Thalamus Anatomy
The thalamus is made up of two symmetrical structures formed from the diencephalon. In addition to the tracts mentioned above.
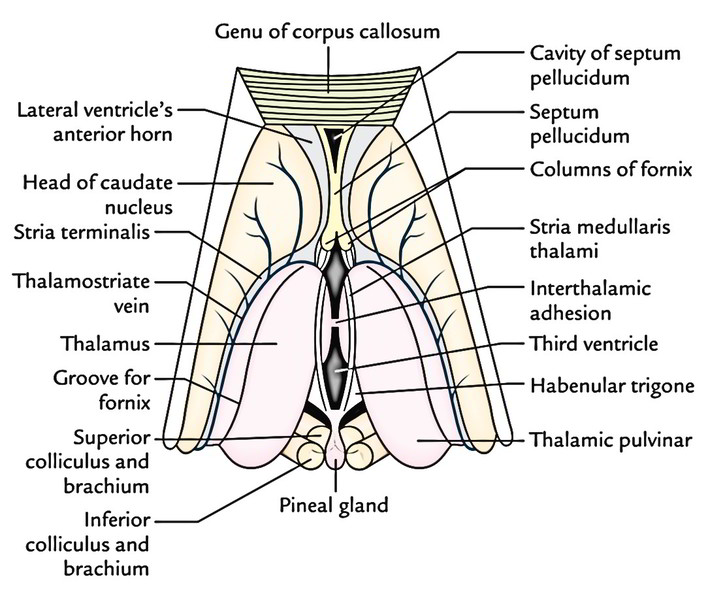 Easy Notes On Thalamus Learn In Just 4 Minutes Earth S Lab
Easy Notes On Thalamus Learn In Just 4 Minutes Earth S Lab
The thalamus lies at the core of the diencephalon.

Thalamus anatomy. It is located deep in the forebrain present just above the midbrain. The medial mass consists of the medial nuclear group. Thalamus plural thalami either of a pair of large ovoid organs that form most of the lateral walls of the third ventricle of the brain.
In addition to being divided into anterior. The thalamus is a limbic system structure and it connects areas of the cerebral cortex that are involved in sensory perception and movement with other parts of the brain and spinal cord that also have a role in sensation and movement. The thalamus translates neural impulses from various receptors to the cerebral cortex.
Medial lateral superior and inferior. Thalamus is a part of the diencephalon. In the rostral part of the thalamus the internal medullary lamina splits to form a partial capsule around the anterior nuclear group.
The medial surface. The superior surface of the thalamus is coated by a band. Thalamus anatomy medial surface.
The anterior end of the thalamus is rounded and narrow which forms the posterior boundary. The anterior pole narrows to form the posterior boundary of the interventricular foramen. The thalamus is a paired structure of gray matter located in the forebrain which is superior to the midbrain near the center of the brain with nerve fibers projecting out to the cerebral cortex in all directions.
The anatomical details such as topography or location structure and nuclei input and output fibers as well as blood supply of thalamus. One thalamus is present on each side of the third ventricle. The medial surface of the thalamus forms the upper part of the lateral wall.
The posterior end of the thalamus is expanded to form the pulvinar. Posteriorly the thalamus expands to form the pulvinar. Structurally the thalamus is composed of two symmetrical egg shaped masses thalami which are usually connected at the midline by a band of grey matter the interthalamic adhesion.
Anatomy of the thalamus the thalamus has two ends the anterior and posterior poles and four surfaces. Anatomy of the thalamus. Nuclei in a given pole or surface regulate specific functions or processing of sensory information and maintain particular connections with parts of the nervous and limbic system.
As a regulator of sensory information the thalamus also controls sleep and awake states of consciousness. The lateral surface of the thalamus is coated by a layer. The lateral mass contains the lateral nuclear group and the ventral nuclear group.
The thalamus separating it into medial and lateral nuclear masses. The inferior surface of the thalamus is continuous with the tegmentum of the midbrain.
:watermark(/images/watermark_5000_10percent.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/atlas_overview_image/130/rbUGADBqRfwtHiT9LRPSmw_coronal-section-brain-thalamus-level_english__1_.jpg) Diagram Pictures Coronal Section Of The Brain At The
Diagram Pictures Coronal Section Of The Brain At The
 Thalamus Vector Illustration Labeled Medical Diagram With
Thalamus Vector Illustration Labeled Medical Diagram With
 Braistem Thalamus Anatomy Mona Y Li Biomedical Visuals
Braistem Thalamus Anatomy Mona Y Li Biomedical Visuals
 Anatomical Localisation Of Thalamus And Basal Ganglia
Anatomical Localisation Of Thalamus And Basal Ganglia
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/9394/thalamus-and-related-structures_english.jpg) Thalamus Anatomy Nuclei Function Kenhub
Thalamus Anatomy Nuclei Function Kenhub
Brain Anatomy The Hippocampus Hypothalamus Thalamus
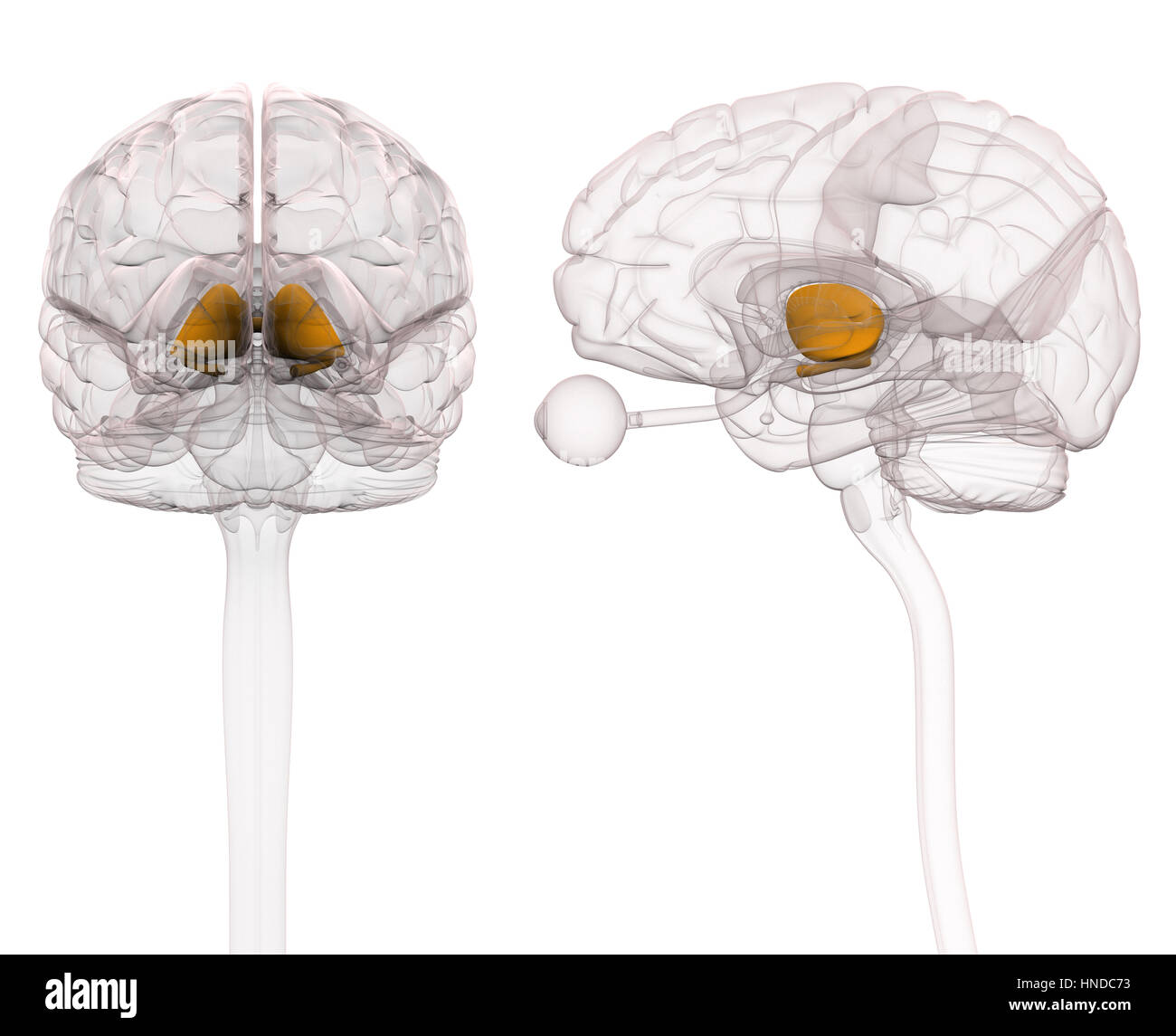 Thalamus Brain Anatomy Stock Photo 133675335 Alamy
Thalamus Brain Anatomy Stock Photo 133675335 Alamy
 Figure 2 2 From Fast Automatic Segmentation Of Thalamic
Figure 2 2 From Fast Automatic Segmentation Of Thalamic
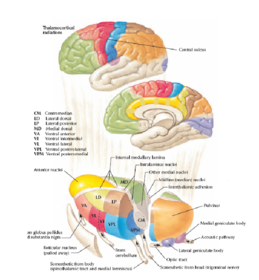 Thalamus Hypothalamus Flashcards
Thalamus Hypothalamus Flashcards
 What Is Thalamus And How It Looks Like
What Is Thalamus And How It Looks Like
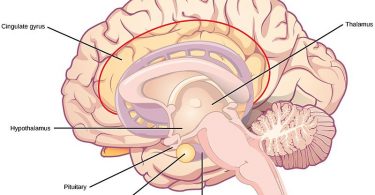 Thalamus Anatomy Archives Pediaa Com
Thalamus Anatomy Archives Pediaa Com
 Thalamus Functions Of Thalamus Anatomy Clinical Significance
Thalamus Functions Of Thalamus Anatomy Clinical Significance
 Anatomy Of Cerebral Cortex Thalamus Interconnexions J
Anatomy Of Cerebral Cortex Thalamus Interconnexions J
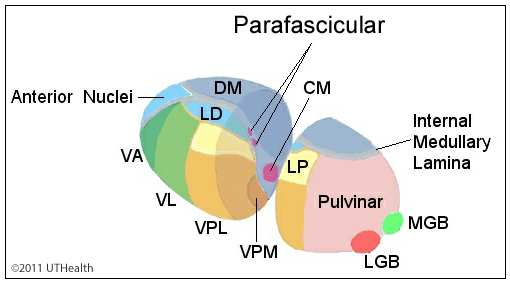 Neuroanatomy Online Lab 8 Higher Motor Function
Neuroanatomy Online Lab 8 Higher Motor Function
:watermark(/images/watermark_only.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/thalamus-9/spA2heICPXnK4xnSNknuA_Thalamus_01.png) Thalamus Anatomy Nuclei Function Kenhub
Thalamus Anatomy Nuclei Function Kenhub
 Thalamus Anatomy Location Structure Function Physiology
Thalamus Anatomy Location Structure Function Physiology
 Thalamus Facts Position In Brain Summary Function
Thalamus Facts Position In Brain Summary Function
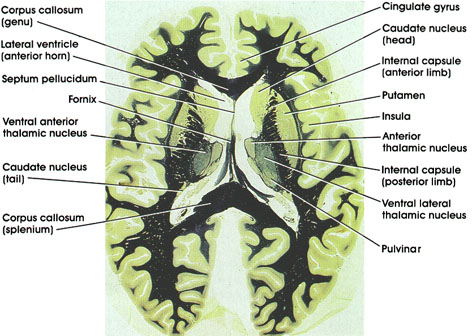 Anatomy Atlases Atlas Of Microscopic Anatomy Section 1 Cells
Anatomy Atlases Atlas Of Microscopic Anatomy Section 1 Cells
 Thalamus Definition Functions Location
Thalamus Definition Functions Location
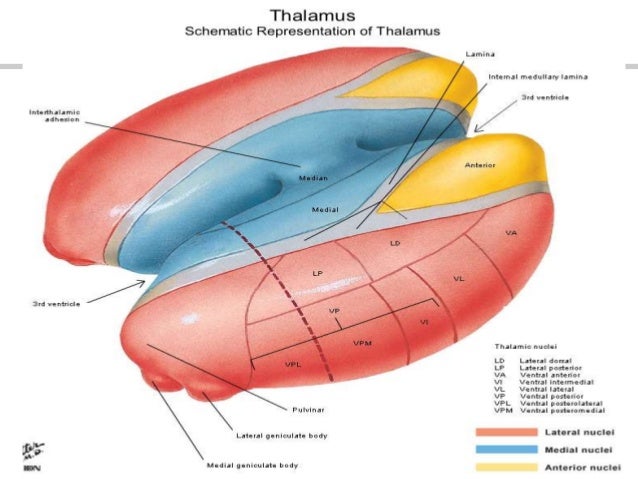
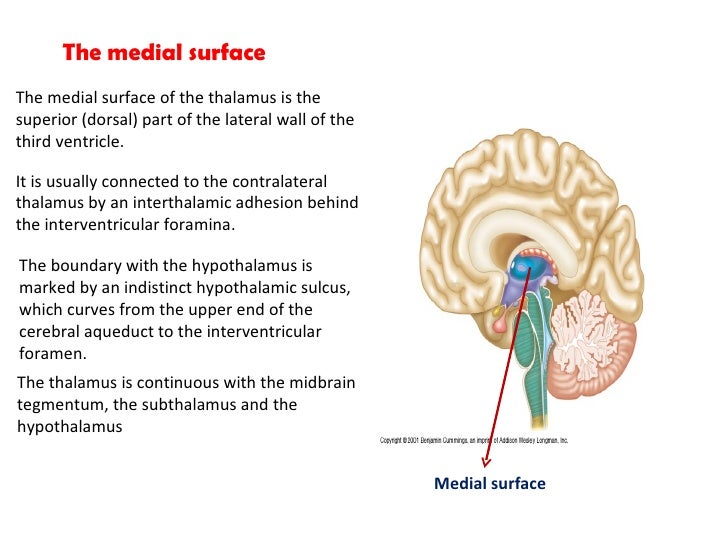

Belum ada Komentar untuk "Thalamus Anatomy"
Posting Komentar