Anatomy Of Mollusks
The radula part of the odontophore may be protruded and it is used in drilling holes in prey or in rasping food particles from a surface. The image above is of a humboldt squid dosidicus which is the largest of the mollusks imaged.
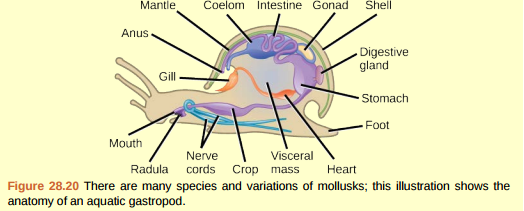 Solved Figure 28 20 Which Of The Following Statements About
Solved Figure 28 20 Which Of The Following Statements About
Gills respiratory organs located between the foot and the mantle formed of two layers of ciliated filaments which filter water and retain food particles.

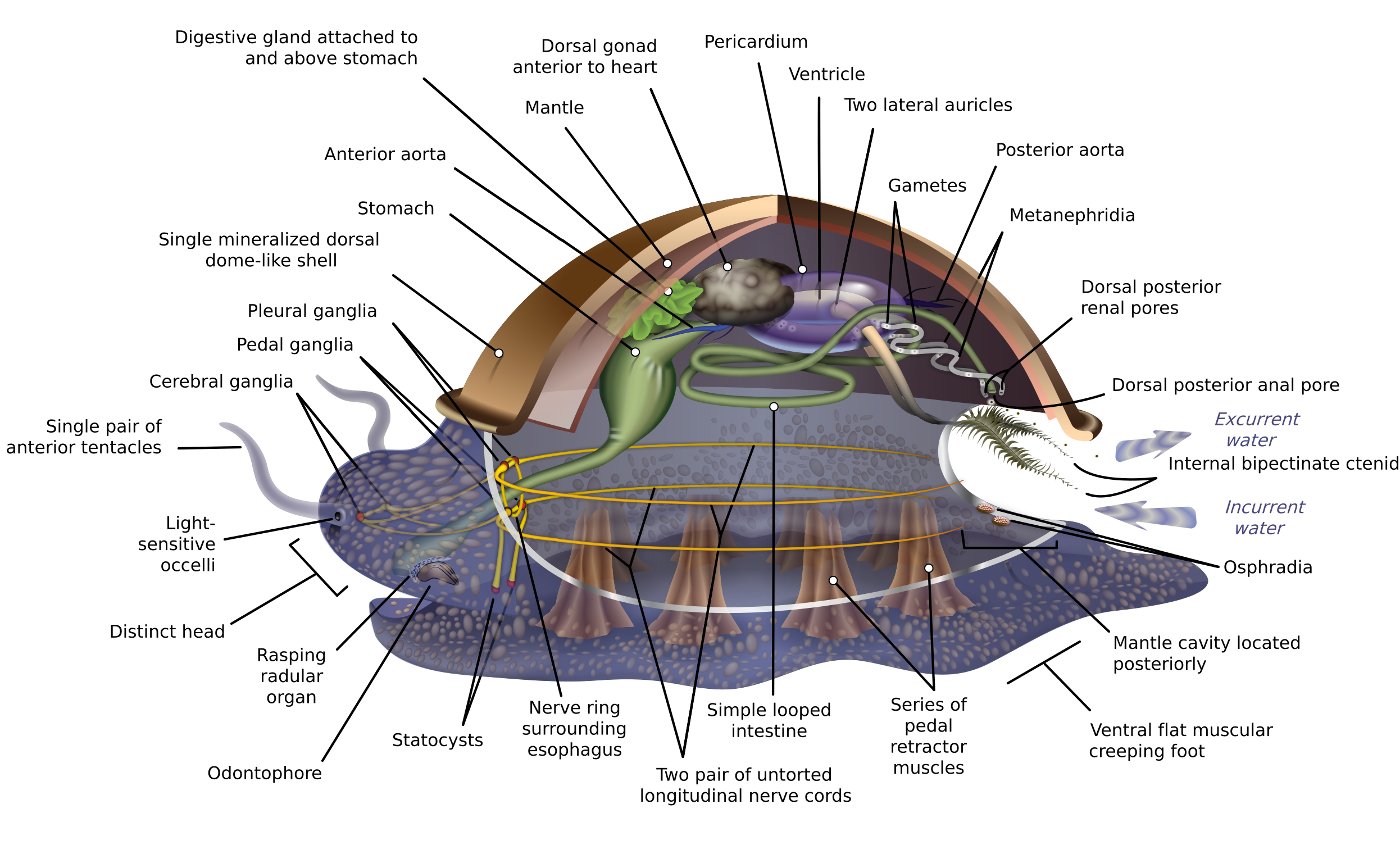
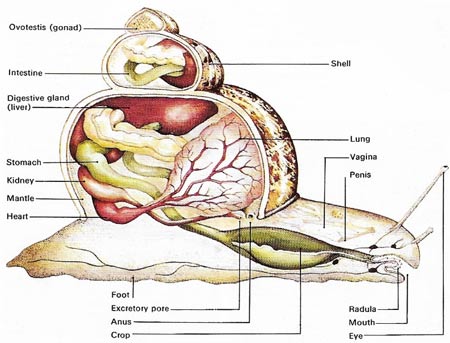
Anatomy of mollusks. They have a mantle a structure of tissue that covers and encloses the dorsal portion of the animal and secretes the shell when it is present. The other members of the lophotrochozoa are the annelid worms and seven marine phyla. Genital gland located at the apex of the shell ensuring production of sperm and eggs.
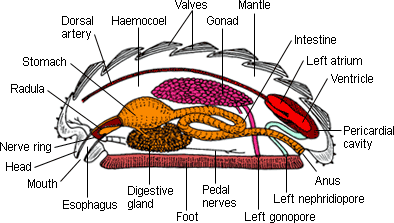
Marine and freshwater filter feeders. The coelom is a cavity present in body of molluscs which contains internal organs suspended from mesenteries. Z class bivalvia clams scallops and oysters.
In swimming and sessile forms however the foot is greatly reduced or greatly modified. Molluscs are generally regarded members of the lophotrochozoa a group defined by having trochophore larvae and in the case of living lophophorata a feeding structure called a lophophore. The anatomystructures of molluscs are complex in nature.
Of the five classes of mollusks four listed below are fairly common and the first three will be studied in the laboratory figure 1. The eyes of the giant squid are the largest in the animal kingdom almost the size of dinner plates. Genital gland producing spermatozoa sperm or ova eggs depending on the sex of the mollusk.
The foot although the basic form of the foot is a flat broadly tapered muscular organ which is highly. Most molluscs have a head with eyes and all have a pair of tentacles with sensors also on the head that detect chemicals vibrations and touch. Radula plural radulae or radulas horny ribbonlike structure found in the mouths of all mollusks except the bivalves.
The snail has both male and female organs. Locomotion the foot is the organ of locomotion in land gastropods. Describe the morphology and anatomy of mollusks a large muscular foot that may be modified into tentacles but it functions in locomotion.
These techniques are relatively quick and allow the anatomy to be scanned in rich detail while leaving the specimen intact and also can be done on live animals says biologist darlene ketten director of the computerized scanning and imaging facility at whoi and a coauthor of the paper. Characterized by a hinged shell of two valves parts and a foot used for digging. One of the special features of their body structure is the presence of a coelom.
Only some species of molluscs have a brain.
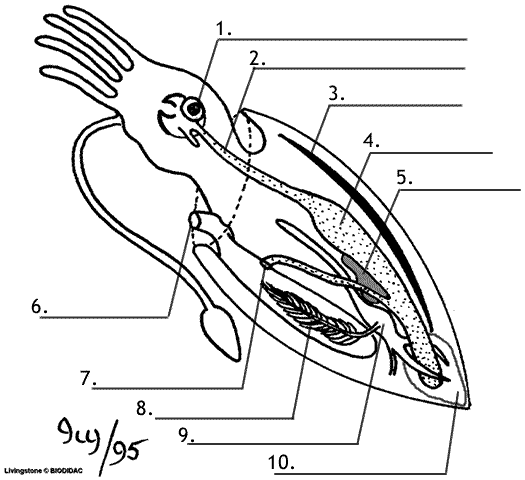 Review Guide Mollusks And Annelids
Review Guide Mollusks And Annelids
 Wisconsin Geological Natural History Survey Cephalopod
Wisconsin Geological Natural History Survey Cephalopod
 Types Of Mollusk Snails Bivalves Squid And More Owlcation
Types Of Mollusk Snails Bivalves Squid And More Owlcation
Solaropsis Brasiliana Anatomy Range Extension And Its
 Parts Of A Clam Zoology 2 Lesson 9 Mollusks Anatomy
Parts Of A Clam Zoology 2 Lesson 9 Mollusks Anatomy
Mollusks Invertebrates Invertebrates Animals Fish

Label The Land Snail External Anatomy Printout
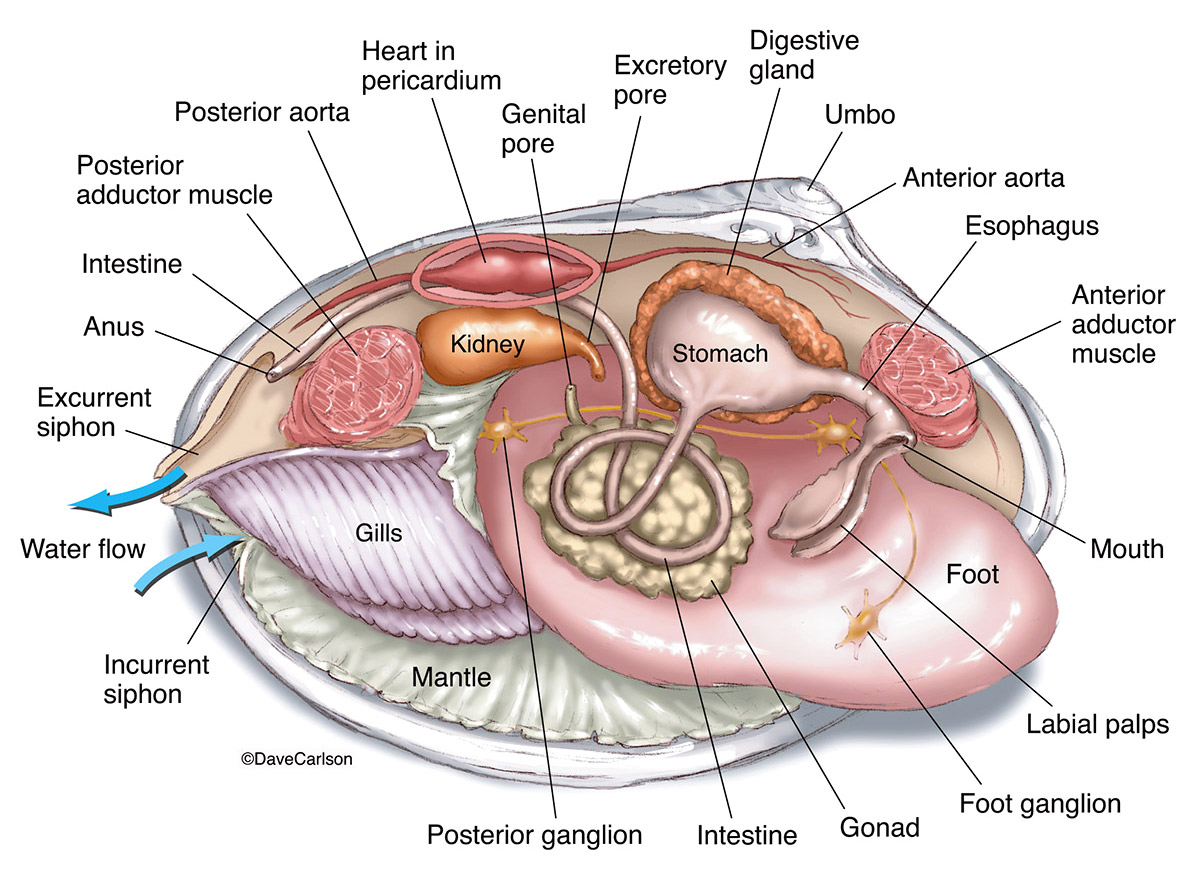 Zoology Life Science Biomedical Carlson Stock Art
Zoology Life Science Biomedical Carlson Stock Art
 Anatomical And Physiological Phylum Mollusca Characteristics
Anatomical And Physiological Phylum Mollusca Characteristics
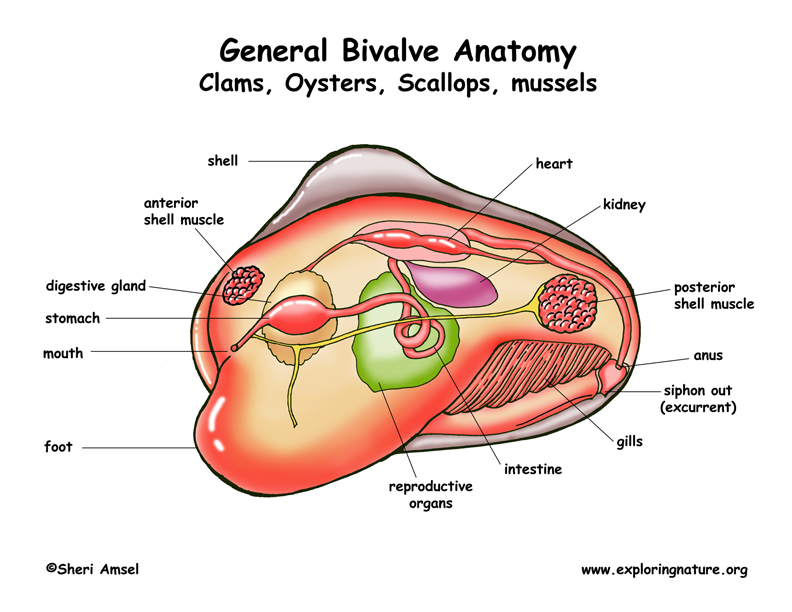 Phylum Mollusca Gastropods Bivalves Cephalopods
Phylum Mollusca Gastropods Bivalves Cephalopods
 Biology Of Animals Plants Mollusks
Biology Of Animals Plants Mollusks

Fresh Water Mussel Collection Introduction Anatomy
 Definition Of Basic Body Plan Of The Mollusks Chegg Com
Definition Of Basic Body Plan Of The Mollusks Chegg Com
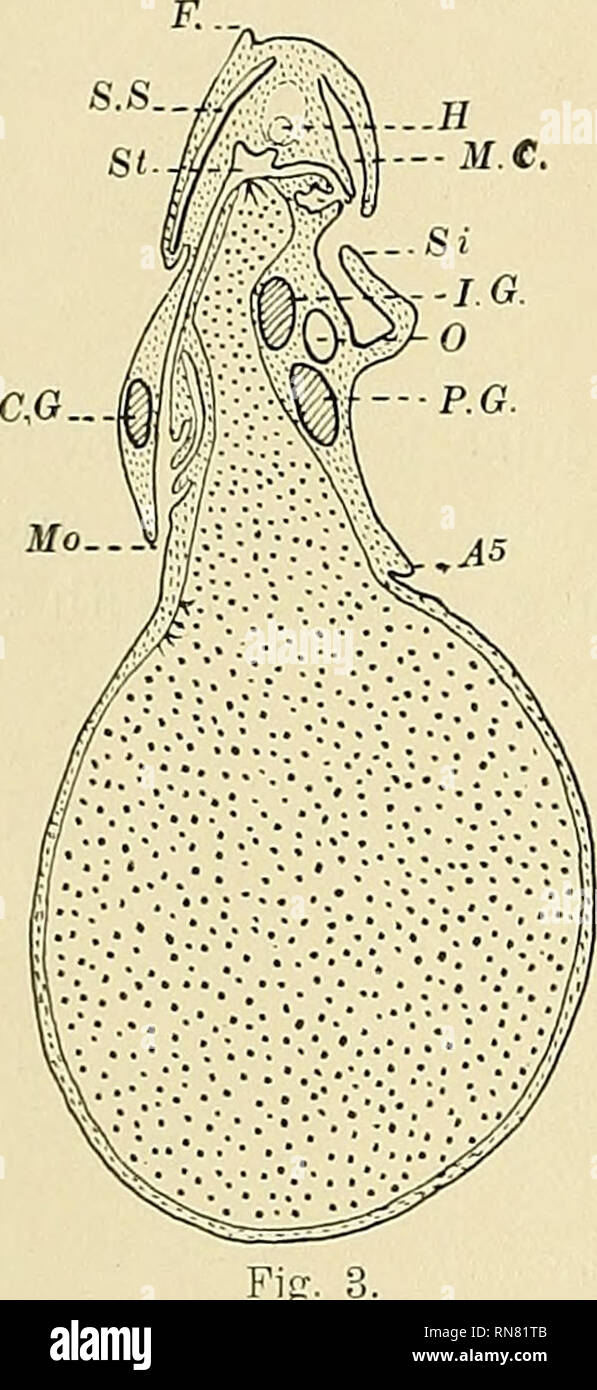 The Anatomy Of The Common Squid Loligo Pealii Lesueur
The Anatomy Of The Common Squid Loligo Pealii Lesueur
 Phylum Mollusca Biology For Majors Ii
Phylum Mollusca Biology For Majors Ii
 Infographic Of The Anatomy Of Molluscs And Their Classification
Infographic Of The Anatomy Of Molluscs And Their Classification
Animal Kingdom Mollusks Octopus Anatomy Of An
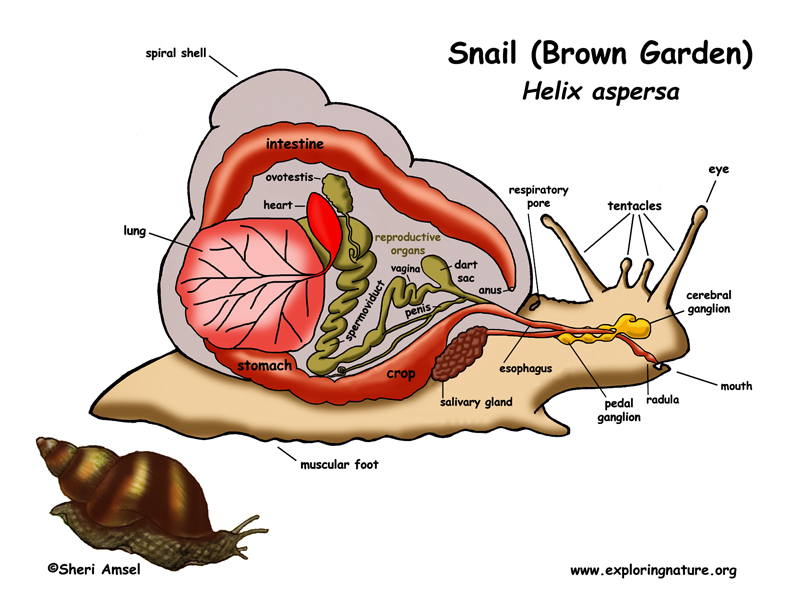 Phylum Mollusca Gastropods Bivalves Cephalopods
Phylum Mollusca Gastropods Bivalves Cephalopods
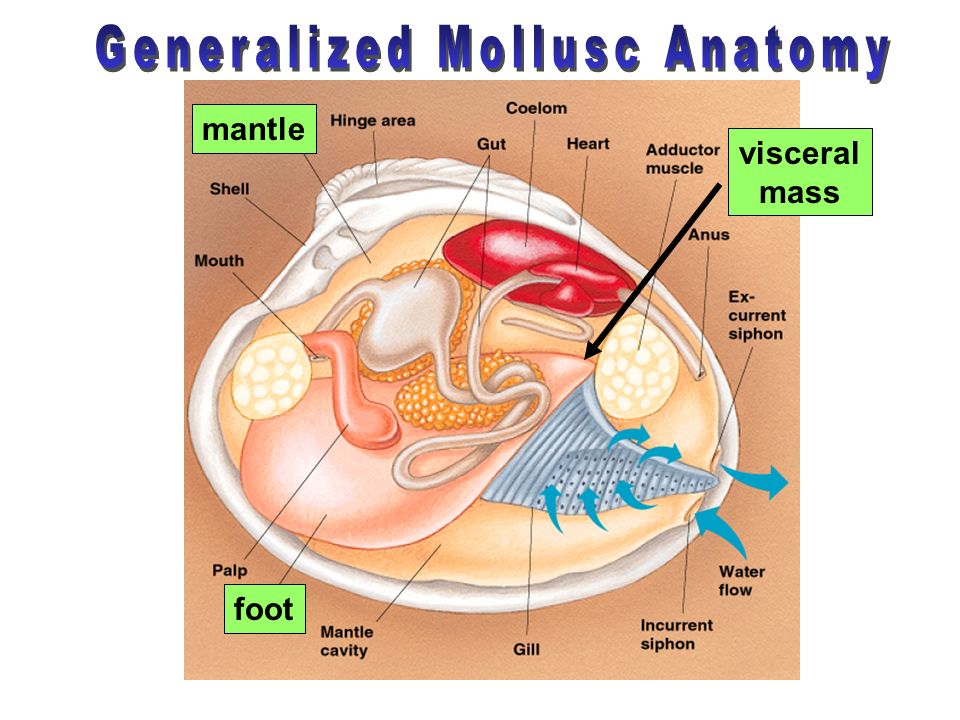 Mollusks Ppt Video Online Download
Mollusks Ppt Video Online Download
 General Anatomy Of The Digestive System Of A Mollusc The
General Anatomy Of The Digestive System Of A Mollusc The
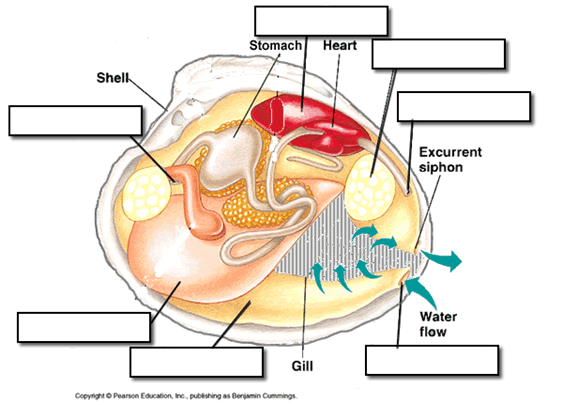
 Mollusk Anatomy Anatomy Shells Cavities
Mollusk Anatomy Anatomy Shells Cavities



Belum ada Komentar untuk "Anatomy Of Mollusks"
Posting Komentar