just have different names.
While the thick layer of subcutaneous adipose tissue on the paw pads helps absorb shock and acts as a protective cushion the surface of the paw pads is protected by conical papillae extensions of the stratum corneum of the epidermis which is the outermost layer of the skin.

Dog paws anatomy. The paw is characterised by thin pigmented keratinised hairless epidermis covering subcutaneous collagenous and adipose tissue which make up the pads. A dogs paw pads might be the most fascinating features of a dogs feet. The claws create traction and help a dog dig and tear at prey.
The dog paw has five basic parts. Dogs have a foot or paw at the end of each leg called the forefoot or hind foot depending on whether its front or back. Composed of keratin collagen and adipose paw pads serve a number of useful functions.
The dermis of the dense connective tissue is papillated. The metacarpal metatarsal and digital pads function as the load bearing shock absorbing pads. It is arranged into conical papillae with sweatmerocrine glands opening onto the surface of the footpad.
After the hock we get to the paw which as we know is their foot. Dog paw anatomy forelimb anatomy of a dog with digit metacarpal and carpal pads. Moving down the leg.
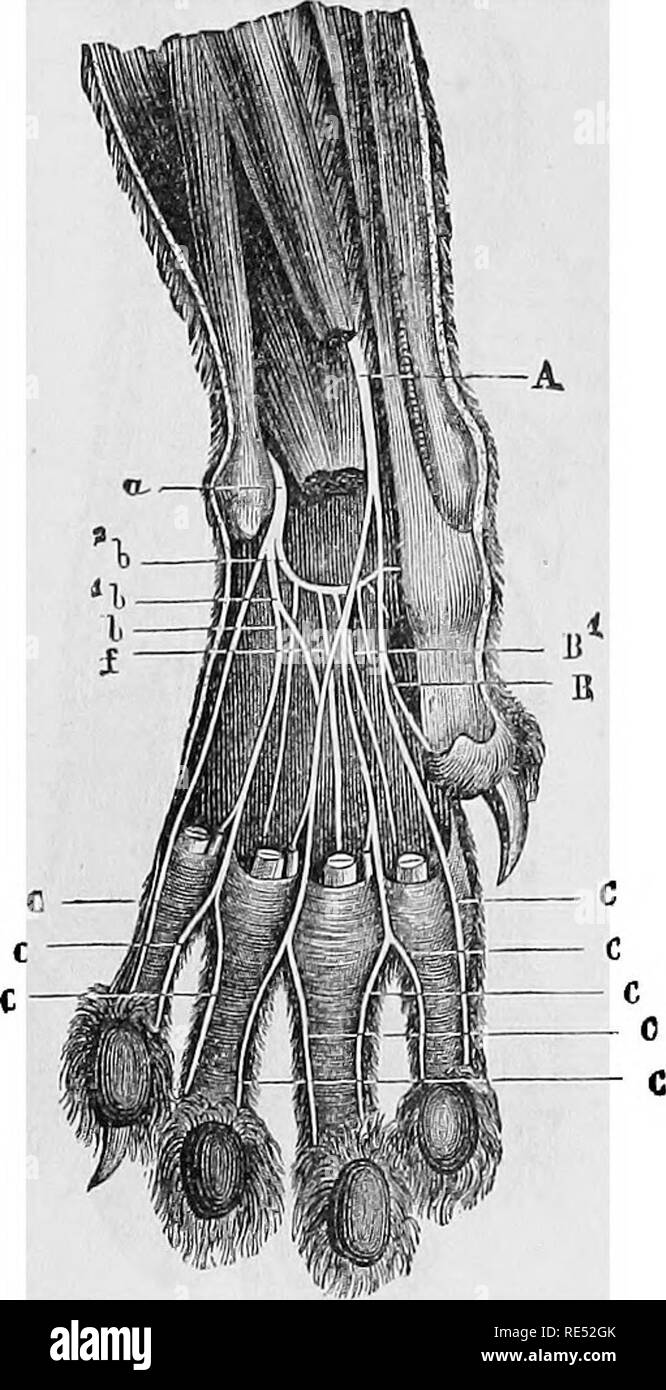
A the claw b digital pads c metacarpal on the front paws and metatarsal on the rear paws pad d dew claw e carpal pad. Enjoy a laugh as we develop comical memes. The canine paw is composed of four weight bearing toes each with a claw and footpad.
A dogs paw pads can be prone to cracks abrasions ulcers and blisters when exposed to heat and cold harsh surfaces and chemicals. The carpal pad helps with skid and traction on a slope or while stopping. From their hock tarsal joint there are metatarsal bones which lead to their toes.
In addition there is a metacarpalmetatarsal footpad. The paw comes with nails sometimes called claws paw pads and usually dewclaws. The epidermis of the footpad is thick pigmented keratinised and hairless.
Most commonly the dogs outer layer of skin the stratum coneum sloughs off exposing a raw layer of skin that is very sensitive and can take even weeks to properly heal.
Chapter 25 Fracture And Dislocation Of The Carpus
 Dog Paw Pad Injury A Helpful Guide Canna Pet
Dog Paw Pad Injury A Helpful Guide Canna Pet
 Dog Paw Anatomy Docx Dog Paw Anatomy Forelimb Anatomy Of A
Dog Paw Anatomy Docx Dog Paw Anatomy Forelimb Anatomy Of A
 Amazon Com Anatomy Of A Corgi Cute Funny Dog Paws Lover
Amazon Com Anatomy Of A Corgi Cute Funny Dog Paws Lover
 18 Things You Didn T Know About Dog Paws Mnn Mother
18 Things You Didn T Know About Dog Paws Mnn Mother
 Bildergebnis Fur Dog Paw Anatomy Animal Drawings Drawings
Bildergebnis Fur Dog Paw Anatomy Animal Drawings Drawings
 How Should You Line Up The Feet In Downward Dog Yoganatomy
How Should You Line Up The Feet In Downward Dog Yoganatomy
Free Cat Paw Drawing Download Free Clip Art Free Clip Art
 The Ultimate Guide To Caring For Your Dog S Paws
The Ultimate Guide To Caring For Your Dog S Paws
 Dog Paw Stock Image Image Of Animal Care Pads Anatomy
Dog Paw Stock Image Image Of Animal Care Pads Anatomy
 18 Things You Didn T Know About Dog Paws Mnn Mother
18 Things You Didn T Know About Dog Paws Mnn Mother
 Anatomy Of A Dog S Paw With A Labeled Diagram
Anatomy Of A Dog S Paw With A Labeled Diagram
Paw Tissues Unique Injuries Need Special Care Attention
 What Are Dewclaws And Do Dogs Need Them Pethelpful
What Are Dewclaws And Do Dogs Need Them Pethelpful
 Paws Anatomy Urinary Tract Cranberry Treats For Dogs Prevent Utis Dog Incontinence Healthy Supplements To Prevent Treat Dog Urinary Tract
Paws Anatomy Urinary Tract Cranberry Treats For Dogs Prevent Utis Dog Incontinence Healthy Supplements To Prevent Treat Dog Urinary Tract

Dog Wolf Paws Tips Tutorial Canine Art Tip Art Resources
 Paw Pad Issues And Injuries In Dogs Symptoms Causes
Paw Pad Issues And Injuries In Dogs Symptoms Causes
Dog Paw Drawing At Getdrawings Com Free For Personal Use
 Vintage Dog Feet Anatomy Illustration Book Page Dog
Vintage Dog Feet Anatomy Illustration Book Page Dog
 Canine Anatomy The Paws And Legs Of A Domestic Dog Image With
Canine Anatomy The Paws And Legs Of A Domestic Dog Image With
 Joint Trauma In Small Animals Musculoskeletal System
Joint Trauma In Small Animals Musculoskeletal System
Dog Anatomical Charts And Posters
Differences Similarities Human Animal Anatomy Kyle
 Cat Paw Anatomy Stock Photos Cat Paw Anatomy Stock Images
Cat Paw Anatomy Stock Photos Cat Paw Anatomy Stock Images
Chapter 25 Fracture And Dislocation Of The Carpus






Belum ada Komentar untuk "Dog Paws Anatomy"
Posting Komentar