Knee Anatomy Left
Acts as a shock absorber. Many types of minor knee pain respond well to self care measures.
 Normal Left Knee Synovial Joint Anatomy Collateral
Normal Left Knee Synovial Joint Anatomy Collateral
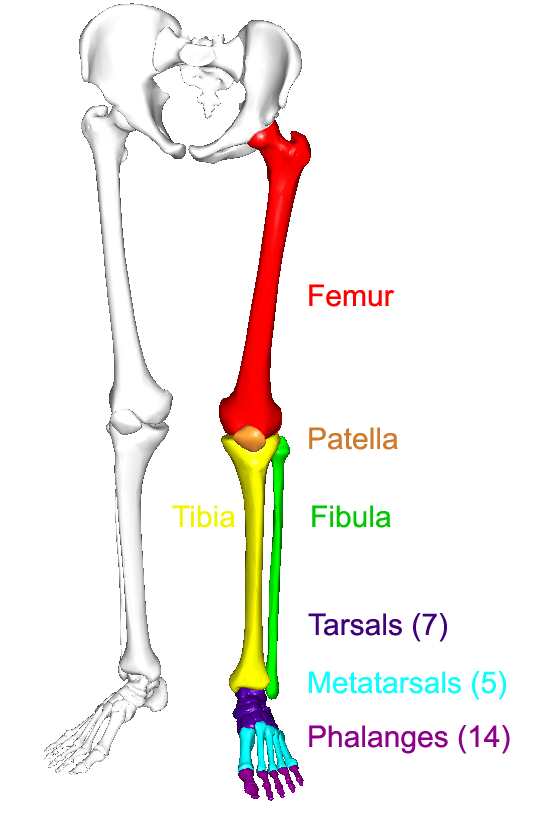
Femur thigh bone the longest bone in the body.

Knee anatomy left. The knee is designed to fulfill a number of functions. This is usually gradual wear and tear damage caused by overuse aging and can be accelerated by poor knee tracking. Knee pain may be the result of an injury such as a ruptured ligament or torn cartilage.
Helps to lower and raise the body. The thigh bone femur the shin bone tibia knee cap patella and the fibula see image to the left. There is usually immediate pain and swelling and a difficulty or inability to stand on the leg.
Ligaments join the knee bones and provide stability to the knee. Knee fractures include a patella fracture and a type of avulsion fracture called a segond fracture. Knee pain is a common complaint that affects people of all ages.
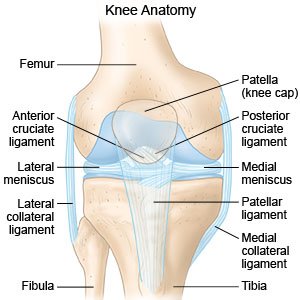
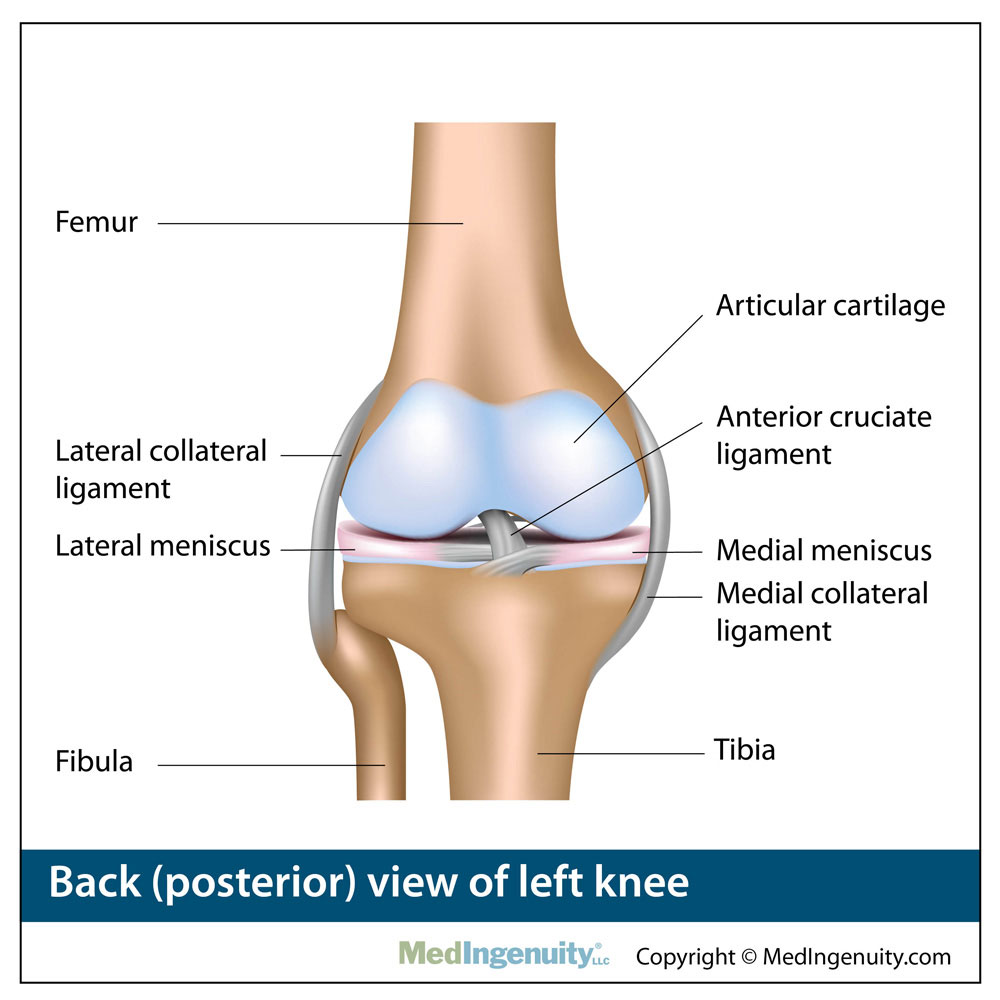
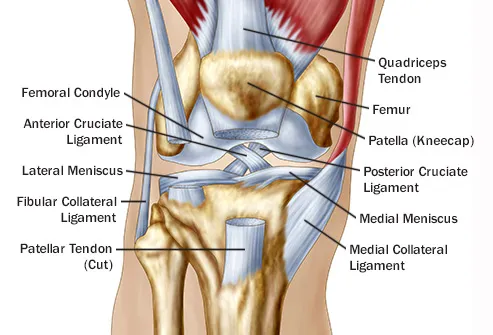
There are four bones around the knee. The anterior cruciate ligament prevents the femur from sliding backward on the tibia or the tibia sliding forward on the femur. The knee is the meeting point of the femur thigh bone in the upper leg and the tibia shinbone in the lower leg.
Support the body in an upright position without the need for muscles to work. Ligament injuries typically result in complaints of instability of the knee joint. The fibula calf bone the other bone in the lower leg is connected to the joint but is not directly affected by the hinge joint action.
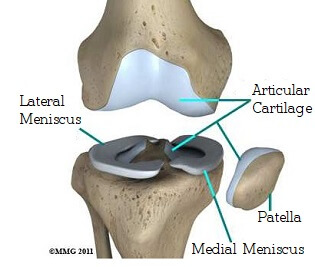
In knee joint anatomy they are the main stabilising structures of the knee acl pcl mcl and lcl preventing excessive movements and instability. The back surface of kneecap end of femur and top of tibia are all covered with articular cartilage. The round knobs at the end of the bone near the knee are called condyles.
The knee is a complex joint that flexes extends and twists slightly from side to side. Medical conditions including arthritis gout and infections also can cause knee pain. There is usually immediate pain and swelling and a difficulty or inability to stand on the leg.
Allows twisting of the leg. The most common ligament injuries are acl tears mcl tears pcl tears and knee sprains which occur when the ligaments are overstretched. The medial collateral ligament on the inner side and the lateral collateral ligament on the outer side.
Makes walking more efficient. Ligaments of the knee. Amicus anatomy knee nerves medial lateral collateral anterior retinacular peroneal cutaneous patellar infrapatellar branches mcnt mrn.
One ligament is on each side of the knee joint. Damage to the articular cartilage is usually diffuse damage. Helps propel the body forward.
 Knee Sprain Aftercare Instructions What You Need To Know
Knee Sprain Aftercare Instructions What You Need To Know
/188058334-crop-56aae7425f9b58b7d0091480.jpg) What Is Causing Your Knee Pain
What Is Causing Your Knee Pain
 The Knee Joint And Leg Yogabody Anatomy Kinesiology And
The Knee Joint And Leg Yogabody Anatomy Kinesiology And
 A Left Knee Showing Both Bundles Anterolateral Bundle Alb
A Left Knee Showing Both Bundles Anterolateral Bundle Alb
 Anteromedial View Of Left Knee A The Superficial Medial
Anteromedial View Of Left Knee A The Superficial Medial
 Anatomy Library Fort Worth Bone Joint Clinic
Anatomy Library Fort Worth Bone Joint Clinic
 Ucsd S Practical Guide To Clinical Medicine
Ucsd S Practical Guide To Clinical Medicine
 Knee Joint Anatomy Motion Knee Pain Explained
Knee Joint Anatomy Motion Knee Pain Explained
 The Lower Limbs Human Anatomy And Physiology Lab Bsb 141
The Lower Limbs Human Anatomy And Physiology Lab Bsb 141
 The Knee Resource Posterolateral Corner Injury
The Knee Resource Posterolateral Corner Injury
 Left Knee Anatomy Google Search Knee Injury Anatomy
Left Knee Anatomy Google Search Knee Injury Anatomy
Search Left Knee Joint Anatomy
 Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome Orthoinfo Aaos
Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome Orthoinfo Aaos
 Human Anatomy Left Knee Front View Stock Illustration 446753422
Human Anatomy Left Knee Front View Stock Illustration 446753422
 Multi Ligament Knee Injuries Jonathan Frank Md
Multi Ligament Knee Injuries Jonathan Frank Md
Common Knee Injuries Orthoinfo Aaos
 Left Knee Injuries Medical Illustration Human Anatomy
Left Knee Injuries Medical Illustration Human Anatomy
 15095 01b Left Knee Anatomy Exhibits
15095 01b Left Knee Anatomy Exhibits
 Reasons For Pain Behind In Back Of The Knee
Reasons For Pain Behind In Back Of The Knee
 Patellar Fracture Of Left Knee Stock Trial Exhibits
Patellar Fracture Of Left Knee Stock Trial Exhibits
 Normal Left Knee Anatomy R15451 09xg
Normal Left Knee Anatomy R15451 09xg



Belum ada Komentar untuk "Knee Anatomy Left"
Posting Komentar